Week 4 Introduction to Time Value of Money
Chapter 4: Introduction to Valuation - The Time Value of Money
4.1 Chapter Overview
Key Concepts Covered:
Future Value and Compounding
Present Value and Discounting
Further exploration of Present and Future Values
4.2 Understanding Time Value of Money (TVM)

Financial managers must ascertain the present value of future cash flows.
Example: Investment worth £100 in one year is not equivalent to £100 today because of potential investment growth.
Conclusion: The value of money increases over time due to potential earnings through investment.
4.3 Future Value (FV) & Compounding
4.3.1 Future Value Defined


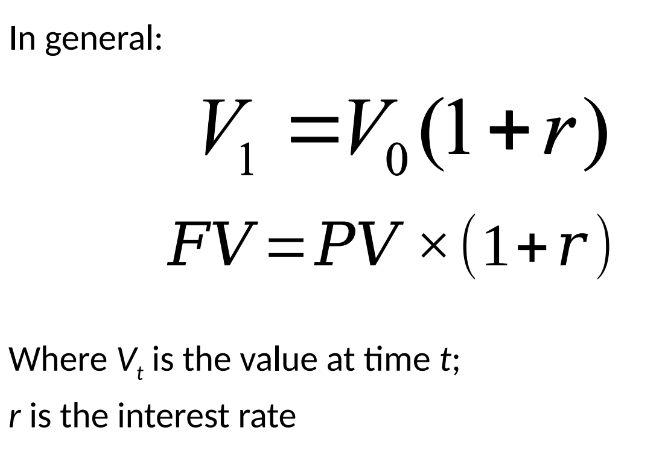
Future Value: Amount an investment grows to after one or more periods.
Example Calculation:
Year 0: Invest £100 at 10%
Year 1: £100 + 10% = £110
4.3.2 Compounding Process

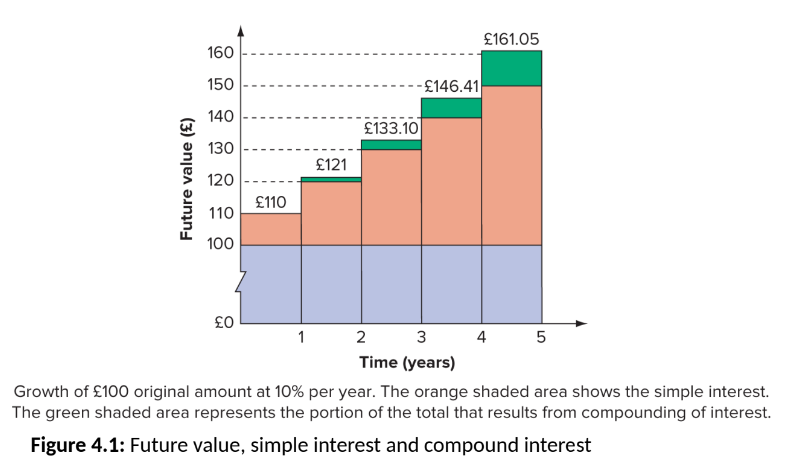
Compounding: Accumulation of interest on an investment, leading to earning interest on interest.
Compound Interest vs. Simple Interest:
Compound Interest: Interest calculated on initial principal and also on accumulated interest.
Simple Interest: Calculated only on the principal amount.

