AP Psychology Notes (Full Year)
Cognitive Biases:
Hindsight Bias: “I knew it all along” idea
Overconfidence: overestimating your ability to do or make something
Confirmation Bias: the tendency to gather information that confirms preexisting expectations
Experimental Design:
Elements of Research Design:
Hypothesis
Operational Definition (creating parameters for your study so it can be replicated)
Reliability (consistency)
Validity (accuracy)
Population (people you’re taking from) and sample size (taken from population)
Convenience Sampling
Measurement Instruments:
Qualitative (non-numerical data)
Quantitative (numerical data)
Survey Method
Conclusions:
Peer Review
Replication
Non-Experimental Design: Non-experimental design lacks manipulation and control and has no cause-and-effect
Case Study:
In-depth investigation of an individual or a small group who may have a highly unusual trait(s)
Pros: details of subjects, unique quality or situation, unethical treatment
Cons: no correlation data, no generalization, time-consuming
Meta-Analysis:
Taking multiple studies that have previously been done and drawing your own conclusions
Pros: accuracy, pose and answer questions
Cons: applicability
Naturalistic Observation:
Observing things in their natural habitat
Pros: ecological validity
Cons: no manipulation
Correlation:
The extent to which to variables are related
Pros: predict behavior
Cons: directionality problem, third variable problem
Illusory correlation: perceiving that a relationship exists when it doesn’t or that it’s stronger than it is
Ethics:
Governance:
American Psychological Association (governing body for psychology)
Federal Regulations (harm to self or others)
Institutional Review Board (local)
Animal Research:
Have to have a purpose
Acquire legally
Humane treatment
Ethical Guidelines:
Informed Consent
Protection from Harm and Discomfort
Confidentiality
Debriefing
AAQ (Article Analysis Question):
Steps:
Identify the research method (1 point)
State the operational definition (1 point)
Describe the meaning of the differences in the means (1 point)
Identify at least one ethical guideline applied by the researchers (1 point)
Explain the extent to which it can or cannot be generalized (1 point)
Explain if the hypothesis is or is not supported by the study (2 points)
Interaction Of Heredity & Environment:
Nature vs. Nurture:
Heredity = nature, genetics, etc.
Environmental Factors = nurture, experience, family interactions, education
Nurture works on what nature endows
Evolutionary Psychology: How natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes.
Natural Selection:
The best traits will be passed down
The unnecessary or negative traits will die off
It's not the strongest species that survives, it is the most intelligent species
Charles Darwin
Eugenics:
Limiting reproduction to only the healthy and desirable genetics
Negative and positive versions of eugenics
Research Tools for Nature vs. Nurture:
Twin Studies
Family Studies
Adoption Studies
Anatomy Of Neurons:
Neurons:
Neurons are nerve cells (building blocks of the brain and nervous system)
Glia cell protects and nourishes a neuron (50x more abundant than neurons)
The nerve is a bundle of neurons
Dendrites:
Branch-like structures that extend out of the cell body
Dendrites have receptors on the ends that receive neurotransmitters to start the chemical signaling process
Soma:
The cell body
The life and support system of the cell
The nucleus
Determines if a neuron will fire or not
Axon + Myelin Sheath:
An axon is a long piece that acts as a pathway for electrical signals that will cause the neuron to fire
Myelin Sheath is a coating that protects the axon and speeds up the electrical signal traveling
Terminal Branches:
The root system of the neuron
Where all the neurotransmitters are housed and sent out of
Vesicles are the sacks that hold the neurotransmitters
Synapse:
Space between two neurons (neurons never touch)
When a neuron fires, it sends neurotransmitters into the synapse, and the other neuron picks up those.
Firing of a Neuron:
Resting Potential:
Dendrites are waiting to receive chemical signals
Neuron is polarized
Potassium ions inside the axon
Sodium ions outside the axon
Action Potential:
When the dendrites have received enough neurotransmitters to reach the required level
The soma initiates action potential and causes an electrical signal
All or none principle
Axon opens channels both potassium and sodium ions mix inside and create the electrical impulse that travels down the axon
Depolarizes the Neuron
Neuron Fires:
The neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft to reach the other neuron
Any leftover neurotransmitters will be reabsorbed (repute)
Refractory Period:
The neurons cool down time before they can be fired again
lasts milliseconds-5 or 6 seconds, depending on the sense
Multiple Sclerosis:
A disease caused by the deterioration of the myelin sheath
Neurons don't function as well and are more susceptible to harm
People who have this have difficulty moving and walking
Myasthenia Gravis:
Connected to muscles raptor sites for acetylcholine
Autoimmune system problems that cause weakness in muscles
The Nervous System:
Functions of The Nervous System:
Sensory Input: gather information
Integration: processes information
Motor Output: The brain sends signals to muscles and glands to respond
Central Nervous System:
Brain: the boss of the nervous system
Spinal Cord: highway from the brain to the body
Peripheral Nervous system:
Nerves: like wires that connect the brain and the spinal cord to the rest of the body
Somatic nervous system: voluntary movements
Autonomic nervous system: involuntary movements
Autonomic Nervous System:
Sympathetic nervous system: fight, flight, or freeze response
Parasympathetic nervous system: calms you down, rests, and digest
Types of Neurons:
Sensory (afferent) neurons: take messages from sensory receptors
Motor (efferent) neurons: transmit signals to muscles and other organs
Interneurons: relay neurons (connectors) help translate information through a motor output
Reflexes:
Reflex: automatic response to a sensory stimulus
Reflex Arc: when sensory organs direct the message to the spinal cord instead of the brain
The Endocrine System:
Endocrine System:
Sending messages long-distance
Circulates and regulates hormones
Transports hormones through the bloodstream
Pituitary Gland:
The master gland
Sending signals to other glands of the body to release specific hormones
Example: puberty
Hormones to Know:
Adrenaline: comes from the adrenal glands and increases heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar. (Long-term adrenaline can cause diabetes and heart disease)
Ghrelin & Leptin (hunger hormones): Ghrelin tells you you're hungry, and leptin tells you you're full
Testosterone & Estrogen (Sex Hormones): Testosterone does human sex drive/aggression, and Estrogen is important for reproduction.
