Business Notes (Unit 1)
1.1 - Introduction to business management
Lesson 1 -
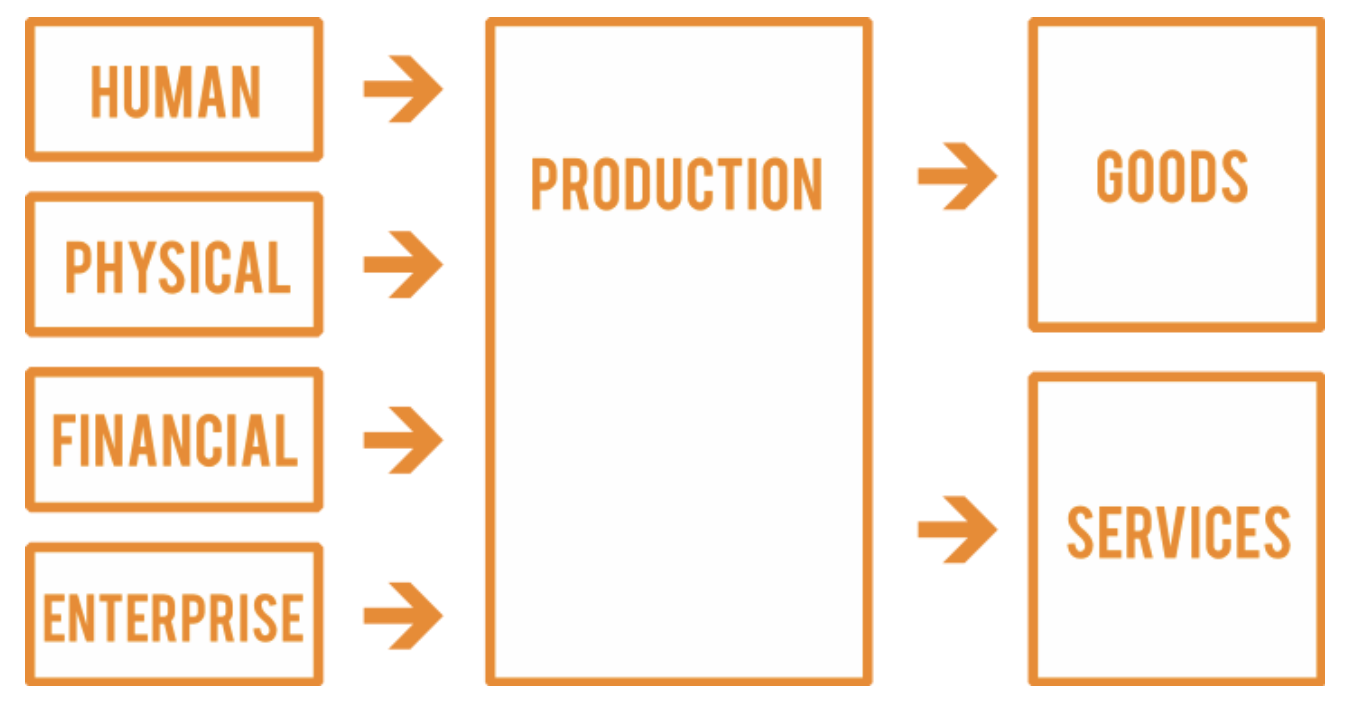
Business: Organization involved in the production of goods and/or provision of services
Product: Tangible; items/objects
Service: Non-tangible
Needs & Wants
A business’ ultimate goal is to satisfy needs and wants of customers (otherwise: failed business)
Backwards business: identify need/want first; create product/service later
Clever business: Invent/create a need/want (e.g. Instagram)
Customer: People of organizations that buy a product
Consumer: The ones that actually use the product
Peter Drucker - Management Guru (1980s)
“The only single purpose of a business is to create customers”
Main Functions of a business
Human resources: right people, right place, right time
Finance & Accounts: manage costs & everything to do with money
Marketing: advertising; identifying & fulfilling needs/wants to sell products (7Ps)
Operations: converting raw materials/components to finished goods
Cost < Revenue → (cost-revenue) cost = low, revenue = high
Lesson 2 -
Business Sectors
Primary: Where raw materials come from (e.g. Ikea needs trees to cut down to make furniture)
Secondary: Manufacturing and construction of products
Tertiary: Providing services e.g. retailing, transport, banking
Quaternary (sub-cat of tertiary): AI, research; intellectual knowledge-based activities for development
Sectoral Change: Shift in the relative share of national output and employment that is attributed to each business sector over time
Typically developing countries → Primary
Developed countries → Tertiary
Sectoral changes in MEDCs
Higher household incomes
More leisure time (e.g. activities, eating out)
Greater focus on customer service
Increasing reliance on support services (e.g. cleaners, nannies)
Entrepreneur: The person that owns the business, comes up with the idea, sells it for a profit
Arthur Fry (1931) invented + commercialized the Post-it-note (1980) → now sold in over 100 countries around the world
Intrapreneur: Employed by a large org. → demonstrates entrepreneurial thinking to develop new products/services → Businesses want these kinds of people
E.g. Paul Buchheit (Google employee) came up with the idea of Gmail (programmed it in 1 day) → lead developer ever since
Entrepreneurship: The process of setting up a new business
Characteristics of Entrepreneurs
Risk-takers
Self-motivated
Confident
Innovative
Competitive advantages come from:
Market reading
Need seeking
Technology driving
Lesson 3 -
Reasons for starting a business (GET CASH)
Money
Self-employed (own boss)
Wanting to make a change in the world
Work-life balance
Innovation
Control
G - growth
E - earning
T - transference & inheritance
C - challenge
A - autonomy
S - security
H - hobbies
Mass Market: Targets everyone/huge population
Niche: Small target market
Process of starting business
Organizing the basics → Research the market → Planning the business → Establishing legal requirements → Raising the finance → Testing the market
OR
Refine the idea → Prepare a business plan → Decide on legal structure → Take care of administrative tasks → Find a locale → Hire employees → Seek financing
Problems new businesses might face
Lack of finance
Cash flow problems
Marketing problems
Unestablished customer base
People management problems
Legalities
Production problems
High production cost
Poor location
External influences
Business Plan - Document that sets out the business idea, goals, objective, and other details → crucial in the attempt to raise external sources of finance
Business idea, aims, objectives
Business organisation
HR
Finance
Marketing
Operations
Why do I need a business plan?