4.4 Investments Over Multiple Periods
4.4.1 Timeline Representation
Timeline helps visualize cash flows, determining if money is received at the beginning, end, or spread over periods.
Cash Flows:
Inflows (positive) and Outflows (negative) indicated on a timeline.
4.4.2 Calculating Future Value



FV Formula:
Formula: FV = £1 × (1 + r)^t
Utilization of Future Value Interest Factor.
4.5 Example of Compound Interest


Investment Scenario: €400 at 12% annual interest.
3-Year Future Value: €561.97
7-Year Future Value: €884.27
4.6 Present Value (PV) & Discounting
4.6.1 Present Value Explained

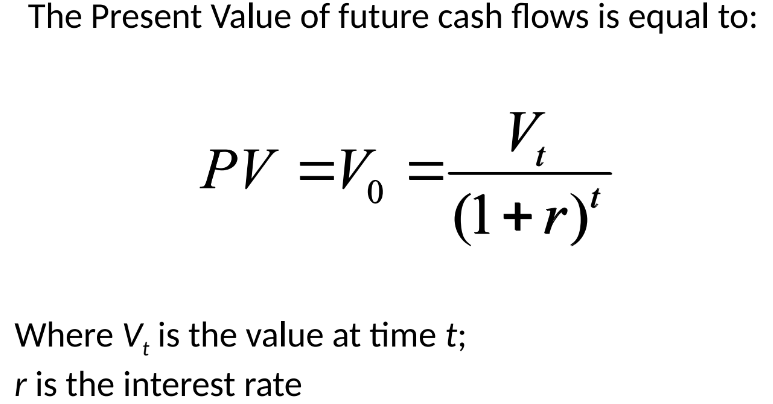

Present Value: Current value of future cash flows discounted at a specified rate.
Formula:
PV = FV / (1 + r)^t
4.6.2 Example Calculation
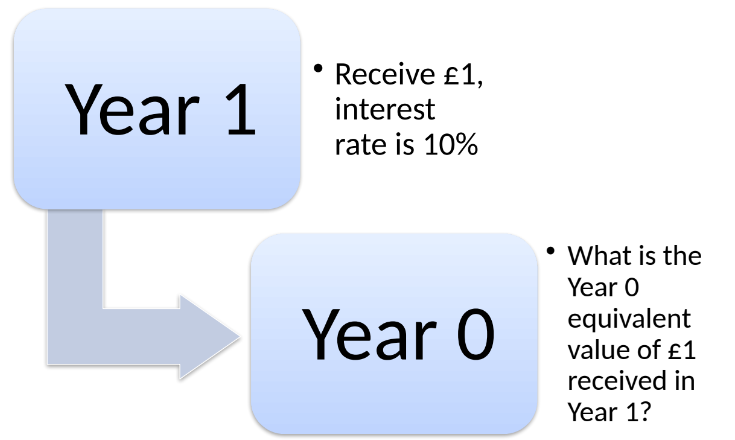
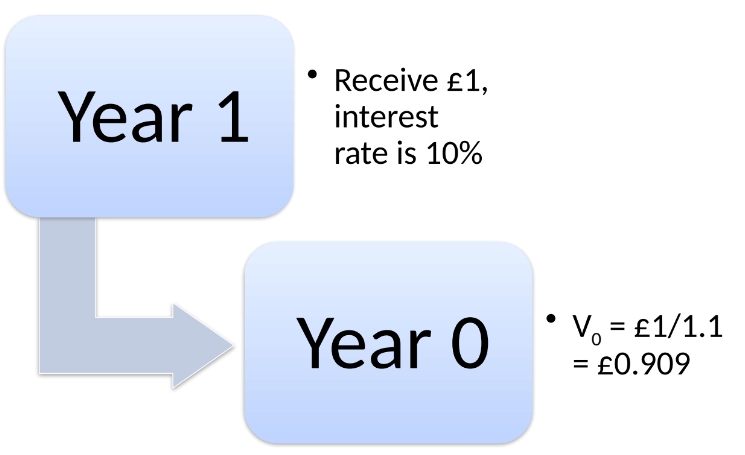
Receiving £1 in Year 1 at a 10% interest rate:
Year 0 PV = £1 / 1.1 = £0.909
4.7 Lump Sum Present Value


