Nigeria Clean Notes
Nigeria Clean Notes
- Historical legacies
- Various ethnic groups
- Colonialism
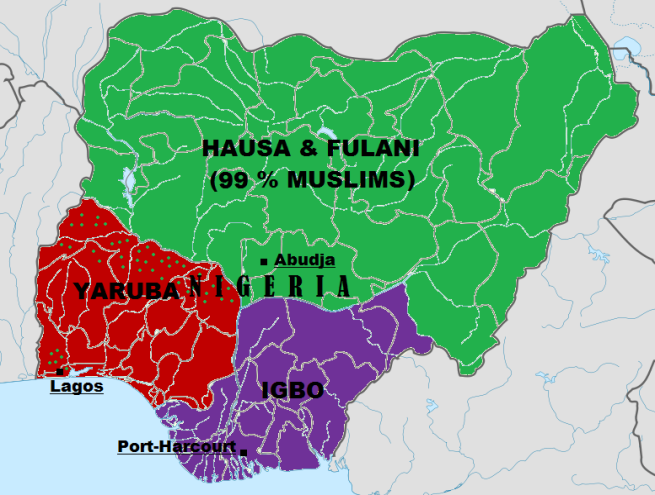
- Military Rule
- Corruption
- North/South and Muslim/Christian Divide
- Nations (do not like the word tribes)
- Hausa
- Northern Nigeria , traders
- Government run by emirs
- Emirs are government leaders who are also religious (Muslim) leaders
- The largest of the nations, practice Islam
- Fulani
- Northern Nigeria, herders
- Also practice Islam
- Hausa and Fulani (H-F) eventually merged, but there are still some cultural differences
- Yoruba (Y)
- Southwest Nigeria, farmers
- Government is based on royalty (Divine Kingship)
- Worked with the Portuguese, very involved in the slave trade (Christian and Muslim)
- Strong military
- Igbo (I)
- Southeast Nigeria, farmers
- Stateless government—as a result, much weaker
- No centralized government, just used village councils
- Many Yoruba sold Igbos into slavery
- Middle Belt
- Band in the center of the country from east to west and along the river leading to the Niger Delta
- Many different nations live along this area and do not associate with the 4 major nations
- Approx. 250 different nations
- Hausa
- Berlin Conference of 1884: Europe cut up Africa, British got the area known as Nigeria
- Under British Rule:
- Creates a regional conflict of North vs. South
- North: Ruled through the emirs, much more decentralized, did not receive the funding, jobs, education or infrastructure that the south did.
- South: Direct rule through appointed “warrant chiefs”
- Kept nations in competition with each other
- Many converted to Christianity
- Yoruba: Treated much more favorably because of their past working with Europeans
- Sent young Yoruba men to Britain for training in the government
- Built roads, schools, provided jobs
- Ibgo: More resistant to British rule than the Yoruba and more impoverished
- British enlisted many Igbo into the military as a way to improve their standing
- Dependency Theory: Brought cash cropping to Nigeria
- H-F: Peanuts
- Emirs pay is based on production
- Yoruba: Cocoa Chocolate
- Igbo: Palm nuts for palm oil (used for greasing machines)
- H-F: Peanuts
- After World War II the British began to allow the creation of some governments and begin the transition to independence.
