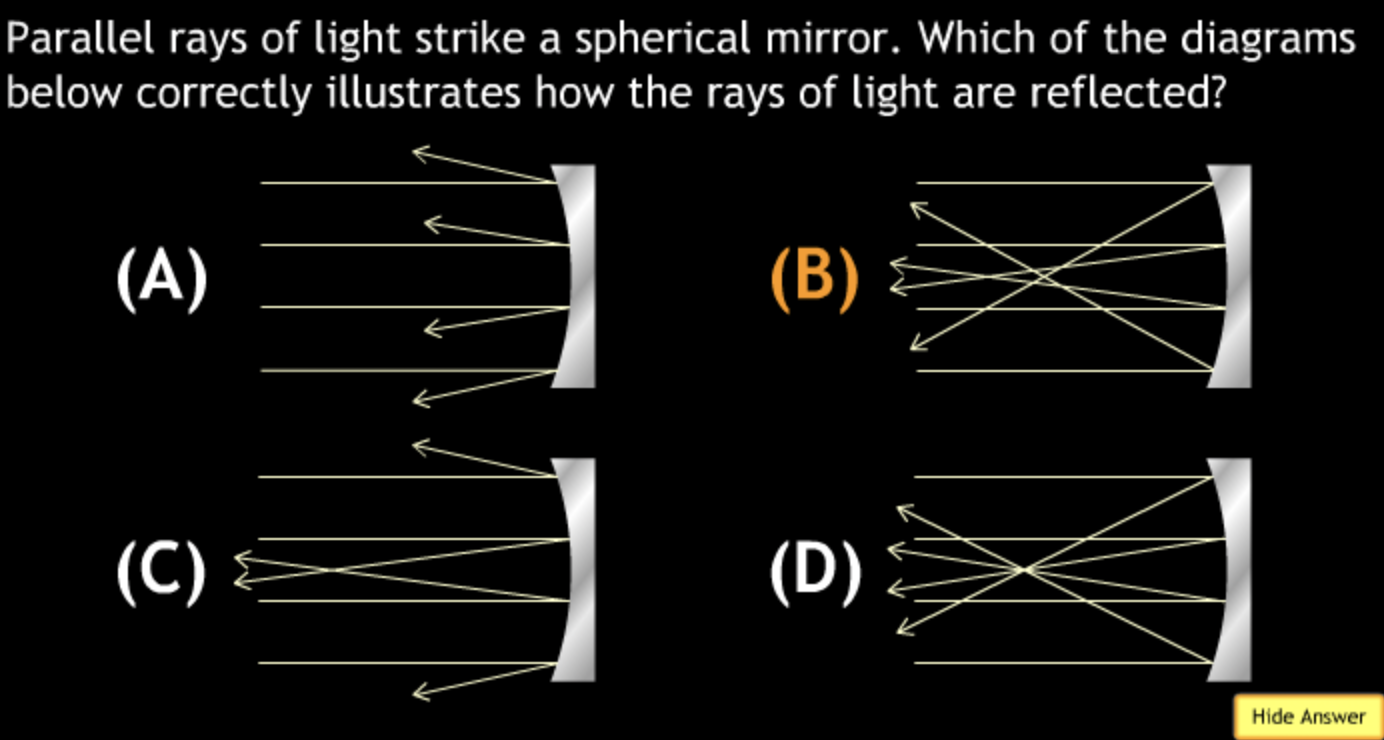
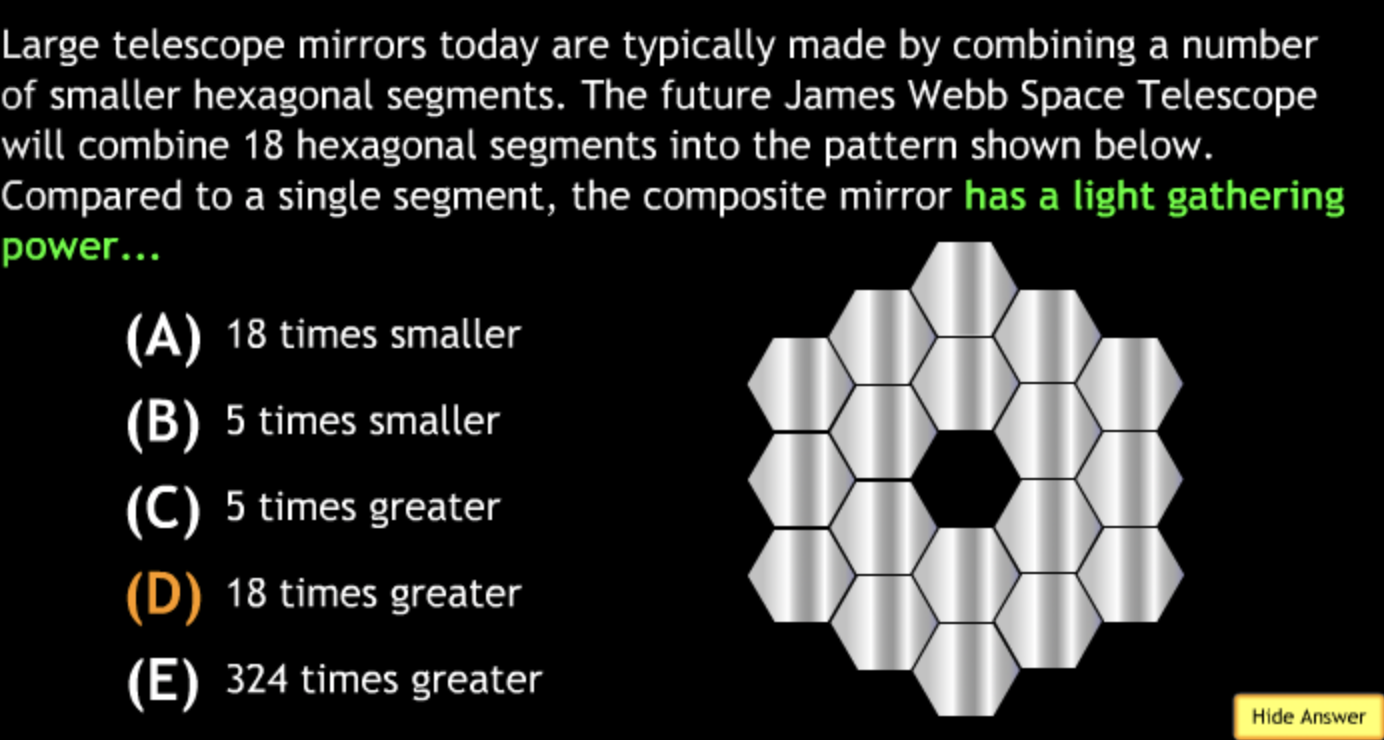
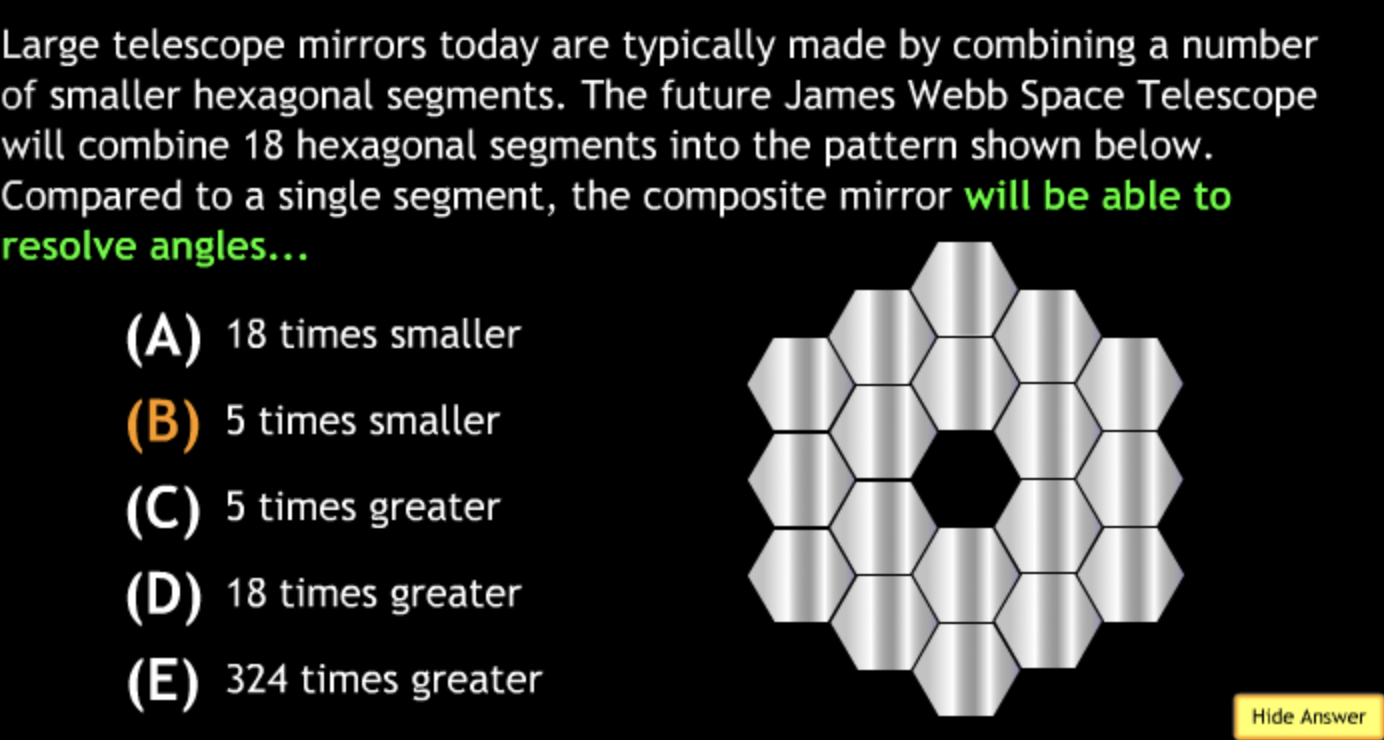
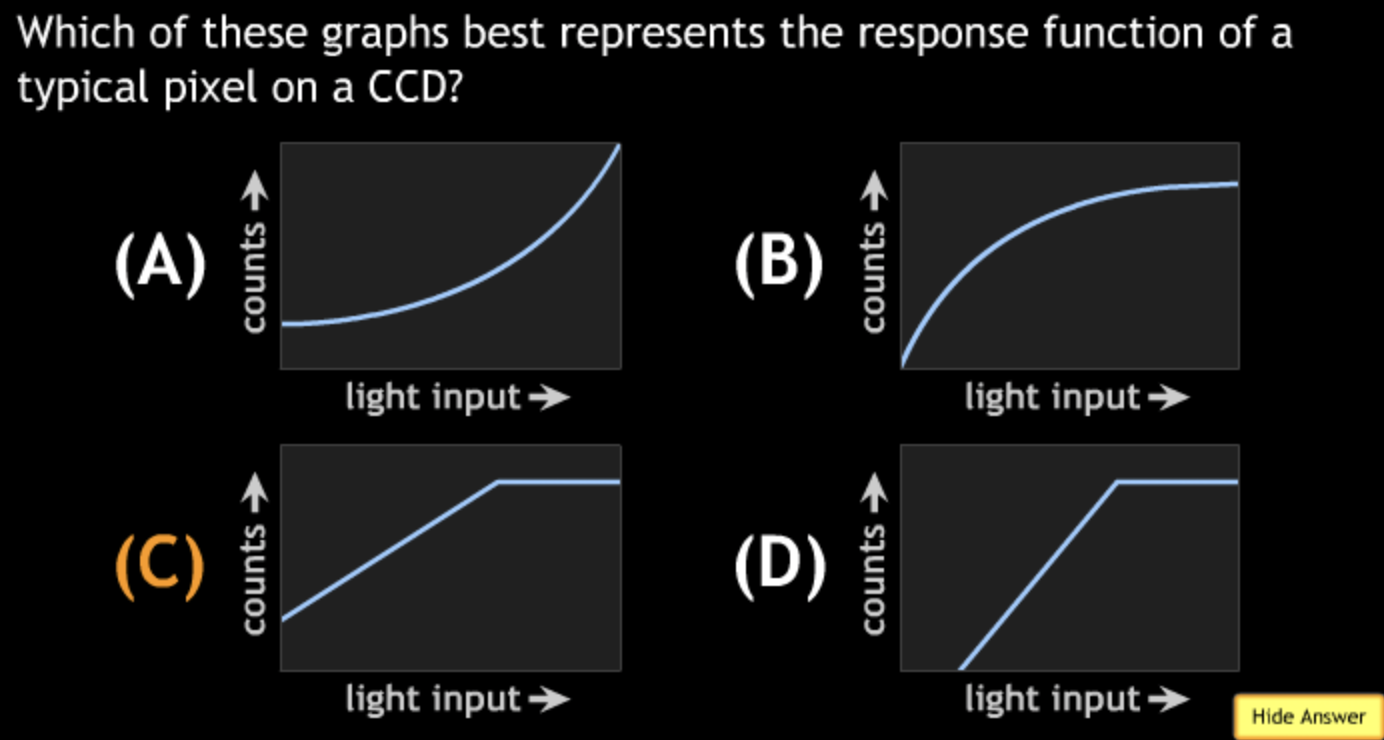
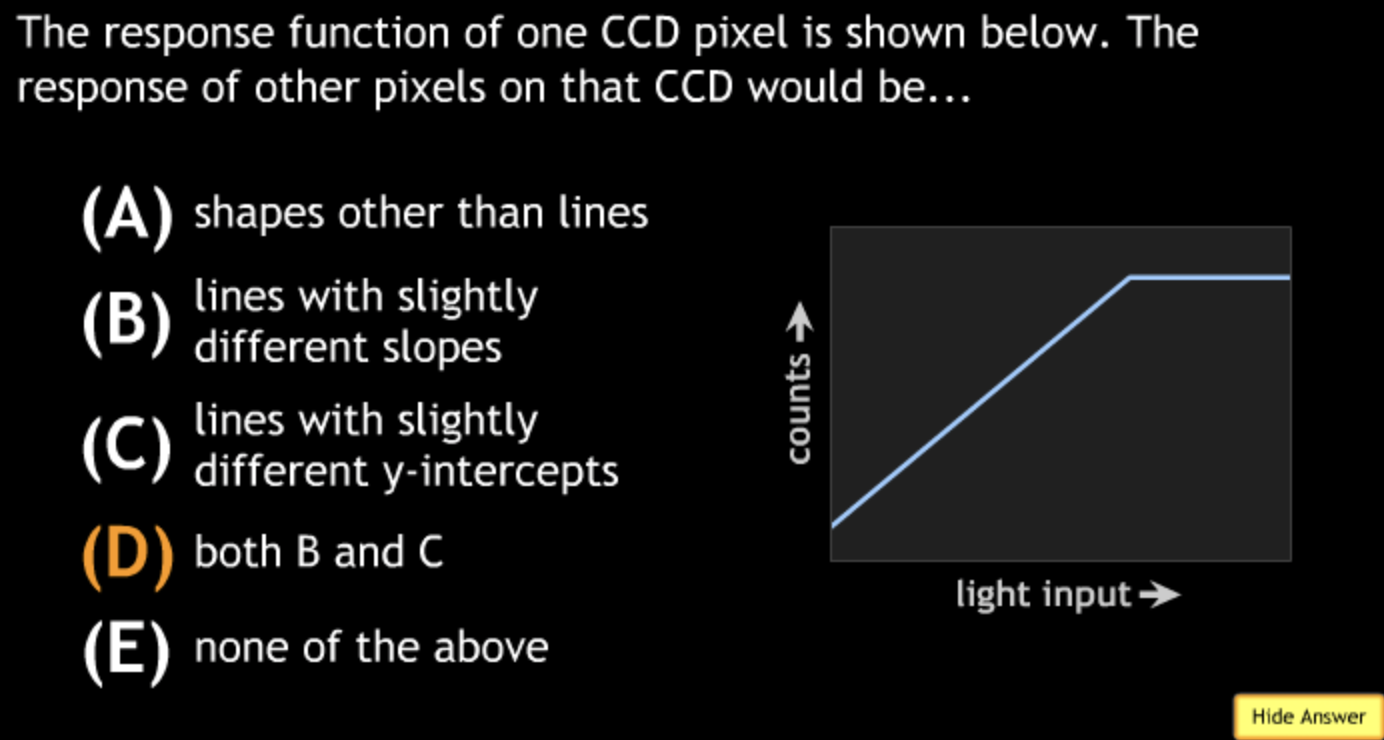
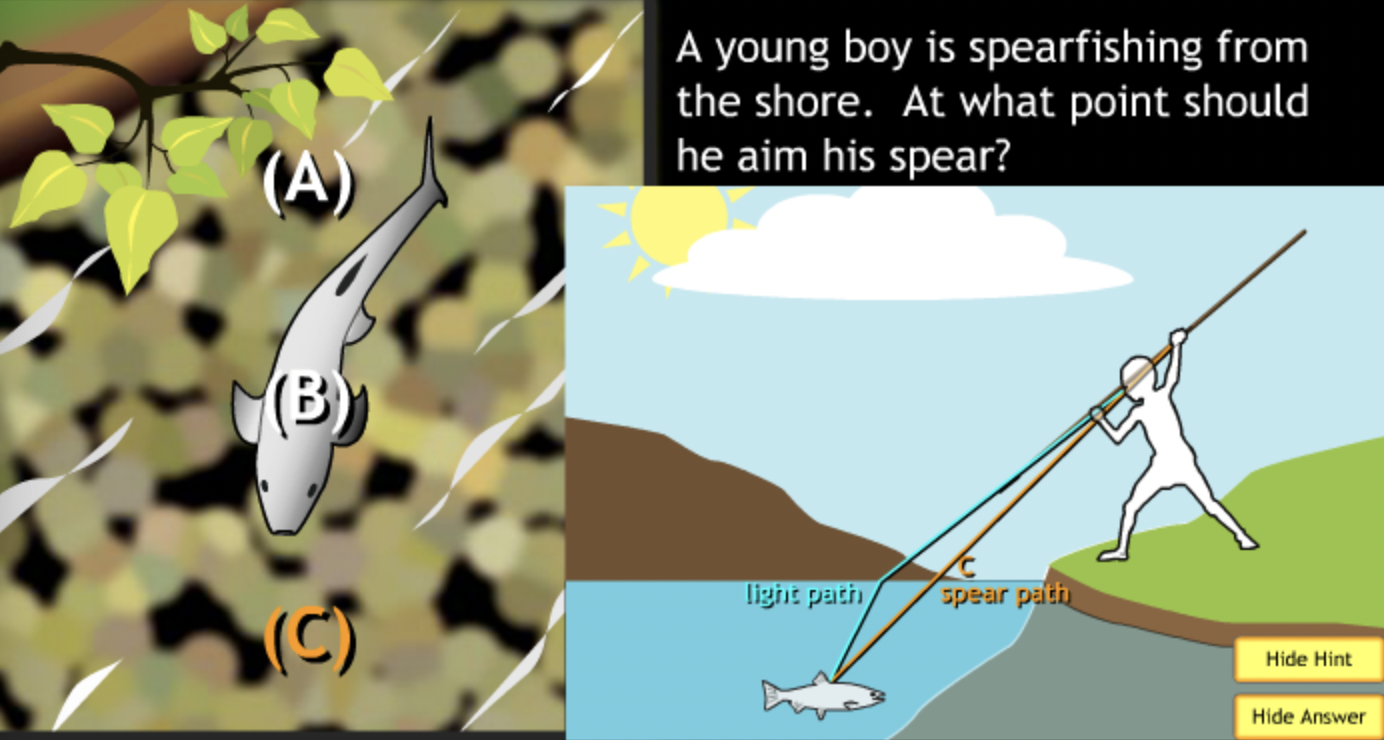
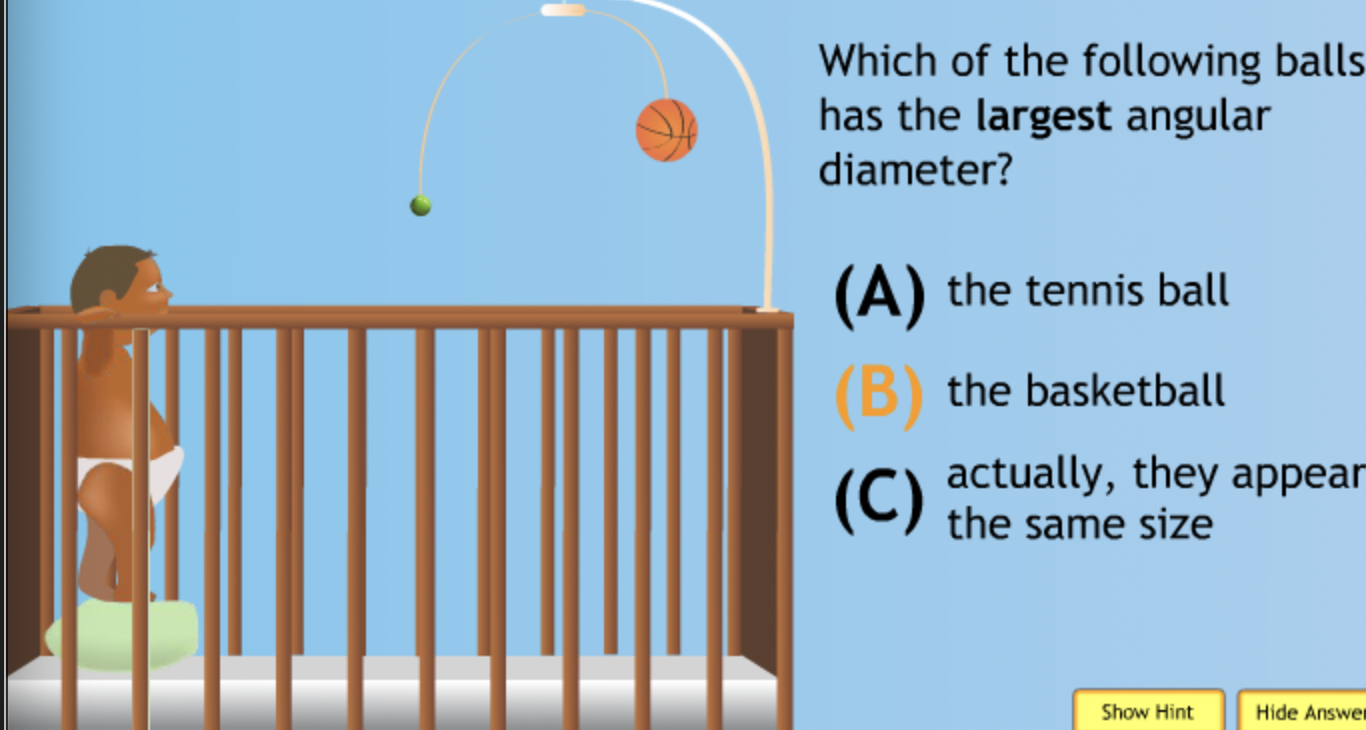
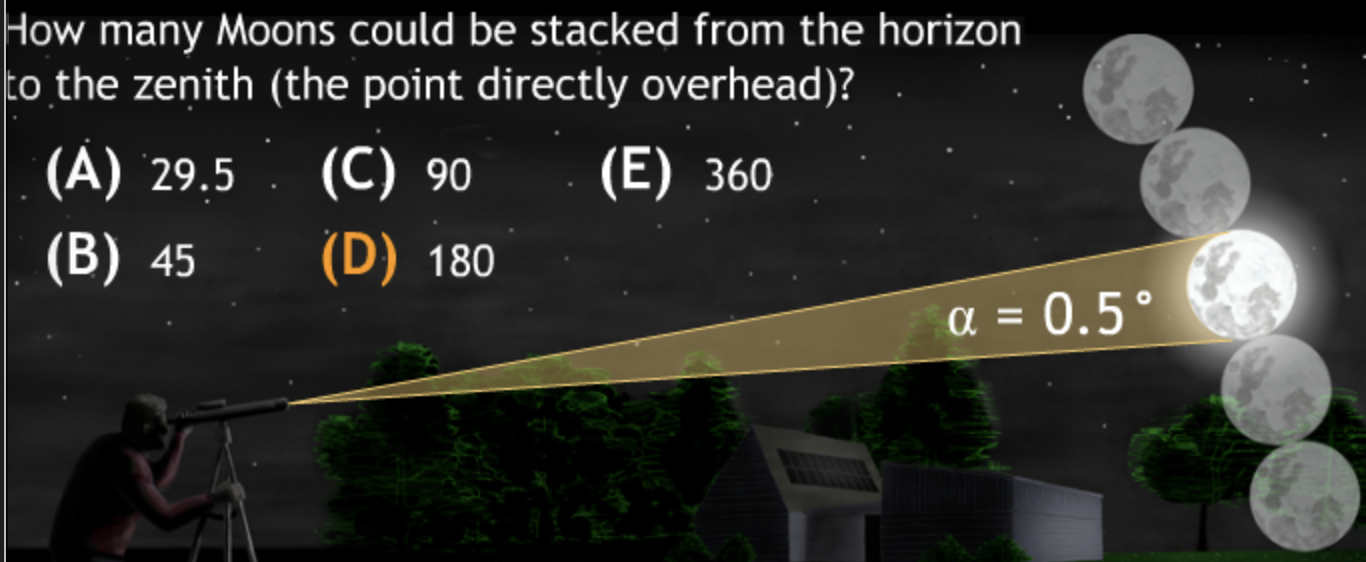