Helps attract funding
Supports strategic planning
Identify all resources needed
Provides a focus for development
Used to measure success
Integrated Business: Business that participates in multiple sectors (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary)
A business has a good chance of success when:
there is a skilled and collaborative team of employees in place;
there is enough funding to run the business;
the marketing has been researched well; and
the operations are efficient and resilient.
SWOT Analysis (internal & external)
SWOT Framework:
S: Strengths
W: Weaknesses
O: Opportunities
T: Threats
STEEPLE Analysis (completely external)
S - sociocultural (demographic, population, beliefs, education, health status, etc)
T - technological (technologies, improve production method, country’s infrastructure)
E - economic (econ conditions, income/demand, GDP, business cycles)
E - environmental (natural resources, climate change, circular business model)
P - political (political parties, law changes)
L - legal (obey country laws, law changes, lobbying, sued by individuals, prosecuted by gov)
E - ethical (profit pressure = unethical decisions, environment & employees, labour practices)

The Business Cycle
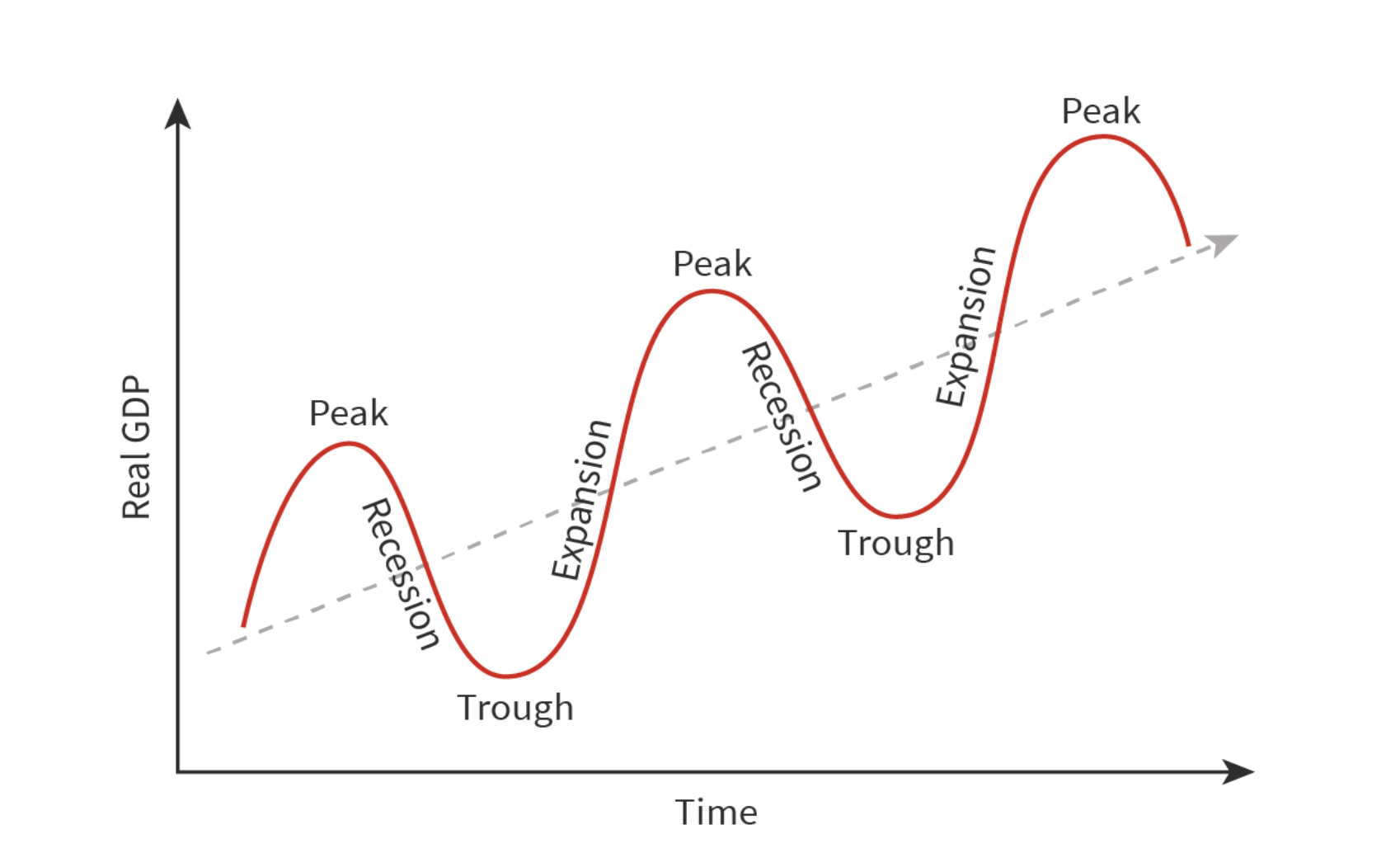
Growth: More goods and services are produced → increase GDP → increase demand for inputs (e.g. labour, capital)
Boom: Peak/highest point of country’s economy → peak of growth
Recession: Limited supply → cost increase → price goes up → customers buy less → production falls → demand for inputs decreases → GDP & Economy contract
Slump: Lowest point of country’s economy → bottom of recession
Terminology:
Gross domestic product (GDP) – the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in a given period of time; represents the size of the economy
GDP per capita – divides total GDP by the population of a country