- Allowed elected regional assemblies and a national legislature which representatives according to each nation
- Created a Nigerian military with British officers and Nigerian soldiers
- Many Igbos signed up for the military because of the lack of opportunity in their region
- Nnamdi Azikiwe petitioned the UN’s Trusteeship Council to try to get independence
- Both the British and most of the Nigerians do not want revolution
- Independence is granted October 1, 1960
- Creates a regional conflict of North vs. South
- The First Republic 1960-1966
- British help set up a Federal Parliamentary system
- Prime Minister: Balewa (H-F)
- Head of State: 1960-1963 Queen Elizabeth II (transitional gov’t) 1963-1966 President Azikiwe
- Parliament:
- House of Representatives (like the HOC)
- Elected every 5 years
- Senate (HOL)
- H-F had 174-312 seats in the House of Representatives
- House of Representatives (like the HOC)
- Regionally
- Divided Nigeria into three states, and allowed state elections
- In 1965 Balewa is again elected PM
- Military Rule 1966-1979
- In Jan 1966 Igbo overthrow the First Republic through General Ironsi (I)
- Tried to set up a unitary government
- Igbos were tired of being oppressed, sought to free themselves from the poverty they experienced. Also had resentment for the British built system
- Assassinated in July 1966
- General Gowon (MB) took over from 1966-1975
- No parliament under any military rule—just military councils
- 1967-1970 Biafran Civil War
- Igbos tried to secede
- Horrible starvation in the area
- Nigeria wins
- Don’t really care about the Igbos, but there is oil on their land
- 1970 Gowon works to forgive and reintegrate them into society
- Economy:
- Emphasizes the rentier state: Dependent on outside countries to pump oil because they lack the technology
- Chevron, Shell and Exxon Mobil
- Tries to build infrastructure
- Emphasizes the rentier state: Dependent on outside countries to pump oil because they lack the technology
- Massive Corruption
- Cement scandal
- Everyone accepted bribes to build infrastructure
- Cement is extremely low quality (remember Mexico?)
- As a result buildings, roads and bridges collapse
- Prebendalism: Form of clientelism putting all your friends into offices
- People are rent-seeking: becoming part of the government in order to exploit it and benefit from corruption
- Also creates a Loyalty pyramid: President pays people who pay people, etc
- “Chop Chop” politics: Extensive network of favors
- Cement scandal
- In Jan 1966 Igbo overthrow the First Republic through General Ironsi (I)
Chop chop is slang for bribes
- Ends up escaping to Britain when there is word he is going to be overthrow
- 1975 General Muhammad (H-F) overthrows Gowon
- Known for working to stop the corruption
- Gets assassinated because people like the corruption
- 1976 General Obasanjo (Y) takes control
- Was General Muhammad’s Chief of Staff, not the person who assassinated him. Manages to take power.
- Wants to return Nigeria to civilian rule
- Calls a national assembly to write a constitution
- Wanted a US style gov’t
- Create more states to dilute the power of the big 3
- 36 states
- Second Republic 1979-1983
- Presidential/Congressional System of Government:
- Moved capital from Lagos to Abuja: Made it a Federal District so no one ethnic group could claim it
- Was located deep in the Yoruba territory, Abuja was much closer to the middle
- Moved capital from Lagos to Abuja: Made it a Federal District so no one ethnic group could claim it
- Shagari (H-F) becomes the first president in the 2nd Republic
- Wins in 79 & 83
- Wanted to continue the growth that Gowan started
- Enhanced the parastatals and focused on ISI—creating revenues for oil
- Massive amounts of corruption
- During the OPEC oil embargo, Nigerian oil became an important commodity, but prices dropped when it ended and oil was discovered elsewhere
- This causes the economy to tank
- When Shagari is re-elected there is obvious voter fraud and the military removes him from power
- Presidential/Congressional System of Government:
- Military Rule 1984-1993
- General Buhari (H-F)
- Created the War against Indiscipline
- Social Indiscipline: People don’t abide by the laws. Lowest level bureaucrats get paid the least and do not follow the laws—paying bribes
- Publicly humiliated civil servants that arrived late. Armed police with whips to keep lines at bus stops orderly
- Wanted people to begin abiding by the laws but it backfired and made people angry
- Created the War against Indiscipline
- General Buhari is overthrown in a year by General Babangida (1986) (MB)
- Is very harsh and corrupt but does a lot for Nigeria
- Creates a National Orientation Movement (NOM) or “Federal Character” program for Nigeria
- Tries to unite Nigeria, create a sense of nationalism instead of allegiance to ethnic groups
- In job interviews or surveys, people were supposed to answer first that they were Nigerian, and second, they were part of an ethnic group.
- People were stopped on the road and asked to sing the national anthem or the pledge of allegiance.
- Creates the Nigerian Youth Service Corps
- Help you go to college if you follow the program
- Volunteer in an ethnic group that is not your own
- Worked to make the military more national
- Tries to unite Nigeria, create a sense of nationalism instead of allegiance to ethnic groups
- Negotiates with the IMF when the economy plummets
- Gets a SAP(structural adjustment program): Loans in exchange for privatizing businesses, raising taxes, etc
- Does not follow the SAP the same way that Mexico or Russia did. Nigeria is just too corrupt to adequately carry out the terms of the agreement. As a result, the IMF places sanctions on Nigeria a number of times.