Oxytocin (Love hormone): plays a role in social acceptance needs and pregnancy/birth with baby bonding
Melatonin (sleep): regulates circadian rhythms, helps you sleep, produces in response to darkness
The Brain:
Brain Stem:
Medulla: controls basic functions like breathing and heart rate
Reticular Activating System: brain’s reward system, learning cognition, etc.
Cerebellum: muscles movements and balance
The Cerebral Cortex (Limbic system):
Hypothalamus: a bridge between endocrine and nervous systems and the 5Fs
Thalamus: directs traffic of senses (except smell)
Pituitary gland: master gland that holds, controls, and releases hormones
Hippocampus: memory base, converts short-term memories into long-term
Amygdala: center for fear, triggers if a threat is posed, intense emotions, etc.
Corpus callosum: connects the two hemispheres of the brain
Gray matter helps keep your brain safe
⭐️ The more brain wrinkles you have the more knowledge you have
The Cerebral Cortex (Lobes of The Cortex):
Parietal Lobe: deals with all sensory information processing
(Sensory Cortex in this lobe deals with touch)
(Wernicke’s Area understands/comprehends and processes speech)
Occipital Lobe: processes all the visual information
Temporal Lobes: deals with auditory information
Frontal Lobes and the Prefrontal cortex: deals with linguistic processing, higher-order thinking, and executive functioning. (Motor Cortex controls muscle and skeletal movements)
Broca’s Area (only in the left hemisphere): responsible for speech production
⭐️ The Prefrontal Cortex doesn’t fully develop until 25 years of age
Eyes & Vision:
Transduction: conversion from environmental stimuli to neural-impulse so the brain can understand
Phototransduction: conversion of light energy (vision) to neural-impulse so brain can understand
Light Characteristics:
Wavelength (hue/color): short wavelengths= bluish colors and high-pitched sounds, Longer wavelengths= reddish colors and low-pitched sounds.
Intensity (brightness): great amplitude=bright colors and loud sounds, small amplitude = dull colors and soft sounds.
Saturation (purity)
The Eye:
Cornea: transparent tissue at the front
Iris/pupil: iris is the muscle that expands and contracts the pupil
Lens: tissue behind the pupil, focuses light rays to retina
Retina: sensory receptors where transduction takes place and sends information to the brain (rods and cones)
Fovea: central focus point of retina (only cones)
(Can I Learn Reading Father)
Optic Nerve:
Carries now nerve impulses from the retina to the brain
Goes to Thalamus first
Then the occipital lobe for information processing
Photoreceptors:
Rods and Cons
More rods than cones in the high
Cones are for color and rods are for light and dark
⭐️ Bipolar cells receives information rods and cones and transduction happens
Theories of Color Vision:
Helmholtz thinks retina contains three receptors that are sensitive to red, blue, and green colors and light triggers certain amounts of each to blend/make other colors we see (Trichromatic Theory)
Hering thinks we have opponent colors (pairs) that battle it out to see what light waves we are seeing (Opponent process theory)
Ears and Audition:
The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves:
Acoustical Transduction: conversion of sound waves to information/neural impulses
Sound waves are the compression and decompression of air molecules
Sound Characteristics:
Frequency (pitch): short wavelengths= higher frequencies, longer wavelengths= low frequencies
Intensity (loudness): great amplitude=loud, small amplitude=quiet
Quality (timber/clarity)
⭐️ Prolonged exposure above 85 decibels starts hearing loss (cannot be fixed)
The Ear:
Outer Ear: pinna, collects sounds
Middle Ear: chamber between eardrum and cochlea. (Has three tiny bones: hammer, anvil, and stirrup which concentrates vibrations to the cochlea’s oval window)
Inner Ear: cochlea, semicircular, canals, and vestibular sacs
Transduction takes place in the cochlea
The cochlea is fluid-filled and lined with tiny hairs (basilar membrane) convert the rhythm of vibrations to an electrical impulse that tells the auditory nerve information
The auditory nerve takes information from the thalamus and sends that to the auditory cortex
Theories of Audition:
(Place Theory): different frequencies affect different parts/places of the membrane and triggers different responses/activations
(Frequency Theory): entire cochlea is activated and the speed at which the frequency gives us specific sounds
Perception:
Types of Perception:
Top-Down Processing: when we observe the whole image first and apply existing knowledge to give it meaning (shorter time, less accurate)
Bottom-Up Processing: when we analyze the individual parts of a stimulus to gain meaning of the whole (takes longer, but more accurate)
Perceptual Set (Top-down processing): perceives something in the way we expect it to be
Schemas: impact/influence perception that is mental filler or mental models that organize our information about the world (accommodate or assimilate)
Perception Rules:
GESTALT Principles: German word for pattern or whole that represents the rules of how we understand and organize information
Proximity: how tendency to group things together if they are close to each other
Similarity: we tend to see similar objects as the same thing (based on shape, color, and size)
Closure: we mentally connect the dots or complete images because we know what's trying to be conveyed
Figure & Ground: In everything we see there is a figure and a ground. We focus on the figure and ignore the ground.