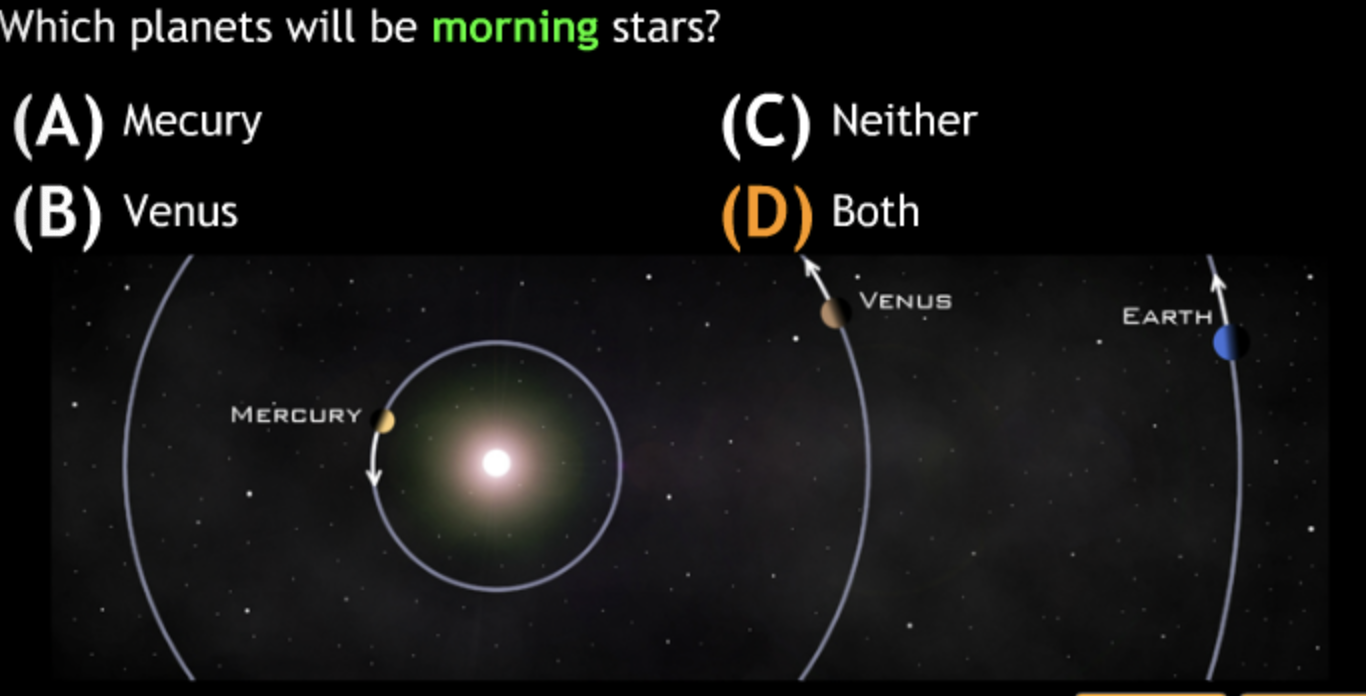
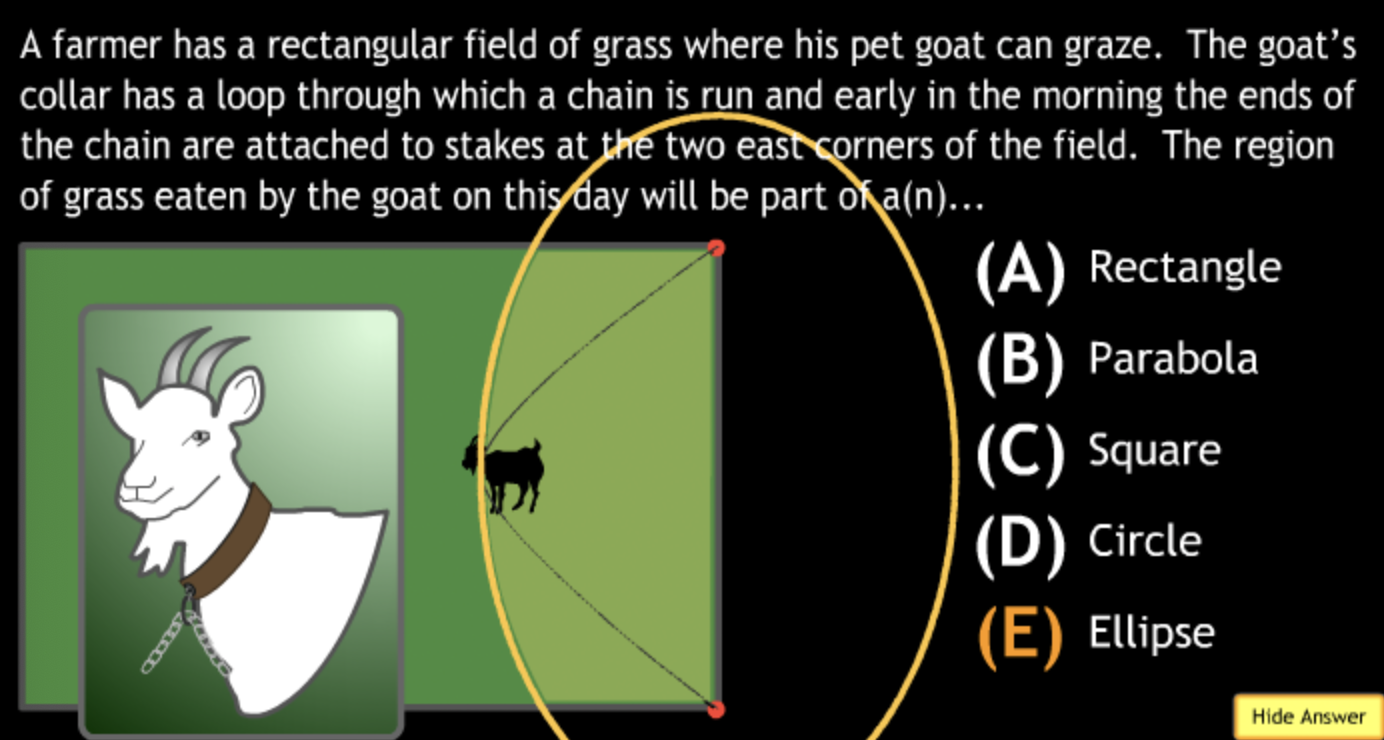
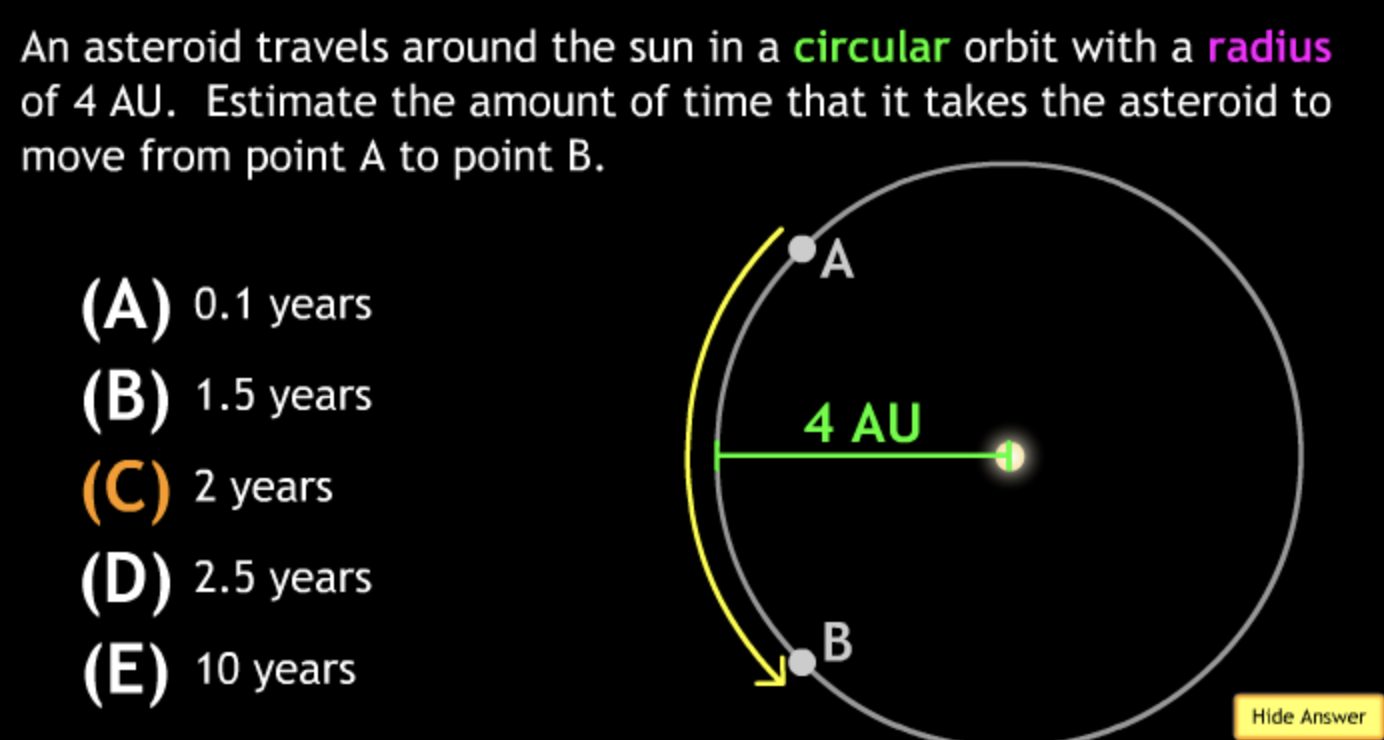
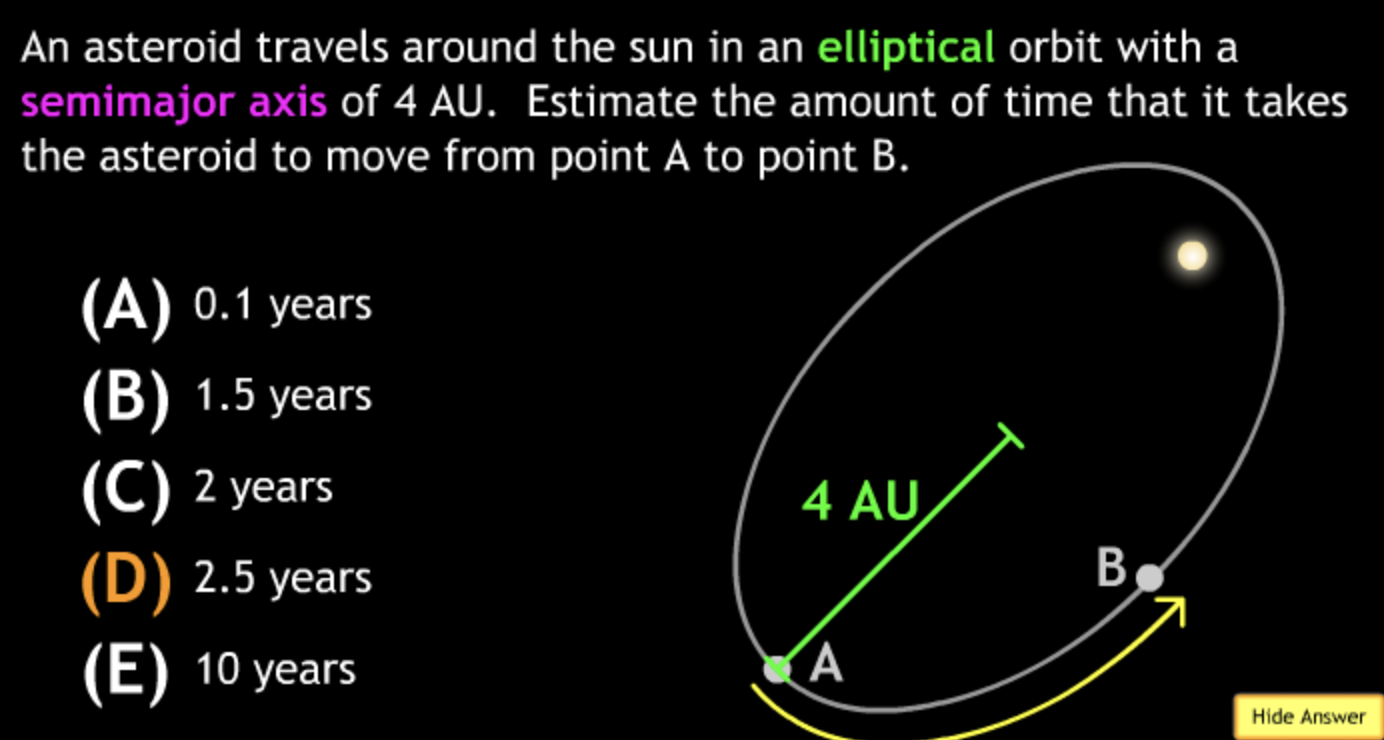
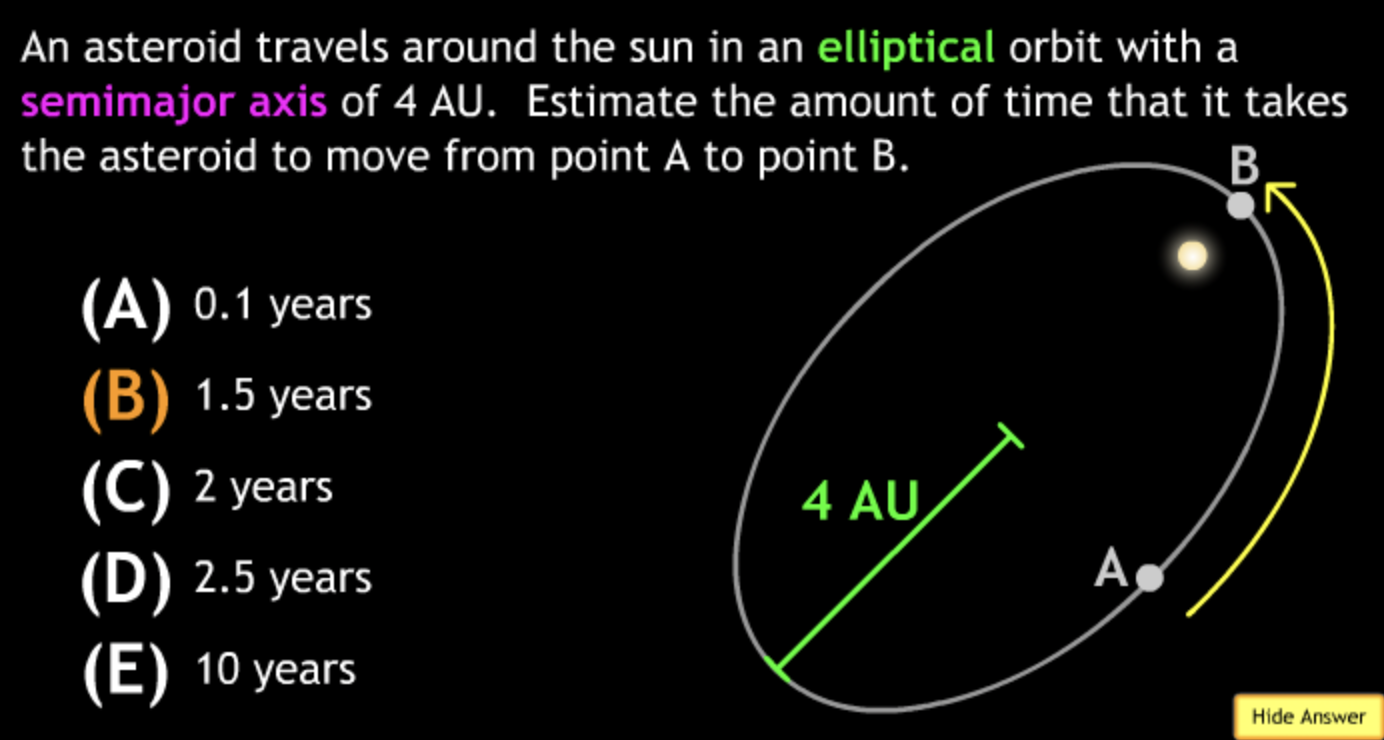
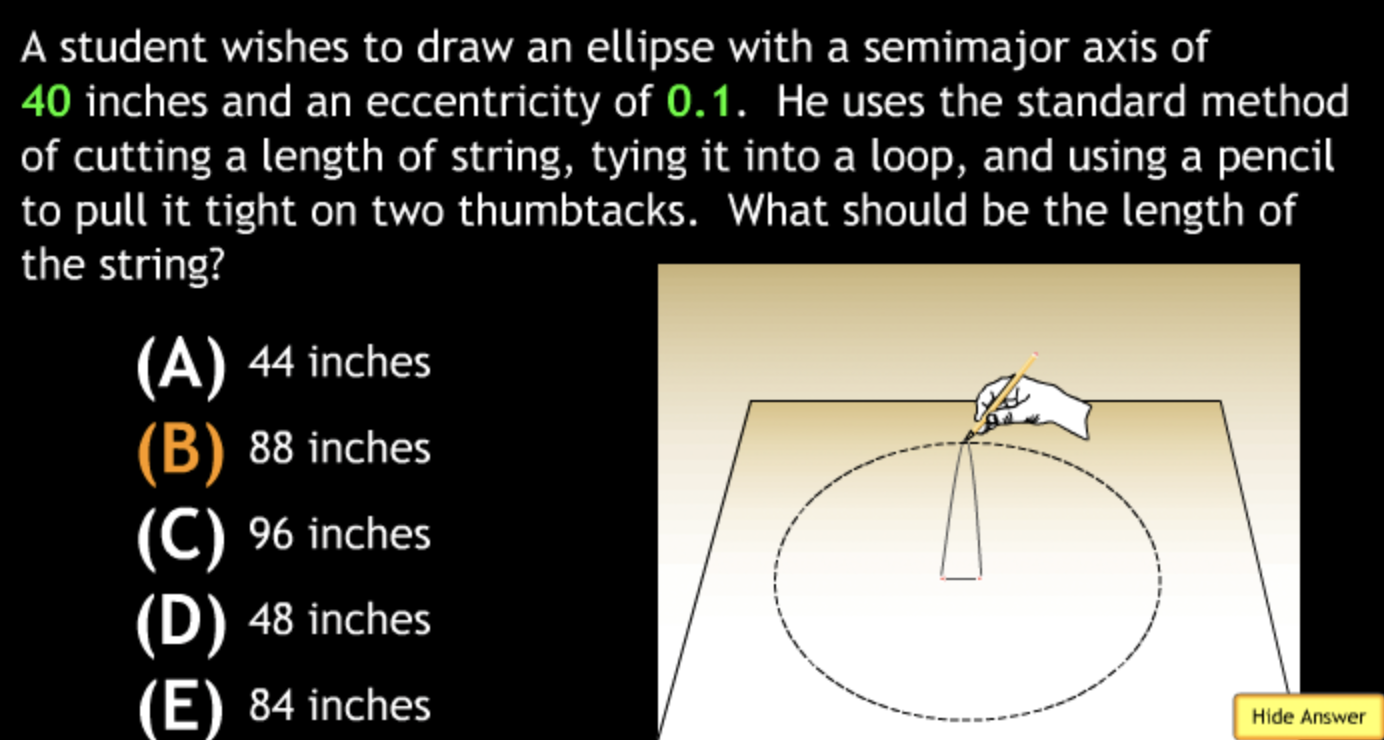
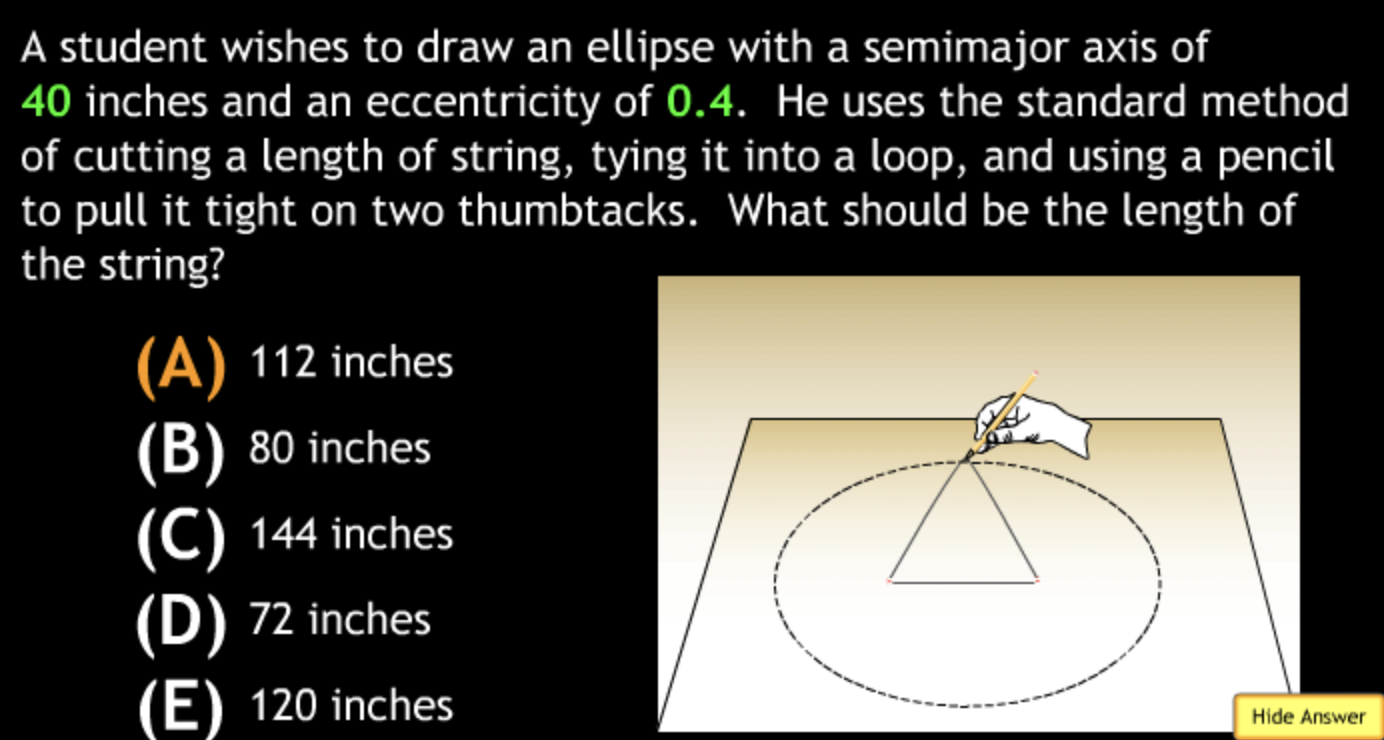
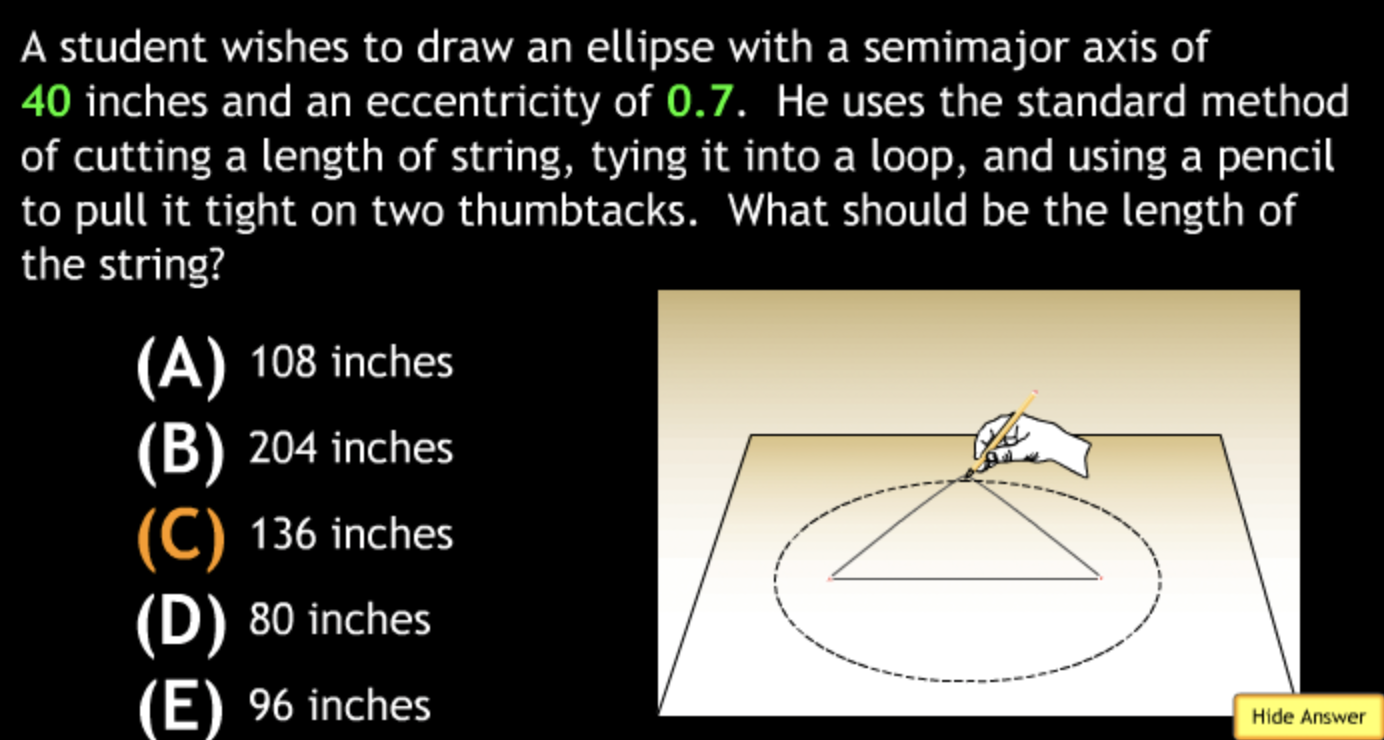
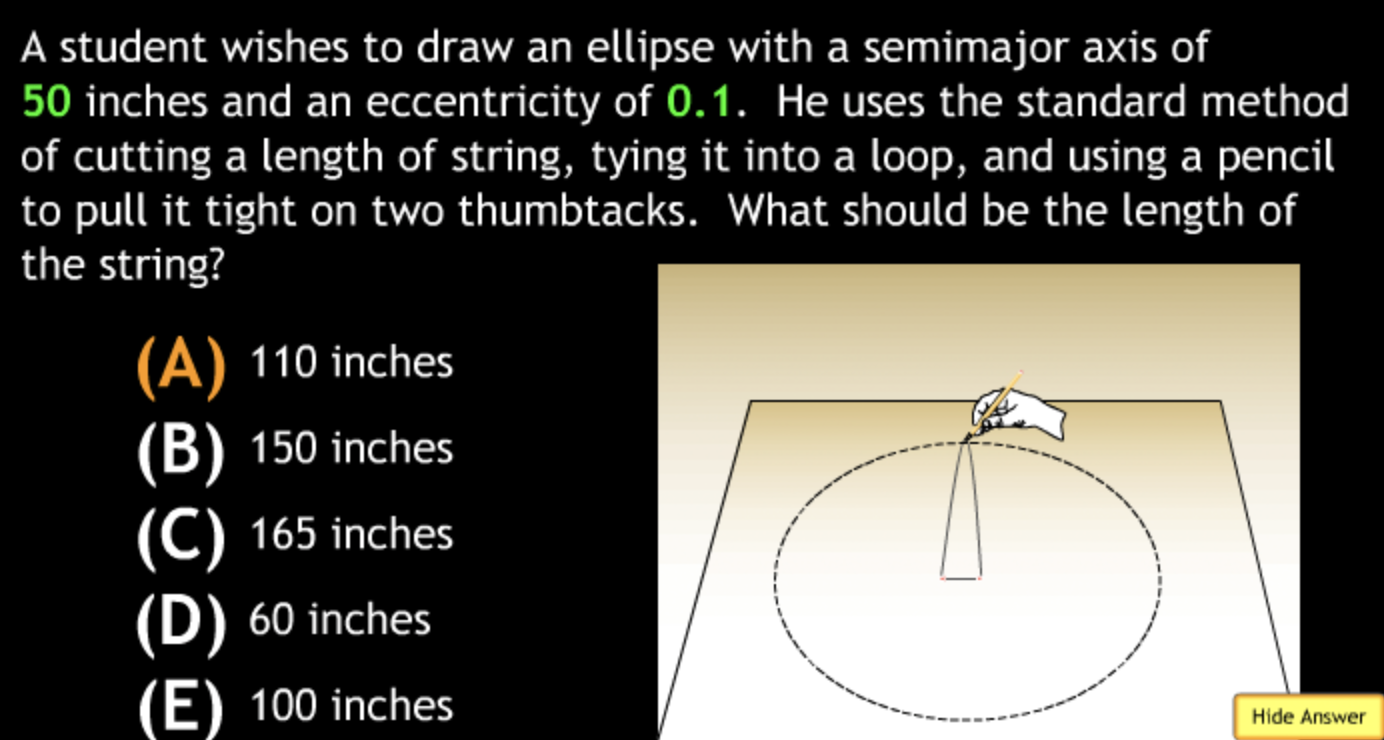