- Joins ECOWAS: Economic Community of West African States
- Supposed to become like the EU and support the growth of trade and commerce between West African nations.
- Has a commission to implement policies and a bank to fund it
- Very ineffectual
- Babangida Wants to move Nigeria back to civilian rule
- In 1992 tries to have local and state elections
- More people vote than exist—too much fraud to count the election.
- Tries to create national parties:
- Parties must get signatures of people in all ethnic groups
- Ends up with 12 political parties
- Lots of fraud: People who don’t exist…AHHH can ANYTHING get done?
- As a result, he creates 2 parties: Social Democrats and National Republicans
- Basically the same structure as the Republicans and Democrats in the USA
- Has an election based around those two parties
- General Buhari (H-F)
- Third Republic (1993)
- Abiola (Y) wins
- Babangida doesn’t want him to win so he throws Abiola in jail (Abacha kills Abiola in 1998)
- Interest group call NADECO forms
- National Democratic Coalition: Created to help get Abiola out of jail
- Mrs. Abiola is killed in a protest
- Babangida flees and leaves Ernest Shonekan in charge
- Ernest is assassinated
- Military Rule (1993-1998)
- General Abacha (H-F)
- Most corrupt of the military dictators
- Extractive Politics: Politics based on manipulating people and the country for higher gov’t positions
- Lootocrats: Another word for rent-seekers
- Kleptocracy: Gov’t steals from the people
- Still a rentier state. Willing to sacrifice the environment and people’s health in order to make more money from the oil industry
- Very few regulations
- A group called the Ogoni people created an interest group called MOSOP, Movement for the Survival of the Ogoni People
- International campaign that brought attention to the devastating effects the oil drilling had on the people. People lived in the Niger Delta, an area that was being destroyed by the oil drilling.
- Also people are desperate for money, and as a result, try to extract oil themselves and get blown up.
- Led by a famous Nigerian writer name Ken Saro-Wiwa
- Abacha had Saro-Wiwa and many of people in the group rounded up and had them executed
- Gallows breaks during the hanging, has to hang them a second time
- In 1998 Abacha dies suddenly, under very shady circumstances.
- Many stories…
- Many international organizations begin trying to trace where Abacha hid his money. It is estimated that Abacha stole $4.3 billion from Nigeria. Only about 500 million has been recovered.
- Lots of people question whether it would benefit Nigeria to have the money returned—because it will probably go into corrupt hands.
- General Abdulsalami Abubakar (H-F) (1998-1999)
- Transitioned Nigeria back to civilian rule
- Makes a law that no active member of the military can run for president
- General Abacha (H-F)
- 4th Republic (1999-present)
- Obasanjo retires from the military and runs for president
- Runs from the new People’s Democratic Party, wins
- Vice President is Atiku Abubakar
- Amends constitution to make 36 states
- Presidential winner must have 25% of the vote in 2/3rds (24 states)
- Begins a financial crimes unit of the government to search for Nigeria’s money
- Mrs. Abacha is stopped at the airport with 40 suitcases of money
- It is estimated that he stole $4.3 Billion from the Nigerian people
- Runs from the new People’s Democratic Party, wins
- Economy
- Works with the World Bank to try to get Nigeria’s finances and economy on track
- Begins re-working with the IMF as well
- Meets with the Paris Club
- Group that voluntarily works with countries with extreme debt
- Works to renegotiate debt
- 1st country: Argentina
- Works with the World Bank to try to get Nigeria’s finances and economy on track
- Civil Society
- Expands
- Lots of free press
- Groups like the National Labor Congress
- MEND: Movement for Emancipation of the Niger Delta
- Against the oil companies
- Kidnap oil workers but have a pledge not to kill
- International issues 1998
- Miss Nigeria won Miss World
- 1999 is going to be in the winner’s country
- Riots as the Pageant begins---they get their contestants outta there!!
- Lots of religious violence as a response
- CAN: Christian group that wants to stop the spread of Shari’a law.