Depth Perception:
Binocular Cues: uses both of our eyes to figure out depth (retinal disparity: each of our eyes perceives different things but the brain connects our image and convergence: when your lines of vision converge and you see double of something)
Monocular Cues: use one of our eyes to figure out depth (relative clarity: the better the focus the closer it is to you, relative size: smaller objects are farther away, interposition: if one object is blocking another we perceive that object as closer, texture gradient: the closer we are the clearer the texture/gradient, Linear perspective: parallel lines appear to converge together as they get farther away)
Visual Cliff Experiment: The baby crawled across a clear table with an optical illusion drop to test babi’s depth perception
Visual Perceptual Constancies:
Color constancy: the colors we see are the same colors no matter if they are changed by light or other conditions but we perceive them as a different shade
Size constancy: we perceive distance as causing objects to change sizes but our brain knows they are the same size
Shape constancy: we perceive shapes as the same even when they appear different
Lightness/Brightness constancy: depending on how lighting and shadows impact an object changes how we perceive the shape/look of something
Phi Phenomenon: an illusion of movement from stationary objects
Relative motion: it looks like fixed objects are moving when you yourself are moving
Attention & Perception:
Selective attention: when we focus on one particular stimulus (Cocktail party effect: the ability to attend to one voice in a room full of other voices)
Selective inattention: lack of registering or perceiving particular stimuli because your attention is on a different task (Change blindness: when we don't see small changes when we don’t expect the change)
Cognition-Thinking, Creativity, and Problem Solving:
Strategies:
Algorithm: a rule that guarantees the right solution to a problem (impractical)
Heuristics: rule of thumb for judgment, not guaranteed (quicker method to solve a problem)
Availability Heuristic: judging a situation based on similar situations that come to mind (most recent information)
Representativeness Heuristic: judging a situation based on prototypes (influences stereotypes)
Creativity: little correlation between creativity and intelligence (convergent thinking: aligns with one idea, divergent: goes another through another idea)
Insight: when the solution to the problem comes out of the blue
Overconfidence Bias:
Belief Bias: people accept any conclusions that fit with their personal beliefs
Belief Perseverance: maintaining a belief even after it has been proven wrong
Cognitive Problems:
Functional Fixedness: the inability to see a new use for an object
Confirmation Bias: we look for evidence to confirm our beliefs and ignore information that disproves our beliefs
Framing: a way a problem is presented changes how we view it
Gamblers Fallacy: when you predict random events based on previous random events
Sunk Cost Fallacy: when you feel you’ve invested so much time, money, ex. into something that you have to stick with it
Cognitive Psychology:
Memory
Memory: the persistence of learning overtime via the storage and retrieval of information
Memory has three parts: encoding, storage, and retrieval
Encoding: putting things into storage
Storage: short and long-term memory
Retrieval: The process of bringing memory into one’s consciousness
Sensory memory: taking in stimuli and selecting one for further processing
Iconic memory: stays for a tenth of a second then refreshes
Echoic memory: stays for 3-4 seconds then refreshes
Initial encoding: starts the creation of new neuron connections (occurs as soon as one stimulus is selected for processing)
Three Ways we Encode:
Semantic Encoding: makes neural connections based on meaning
Visual Encoding: makes neural connections based on appearance
Acoustic Encoding: makes neural connections based on sounds and words
Automatic vs. Effortful Encoding:
Automatic Encoding: we automatically encode information, unconscious encoding, well-learned information, parallel processing
Effortful Encoding: requires attention and conscious effort
Short-Term Memory (Storage):
Only stores 5-9 items
The magic number is 7 (plus or minus 2)
Working memory: takes 20-30 seconds
Is concerned with only immediate processing
⭐️ Encoding gets short-term memory to long-term memory (the best way is semantics)
Long-Term Memory (Storage):
Long-term Potentiation: long-lasting and strengthening the connections between two neurons through semantics, association, etc. (Strong emotions can make for stronger/longer memory) Drugs can block LTP and affect learning
Long-term memory types: explicit and implicit
Explicit: facts and experiences memory (Types: flashbulb ex. 9/11, episodic ex. wedding, and semantic ex. school facts)
Implicit: procedural, muscle, or skill memory, and the cerebellum helps facilitate that response
Prospective memory: remembering future things
Retrospective memory: remembering past things
Retrieval:
Retrieval: getting information out either through recall or recognition
Retrieval cues: priming (association activation) and context (environment matches memory)
State-Dependent memory: information is easily recalled when in the same “state” of consciousness it was learned in
Mood congruent memory: the tendency to recall experiences consistent with one’s mood
Hermann Ebbinghaus: did research on the capacity of verbal memory and he found practice makes perfect (repetition), the spacing effect (studying over a long period of time is better for memory than cramming), and the serial position effect (our tendency to best recall the first ex. primary effect and last ex. recency effect items in a list) *middle information is forgotten most often
Phobias:
What is a Phobia:
A phobia is a disruptive/excessive fear of a particular object or situation
Two types: specific and social
Affects people’s work, school, and social life
Anxiety that comes with phobias negatively impacts a person's life
Intelligence & Achievement:
What is intelligence, and how do we measure it?