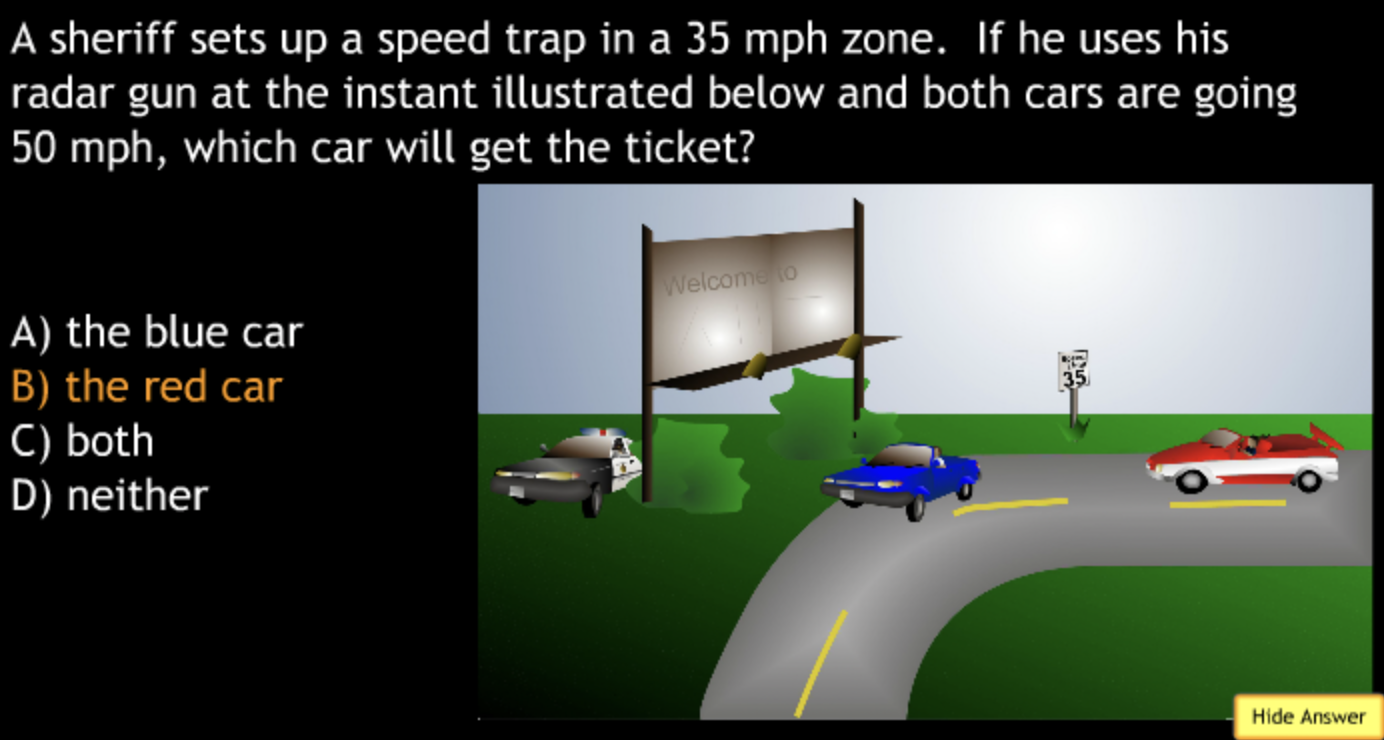
Class Action
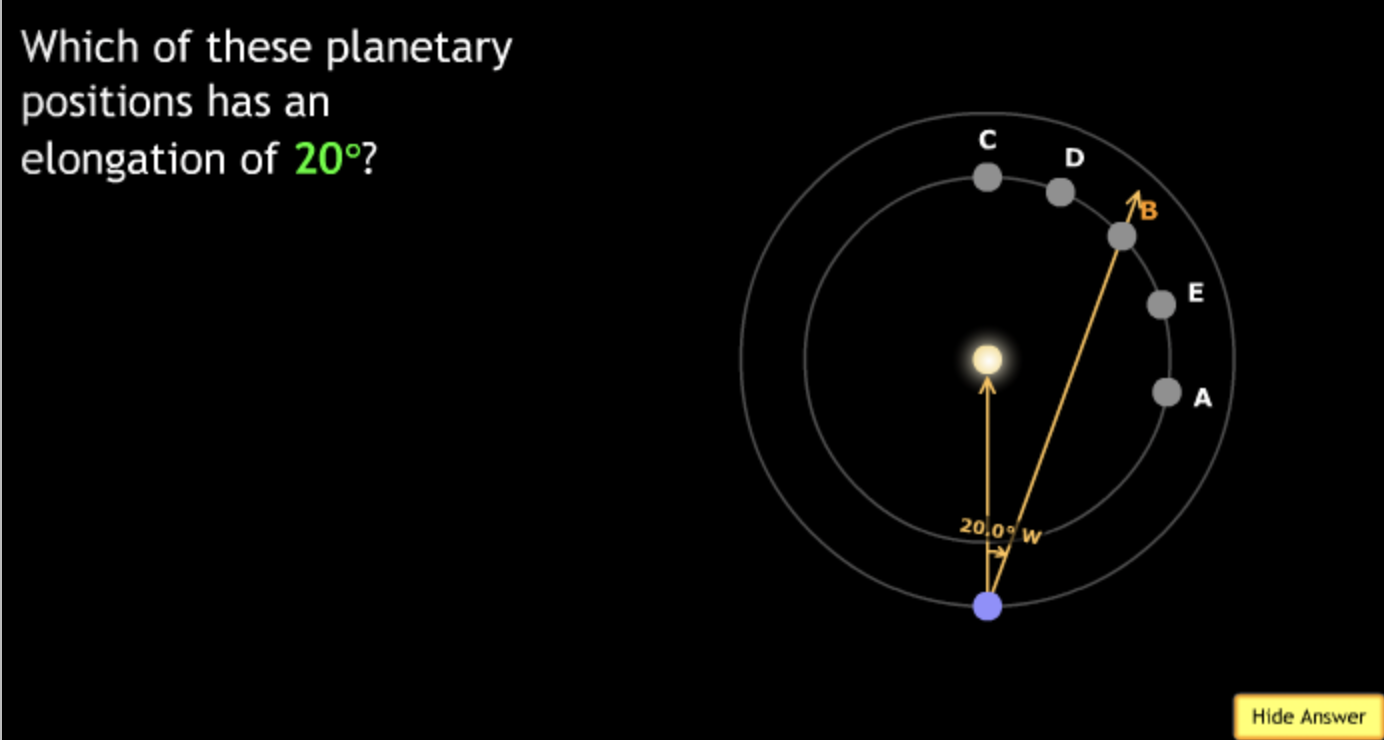
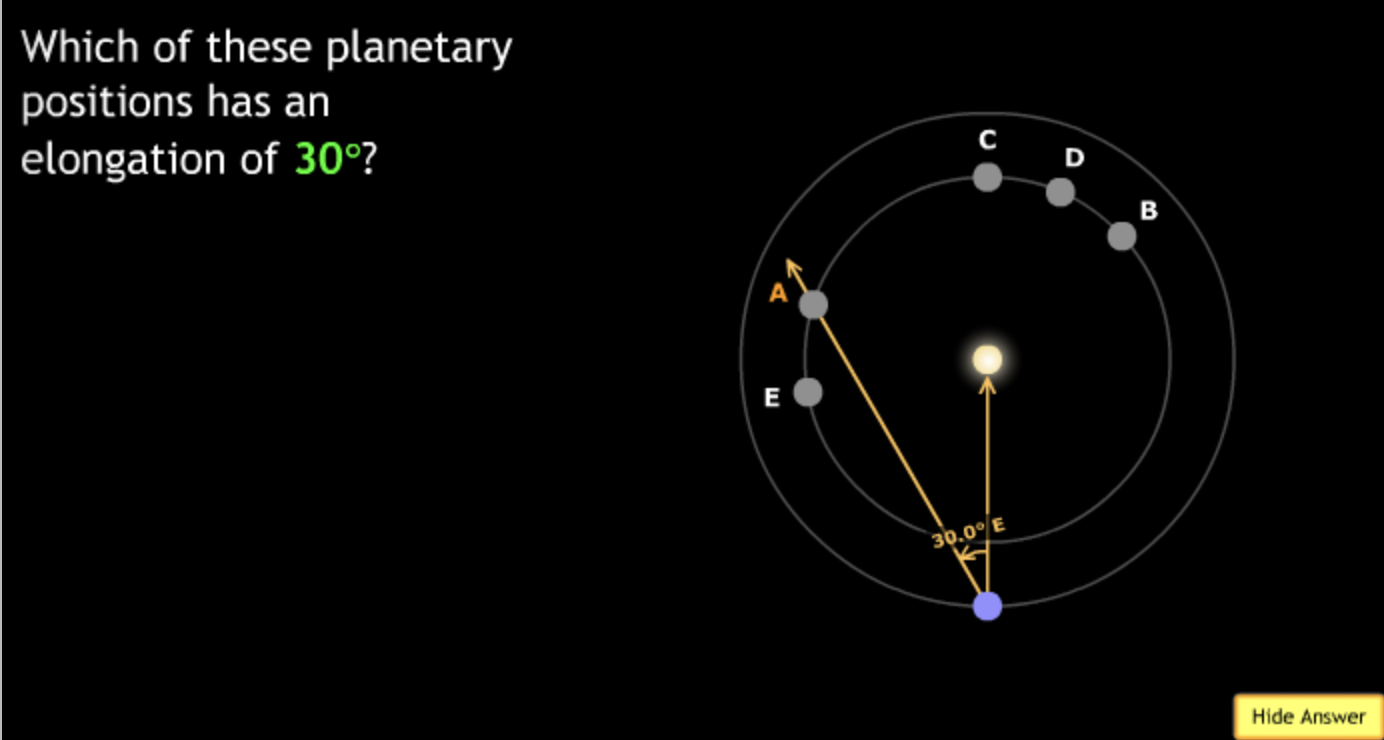
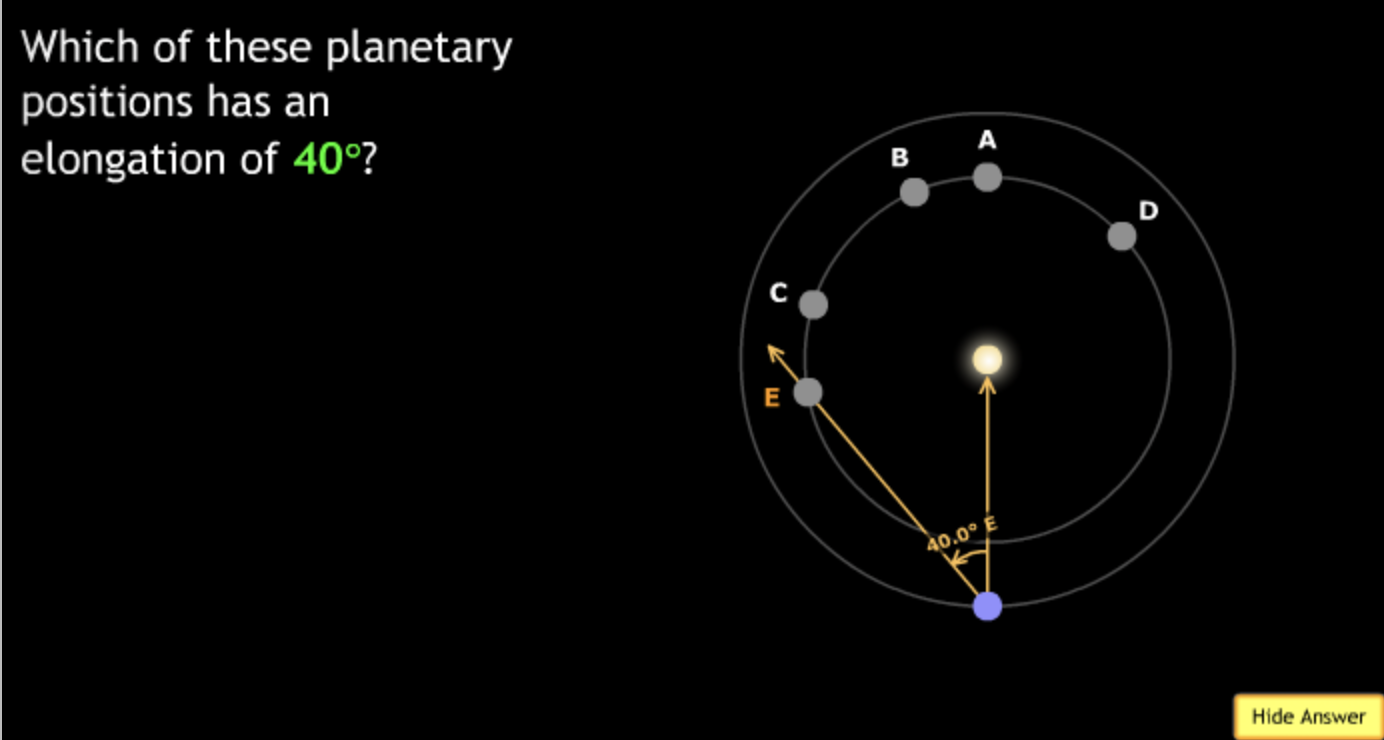
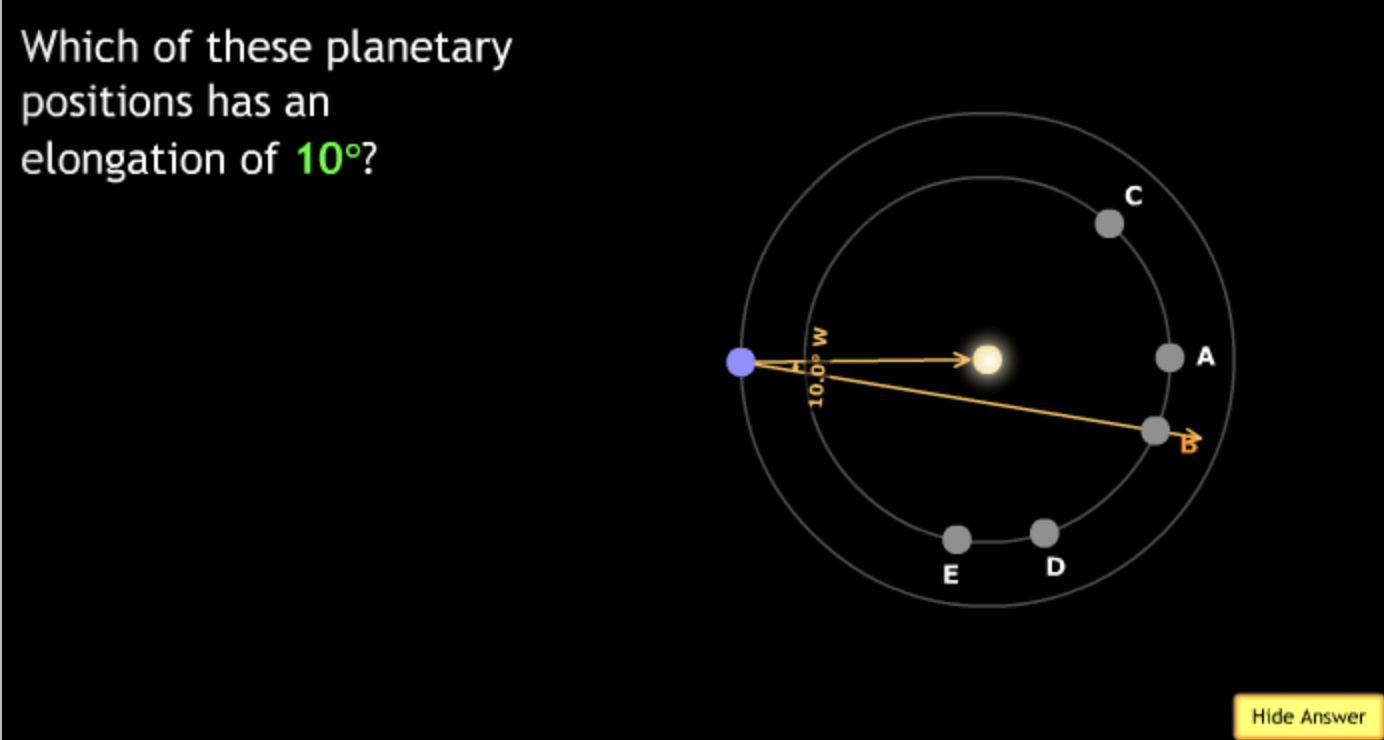
In the organizational diagram below, the term Jupiter would most appropriately fit in the area labeled?