Inflation – an increase in the general price level, usually expressed as a percentage change
Deflation – a decrease in the general price level, usually expressed as a percentage change
Interest rate – the cost of borrowing money; important for businesses because they may need to borrow money for business investments
Unemployment rate – the percentage of the labor force that is out of work but actively seeking employment at a given time
Import – goods brought into a country
Export – goods manufactured in a country and sold abroad
Exchange rate – the price of one country’s currency in terms of another country’s currency
Subsidy – government payment to businesses
Tax – payment from individuals or businesses to the government
1.2 - Types of Business Entities
Kognity Lesson -
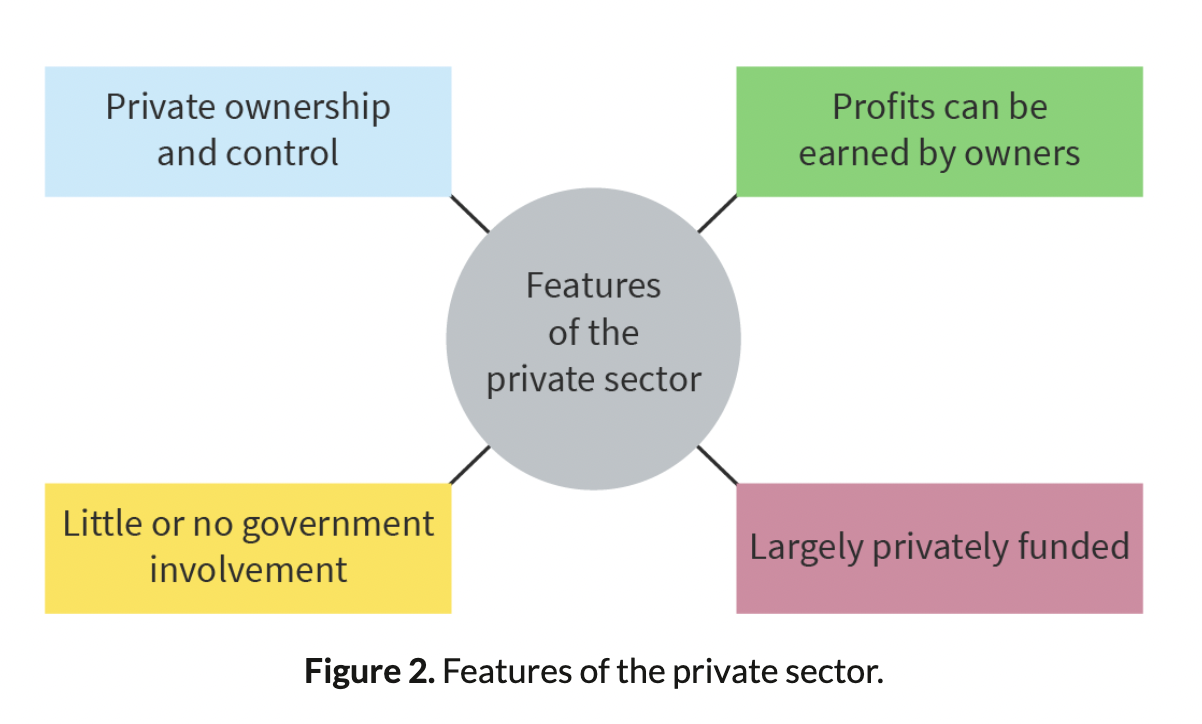
Private sector
Creates employment
Helps the development and growth of the economy
Provides a wide variety of goods and services
For-Profit Commercial Enterprises
For-profit commercial enterprises: A type of business that earns profits, which are distributed to owners or shareholders; profits may have priority over other objectives.
Main types of ownership structure:
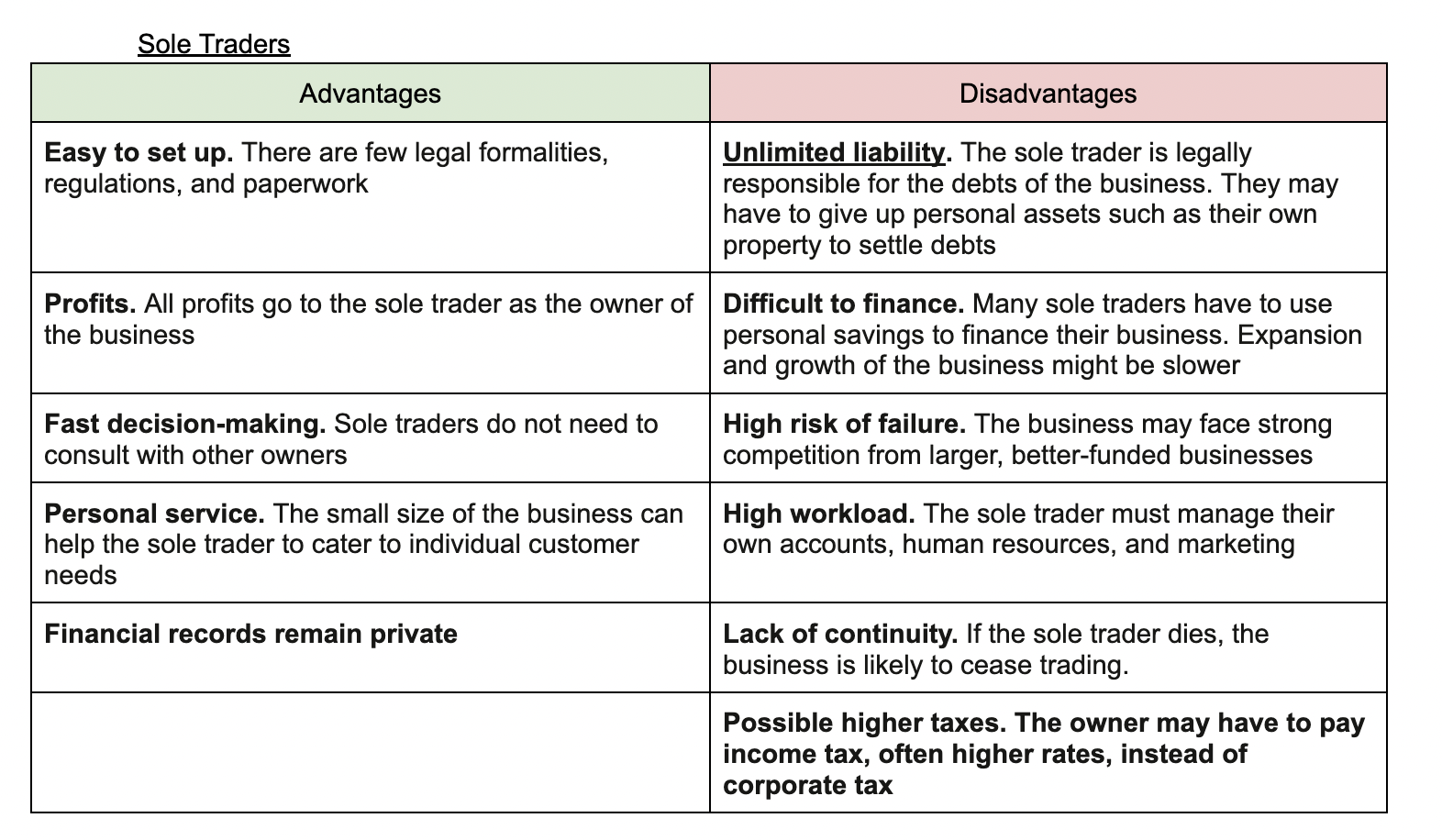
Sole traders - an individual who owns and runs a business alone
Person and business is the same (legally no differentiation) → unlimited liability (no limit to risks)
Partnerships - the creation of a business by 2 or more partners (put to 20), the agreement will likely include
the amount of money put in by each partner
the sharing of profits and losses by each partner
the roles and responsibilities of each partner
the rules around accepting new partners or withdrawal of existing partners
the procedures for ending the partnership
“sleeping partners” → puts money in business but doesn't run it (the person doing the work usually gets the larger share)
Deed of partnership → contract that splits the business (e.g., 40% / 60%) doesn’t come up in the exam!