- Go tit for tat with the Islamic rebels, violence.
- CAN: Christian group that wants to stop the spread of Shari’a law.
- Miss Nigeria won Miss World
- Northern part of the country wants Shari’a law
- Obasanjo decides to let the states decide what they want
- 12 northern states vote to have Shari’a law
- Boko Haram: terrorist group that claims to be carrying out Shari’a law
- Name means “Western Education is sinful”
- Boko Haram: terrorist group that claims to be carrying out Shari’a law
- In 2005 Obasanjo calls a conference to try to change the constitution so he can have a third term
- Opposition boycotts including the VP Abubakar
- The people do not allow the third term
- Obasanjo backs Yar’Adua (H-F) instead for the 2007 election
- Has Abubakar disqualified from the Independent Nigerian Election Commission
- 4 days before the election the Supreme Court ruled that Abubakar could be on the ballot.
- His new party is the Alliance for Democracy Party
- Buhari also ran and lost
- Yar’Adua wins: First to not be involved in the military!
- President Yar’Adua
- 2010 Yar’Adua went to Saudi Arabia for 3 months for medical treatment
- Goodluck Jonathan (Y) (VP) served as Acting President
- Yar’Adua came back to Nigeria but died a few months later
- Boko Haram threatened to overthrow the government
- 2010 Yar’Adua went to Saudi Arabia for 3 months for medical treatment
- President Jonathan
- Struggled to improve the economy
- In 2014, 276 schoolgirls were kidnapped in Chibok by Boko Haram. This received intense international coverage with the movement #bringbackourgirls. Over the years many of the girls have been released, but not all have been found. It is assumed that many were sold off as child brides.
- Strong criticism of his inability to stop Boko Haram from growing and terrorizing citizens.
- 2015 Presidential Election
- Muhammadu Buhari (H-F): All Progressives Congress 53.96%
- Goodluck Jonathan: People’s Democratic Party 44.96%
- Nuhu Ribadu (MB): Action Congress 16.3%
- Former head of the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission
- Obasanjo retires from the military and runs for president
The Government of Nigeria
This government was created with by the 1999 Constitution and is a presidential federal system with separation of powers, checks and balances, and federalism.
- The President: The president of Nigeria serves a four year terms and may be reelected for a second term. The president is the Head of State and Head of Government. Powers of the president include:
- Signing or vetoing bills from the National Assembly
- Refer a bill to the Constitutional Court to consider the bill’s constitutionality
- Call the National Assembly for a special session in emergencies
- Appoint commissions to investigate issues
- All a national referendum on a bill from the National Assembly
- Appoint ambassadors, diplomatic recognition
- Issue pardons
- Appointment of almost all public officials—creates an opportunity for patronage and nepotism. While the Cabinet and a few other top positions are confirmed by the Senate, most are not subject to confirmation.
- The National Assembly: Bicameral legislature containing the House of Representatives and the Senate. Both have members that are elected for four year terms at the same time as the president.
- Passing laws: Both houses must pass a bill and it be signed by the president to become law. Both houses can override a President’s veto if they have a 2/3rds majority in each house.
- Houses have identical powers EXCEPT:
- Senate can impeach judges and executive commissions (but the president has to first recommend it)
- Senate confirms the Cabinet and top-level court nominations
- No time limit on the president signing bills means that the president can ignore legislation that comes out of the National Assembly
- While theoretically powerful, the legislature is largely restrained by the president’s power.
- The Judicial Branch
- Federal system so the courts are divided into federal and state systems.
- Common law: precedents allow interpretations of laws.
- Supreme Court: Court of last resort for all appeals for both the state and federal systems
- Up to 21 justices
- Has judicial review---not exercised
- Courts don’t have a lot of independence as a result of the military rule
- The north has Sharia courts which run parallel to state courts
- Elections
- Independent National Electoral Commission: Determines which parties can run based on a set of criteria.
- Count ballots
- Lots of efforts to try and have free fair and competitive elections. Boko Haram seeks to disrupt this effort with violence.
- There are often lost ballots and accounts of voter fraud but it has gotten significantly better
- Presidential elections:
- President and VP are elected together in a nation-wide vote every four years.