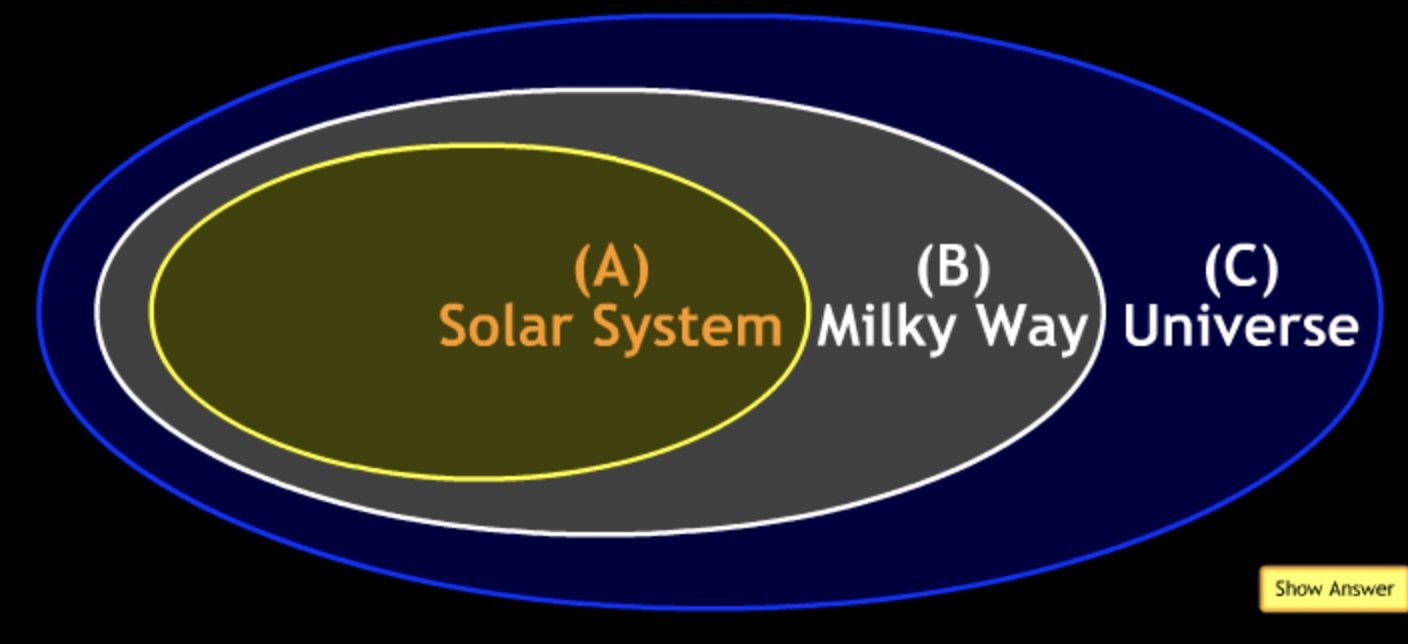
→ Solar System
the term Virgo Supercluster would most appropriately fit in the area labeled?
→ Universe
the term Polaris would most appropriately fit in the area labeled?
→ Milky Way
the term Andromeda Galaxy would most appropriately fit in the area labeled?
→ Universe
the term Comet Halley would most appropriately fit in the area labeled?
→ Solar System
the term Orion Nebula would most appropriately fit in the area labeled?
→ Milky Way
Increasing Distance
sequences of objects in the correct order of increasing distance
→ Moon, Venus, Saturn, Polars, Andromeda Galaxy
→ Moon, Jupiter, Sirius, Large Magellenic Cloud, Virgo Supercluster
→ Mercury, Uranus, Alpha Centauri, Small Magellenic Cloud, Coma Supercluster
→ Moon, Jupiter, Pluto, Large Magellenic Cloud, Andromeda Galaxy
→ Moon, Mars, Neptune, Orion Nebula, Small Magellanic Cloud
The age of the universe is estimated to be:
→ 1.37 × 10^10
→ 13.7 Gyr
→ 13,700,000,000
The wavelength of the H spectral lines (red light produced by hydrogen atoms) is:
→ 0.0000006656 m.
→ 6.56 × 10^-7
→ 656nm
The speed of light is:
→ 300,000,000 m/s
→ 3.00 × 10^8
→ 300Mm/s
The radius of the sun is:
→ 696,000,000 m.
→ 6.96 × 10^8
→ 696 Mm
The rapidly spinning pulsar PSR 1937+21 has a rotational period of:
→ 0.00156 s.
→ 1.56 × 10^-3
→ 1.56 ms.
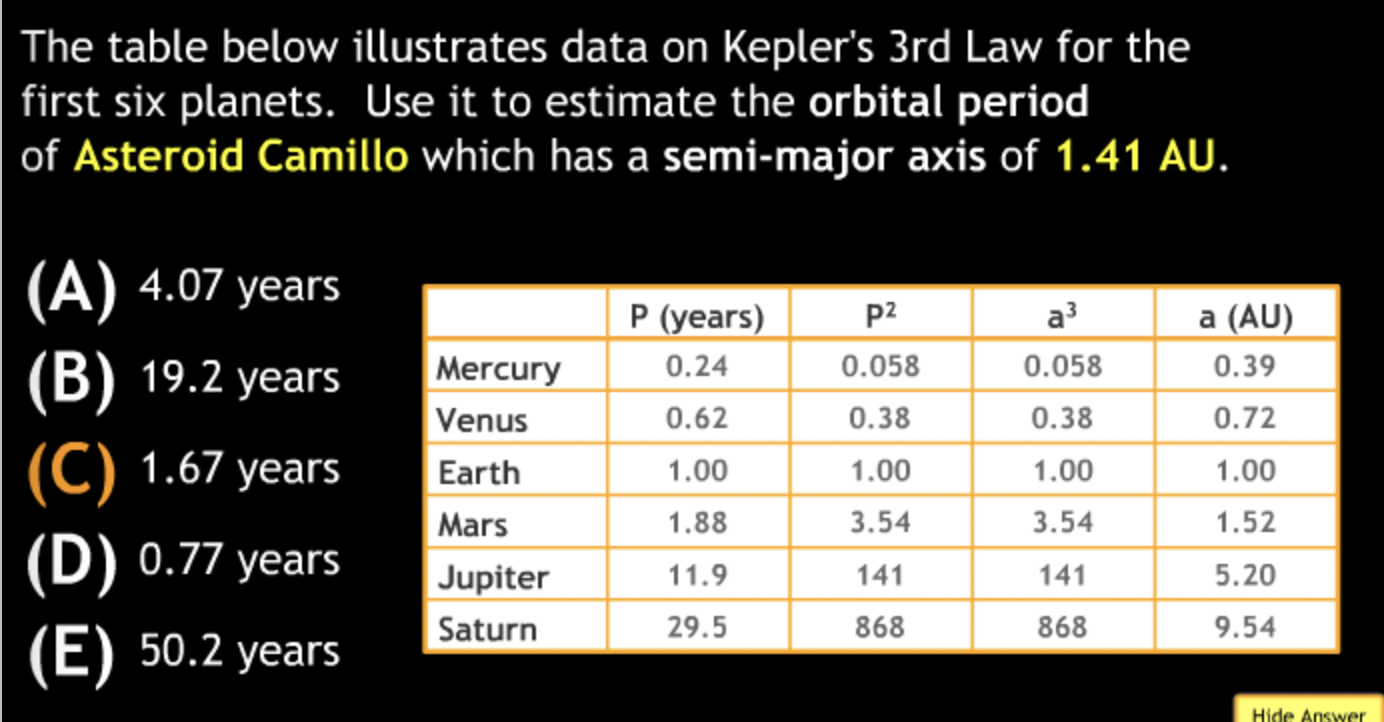
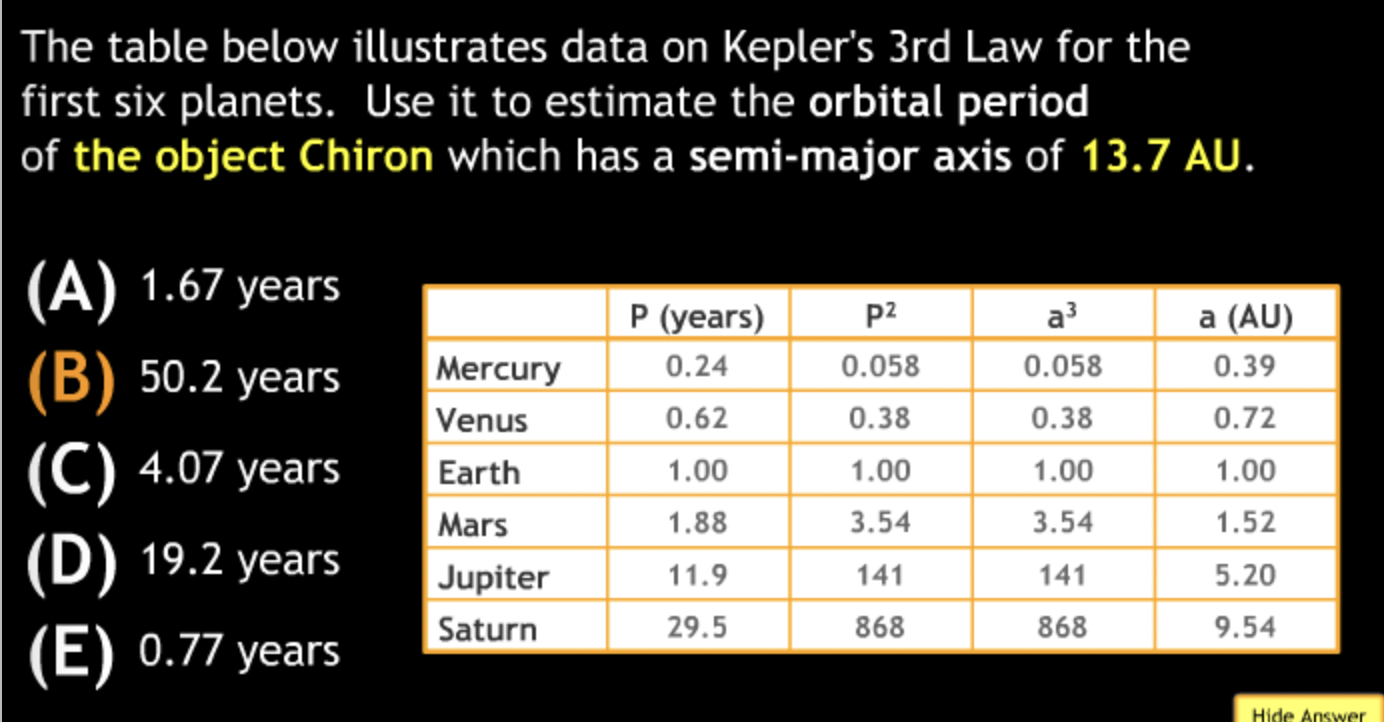
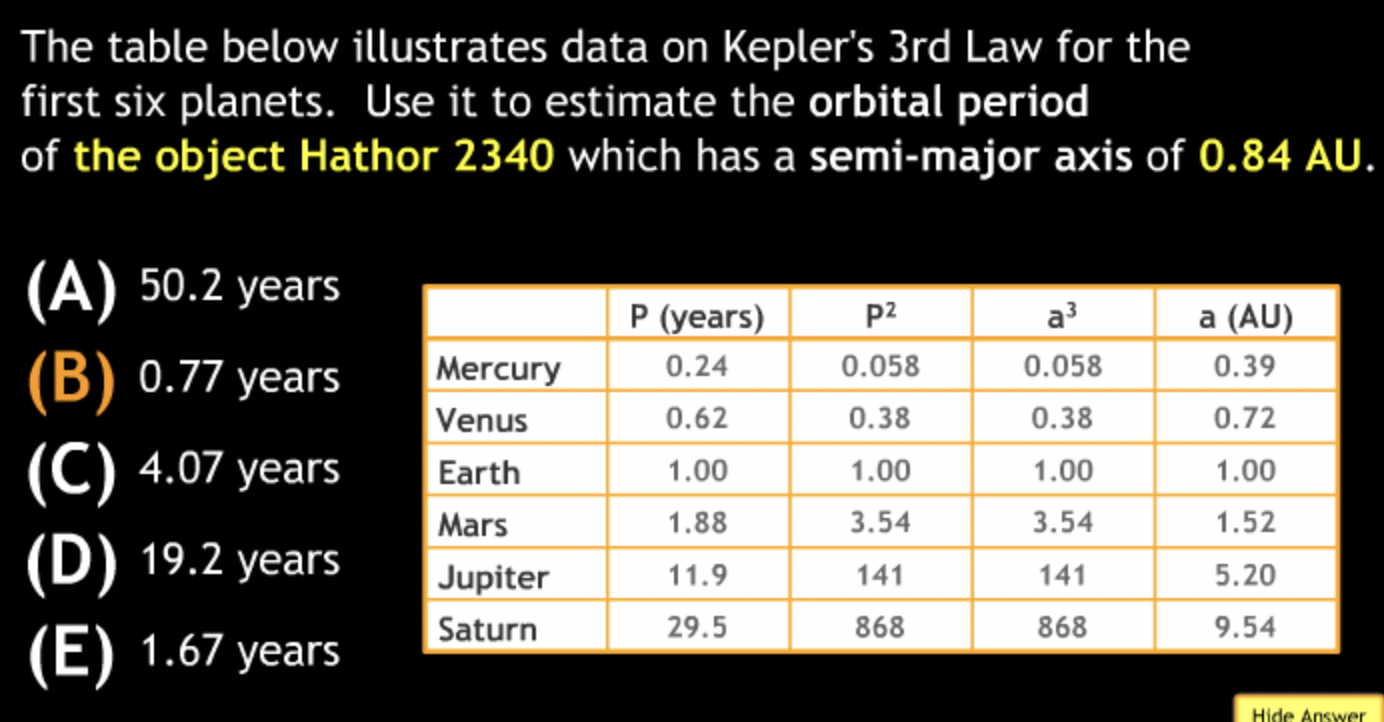
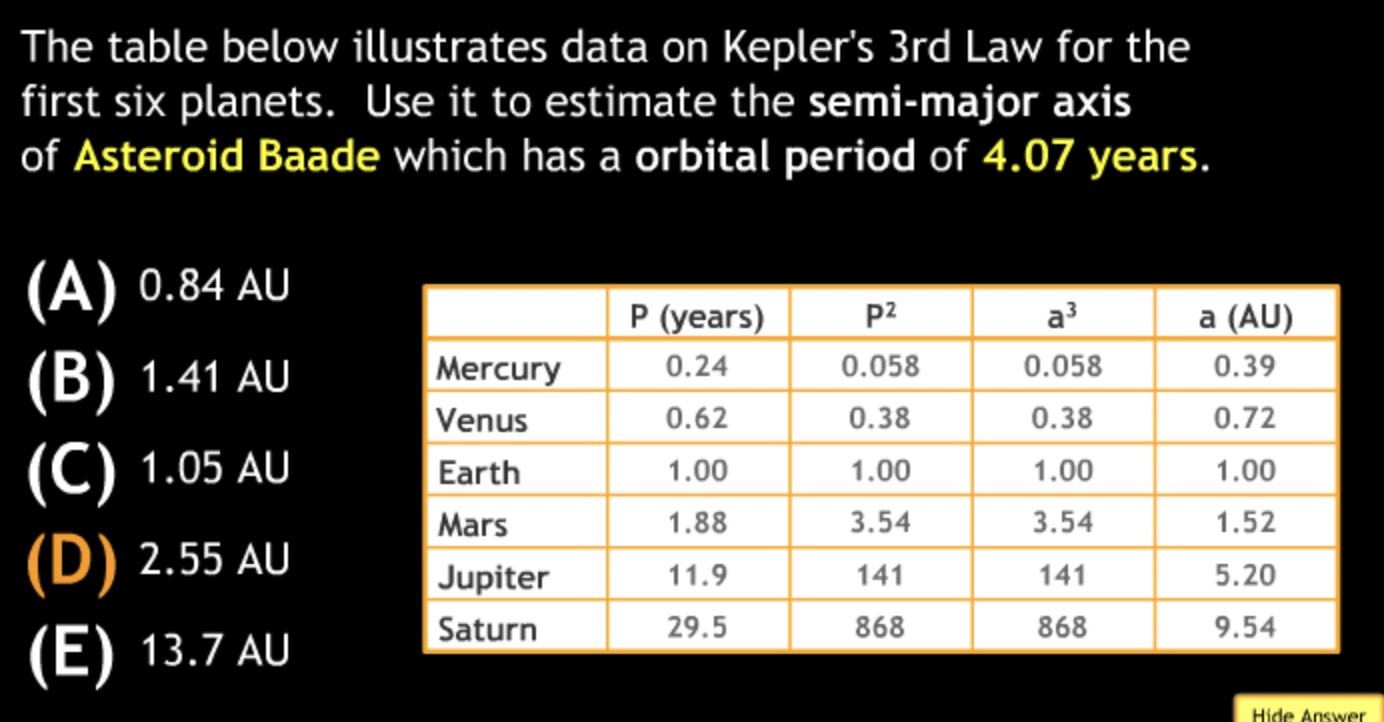
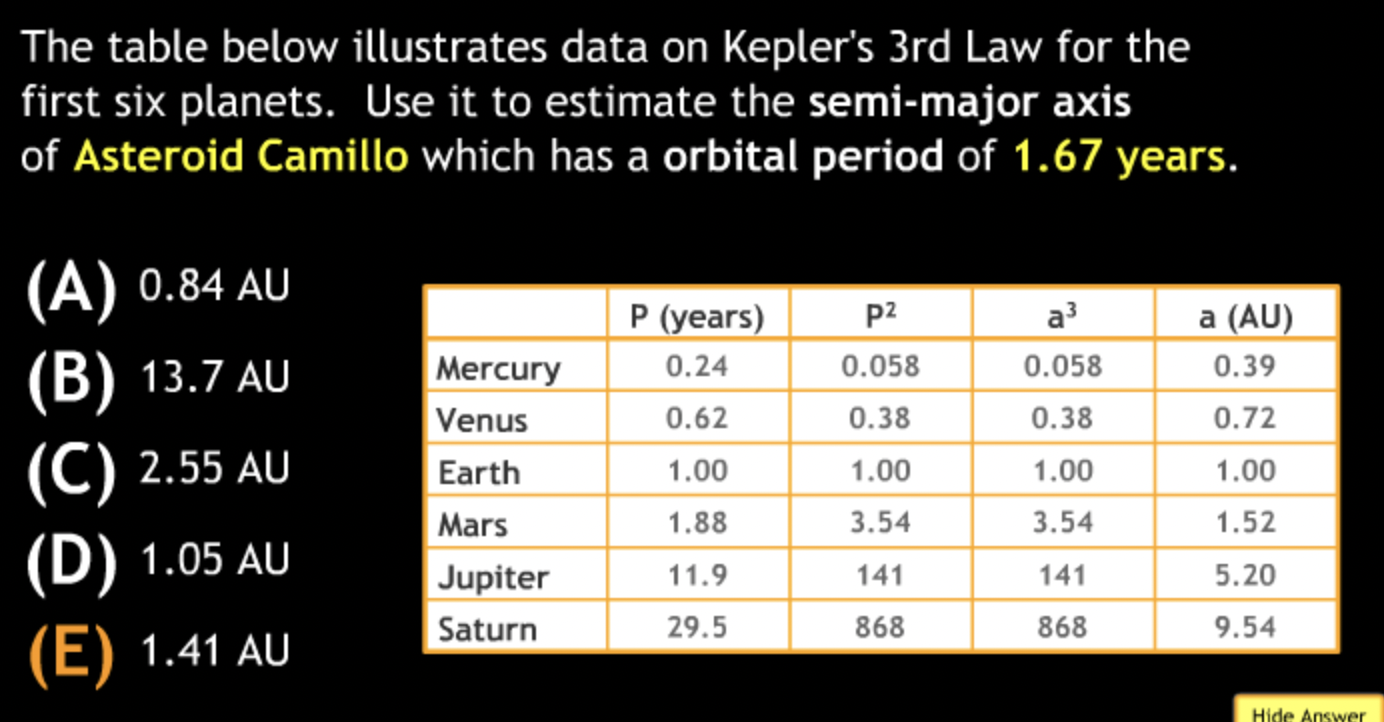
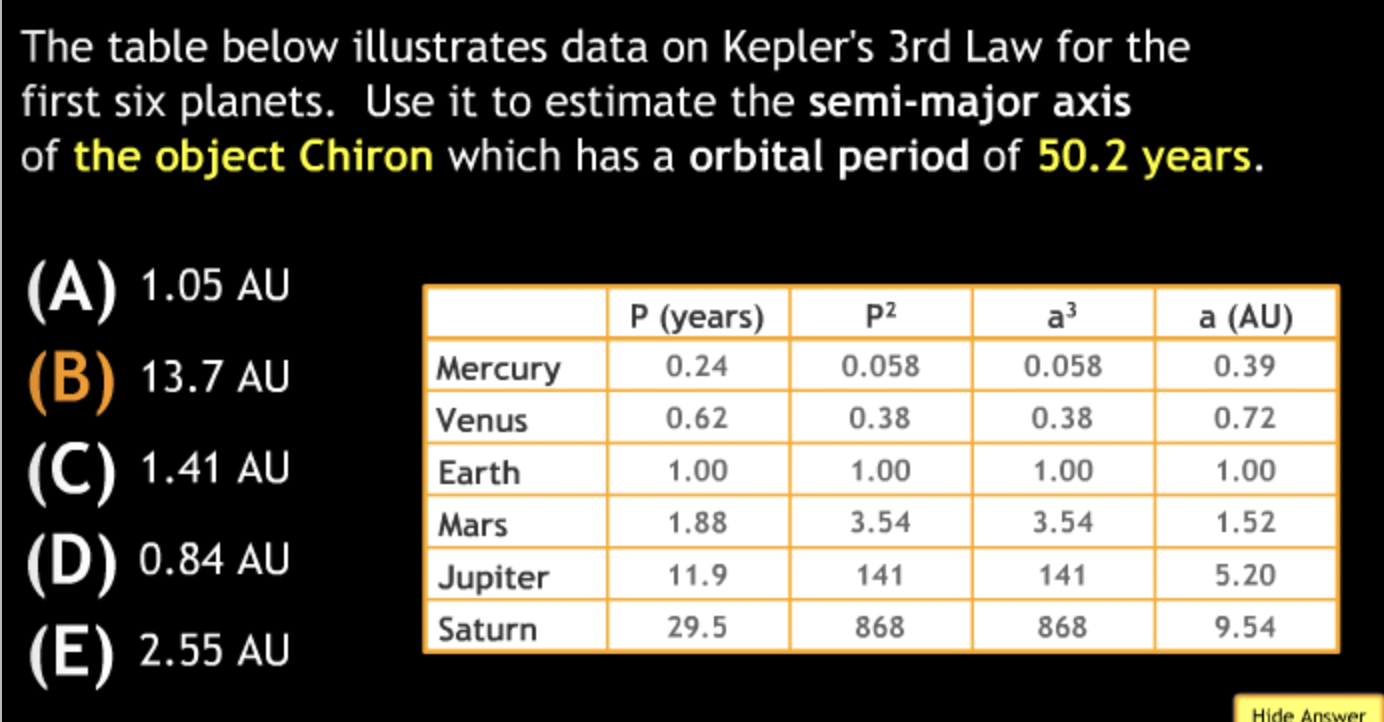
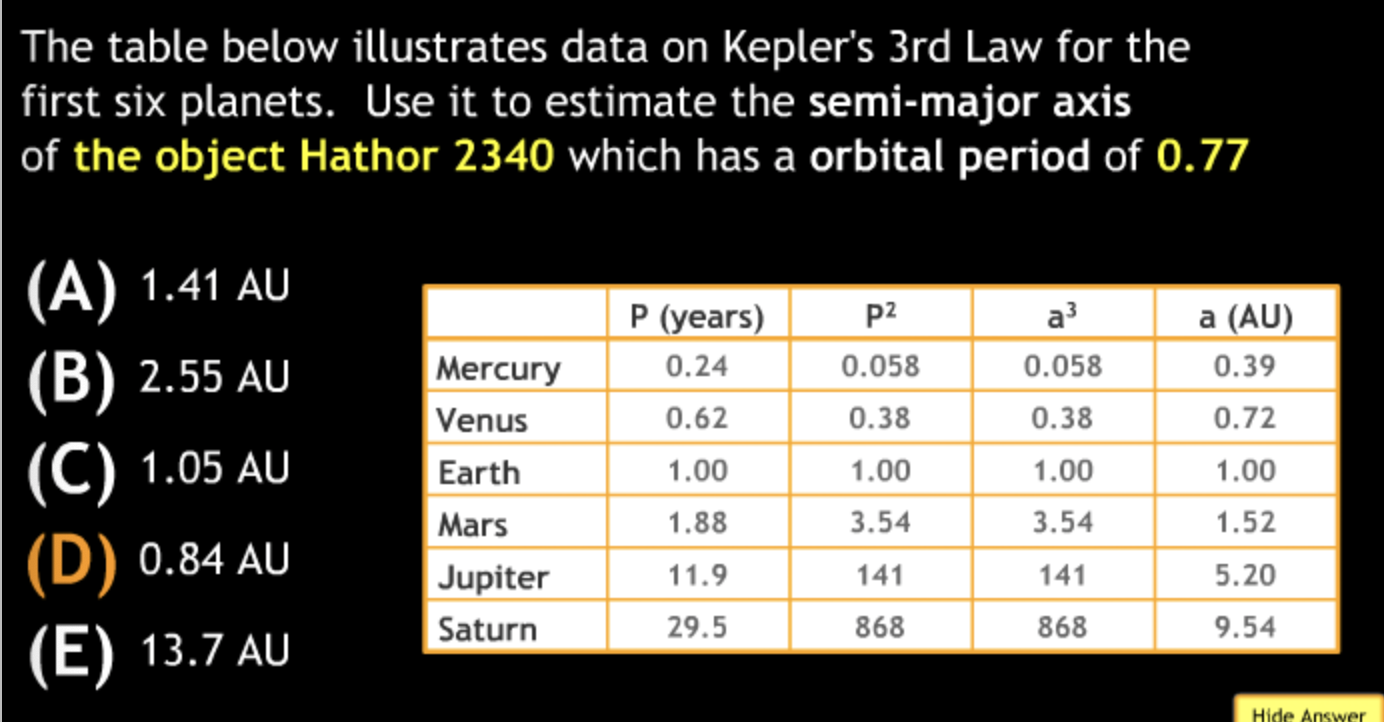
Calculation in Scientific Notation
The Earth’s average distance from the sun is 1.5 × 10^8km, which is known as 1 Astronomical Unit (AU). Pluto’s average distance from the sun is 40 AU. How far is that in km?
