Joints of the Lower Limb (KNEE JOINT)
Type and description of joint: This is a hinge synovial joint which mainly allows flexion and extension and a small degree of medial and lateral rotation. It is formed by the articulations between the patella, femur and the tibia.
Articulating Surfaces:
The knee joint consists of two articulations - tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. The joint surfaces are lined with hyaline cartilage and are enclosed with a single joint cavity.
Tibiofemoral articulation- medial and lateral condyles of the femur articulates with the tibial condyles. It is the weight-bearing component of the knee joint.
Patellofemoral articulation: The anterior aspect of the distal femur articulates with the patella. It allows the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle (knee extensor) to be inserted directly over the knee thus increasing the efficiency of the muscle.
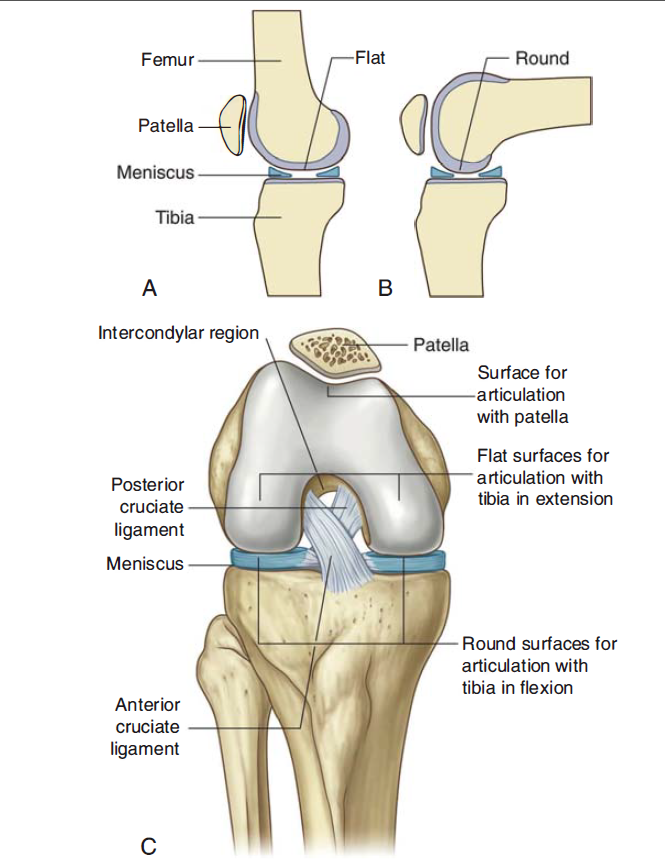
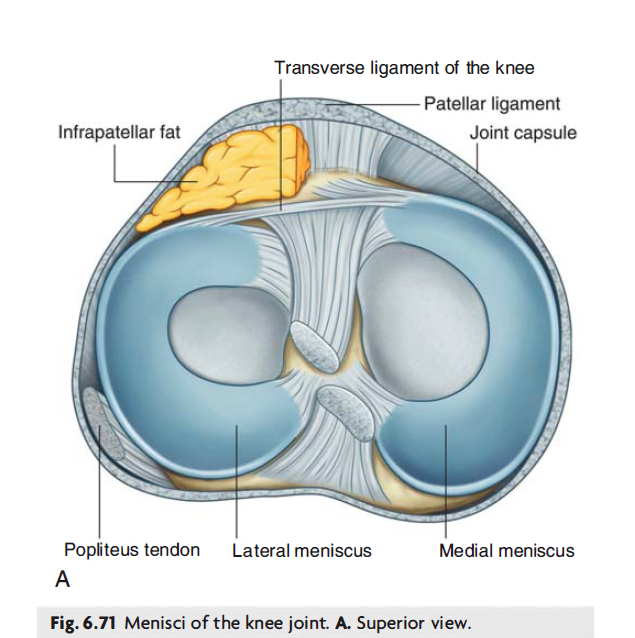
Menisci:
The medial and lateral menisci are C-shaped fibrocartilage rings located within the knee joint.