- Wins through plurality however--- the candidate must receive 25% of the vote in 2/3rds of the states
- No party can run a candidate for presidential elections unless they receive at least 5% of the vote in 2/3rds of the legislative districts from the previous election.
- House of Representatives Elections:
- Nigeria is divided into 360 single member districts—each state receiving a number of districts (seats) based on population
- Elections are every four years with the presidential elections. Winners are based on plurality.
- Senate
- Each state is represented equally in the Senate. Each of the 36 states elects 3 Senators and the Federal Capital of Abuja elects one for a total of 109 Senators.
- States are divided into three districts, each electing one senator through plurality.
- Independent National Electoral Commission: Determines which parties can run based on a set of criteria.
- Political Parties
- All Progressives Congress (APC): Formed in 2013
- Won presidency and both houses
- Alliance of the political parties: Action Congress of Nigeria, Congress for Progressive Change and the All Nigeria Peoples Party. Largely northern support.
- People’s Democratic Party (PDP):
- Still the most recognized party, despite recent loss.
- Supported Obasanjo, Yar’Adua and Jonathan but had widespread fraud in the Yar’Adua election—hard to know how supported the party actually is
- Northern support—but also support from the Yoruba people
- Alliance for Democracy: Yoruba
- All Progressives Congress (APC): Formed in 2013
- Economy in Nigeria
- Nigeria is a mixed-market economy with more free-market principles in the south and stricter market controls in the north
- We generally see practices of economic liberalization, privatization and FDI by MNC in Nigeria. Nigeria absolutely participates in the Race to the Bottom.
- Nigeria is a rentier state and depends heavily on its oil industry for revenue
- As stated throughout this notes packet, the cost of this is enormous environmental degradation of the Niger Delta
- Agriculture remains a really important aspect of Nigeria’s economy
- Nigeria regularly competes with South Africa in population and economic strength for dominance on the African continent
- Nigeria also finds revenue in allowing developed countries to pay them to dump trash in Nigeria. Didn’t know this was a thing? Yep.
- Remember that the northern part of Nigeria still is extremely underdeveloped, mostly rural and controlled by Muslim leaders
- Parts of the south are more developed and more urban
- Nigeria’s urban areas have been developing stronger industries that are helping grow the economy
- Nollywood: Nigeria’s version of Hollywood (Approx. 5% of their GDP which is a lot!)
- Nigeria is a mixed-market economy with more free-market principles in the south and stricter market controls in the north
Issues in Nigeria Today
- Problems:
- Legacy of Military Rule
- Environmental degradation
- Youth bulge
- Social Indiscipline and Corruption
- Poverty: More than 40% live on less than $1 a day
- Health problems: HIV/AIDS, Polio, lack of clean water
- Drug trafficking
- Government is importing major goods like gas, kerosene diesel fuel and food
- Lack of foreign investment
- Cleavages
- Mostly coinciding
- Religion, geography, post-colonialism, ethnic groups
- Boko Haram
- Political Culture
- Corruption is the name of the game.
- Acceptance of hierarchical relationships
- Patrimonialism: Method of governing in which authority is maintained through patronage
- State is seen as his personal property and relies on those he appoints to office to provide unswerving loyalty
- Loyalty Pyramid: Structure of prebendalism
- Rent-seekers, Prebendalism, Chop chop politics
- The Big Men: Elites from the military, politics, bureaucracy, states governors, religious leaders
- Patrimonialism: Method of governing in which authority is maintained through patronage
- Cynicism about government
- Very little nationalism
- Corporatism:
- NACCIMA: National association of Chambers of Commerce, Industry, Mines and Agriculture
- NADECO, National Labor Congress, MEND, MOSOP, CAN, Kaduna Mafia and Islamic League
- Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation: N.N.P.C
- Joint venture with multinational corporations—still a rentier economy
- Civil Society:
- Independent interest groups: Some. Ex: Christian Association of Nigeria
- Labor Unions: Oppressed in the 1980’s but are gaining strength today. Protests and strikes occur.
- Free Press: Mostly free except that many tv and radio stations are government controlled
- Independent Universities
- Political Legitimacy
- The National question: Can Nigeria function as a country despite the deep rooted ethnic, cultural and religious differences?
- Is Nigeria a failed state?