Intelligence: the ability to derive information, learn from experience, adapt to the environment, understand, and correctly utilize thought and reason
Historically, we measure intelligence by your IQ score
Psychometric Principles:
Standardization: uniform test administration
Reliability: if a test yields similar results each time it’s measured
Validity: measures what it’s intended to and anticipates a future measure
Socio-Cultural Responsiveness: stereotype lift vs. stereotype threat
⭐ The Flynn Effect: the observation that IQ scores have been steadily increasing over time due to a combination of factors
Academic Achievement:
Fixed Mindset: the belief that abilities and intelligence are fixed traits
Growth Mindset: the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work
Classical and Operant Conditioning:
Classical Conditioning:
A learning process that occurs through associations between an environmental stimulus and a naturally occurring stimulus, famously demonstrated by Pavlov's experiments with dogs. *associative learning*
Unconditioned Stimulus: a stimulus that elicits an automatic or involuntary response
Unconditioned Response: natural response to an unconditioned stimulus
Neutral Stimulus: association to unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned Stimulus: a repeated neutral stimulus that now elicits a conditioned response
Conditioned Response: a learned or required response
Classical Procedures:
Acquisition: When a behavior, such as a conditioned response, has been learned
Extinction: the association of the conditioned response when the unconditioned stimulus is no longer presented
Spontaneous Recovery: when a behavior is believed to be extinct (the conditioned behavior disappears or stops occurring when the stimulus is present) unexpectedly and quickly returns after a period of rest or a lessened response.
Generalization: the response happens to similar but not exact stimulus
Discrimination: the response only happens to the precise stimulus
Operant Conditioning:
Operant Conditioning: a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior, as illustrated by B.F. Skinner's work with rats and pigeons.
The Law of Effect: Learning = Behavior + Consequences
The frequency with which the consequences are happening will dictate how likely the behavior will happen
Positive Reinforcement: increasing likelihood of behavior by added reinforcement
Negative Reinforcement: increasing the likelihood of behavior by not adding reinforcement
Positive Punishment: decreasing the likelihood of behavior by adding punishment
Negative Punishment: decreasing the likelihood of behavior by not adding punishment
Aspects of Reinforcement (P1): Primary Reinforcement (need to stay alive) vs. Secondary Reinforcement (not the things you NEED to stay alive)
Aspects of Reinforcement (P2): Immediate Gratification (immediate reward for connecting situations) vs. Delayed Gratification (delayed reward might not always connect situations)
Schedules of Reinforcement:
Continuous: every time the behavior is done they get the punishment or reward
Partial: only some behavior is punished or reinforced
Types: Fixed ratio (how many times you need to do the behavior to get punished or reinforced), Variable Ratio (it’s unknown how many times you need to do the behavior to get punished or reinforced), Fixed interval (a known periodic time frame reinforcement), Variable Interval (an unknown periodic time frame reinforcement)
Observational Learning:
Objectives of Observational Learning:
Modeling: mimicking the behavior observed
Observational Experiment (BoBo Dolls): Stage 1: observe adults, Stage 2: New room, Stage 3: Child Plays
Children imitate others regardless of where or how they observe information
The Social Learning Theory: learning is a cognitive process that takes place in social settings, learning can happen by observing behavior and change by observing the consequences of such behavior, learning can happen by reinforcement and punishment but that is not the foundation of learning, Reciprocal Determinism (a social-cognitive theory which argues that behavior, cognition, and environment all interact with and influence one another)
Themes and Methods in Developmental Psychology:
Enduring Themes:
Chroniclogical Order: birth to death
Thematic Lenses: specfic focuses
Thematic Lenses:
Stability vs. Change
Nature vs. Nurture
Continuious vs. Discontinuous
Design Methods:
Longitudial study: same group observed at different periods of time
Cross-sectional: different groups observed at the same time
Physical Development Across our Lifespan:
Factors That Can Imapct Birth:
Maternal illness
Teratogens (negative outside infulences that impact fetal development)
Genetic Mutations
Hormonal Factors
Enviromental Factors
Childhood:
Reflexes: rooting reflex (suckling when object enters the mouth)
Motor development: Gross Motor Skills (universal order: roll, rock, crawl, walk, run) vs. Fine Motor Skills (detailed skills: not always taught at the same time/order)
Critial (happens or doesn’t) vs. Sensitive (can learn at anytime) Periods:
Language
Imprinting
Adolesence:
Physical and Psychological Milestones: growth spurts, puberty, etc.