They serve two main functions:
Deepens the articular surface of the tibia- thus increasing the stability of the joint.
Acts as shock absorbers- the menisci increase the surface area to further dissipate forces that are transmitted across the joint.
They are attached at both ends to the intercondylar area of the tibia. The medial meniscus is also fixed to the medial collateral ligament (also known as the tibial collateral ligament) and the joint capsule so is less mobile compared to the lateral collateral ligament. So damage to the medial collateral ligament is often associated with a medial meniscal tear.
The lateral meniscus is smaller and does not have additional attachments so is more mobile.
LIGAMENTS: A ligament is a thick fibrous connective tissue that reinforces joints and stabilises joints.
Patellar Ligament
Collateral ligament
Cruciate ligament
Patellar Ligament: This is a continuation of the quadriceps femoris tendon distal to the patella. It attaches to the tibial tuberosity.
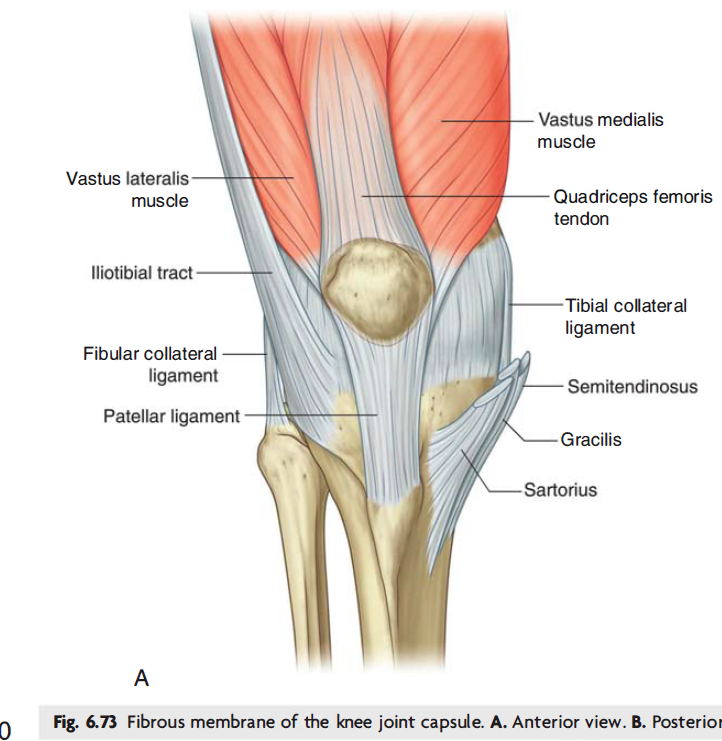
Collateral ligament: These ligaments stabilise the hinge motion of the knee thus preventing excessive medial and lateral movement. The two collateral ligaments are:
Medial collateral ligament- This is a wide and flat ligament found on the medial side of the joint. Proximally, it attaches to the medial epicondyle of the femur, distally it attaches to the medial condyle of the femur.
Lateral Collateral ligament- This is also called the fibular ligament. This ligament is thinner and rounder than the medial collateral ligament. It attaches to the lateral epicondyle of the femur and distally to a depression on the lateral surface of the fibular head.