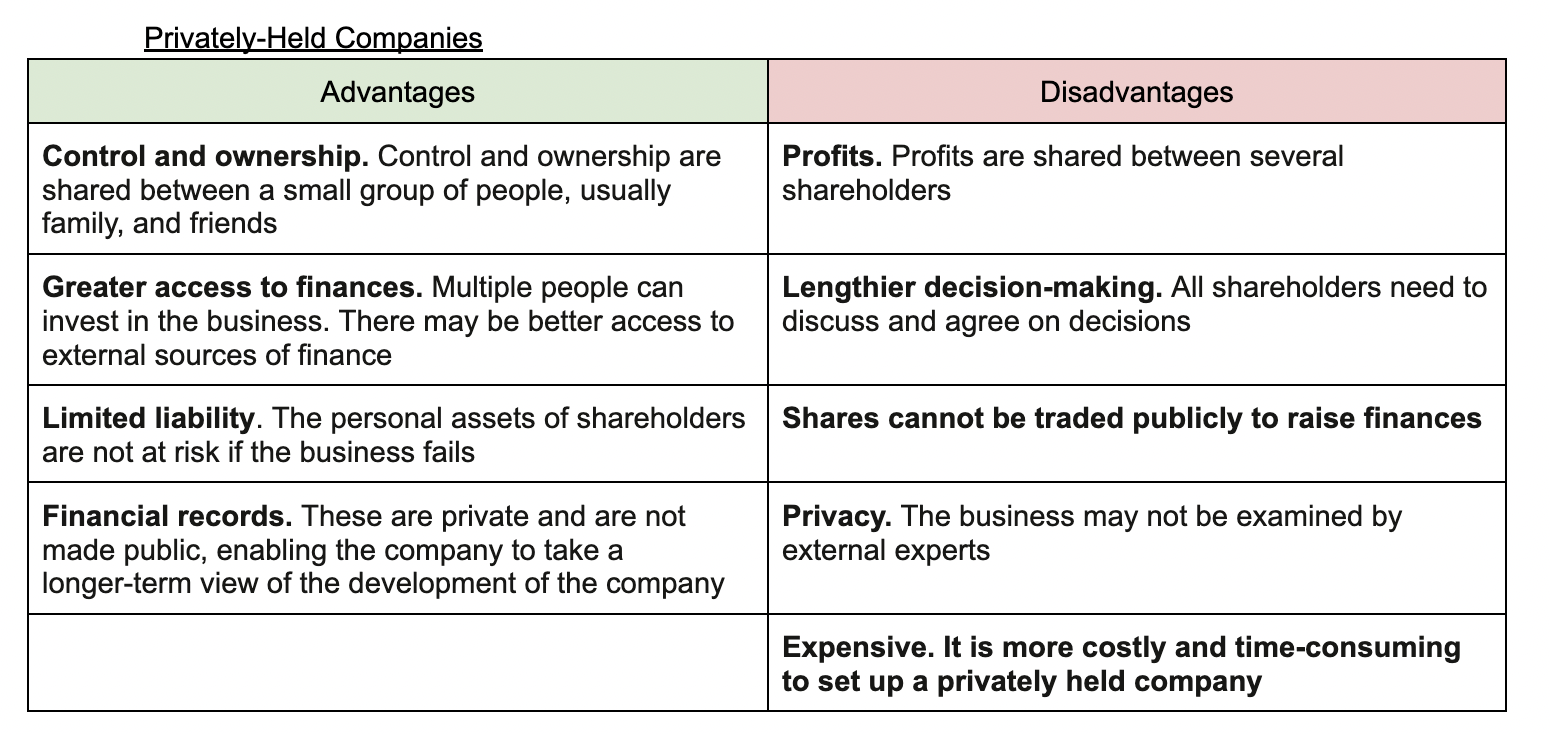
For-profit privately held companies - Privately owned company and often has family or friends as the shareholders; 2 documents needed
the Memorandum of Association, which states the details of the company
the Articles of Association, which states the internal roles and responsibilities of the board of directors and shareholders
For-profit publicly held companies - A company that is publicly owned and has many shareholders who can buy and sell their shares through a stock exchange; 2 documents needed
a memorandum of association, which states the details of the company
articles of association, outlining the internal roles and responsibilities of the board of directors and shareholders

Vocabulary
Shareholders: Someone who owns part of a business
Dividends: A portion of a business’s profits distributed to the owners/shareholders
Limited Liability: A situation where the owners of a business are not personally responsible for the debts of the business if it fails; the owners and the business are legally separated
For-Profit Social Enterprises
For-profit businesses: Realise that their business objectives now need to focus more on social and environmental sustainability, while still earning the revenues and profits that ensure economic sustainability
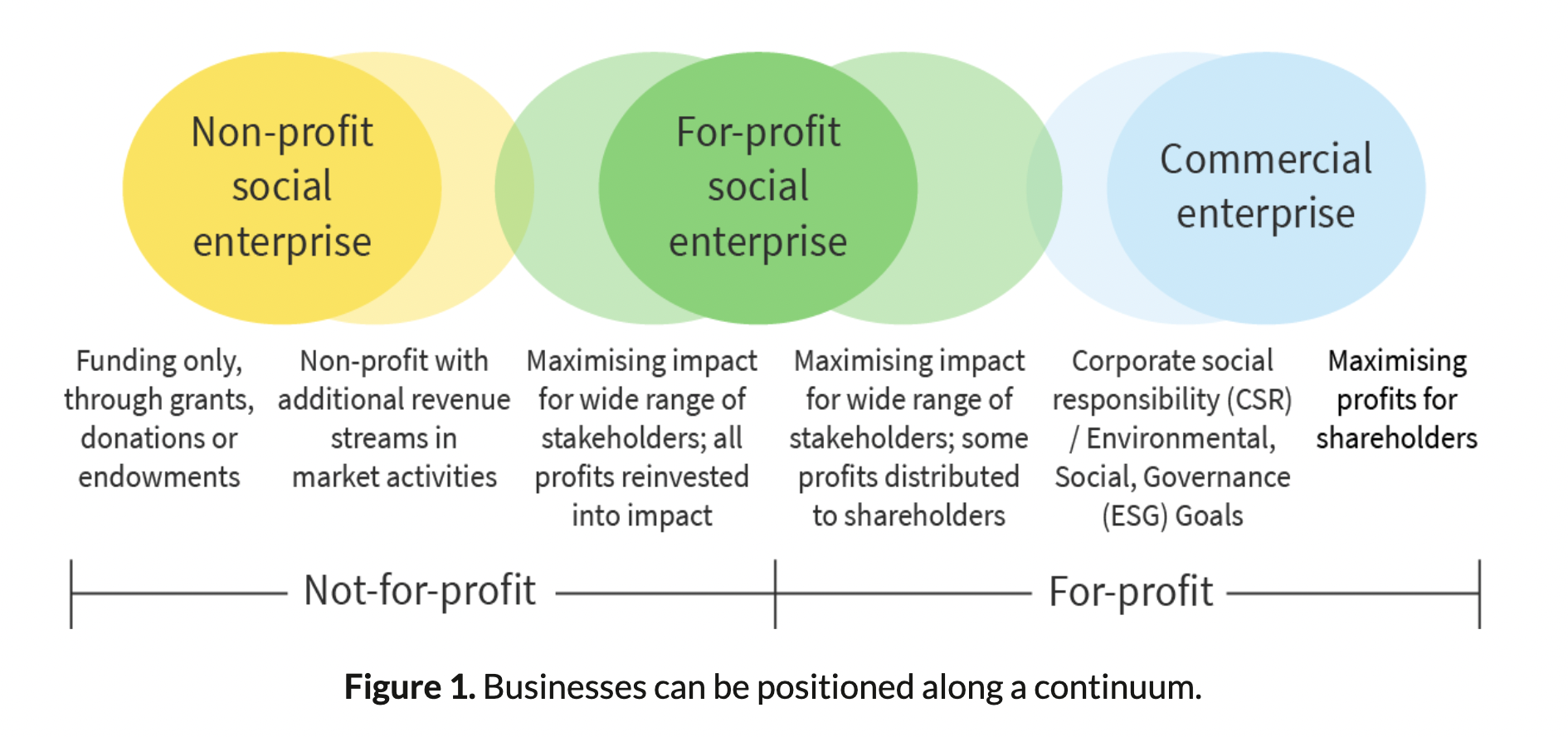
Social Enterprise: Any organization that has a social and environmental purpose at its core
Profit high/low → low-cost product/service → small profit but a large impact (accessibility)
Social enterprises are not judged on profit but on multi-stakeholder impact
3 types of for-profit social enterprises
Private sector enterprises (produces goods and services that are typically sold in markets for a price by for-profit businesses)