Calculation for €400 needed next year, with 7% interest:
Today’s investment = €373.83 (which will grow to €400 in a year)
4.8 Present Value of Cash Flow Streams
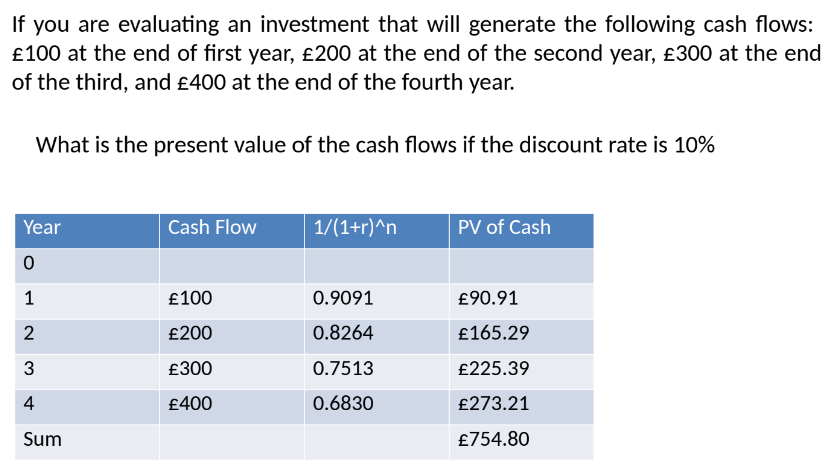
Example: Cash flows of £100, £200, £300, and £400 over four years discounted at 10%:
Total Present Value = £754.80
4.9 Solving for Interest Rate

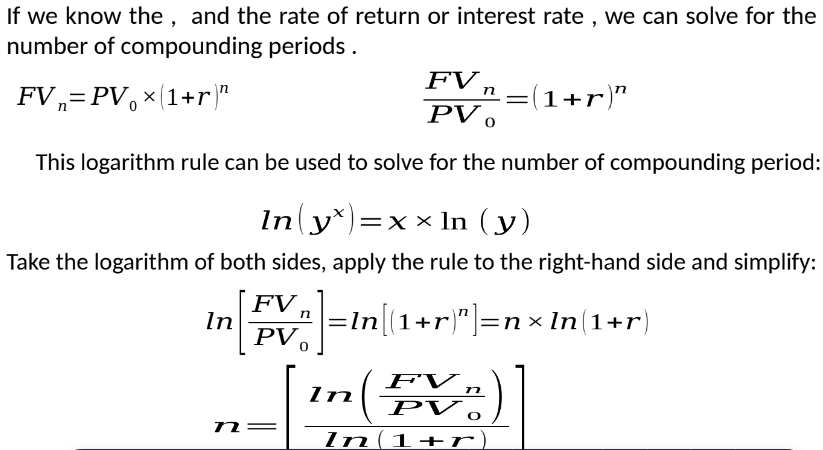
Reverse calculation to find interest rate with both FV and PV known:
Formula: r = [FV / PV]^1/n - 1
4.10 Compounding Periods Calculation
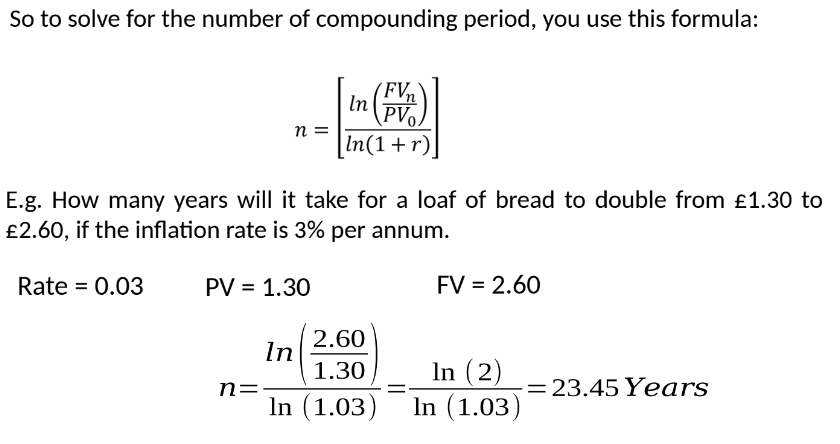