→ 6.00 × 10^9
The nearest star to our solar system, alpha centauri is 4.0 × 10^16m (4.3 light-years) away. The diameter of the sun is 1.4 × 10^9m. How many suns would have to be lined up adjacent to each other to reach alpha centauri?
→ 2.80 × 10^7
There are approximately 100 billion stars in our galaxy. If there are 100 billon galaxies in the observable universe, what is a reasonable estimate for the total number of stars in the universe?
→ 1.00 × 10²2
The Milky Way galaxy has a diameter of approximately 100,000 light-year. The nearest large galaxy to us, the Andromeda galaxy, is 2,000,000 light-years away. How many Milky Way’s would have to be lined up adjacent to each other to reach the Andromeda galaxy?
→ 20
The distance to a neighboring state might be…..
→ 100km
The distance to a nearby star might be..
→ 10 ly
The distance to a jovian planet might be..
→ 10 AU
The distance to a globular cluster near the center of the Milky Way might be..
→ 10 kpc
The distance to a supercluster of galaxies might be.
→ 100 Mpc
Approximately 1000 Earths would fit inside of Jupiter. Thus, Jupiter’s radius must be about 10 times larger than the Earth’s radius.
A spherical particle in the rings of Saturn has a radius of 1 m. The particle’s surface area must be about 12.6m²
A spherical particle in the rings of Saturn has a radius of 1m. The particle’s cross-section area to the flow of radiation must be about 3.14 m²
Sirius - the brightest star in our sky - is about 9 light-years distant. If the speed of light were half its present value, how far away would Sirius be?
→ 18 light years
The bright star Betelgeuse is about 520 light-years distant. if the speed of light were twice its present value, how far away would Betelgeuse be?
→ 260 light years
Landing lights at the Lincoln, Nebraska, airport are suddenly switched on. In one second the photons from these lights travel to.. The moon (384,000 km)
The speed of light travels at 3.0 × 10^5 km/sec through the vacuum of space. Since light from the sun has to travel 1.5 × 10^8 km (1AU) to reach the Earth, how long does it take for light from the sun to reach the Earth?
→ about 8 minutes
The speed of light travels at 3.0 × 10^5 km/sec through the vacuum of space. Since light from the sun has to travel 6.0 × 10^9 km (40AU) to reach Pluto at the edge of our solar system, how long does that take?
→ over 5 hours
The Andromeda Galaxy is about two-thirds of an Mpc (or 2,000,000 light-years) away. Thus, the light that we observe from Andromeda was emitted… 2,000,000 years ago
The Crab Nebula is the ramnant of an actual supernova observed by Chinese astronomers is the year 1054 AD. Since the Crab Nebula is approximately 6500 light-years away, the supernova occurred in the year closest to… 5450 BC
Eta Carina is a southern hemisphere object located about 10,000 ly away. It is a massive star expected to die in a violent explosion known as a supernova. Suppose that this star went supernova in the year 2000 BC. How long would it be (from today) until we would know about it?
→ 6000 years.
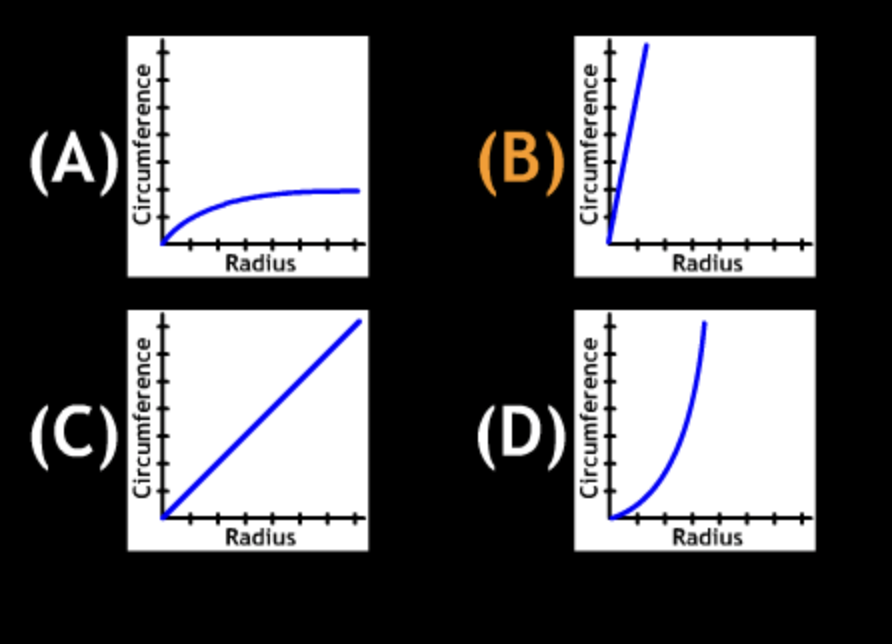
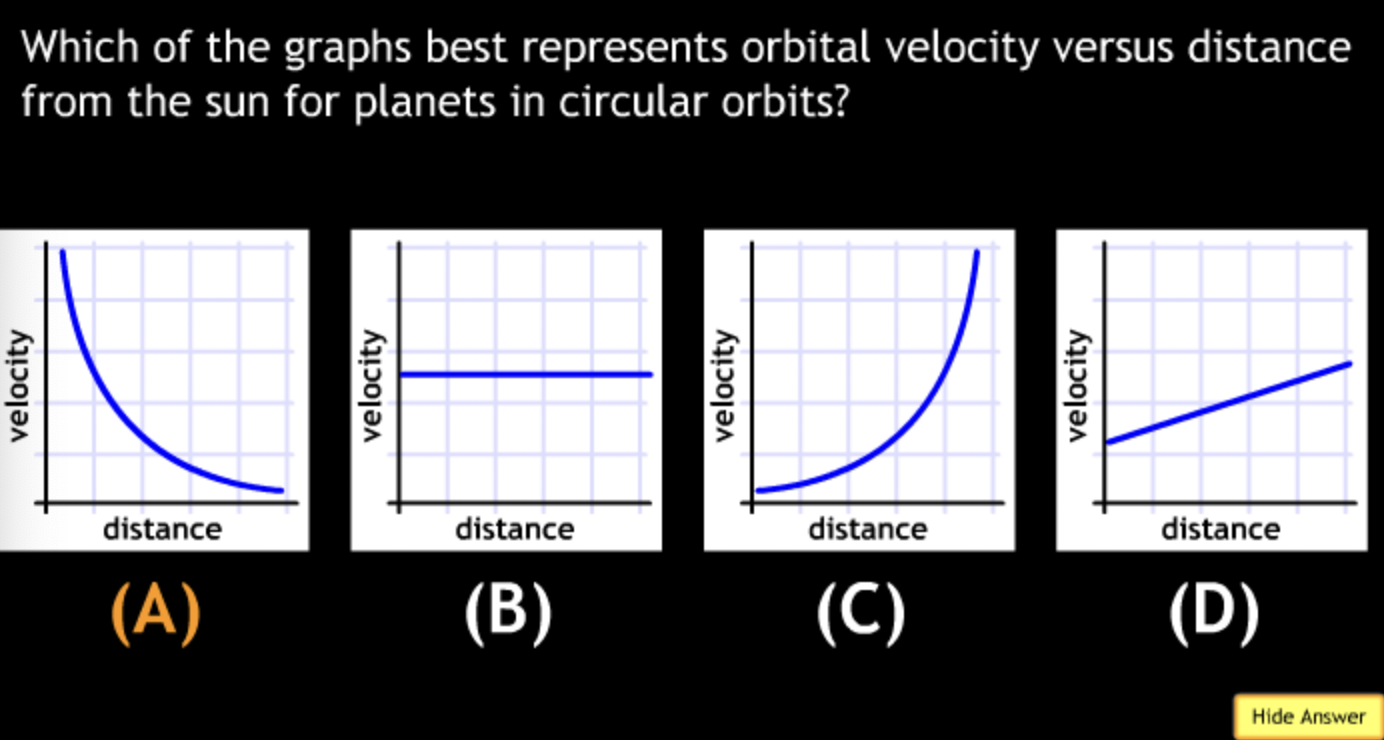
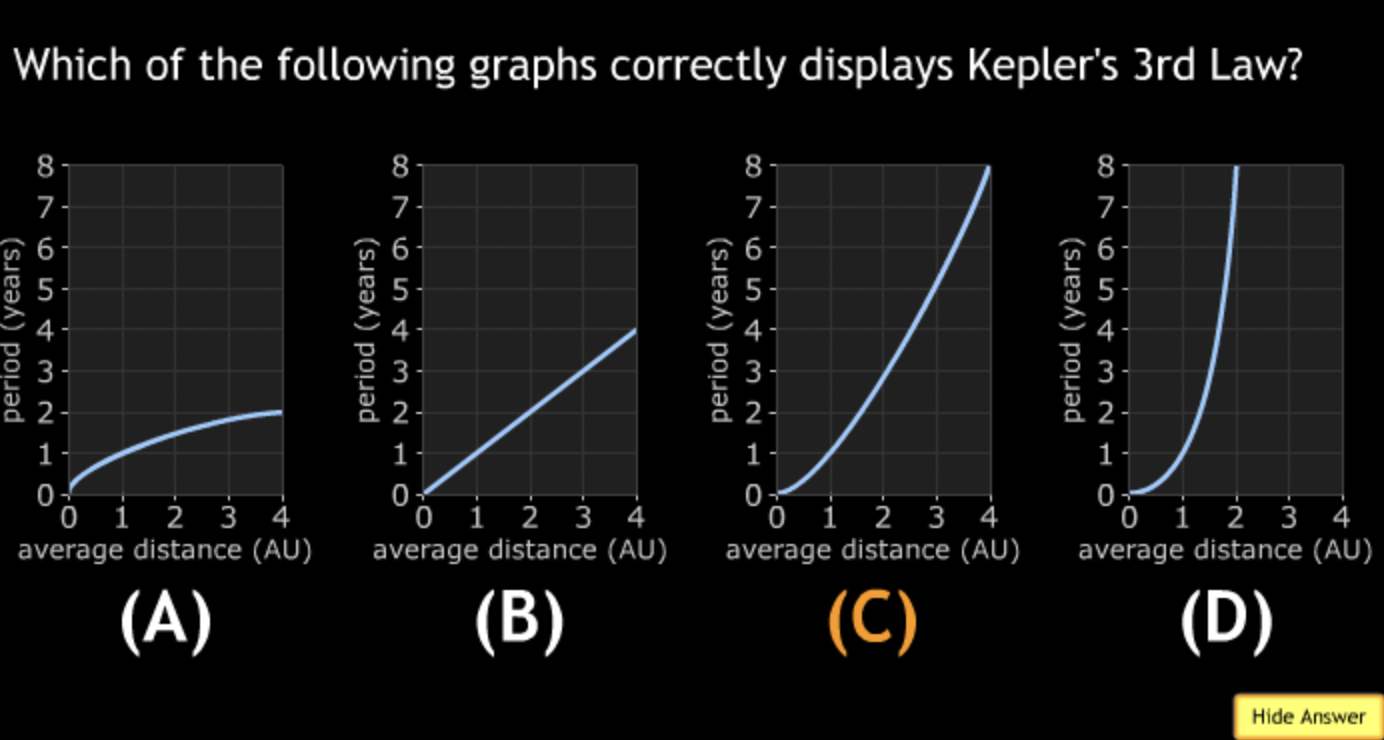
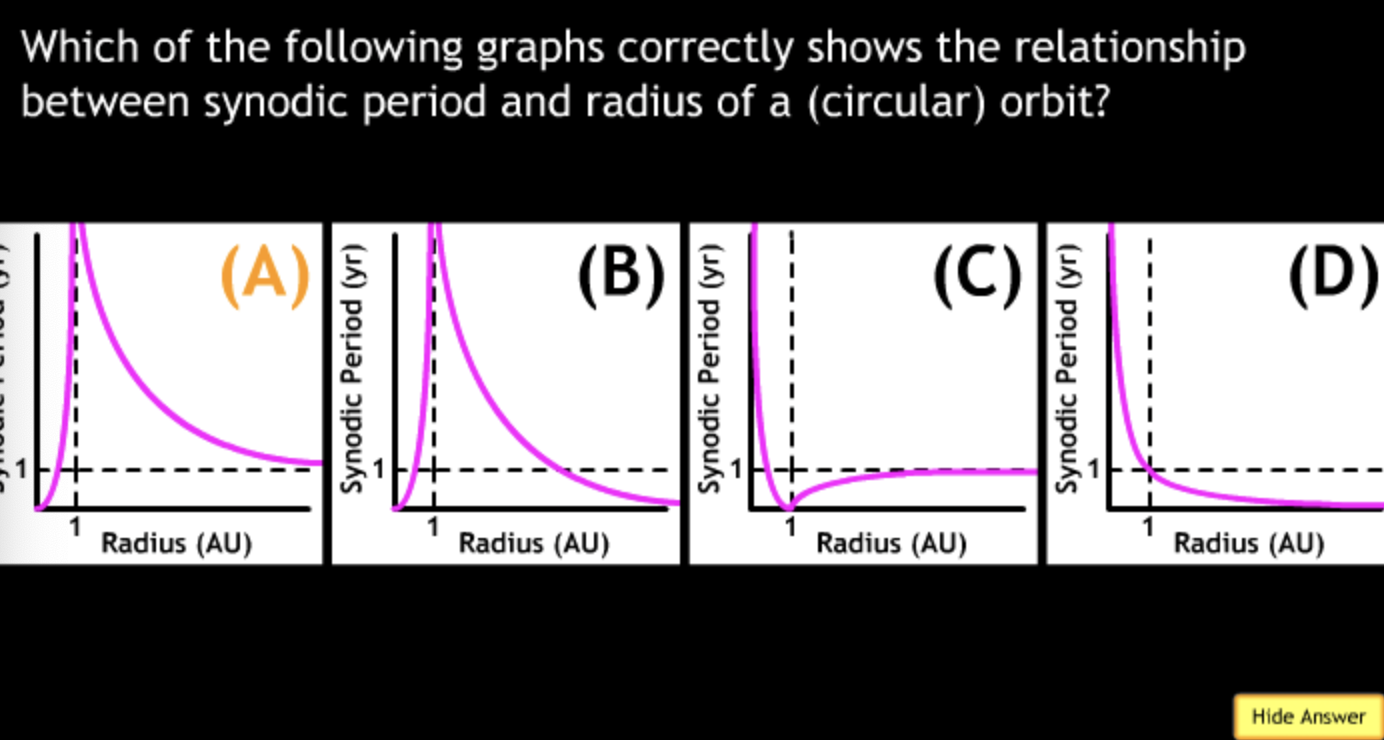
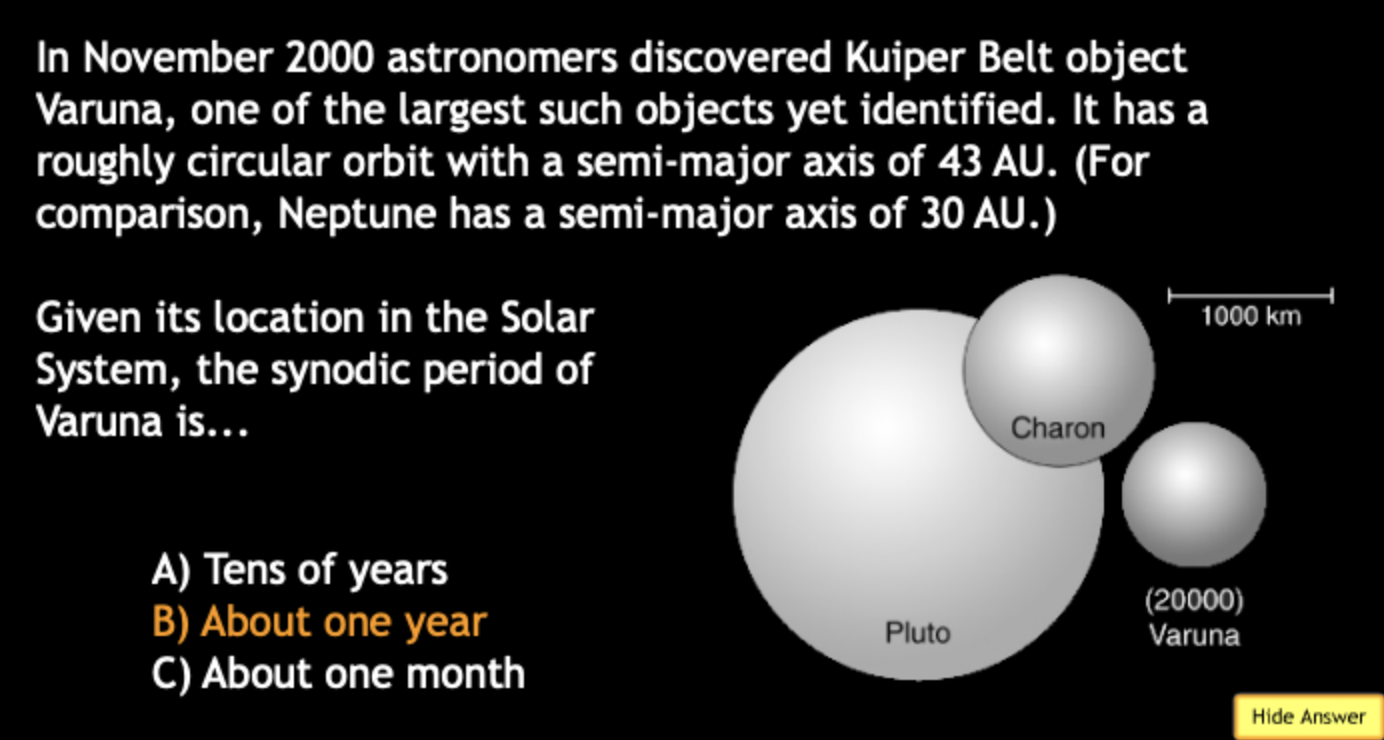
An astronomer collects data for terrestrial planets, including the radius R and equatorial circumference C (where C = 2πR) for each planets. This data is represented in which graph?