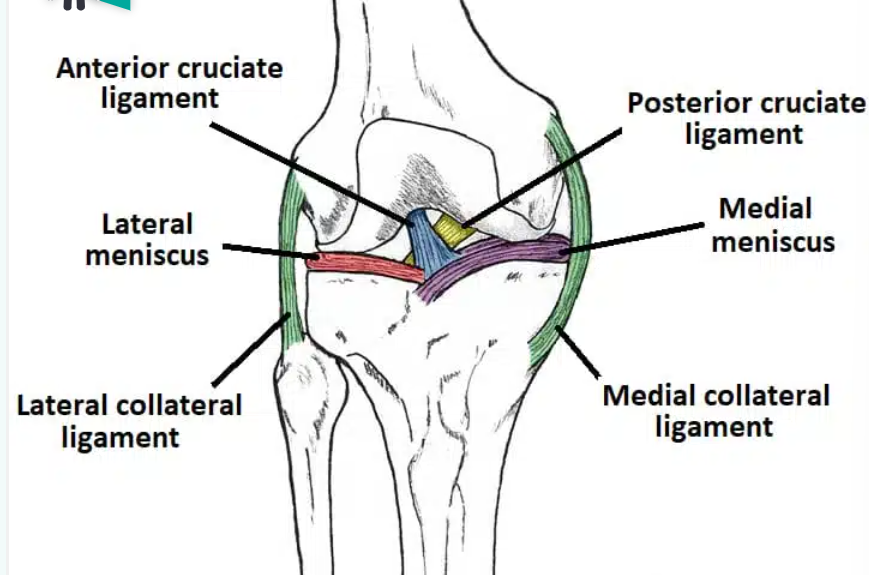
Cruciate Ligaments: These two ligaments connect the femur to the tibia. In doing so, they cross each other (that is why they are called “cruciate” ligaments since they “cross” each other). The two cruciate ligaments include:
Anterior cruciate ligament:

The anterior cruciate ligament prevents the tibia from sliding forward out of the joint since this ligament attaches to the tibia anteriorly.
Posterior cruciate ligament: It attaches to the posterior intercondylar region of the tibia ascends anteriorly and attaches to the anteromedial femoral condyle.

The posterior cruciate ligament prevents the tibia from sliding out posteriorly.
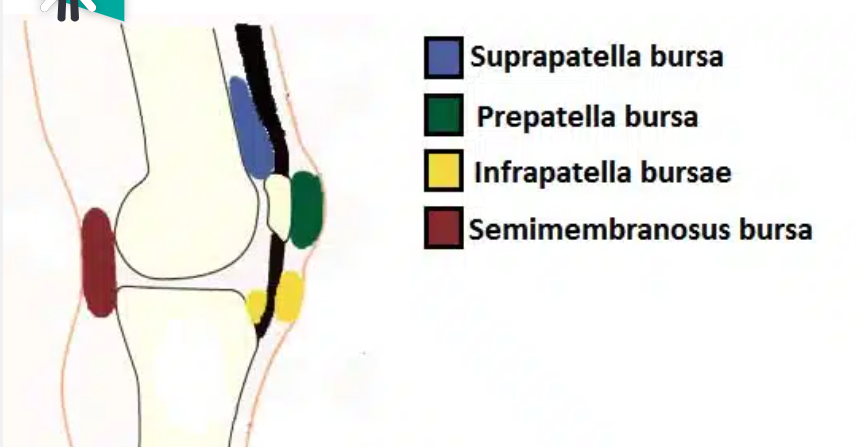
BURSAE:
Acronym SIPS- Suprapatellar- Infrapatellar- Prepatellar- Semimembranosus.
A bursa is a sac-like structure containing a small amount of synovial fluid. It helps to decrease friction between tendons, bones and skin during movement. The 4 main bursae found in the knee joint are:
Suprapatellar bursa
Prepatellar bursa
Infrapatellar bursa
Semimembranosus bursa
Suprapatellar bursa- this is located between the quadriceps femoris and the femur.
Prepatellar bursa- This is located between the apex of the patella and the skin.
Infrapatellar bursa- split into the deep and superficial. The deep bursa lies between the tibia and the patella ligament. The superficial lies between the patella ligaments and the skin.
Semimembranous bursa- located posterior to the knee joint between the semimembranosus muscle and the medial head of the gastrocnemius.
Movements:

Remember: The quadriceps femoris muscle passes the patella anteriorly.