To find how many periods it takes for an investment to grow:
Use logarithmic properties to simplify calculations.
4.11 Spreadsheet Applications for TVM
Excel Formulas:
FV: =FV(rate,nper,pmt,pv)
PV: =PV(rate,nper,pmt,fv)
RATE, NPER for discount rate and number of periods respectively.
4.12 Application of Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
4.12.1 DCF Overview
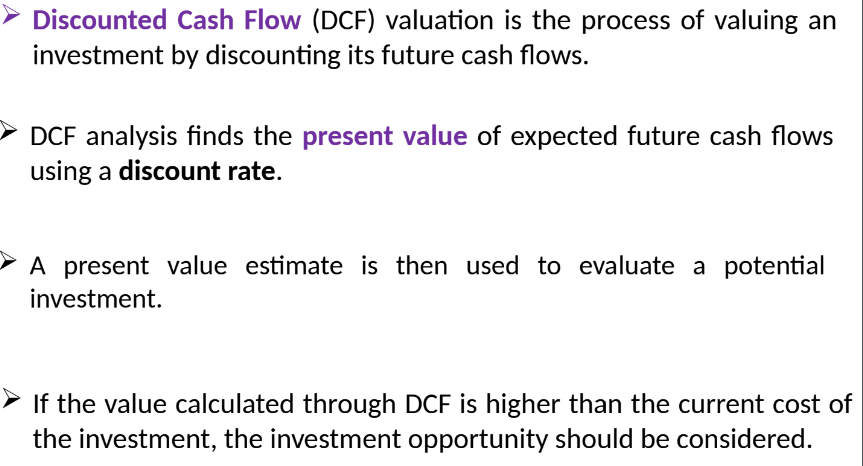

DCF valuation: Valuing an investment based on future cash flows discounted to present value.
If DCF value exceeds investment cost, it is a viable opportunity.
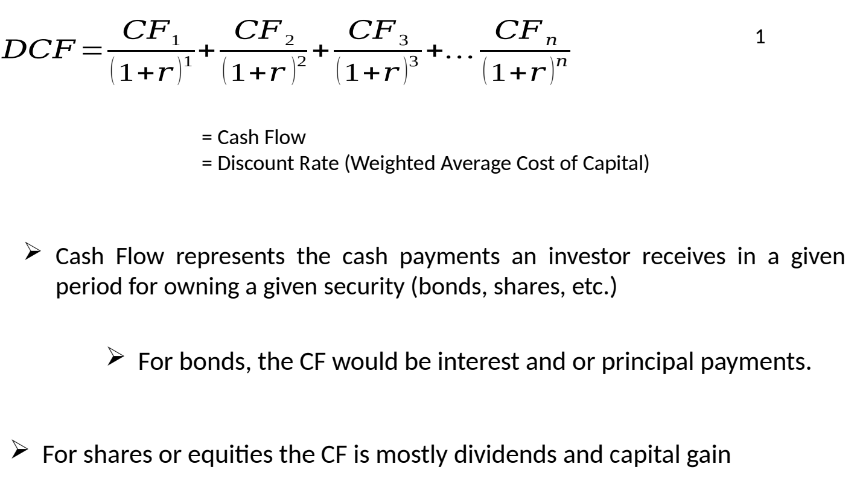
4.12.2 DCF Formula
Formula: DCF = CF1/(1+r)^1 + CF2/(1+r)^2 + ... + CF_n/(1+r)^n
4.13 Purpose of DCF Analysis
Estimates actual cash received from an investment, reflecting the time value of money.
Determining investment worth based on required return rate.
4.14 Applications of DCF Valuation Models
To value businesses, projects, bonds, shares, and income-producing properties.