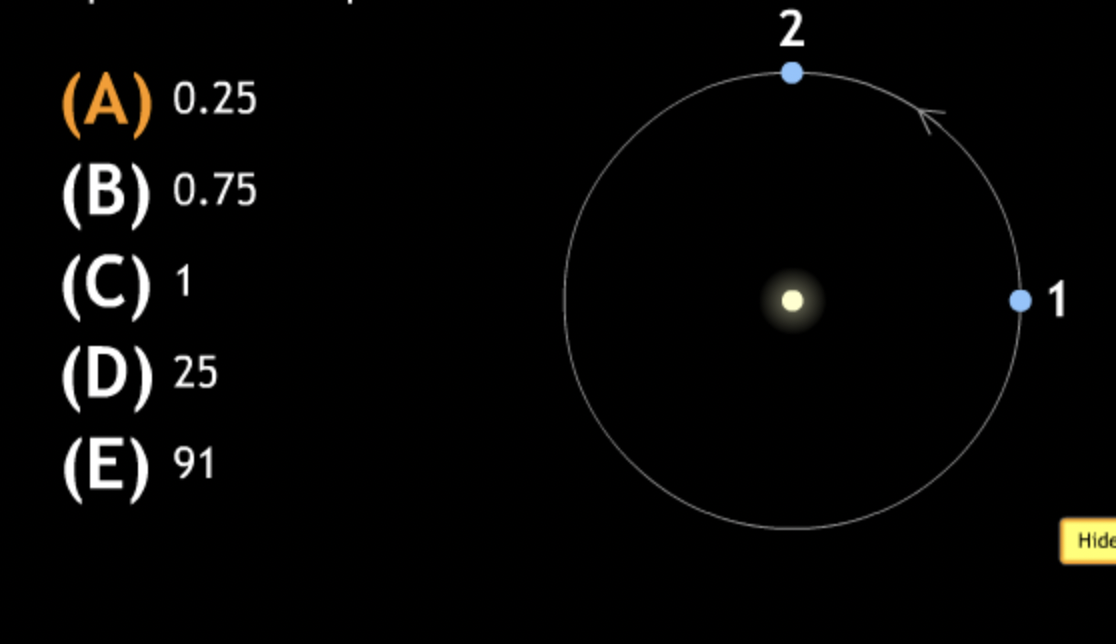
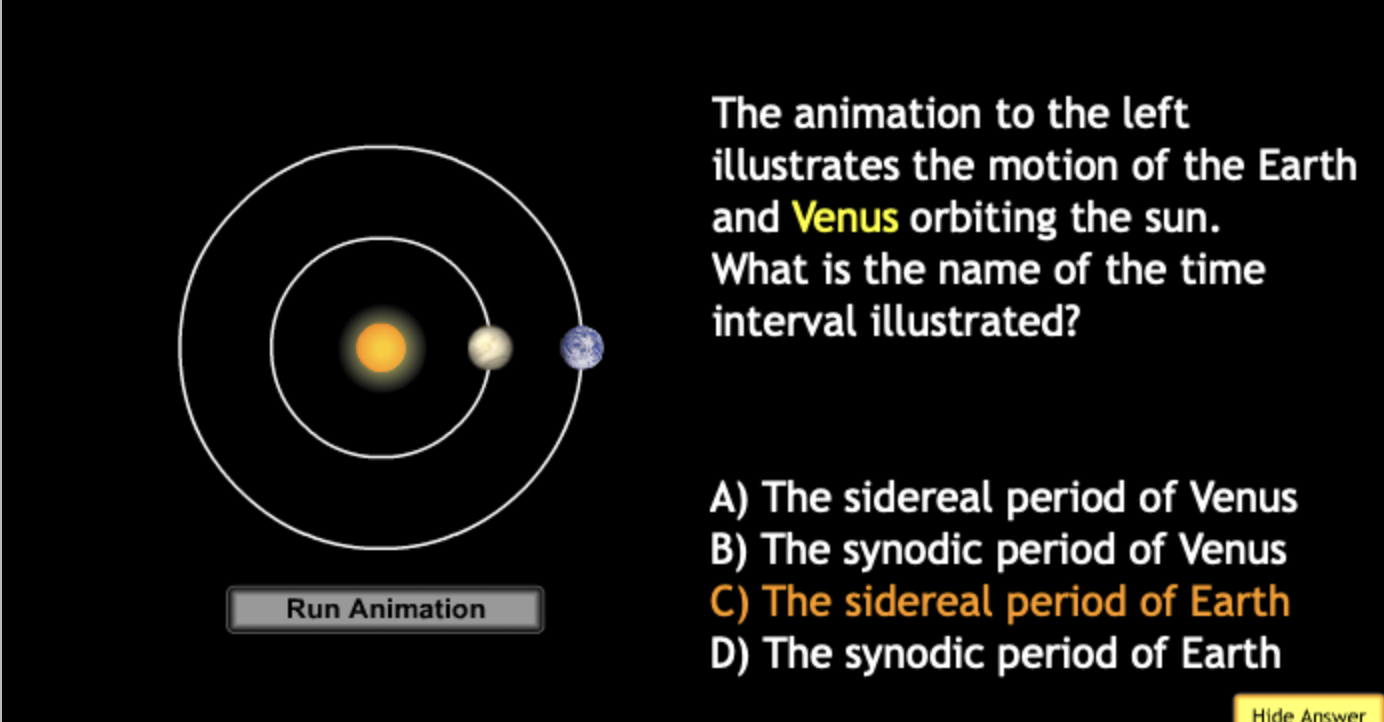
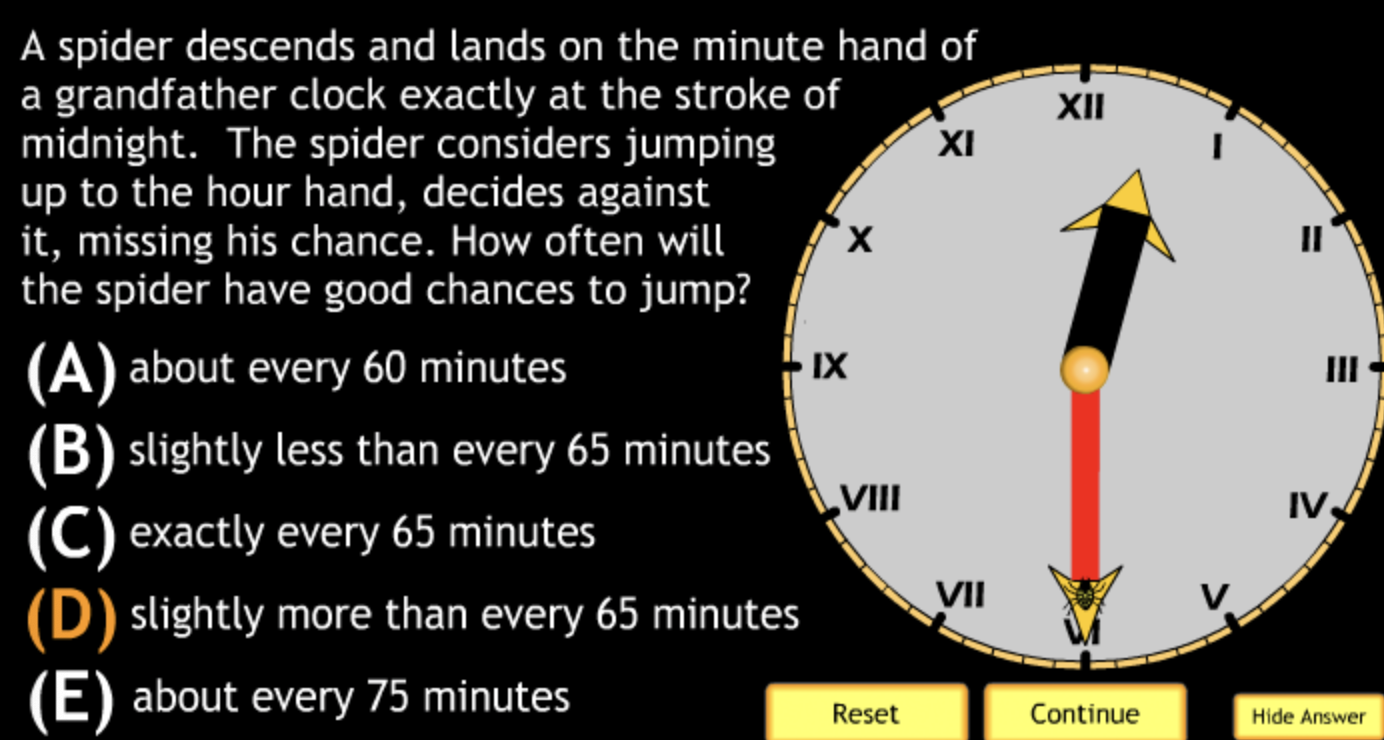
In the diagram below the Earth is shown at two points in its orbit around sun. How many rotations does the Earth go through in moving from position 1 to position 2?
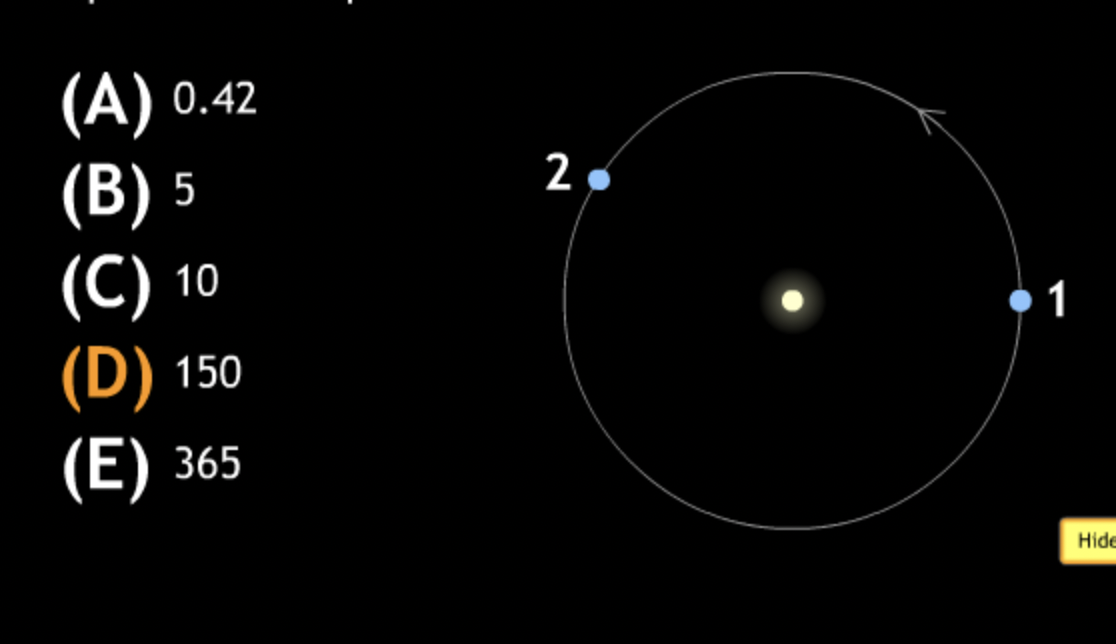
In the diagram below the Earth is shown at two points in its orbit around sun. How many revolutions does the Earth go through in moving from position 1 to position 2?
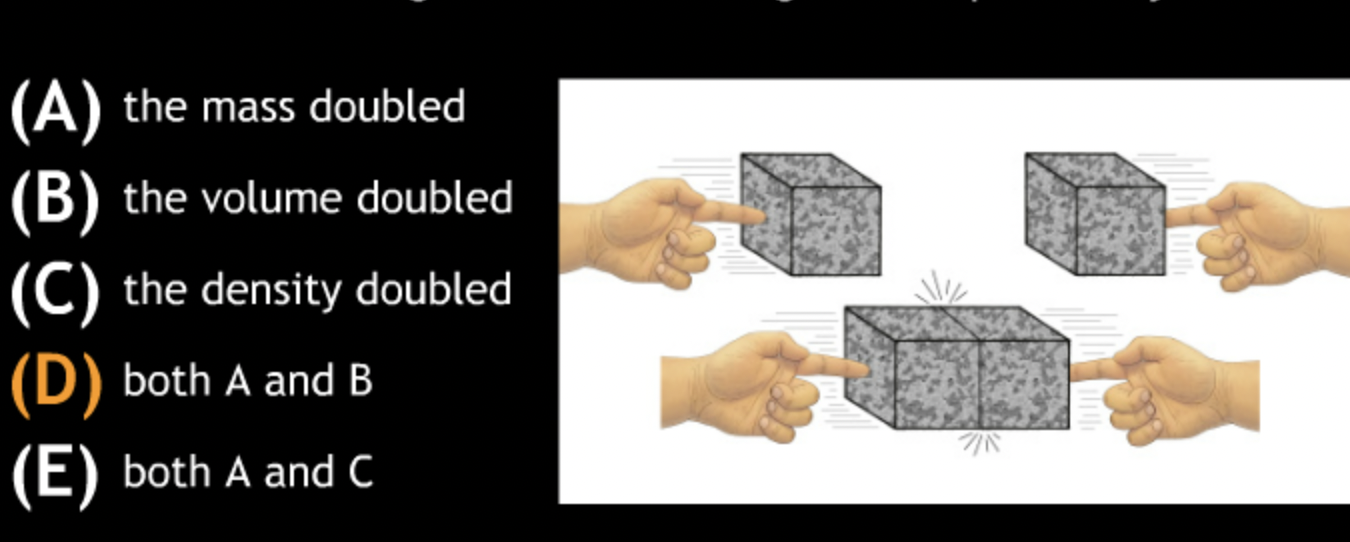
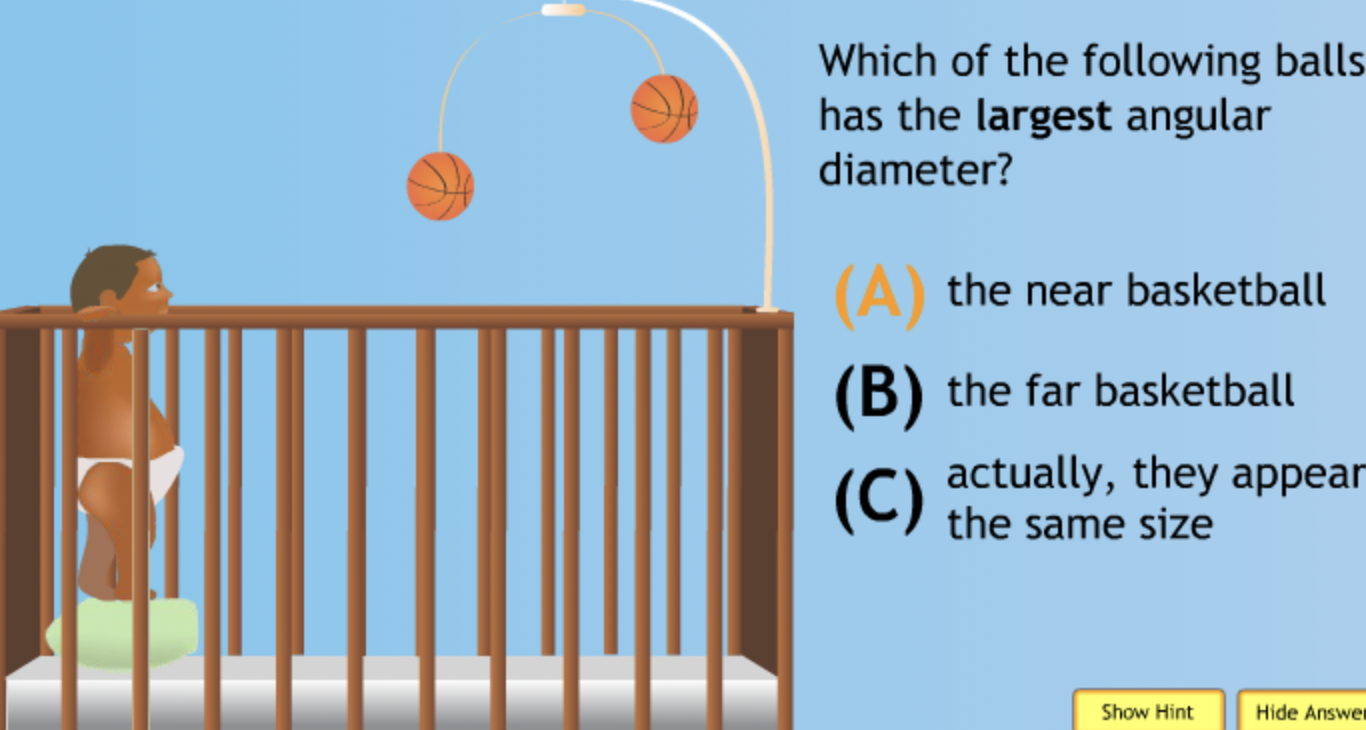
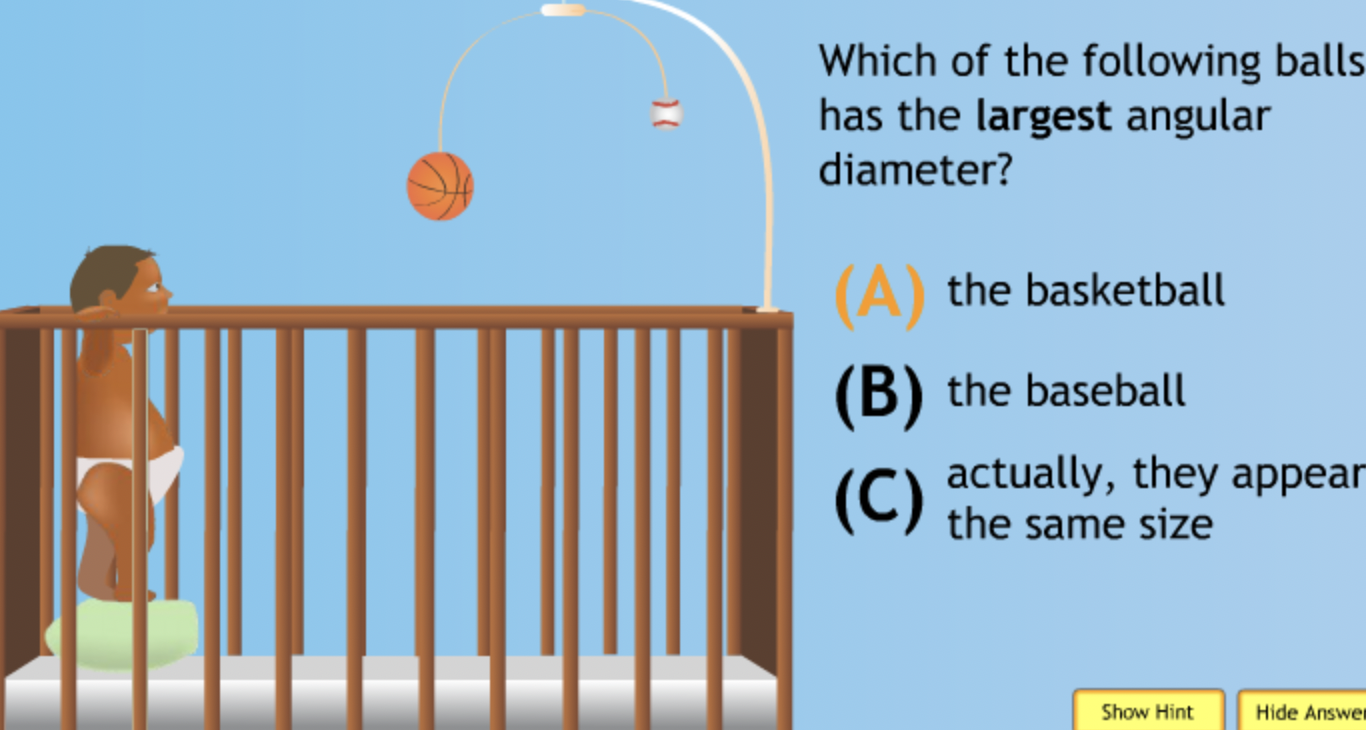
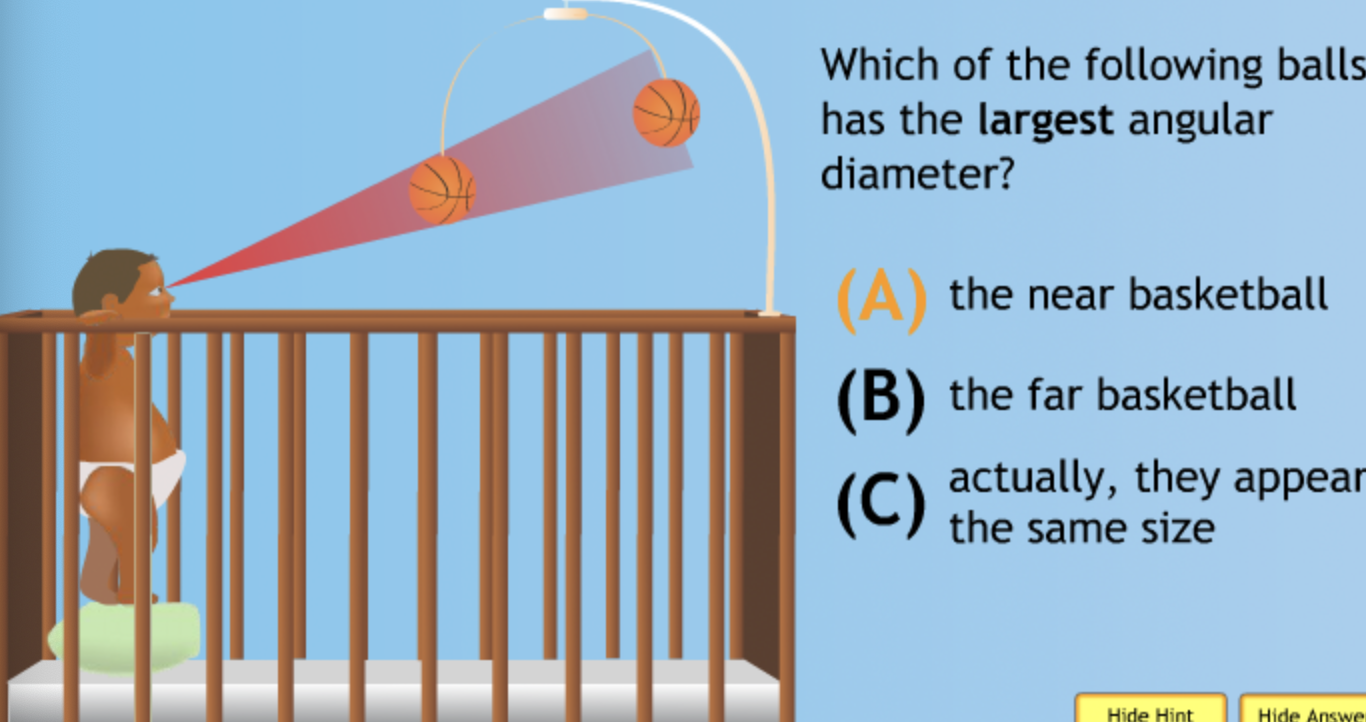