Public sector enterprises (produces goods and services that are typically provided by the public sector → bid for contracts with regional/local governments that outsource some essential services to for-profit businesses → gov. can focus money on other public areas)
Cooperatives (a business that is owned by its members → Members participate in decision-making either directly by voting on important decisions or through representation, where members elect representatives to make decisions for them → have limited liability)
Cooperatives employ 10% of people worldwide
Private limited: shareholders you know → you personally share your shares (e.g. Miki sells to Chloe → Chloe cannot share further)
Public limited: anyone can buy stock shares → you just need to own more than others to be “majority shareholder”
Economies of Scale: The large quantities you buy → the cheaper it is + efficient (well-oiled machine)
Incorporated: legal differentiation between owners of the company and business itself → owner’s liability is only how much they invested (e.g. Ms. Edge invested $10,000 into Edge Cafe, Edge Cafe poisoned someone, only Edge Cafe is responsible + Ms. Edge invested $10,000 is at risk → not her house, car, pokemon collection, etc)
B2B - business to business (e.g. Seqta sells to Ishcmc)
B2C - business to customer (Ishcmc sells to students)
1.3 Organisational Objectives
Vision Statement: What do we want? → very aspirational (e.g. Ikea: create a better everyday life for many people)
Definition: Written expression of the long-term ambitions
Mission Statement: Why are we doing what we are doing? → more grounded (e.g. Harley Davidson: fulfill dreams through motorcycling)
Definition: Written expression of purpose and reason for being

Aims: Long-term goals → unquantifiable; vague
Objectives: Short-medium term goals → more specific; things we do to achieve aim
- Strategic: big ones (e.g. lose weight; monthly)
- Tactical: medium (weekly)
- Operational: very short term (day to day)
Exam Tip: Aims and objectives are not interchangeable!