Reproductive Ability Development: Menarche (girls first period) and spermarche
Puberty: Primary: allow the ability to reproduce and Secondary: don’t allow the ability to reproduce
Adulthood:
Steady-Decline
Men and Women hard stop development at 25 (years)
Order of decline: Reproductive ability (menopause), Mobility, Flexibility, Reaction time, Senses (vision/hearing)
Gender and Sexual Development:
Sex (biological bases) vs. Gender (how you identify)
Variations of Biological Terms (Intersex, Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome)
Gender Roles: Impacts development and stereotypes (effects marketing, identification, etc.)
Gender Identity and Variations: Gender Non-Conforming, Androgyny, Transgender
Sexual Orientation: LGBTQai+ (who you are sexual attracted to)
Orgins of Sexual Orientation: genetics, prematal horomones, social influnces play a role in sexual orientation
Cognitive Development:
Jean Piaget and His Research:
Jean Piaget studied stages of cognitive development (general)
Schemas: an idea you have in your mind when given a concept
Assimilation: same shemas
Accomodation: changes shemas
Sensorimotor Stage (1): All about your senses and how these help you learn
Object Permanence: the awarness that objects continue to exist even when not percieved
Preoperational Stage (2): mental symbols in toddlers through early adulthood
Egocentrism: the inability to see the world through the perpective of another
Animism: the belief that an inanimate object is alive/has lifelike characteristics
Conservation: mass, volume, numbers stay the same desipte change in shape (comes naturally)
Reversability: child’s ability to reverse a sequence of events in an orginal situation
Theory of Mind: the ability to see others perspective
Concrete Operational Stage (3): think about things more logically (earlythrough late childhood)
Formal Operational Stage (4): hypothetical reasoning and abstract thinking (adults)
Lev Vygotsky and His Research:
Lev Vygotsky studied stages of cognitive development (sociocultural)
Scaffolding: pushing out of your comfort zone so you learn
Zone of Proximal Development (rings): start: what the learner can do alone, second: what the learner can do with help, third: what the learner cannot do
Adulthood: crystallized intelligence (things you know always) and fluid intelligence (thinks you know that deteriorate)
Lawrence Kohlberg and His Research:
Lawrence Kohlberg studied Moral Development
Preconvential: (late elementary) stage 1: punishment vs. reward and stage 2: intrumental relatvist
Conventional: (adolescence through adulthood) stage 3: Good boy/nice girl and stage 4: Law & Order
Postconventional: (15% of adults) Stage 5: social contract and stage 6: universal ethical
Social-Emotional Development:
Ecological Systems Theory:
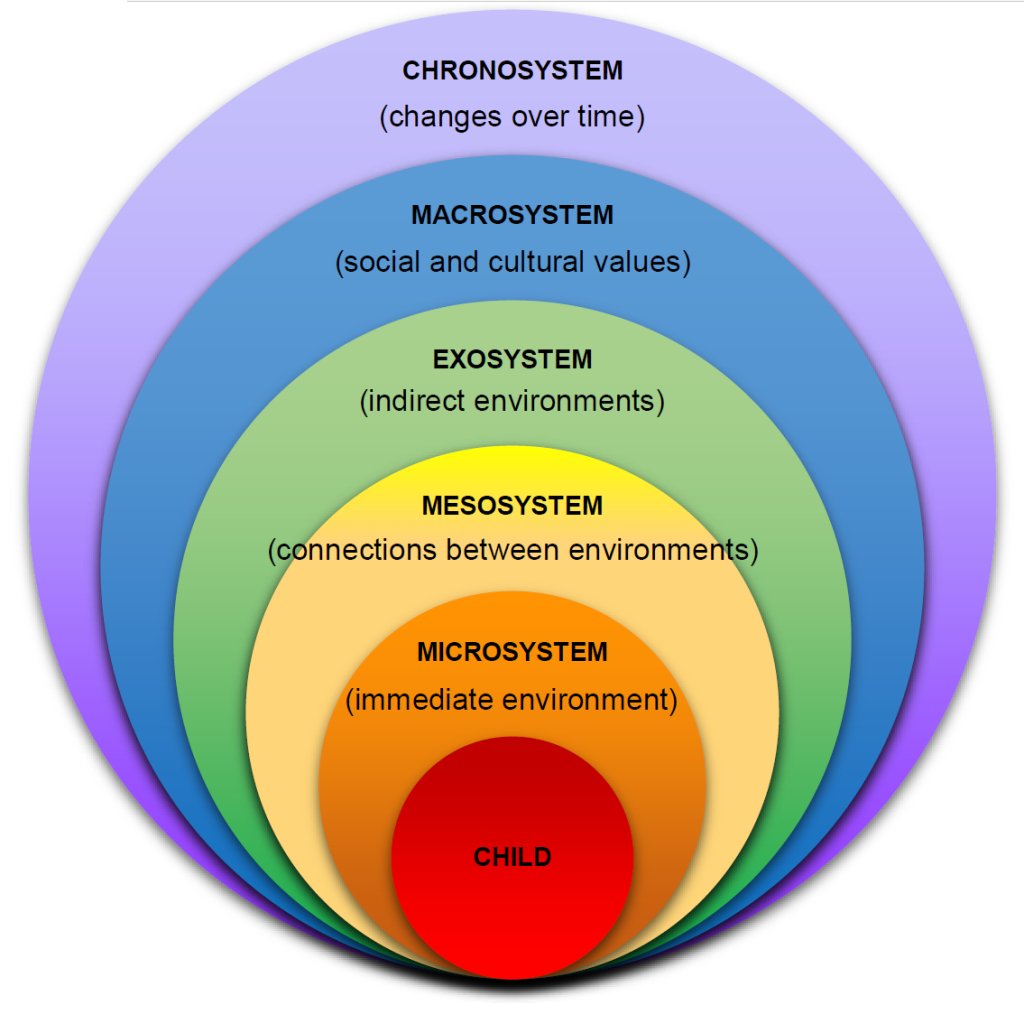
Parenting Styles:
Authoritarian: high expectations with low emotional support
Authoritative: high expectations with high emotional support
Permissive: low expectations with low emotional support
Attachment vs. Temperment:
Attachment: bond between child and caretaker
Temperment: emotional dispositon (wants mom over dad)
Attachment Styles: secure attachment (clingy), insecure aviodant (doesnt care either way), insecure anxious (upset always from change), insecure disorganized (mixture of insecure aviodant and insecure anxious)