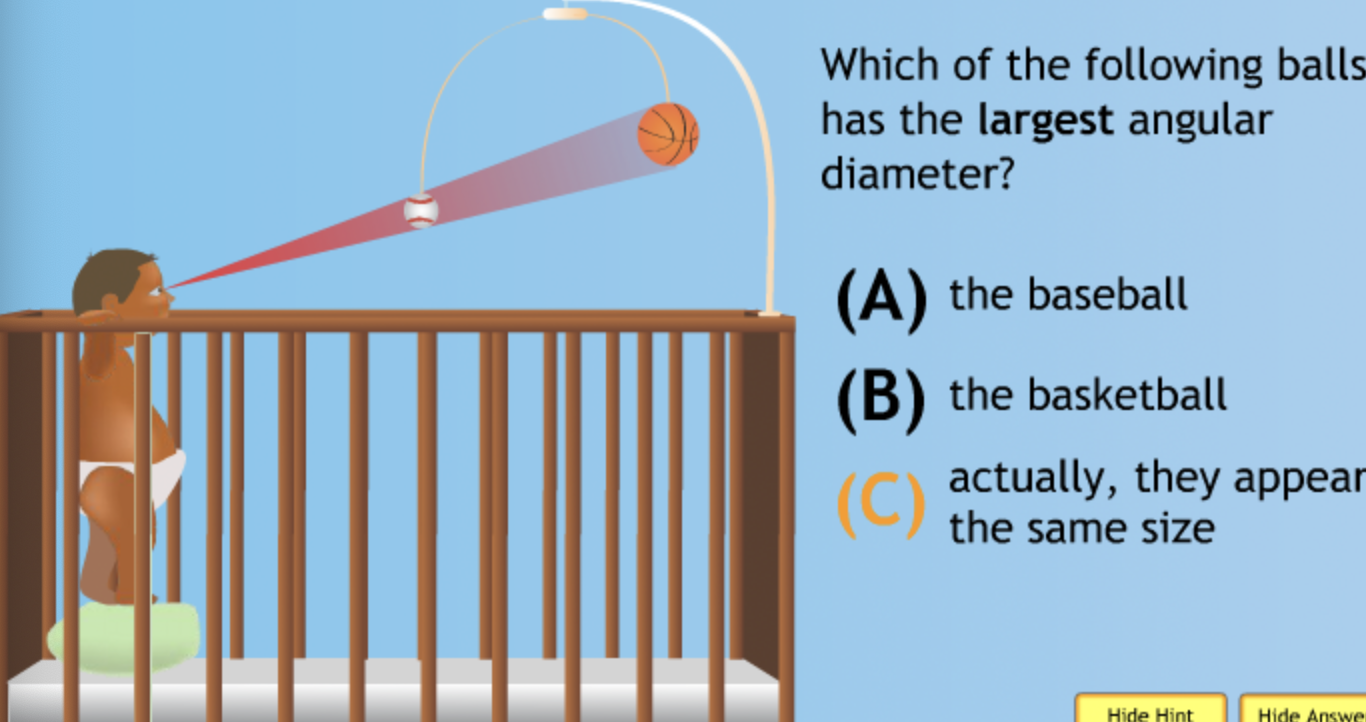
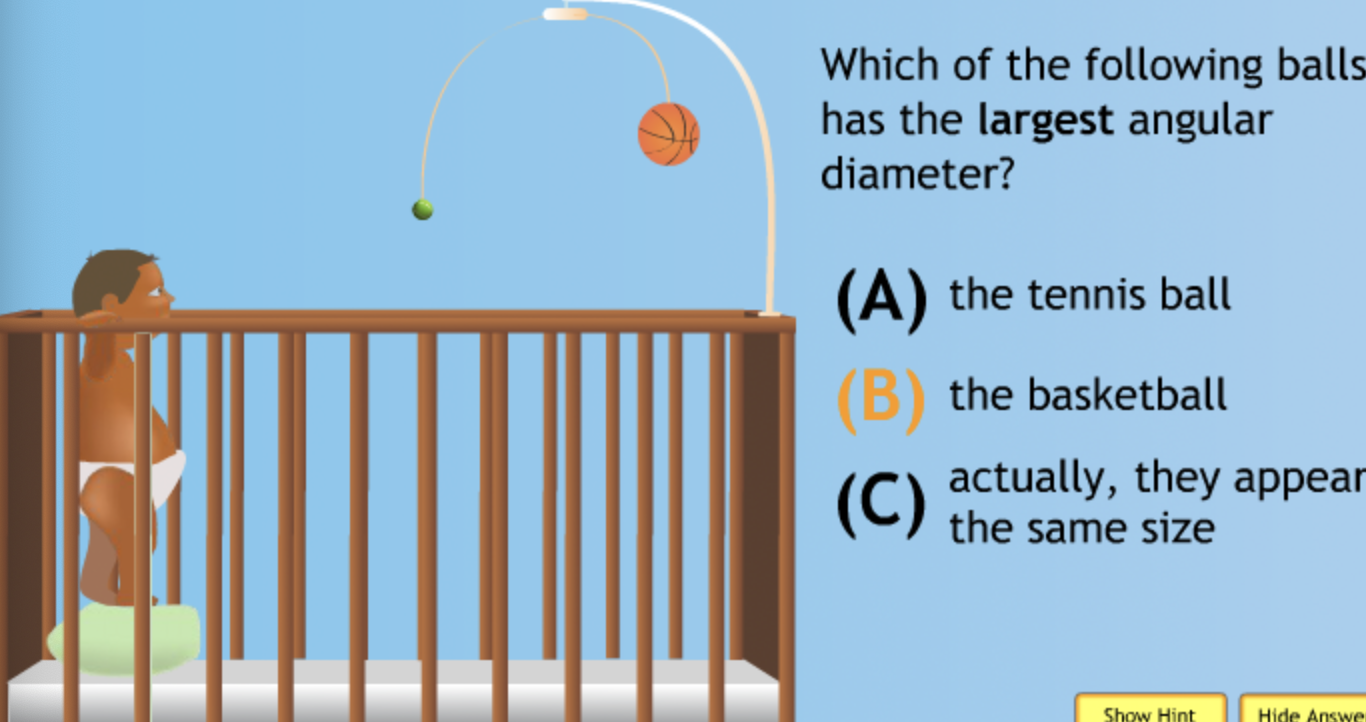
Which of the following has the largest volume?
→ 1 kg of styrofoam
Which of the following has the smallest volume?
→ 1 kg of lead
Which of the following has the largest mass?
→ all are equal
Which of the following has the largest density?
→ 1 kg of lead
Which of the following has the smallest density?
→ 1 kg of stryofoam
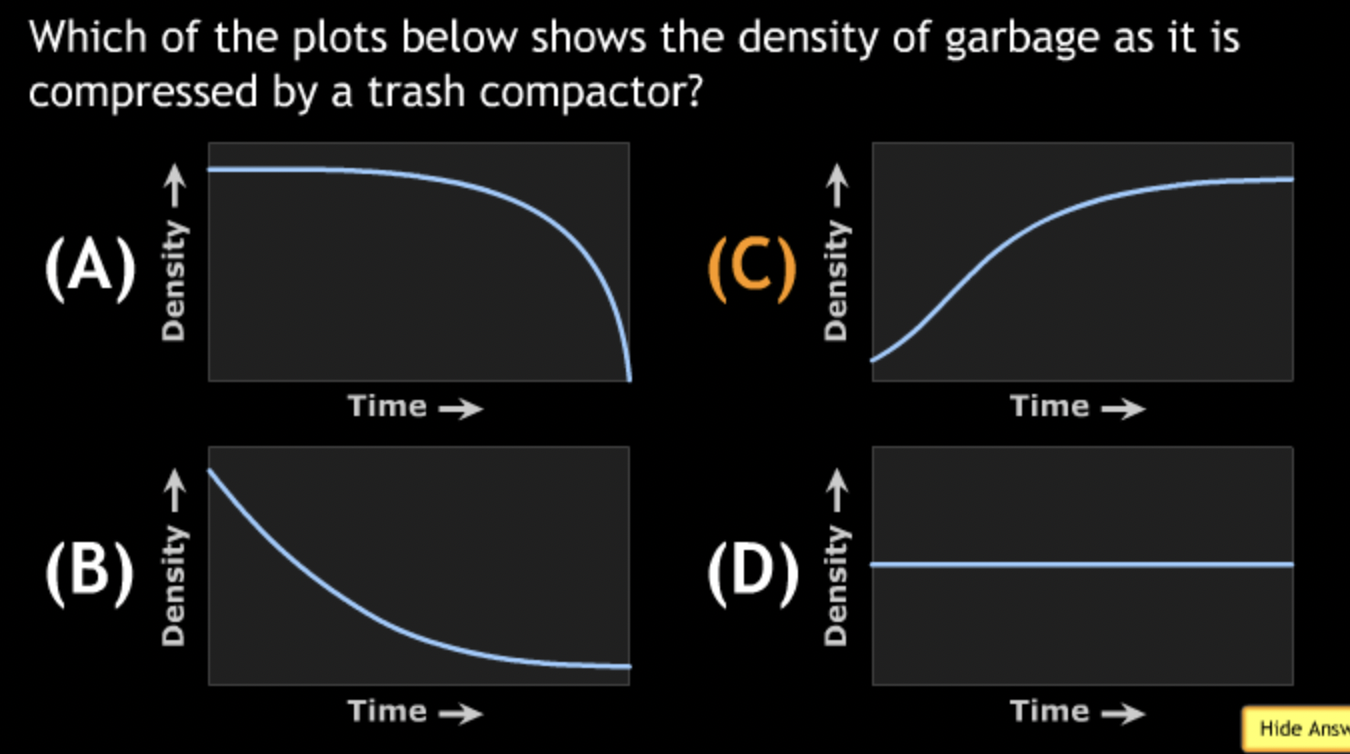
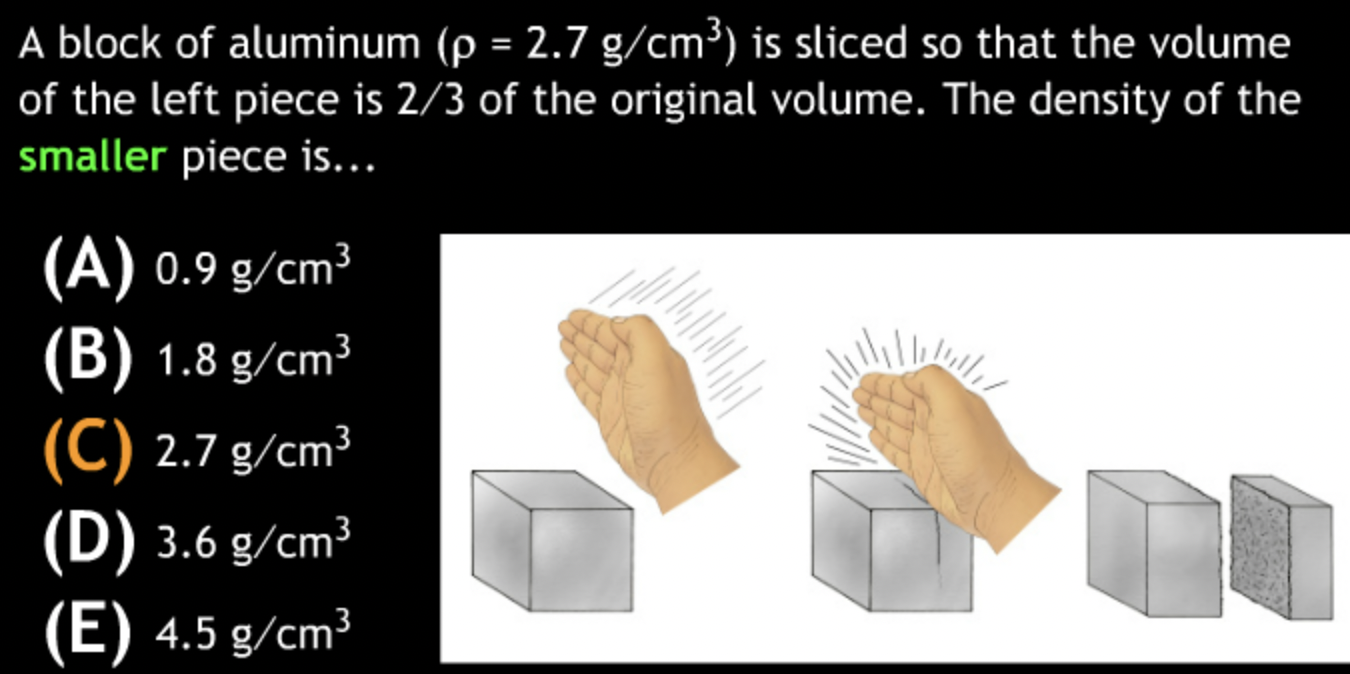

In the sci-fi novel Spin, all of the stars in a clear night sky suddenly disappear. One explanation for this is that they have actually “gone out”. What does your understanding of lookback time tell you about this theory?
