6.3 - Translation (mRNA to protein)
Unit 3: Molecular Genetics
Lesson 6: Protein Synthesis - Translation
Overview of Translation
Translation: The process where ribosomes create proteins by decoding the mRNA sequence
Key Components:
mRNA
tRNA (transfer RNA)
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
Ribosomes
Amino-acyl tRNA synthetases
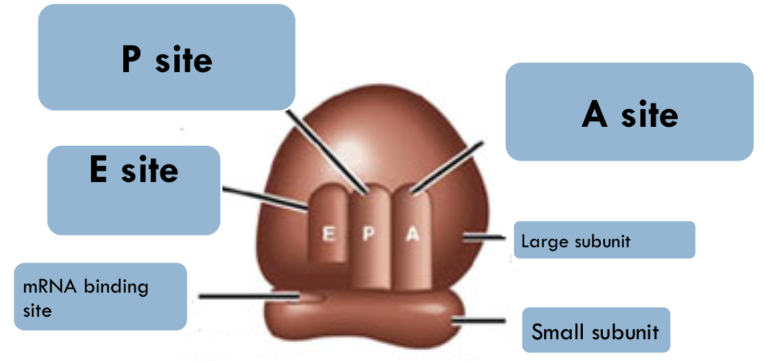
Ribosomal Structure
Ribosome Components:
Large Subunit: Contains the E, P, and A binding sites
E Site: Exit site for tRNA
P Site: Peptidyl tRNA binding site
A Site: Aminoacyl tRNA binding site
Small Subunit: Provides the platform for mRNA binding and decoding
Ribosome Composition: Made of rRNA and proteins
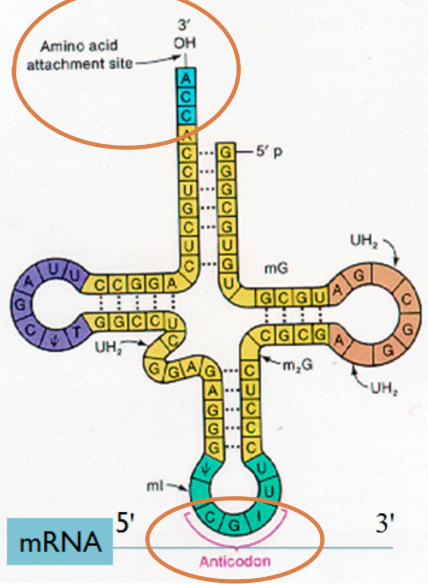
tRNA Structure
Structure Features:
Amino acids attach to the 3' OH site of tRNA
Anticodon: A specific three-nucleotide sequence that pairs with the mRNA codon
Example mRNA sequence and corresponding tRNA anticodon:
mRNA: 5' - AUG - 3'
tRNA anticodon: 3' - UAC - 5'
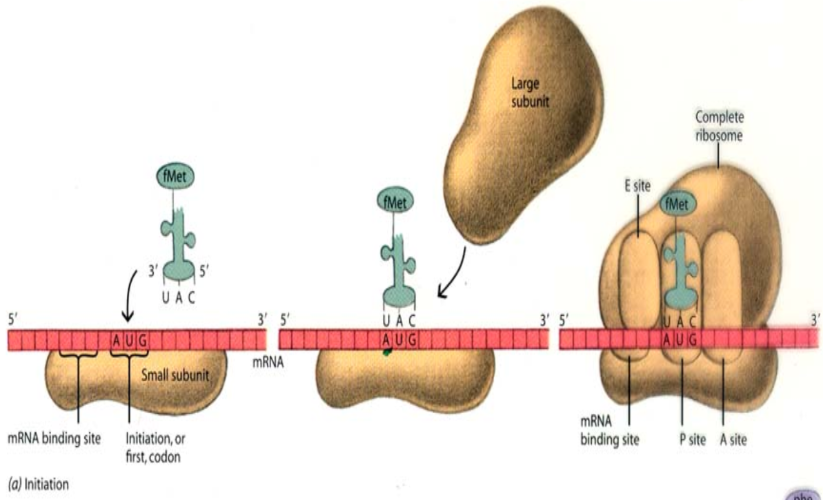
Initiation Stage
mRNA Binding:
mRNA binds to the small ribosomal subunit
Ribosome recognizes the 5' cap of mRNA
Codon Recognition:
Initiator tRNA (met-tRNA) binds to the start codon (AUG) on the mRNA
Formation of Active Ribosome:
Large subunit joins, completing the initiation complex