Seperation Anxiety: normal regardless of attachment style
Research on Attachment:
Rhesus monkeys
Found physical touch is a key factor in bonding
Social Development:
(Childhood) Parallel Play: playing with the same toys/activity but not playing with each other
(Adolesance) Imaginary audience: beilef that you are constantly being focused on, Personal fable: a belief that ones uniqueness/invulnerability extends the social lifespan
(Adulthood) Support and care: deeper bonds than coexsitance, Attachment: recieves and giving support and care deepens attchment to these social relationships
Social Clock: the social norm sequence of life events according to society
Emerging Adulthood: developmental stage where you learn and build your adulthood in ages 18-25
Stage Theory of Psychological Development:
Argues what has the most developmental influnces on a child
Each developmental stage has a conflict, where you end up creates the path you follow as you grow
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795740-article-erik-eriksons-stages-of-psychosocial-development-5ac3df9e875db90037ffa803.png)
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACES):
Traumatic events that happened before age 18 that affect later life and developmental stages
Theories of Motivation
AP Groundwork:
Arousal: a cortical response to someone’s approval of an event or a sensory stimulus
Motivation Theories:
Drive-Reduction Theory: to achieve a state of homeostasis biological needs drive the behavior
Arousal Theory (Optimal Arousal): we are all trying to find our own optimal level of arousal (where we are most productive, happy, etc.) changes from person to person (Yerkes Law: sweet spot because too much intensity or too little drops our performance on a task)
Self-Determination Theory: deals with intrinsic motivation (internal factors) to fuel motivation
Incentive Theory: deals with extrinsic motivation (external factors) to fuel motivation
Instinct Theory (non-human animals): what an animal instinctively knows (how sea turtles know to get to the water)
Sensation-Seeking Theory: finds one end of the arousal spectrum (experience seeking: seeking thrill) (Thrill or adventure seeking: seeking intense adventure) (disinhibition: trying to challenge or go against social norms) (Boredom susceptibility: avoiding boredom)
Lewins Motivational Conflicts:
Approach-Approach: two desirable options so you are motivated to approach both
Approach-Avoidance: one option with good and bad components so you are motivated to approach this option and avoid it at the same time
Avoidance-Avoidance: two undesirable options so you are motivated to avoid both of them
Main Motivators of Human Behavior:
Eating/Hunger:
Hormones (pituitary gland): Ghrelin = makes you hungry and Leptin = tells you that you’re full
Brain Parts (hypothalamus): Lateral= makes you hungry and Ventromedial = makes you full
External factors: presence of food, time of day, social gatherings, etc.
Belongingness:
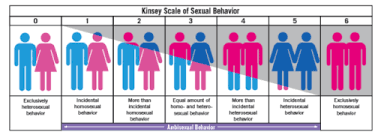
Kinsey Scale: sexuality ⬇
Sexual Response cycle: excitement (blood starts to go to the genitals), plateau (all sexual arousal and responses increase), organism (climax), Resolution (body returns to “normal”).