SMART Objectives
S: Specific
M: Measurable
A: Achievable
R: Relevant
T: Timely
(e.g. make 3 customer referrals in the next 2 weeks)
Problems meeting objectives:
- Culture clash: If operating in multiple countries targets may apply/not apply in some countries or culture
- Financial constraints: when there is a sales target it’s easy to forget to spend money
- Conflict: Internal conflicts between management
Changes to organizations
- Internal environment (e.g. leadership change, HR, finance)
- External environment (e.g. covid pandemic, STEEPLE)
Merger: When 2 business merge together
Acquisition: When one business buys another one → sometimes linked sometimes not
Exam Tip: Changes may be positive → creates opportunities
Ethical Objectives (code of behavior) → Why business set these
- Building customer loyalty
- Creating a positive image
- Developing a positive work environment
- Reducing the risk of legal redress
- Satisfying customers’ higher expectations
- Increasing profits
People impacted by ethical objectives (bottom line)
- Business itself
- Customers
- Competitors
- Suppliers
- Local community
- Government
(Ethical Objective: Just 1 element of Corporate Social Responsibility)
CSR: Conscientious considerations of ethical and environmental practices related to business activity
Ethics: Moral principles that guide our decision-making and strategy
Ethical Code of Practice: Documented beliefs and philosophies of an enterprise

Ansoff Matrix: Analytical tool designed to look at market growth strategies
Exam Tip: You could be asked to draw an Ansoff Matrix (even if not stated)!
Market Penetration Strategy: Existing customers & existing products → taking existing products to find even more customers like current ones
e.g. scrub daddy
Product Development Strategy: New product to the existing customers
e.g. nail bar expands to a hair salon next to it
Market Development Strategy: Existing product and find new customers
e.g. Starbucks brings American coffee shops to Vietnam
Diversification Strategy: New products to new customers
e.g. Mars Bar developing dog food
Advantages of Ansoff:
- Analytical framework to make strategic marketing strategies
- Highlights various degrees of risks of marketing
- When quadrant is identified → marketing tactics that can be used
Disadvantages of Ansoff:
- Only a tool → can be misused
- Oversimplification of complex problem
- Cannot predict actual events → misleading
Exam Tip: Exam Ansoff questions are usually combined with case study → have to identify which quadrant + justify + draw matrix
1.4 Stakeholders
Stakeholder: A stakeholder is an individual or group that is affected by the business
Shareholder: Are the owners of a limited liability company
All shareholders are stakeholders but not all stakeholders are shareholders! (Shareholders are the owners of a company, so there is only one stakeholder group in the business.)
Internal Stakeholders: Members of the org. but have a direct interest in activities and performance (e.g. managers, owners, workers, shareholders)
External Stakeholders: Individuals and organizations not part of the org. but have a direct interest in its activities and performance (customers, suppliers, government, media)
Exam Tip: Some shareholders are internal stakeholders others are external stakeholders!
Interests
Internal Stakeholders:
- Shareholders - Return on investment