Elongation Stage
Steps of Elongation:
Aminoacyl tRNA Binds:
The appropriate aa-tRNA binds to the A site based on codon-anticodon pairing
Peptide Bond Formation:
A peptide bond forms between the amino acids at the P site and A site
Translocation:
Ribosome shifts along the mRNA to the next codon
The empty tRNA exits from the E site
The polypeptide-bearing tRNA moves to the P site
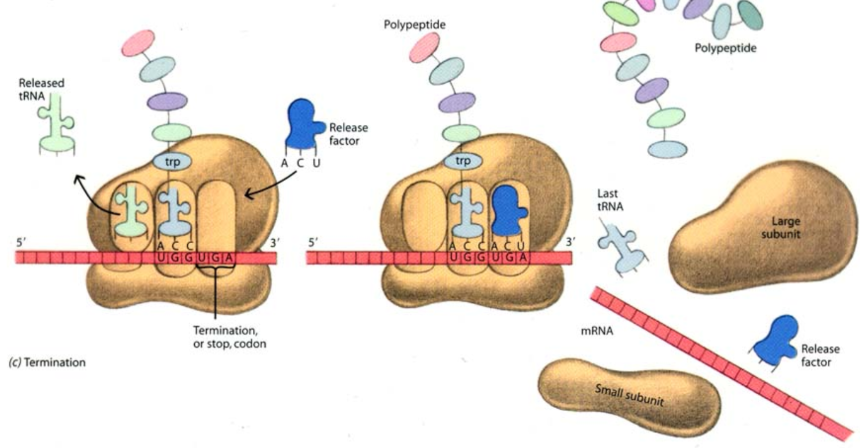
Termination Stage
Stop Codons:
The ribosome reaches a stop codon (UGA, UAG, UAA)
Release Factor: A protein that triggers polypeptide release
Separation of Translation Machinery:
The complex disassembles, releasing the newly synthesized protein
Polysomes
Efficiency of Translation:
Multiple ribosomes can translate the same mRNA simultaneously
Facilitates rapid synthesis of polypeptides
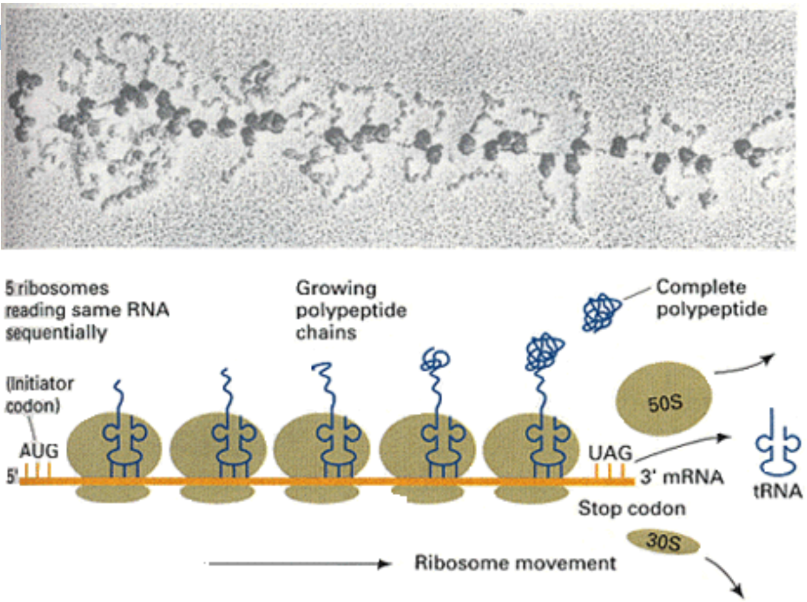
Post-Translational Modifications
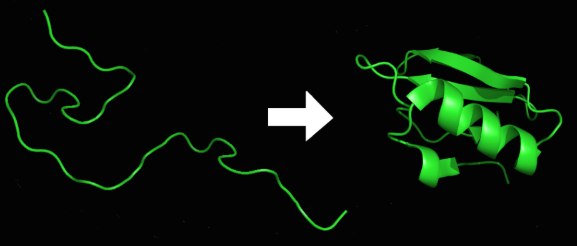
Processing Steps:
Proteins often undergo modifications after translation
Involves folding and modifications by molecular chaperones
Significance of Folding:
Proper folding is crucial for protein function
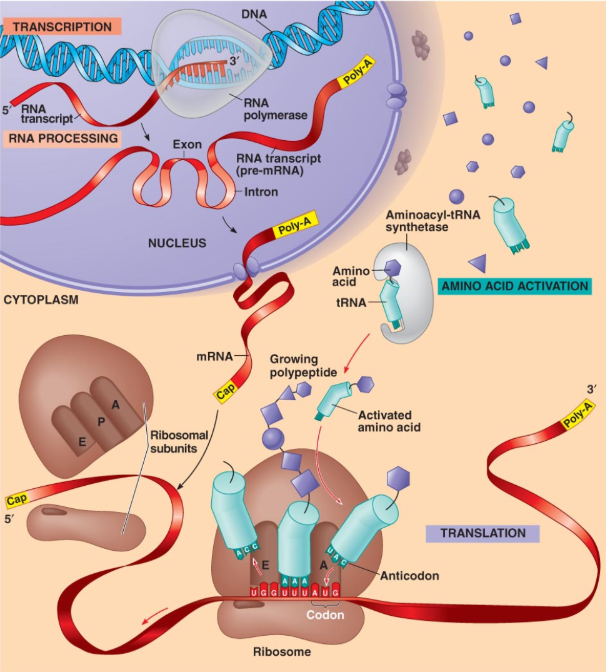
Review : Summary of Translation Process
Animation and Visual Aids: Understanding of the translation process can be enhanced through visual aids and animations.
 Knowt
Knowt