“Eat Plenty Of Radishes”
Achievement:
Need for social belongingness and aligns with our extrinsic or intrinsic motivations
Biological level: need to survive and pass down genes
Driven by reward/punishment
Goal Setting: S(specific)M(measurable)A(attainable)R(relevant)T(time based) GOALS
Emotion (Unit 4: Social Psychology & Personality)
Emotions (General Knowledge):
Separate from reasoning and knowledge
Internal and external components factor into the emotions you feel
Early Theories of Emotion:
Succession Theory (James-Lange Theory): Event + Arousal = Emotion. Supports this idea: Facial Feedback happens before emotion and polygraph tests
Simultaneous Theory (Cannon-Baro): Event = Arousal and Emotion (happen at the same time
Cognitive Label Theory (Schacter-Singer): 2-Factors→ Event + Arousal and Cognitive Appraisal = Emotion
Recent Applications (Positive Psychology):
Broaden and Build Theory ⬇

Emotional Expression:
Regardless of social and economic backgrounds, everyone can recognize emotional expression
Emotions are universal
Social Psychology:
Social Psychology vs. Sociology:
Social Psychology = study of how individuals interact with others
Sociology = human behavior at a group or society level
Fundamental Attribution Error:
Fritz Heider proposed the Attribution Theory
Fundamental Attribution Error: overestimate the influence of personality (disposition) and underestimate the influence of situations
Social Psychology Vocabulary:
Self-Serving Bias: attribute success to internal causes, yet blame failure on external causes
False Consensus Effect: the tendency to think other people share our mindset more than they actually do
Confirmation Bias: The tendency to only gather evidence to support one side (the side they argue) of an argument
The Halo Effect: the tendency to give someone a more positive view in our minds due to others giving them a more positive reputation than reality
Just-World Hypothesis: the idea that the world is fair, you work hard, you get good things, if you do bad, you get karma
Dispositional Attribution: focus on internal factors
Situational Attribution: concentrate on external factors
Foot in the Door Phenomenon: when you ask for something likely and small before you ask for something larger and less likely to be granted
Door in the Face Phenomenon: start with a large request to make a small request look easier to grant
Attitudes Affect Actions:
Peripheral Route Persuasion = people are influenced by incidental cues (pathos)
Central Route Persuasion = Interested people focus on evidence and arguments (logos)
Cognitive Dissonance Theory:
Leon Festinger
Discomfort (dissonance) we feel when our thoughts and actions clash
We work to reduce discomfort, often by rationalizing our behavior, changing our attitudes
Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
Three Main Psychologists in Social Psychology:
Solomon Asch
Philip Zimbardo
Stanley Milgram
Conformity:
Asch Experiment (Solomon Asch)
If people conform to a group opinion or stick with their own (we often conform to a group even if we don’t believe what the others think)
Confederates vs. participants
Compliance:
The Stanford Prison Experiment (Philip Zimbardo)
The roles that people play can influence compliance
Authority vs. submission
Obedience:
Milgram Experiment (Stanley Milgram)
People will obey authority even if the actions go against their morals
obedience vs. guilty conscience
Group Psychology
Group Influences:
Social Facilitation: improved performance based on the influences around
Social Inhibition: worsened performance based on the influences around
Social Loafing: In a group situation, other individuals slack off because they know the others will pick up the slack
Deindividuation: making someone part of a group instead of having individual responsibilities (peer-pressure can play a part)
Social Trap (conflict of interest):

Bystander Effect: you assume other people will do something (passing the responsibility to others)
Interpersonal Attraction:
The most important qualities of attraction: proximity (mere-exposure effect), physical attractiveness (symmetry), and similarity (self-serving bias)
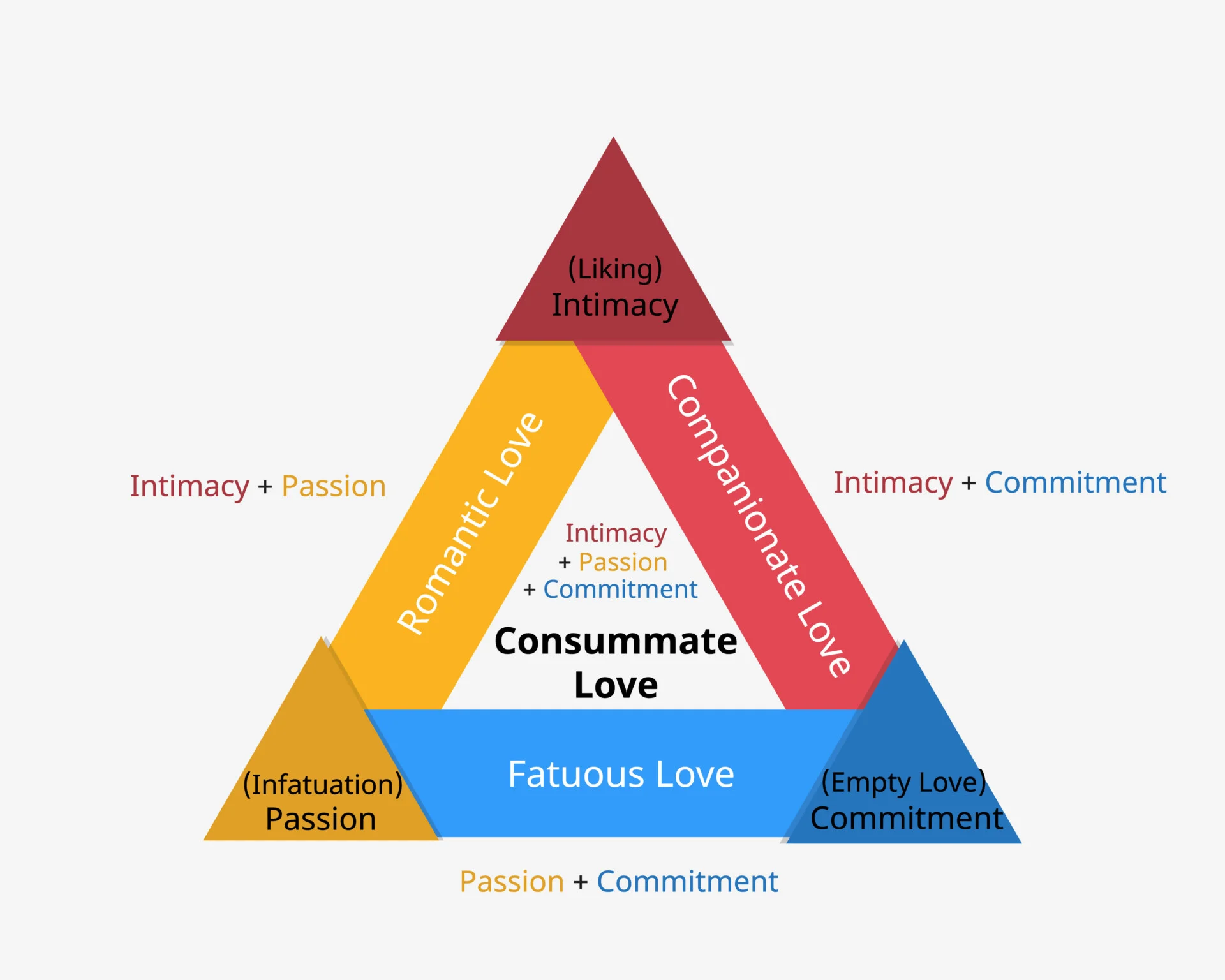