- Workers – good pay and conditions
- Managers – meeting objectives and job security
External Stakeholders:
- Government – employs people and pays taxes
- Suppliers – stable relationship
- Customers/consumers – want the best product at the best price
- Local community – how does the business affect them?
- Pressure Groups
Exam Tip: Although most sources consider competitors to be stakeholders, it is preferable to not include them for the purpose of exam questions!
Pressure Groups: Individuals with a common concern who seek to place demands on organizations to act in a particular way (e.g. Greenpeace → climate change)
- Boycotting
- Lobbying
- Public Relations
- Direct Action
Conflict: Situations where stakeholders have disagreements on certain matters due to differences in their opinions
Dealing with Conflict (3 key issues):
- Type of organization in question
- Aims and objectives of the business
- Source and degree of power (influence) of each stakeholder group
1.5 Growth and Evolution
Total costs (TC) = Fixed costs + Variable costs
Variable cost → ones that vary with production (e.g. how many cookies you make)
Fixed costs. → ones that remain the same no matter how much you produce (e.g. oven)
Average costs (AC) = cost per unit of output
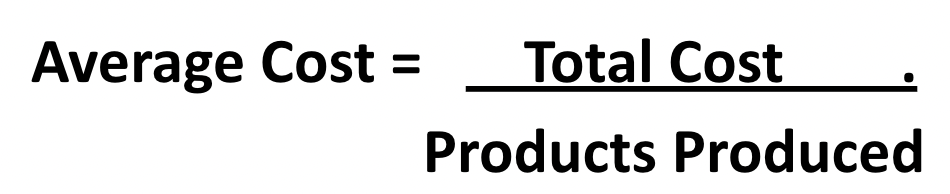
AC = TC / Quantity of Output
Economies of scale = the more I’ve produced, the lower my average cost is
- Helps businesses gain a competitive advantage
- Major benefit of growing a business
Exam Tip: Don’t define EOS as ‘bulk buying’
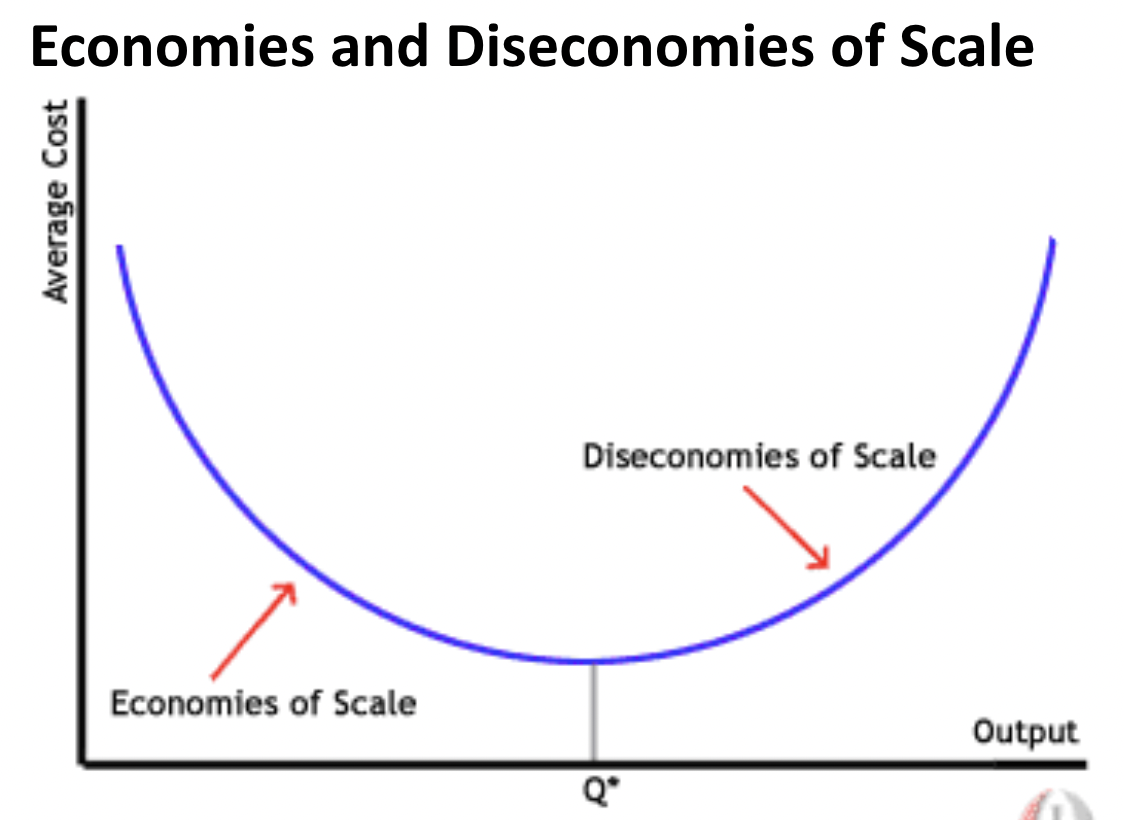
Diseconomies of Scale: Going past the ‘sweet spot’ where production becomes inefficient again → the cost disadvantages of growth. Unit costs are likely to eventually rise as a firm grows
Optimal level of Output: The most efficient scale of operation for a business occurs at the level of output where the average costs of production are minimized
Size of an organization → The size of a business can be measured in several ways:
Market share - a firm’s sales revenue as a percentage of the industry’s total revenue.
Total revenue - the value of a firm’s annual sales turnover per time period.
Size of workforce - the total number of employees hired
by the business.
Profit - the value of a firm’s profits per time period.
Capital employed - the value of the firm’s capital investment for the business to function.
Benefits of larger business:
- Brand recognition
- Brand reputation
- Value-added services
- Lower price
- Greater choice
- Customer loyalty
Benefits of smaller business:
- Cost control
- Financial risk
- Government aid
- Local monopoly power
- Personalized services
- Flexibility
- Small market size
Internal Growth (organic): Using its own capabilities and resources to increase the scale of its operations and sales revenue (financed through a combination of retained profits, borrowing and issuing of new shares)
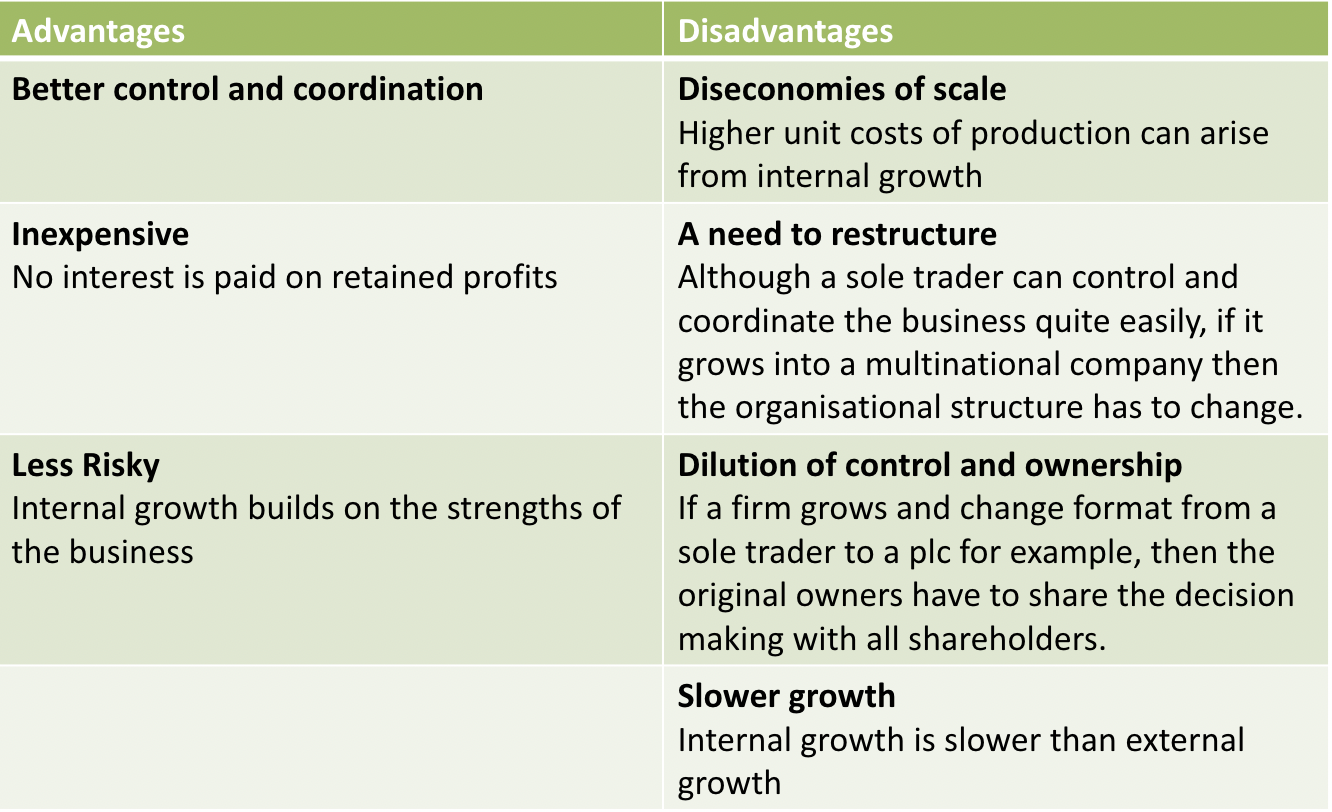
External Growth (fast track growth): Occurs through dealings with outside organizations. Such growth usually comes in the form of alliances or mergers with other firms or through the acquisition (takeover) of other businesses
- Disadvantages: Huge costs → tend to be higher than needed for internal growth
Merger – 2 businesses merge and form a new business
Acquisition (takeover) – when 1 business buys a controlling interest in another business.