Types of love: romantic love, companionate love, fatuous love, and consummate love
Clinical Psychology and Treatment
Important Terms:
Psychological Disorder: a condition that involves significant disturbance in a person’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
Comorbidity: The simultaneous presence of two or more chronic diseases or conditions in a patient
Medical Model: treating mental illness as any other sort of physical ailment through diagnosis and treatment
Mental Illness = psychopathology
DSM-V:
Stands for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
297 different disorders (will not increase in this edition)
Living document that can be amended at any point
Previously 5 sections→ now only 3 sections
Aligned with the World Health Organization (mostly used in the northern countries)
Introduced the “spectrum” for disorders
Disorders Statistics:
About 1 in 5 adults have a mental disorder (excluding substance abuse or intellectual disabilities)
Risk factors increase the chance someone might become diagnosed with a disorder (academic failure, abusive parents, genetic mental illness, chronic pain, etc.)
Protective factors decrease the chance someone might become diagnosed with a disorder (exercise, effective parenting, social and economic support, etc.)
What each disorder “needs”:
Signs and symptoms
Causation (nature/nurture/multifactorial)
Prevalence rate (how often it gets diagnosed in gender, ethnicity, etc.)
Treatment options
Prognosis
Research and Treatment:
Evidence-Based Interventions:
A combonations of therapy and medication gives the best treatment
Effective Psychotherapy: cultural humity (cultural differences) and theraputic alliance (trust being built through therapist and client)
Late 20th Century: psychotropic medications increased and deinstitutionalzation decreased.
Current Treatment Methods: a combonations of therapy and medication gives the best treatment
Ethical Procedures:
Nonmaleficenece: can’t cause any harm to clients, conflict of interest, appropriate treatments, etc.
Fidelity: trust, professional standards of conduct, aviod exploitation or harm
Integrity: honesty, accuracy, and truthfulness (within treatment plans, conversations, etc.)
Respect for people’s rights and dignity: privacy, confidentiality, respecting boundaries, seeking a good fit (referrall if needed) etc.
Techniques of Psychological Therapy:
Psychodynamic therapies: free assosciation, dream intervention, unconsious mind
Cognitive therapies: just dealing with the thought side of therapy (cognitive restructuring, Fear hierarchies)
Cognitive triad: how you view yourself, how you view the world, how you view the future, (reframing these three zones will help other thought processes)
Applied Behavior Analysis: works best for autism specturm disorder (exposure therapies, aversion therapies, token economy, and biofeedback)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: changing behaviors by changing the thoughts of a patient. Add behviors to restructer thoughts. (dilectical behvior therapy-borderline personality disorder) (rational-emotive behavior therapy)
Humanistic Therapy: person-centered therapy, active listening (untangling thoughts, picking out important moments in a persons life)
Medications: anti-depressants, anti-anxiety drugs, lithium (bipolar), antipsychotics (schizophrenia)
Medications alter neurotransmitters y causing: agnosist, antagonist, and reuptake inhibitors
Tardive Dyskinesia: prolonged exposure to gen 1 antipsychotics causes this side effect (lip smacking, tounge outside of the mouth, lack of dopamine, etc.) happens with the homeless community a lot
Last Resort Interventions:
Psychosurgery or Lesioning: cutting communications for certain parts of the brain
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): used mostly for depression (stimulates certain responses)
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): triggering a sezuire to change brain chemistry/reset the brain (personality and lifestyle can change)
Lobotomy: cutting access from the frontal to the brain (causes more aggression and rash decsions) Finn Gauge-unintentional lonotomy