Hostile takeover – when the acquisition is unwanted
1.6 Multinational Companies (MNCs)
Globalization Effects: Increased competition, greater brand awareness, skill transfer, closer collaboration
Growth of MNCs: Improved communication, dismantling of trade barriers, deregulation of world financial markets (e.g. switch to Euro currency), increasing economic/political power of MNCs (e.g. Coca Cola impact on US election ‘don’t vote for Trump’)
MNC: An organization that operates in two or more countries, with its head office usually based in the home country
Why do businesses want to be MNCs?
- Profit
- EOS
- To reduce transport and distribution costs
- Sell in new markets by locating in them
- Cheaper supplies of raw materials or markets
- Cost advantages → low labor costs
- Overcome barriers to trade
- Reduce risk
Impact of MNC on the host country:
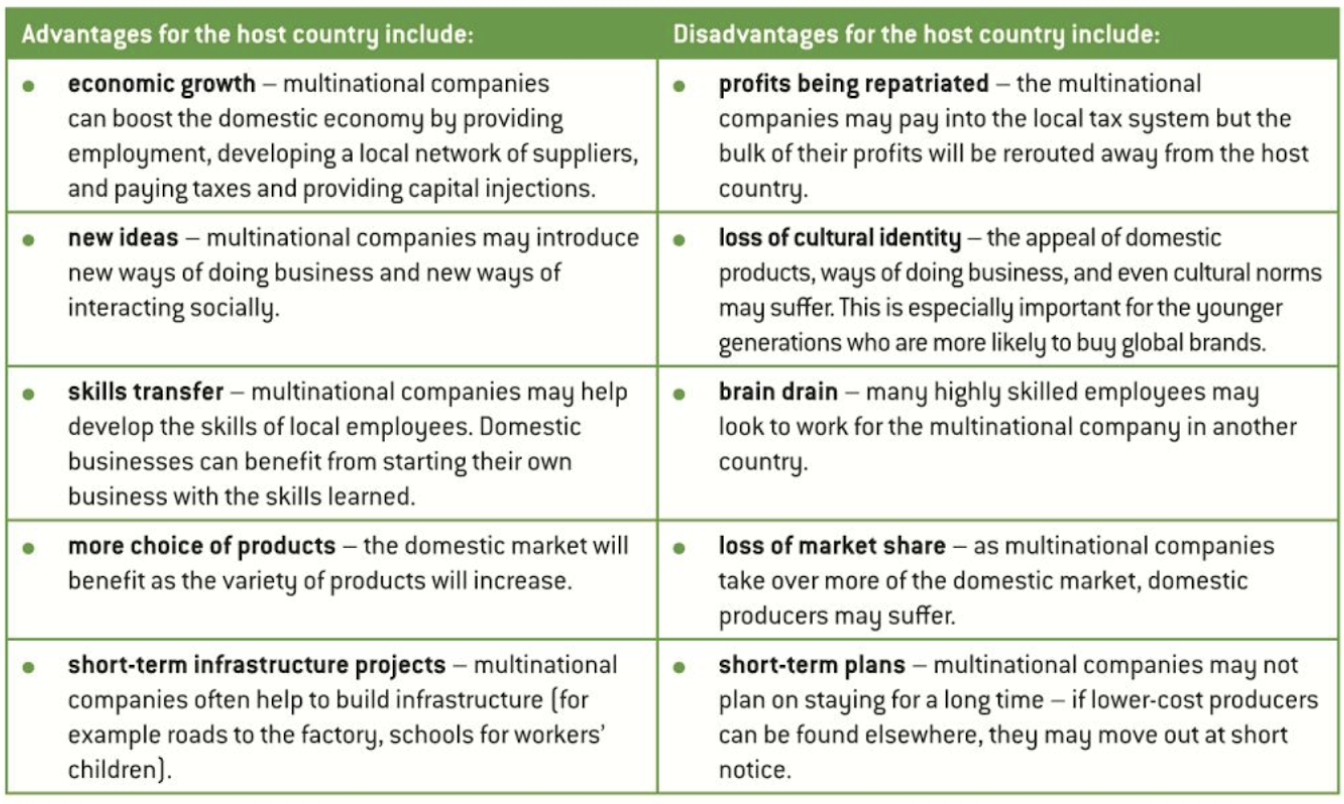
Government relationship with MNCs:
- Tax avoidance
- Global tax disputes
- Strategic investments
- Governments as customers
Business Toolkit - Decision Trees