→ Light from distant stars and galaxies takes time to travel to Earth. The farther away an object is, the longer its light takes to reach us.
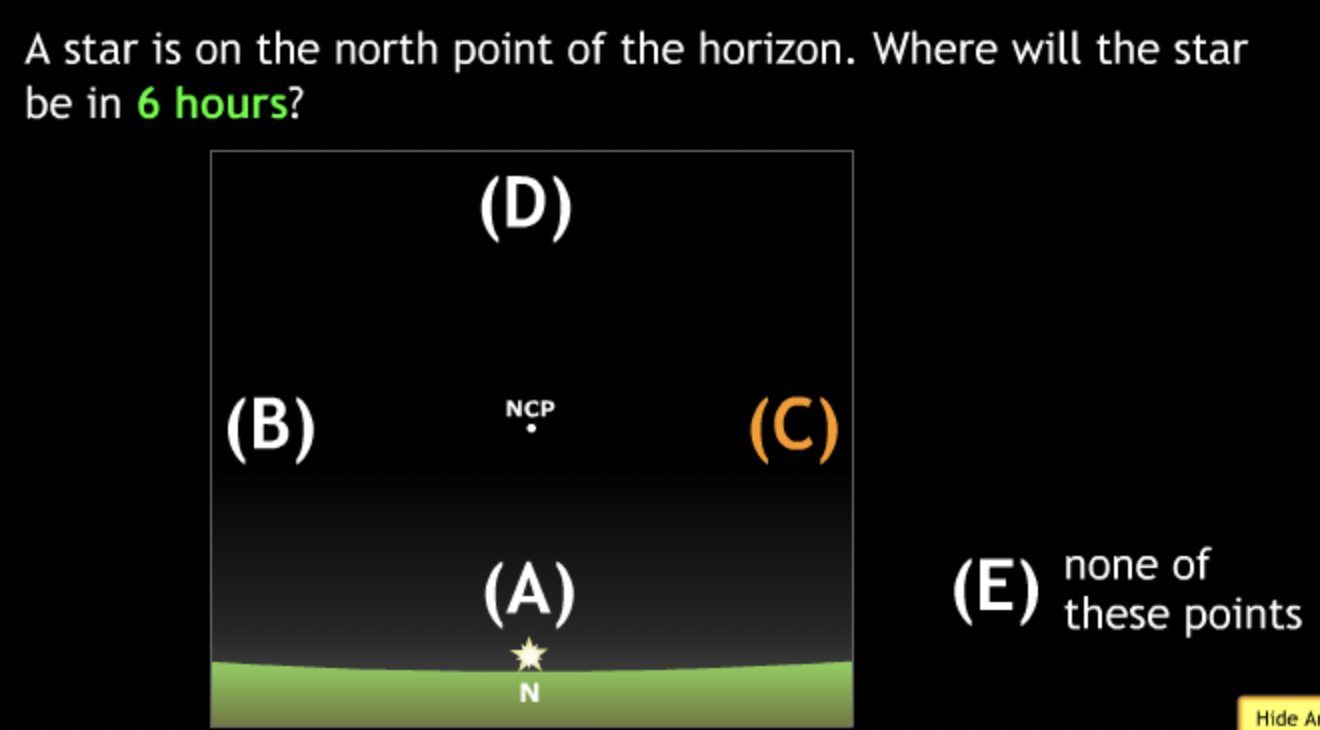
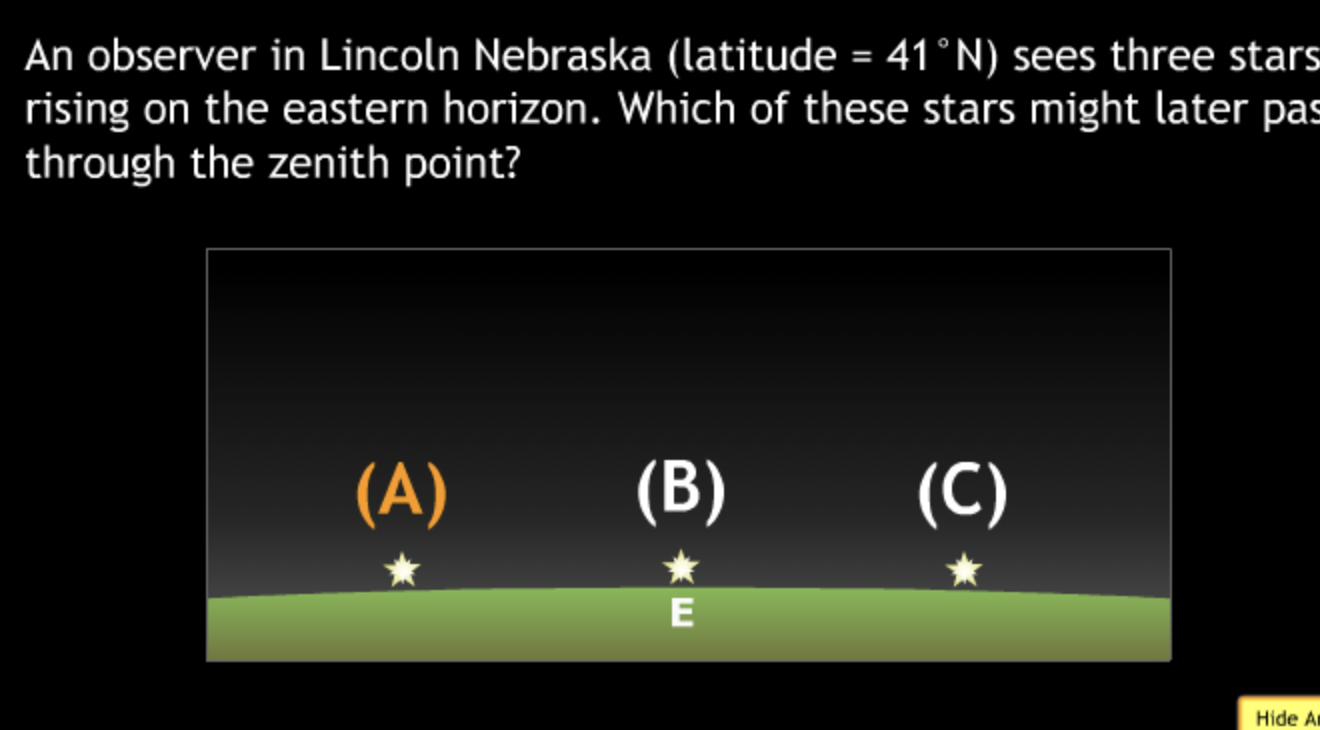
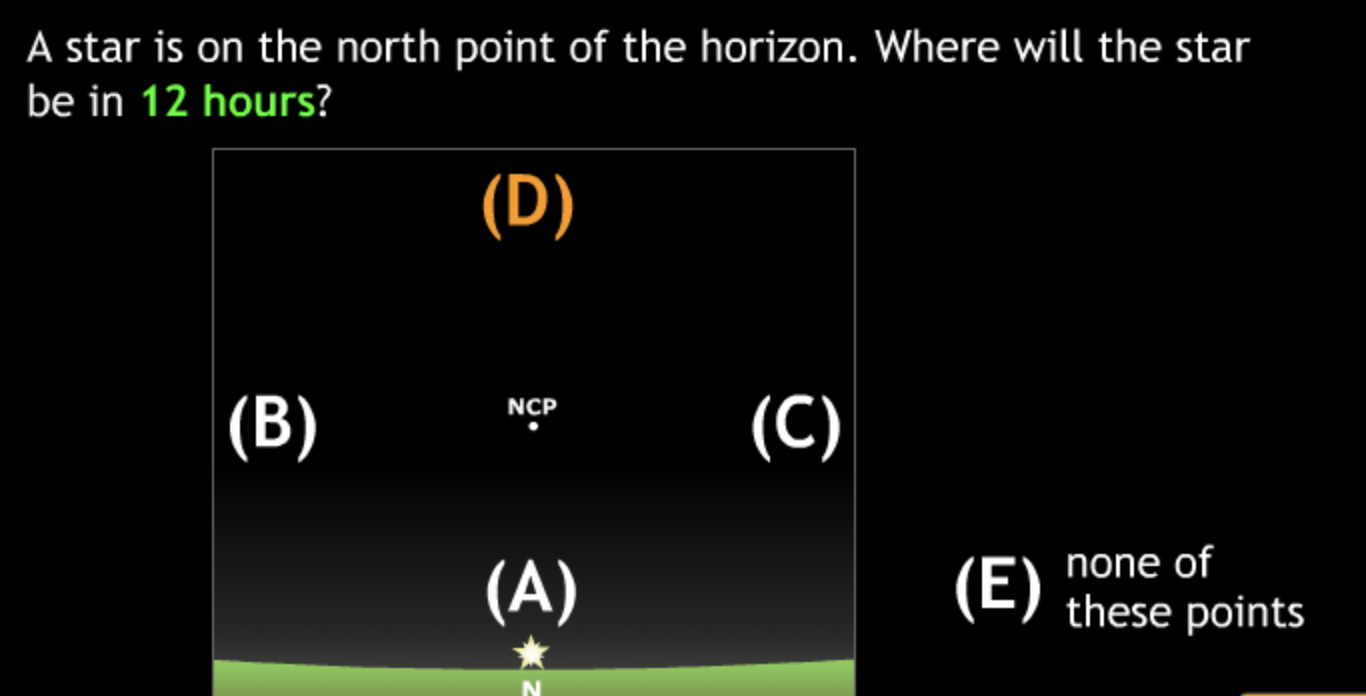
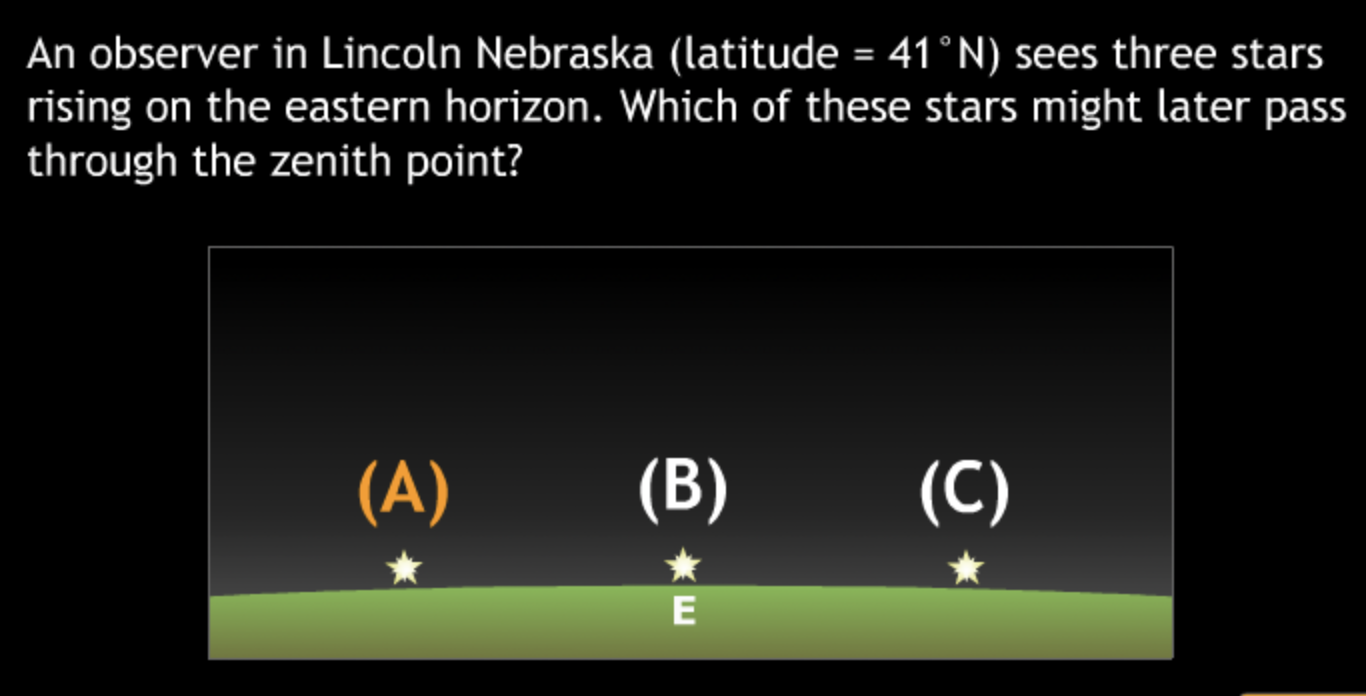
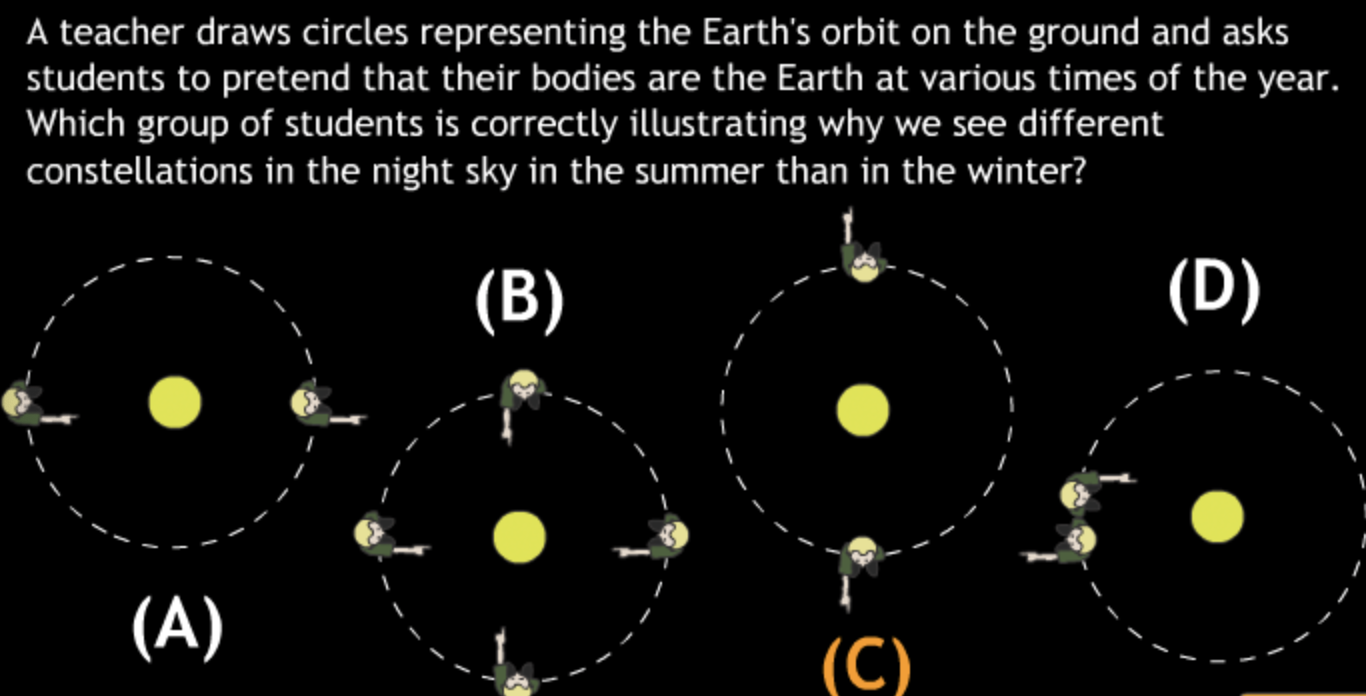
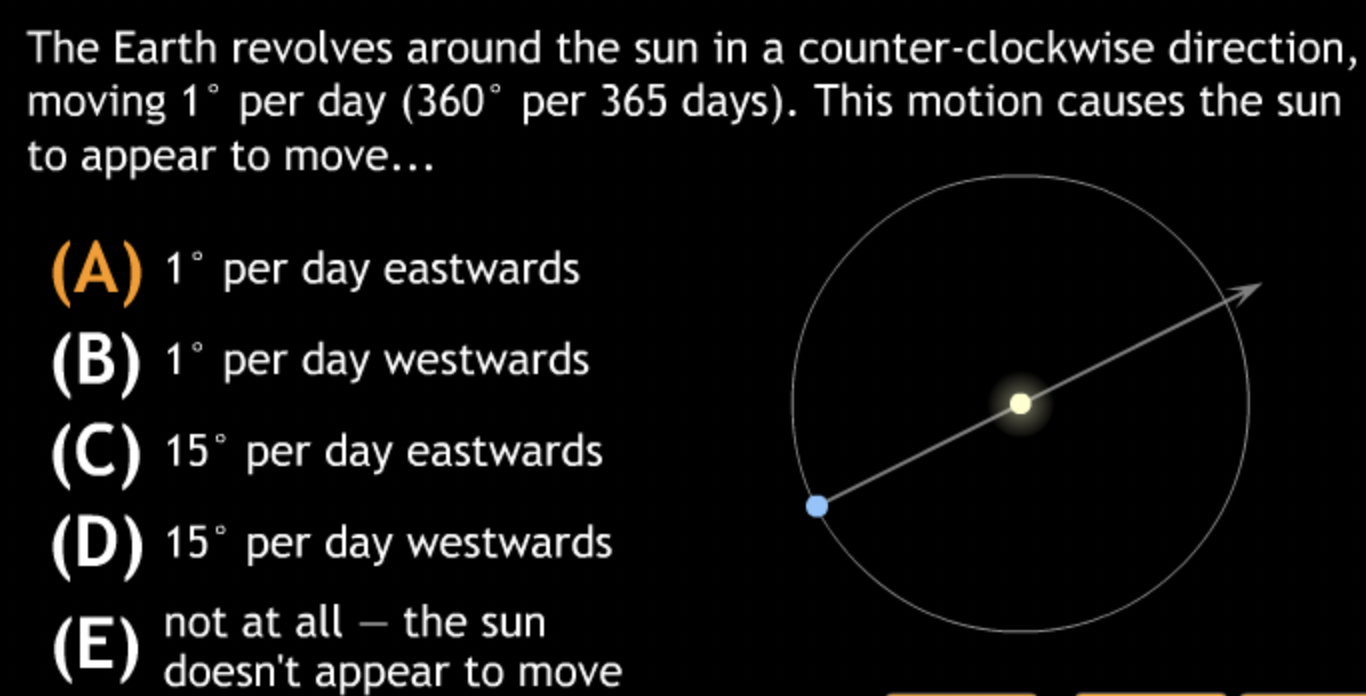
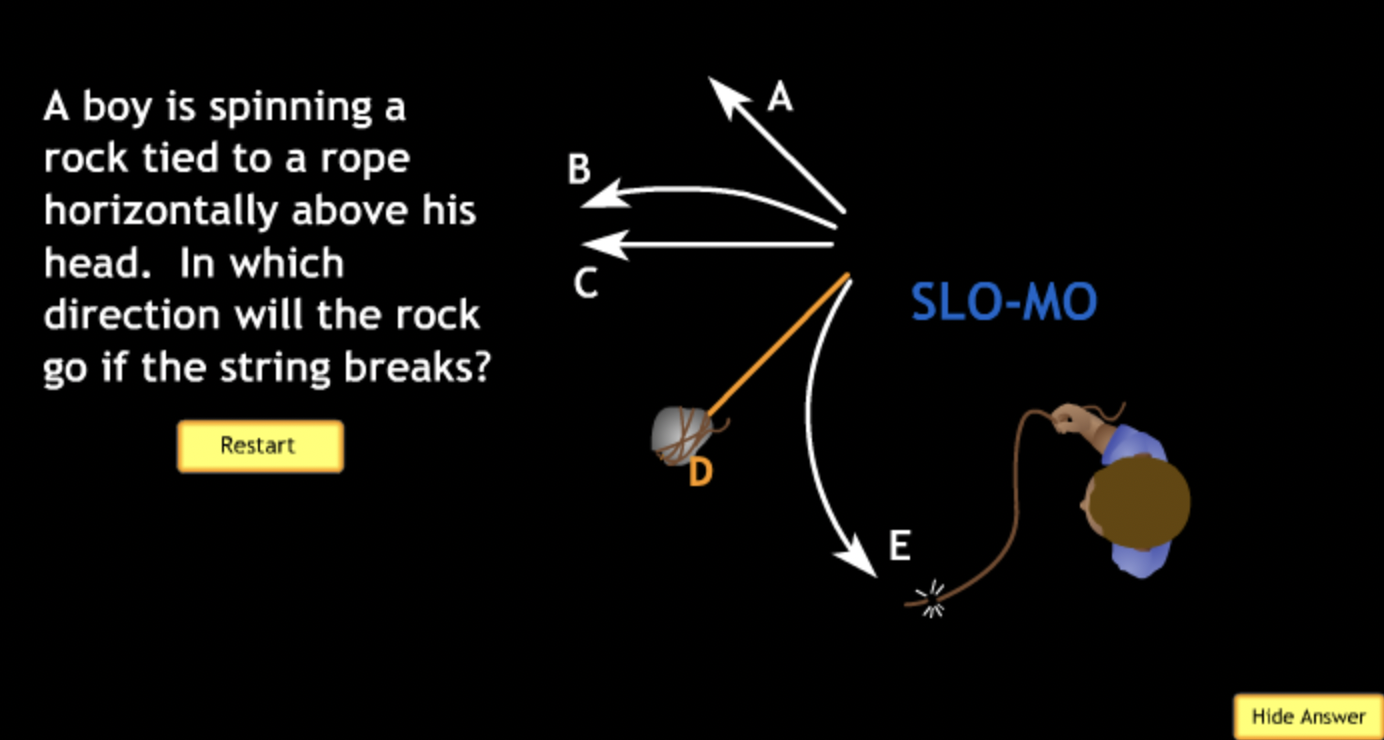
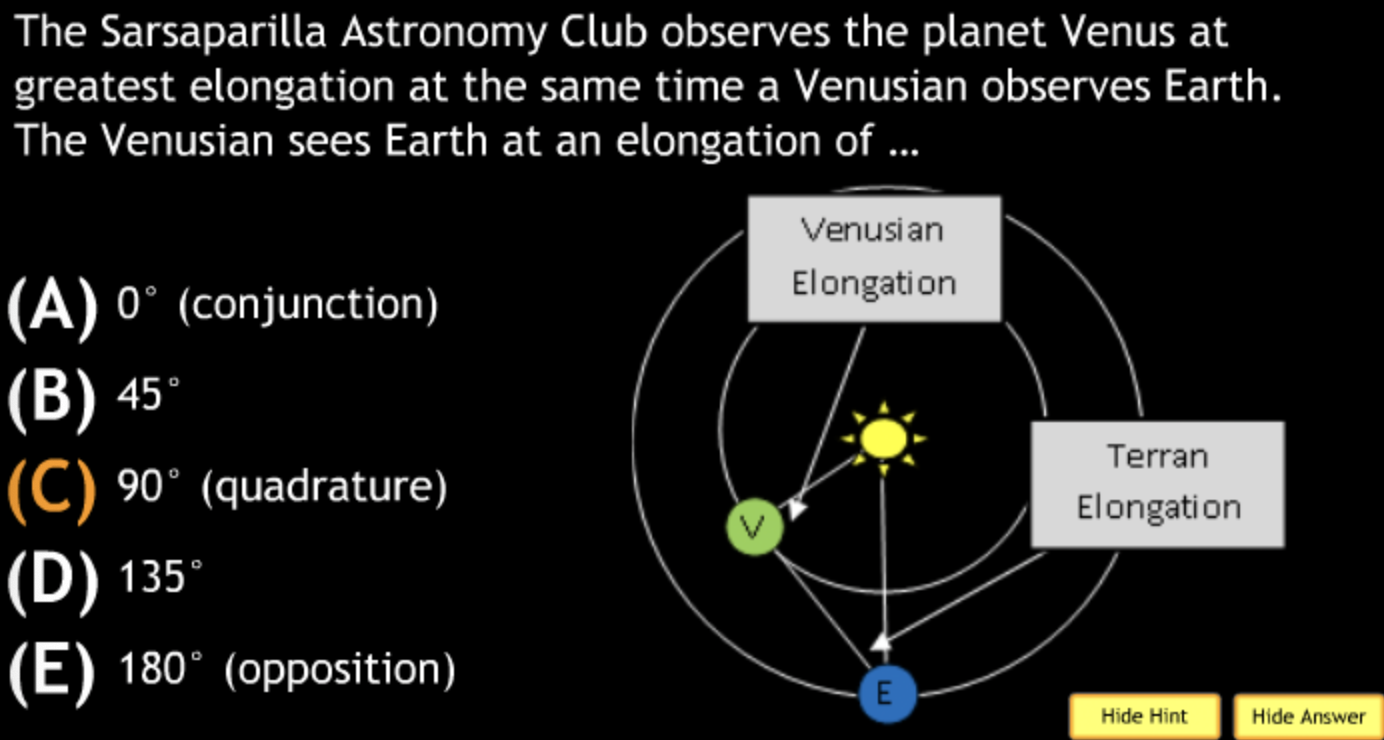
Basic motions & Ancient Astronomy



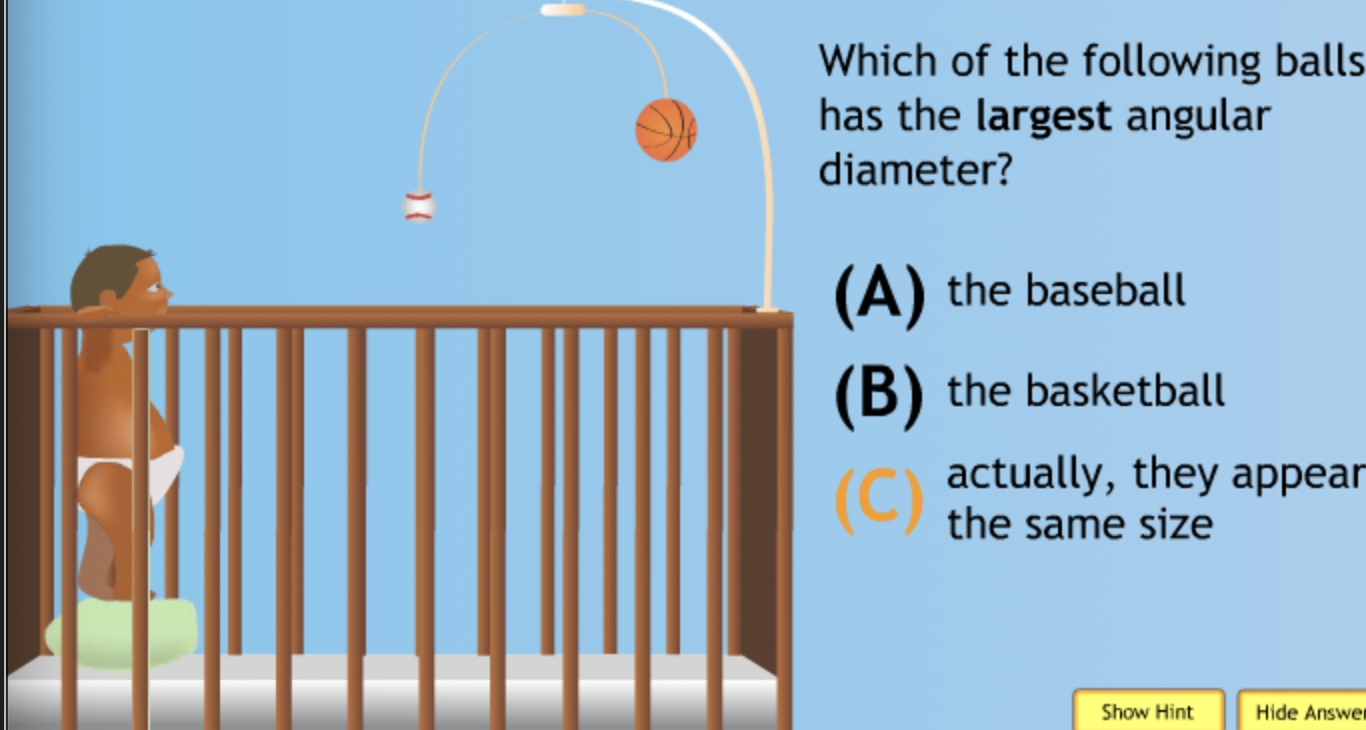









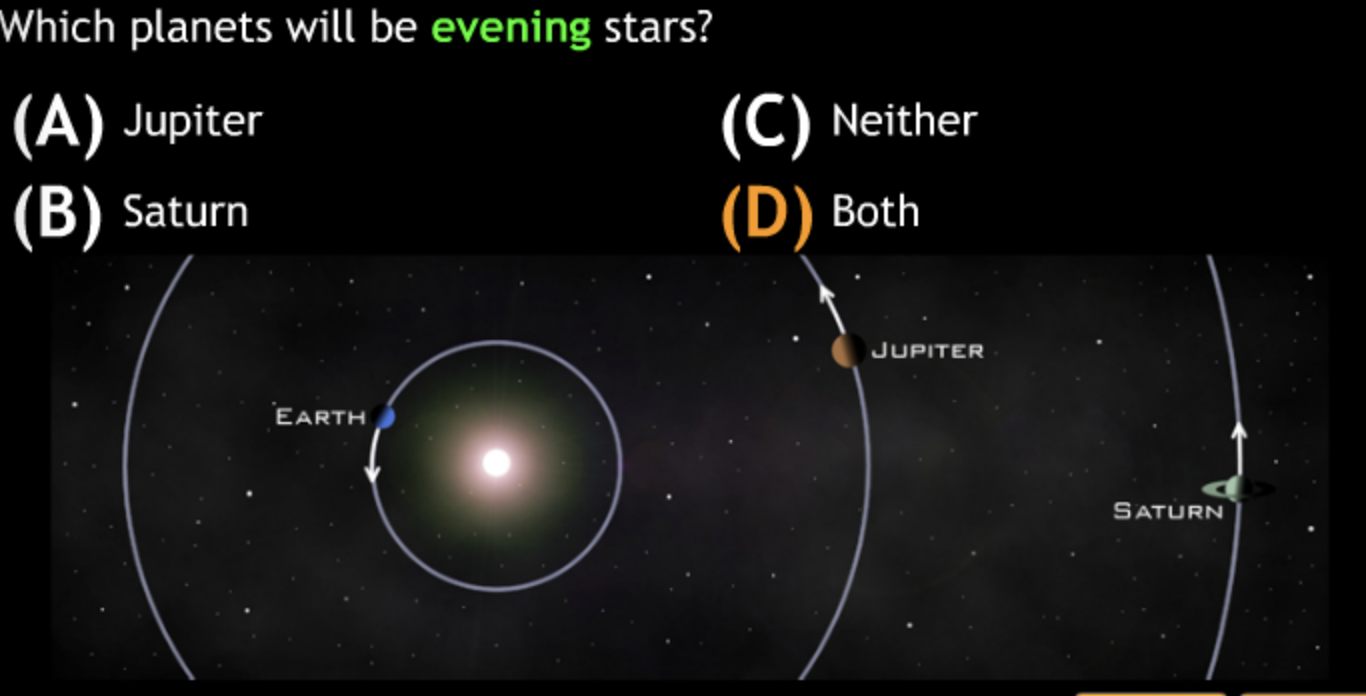
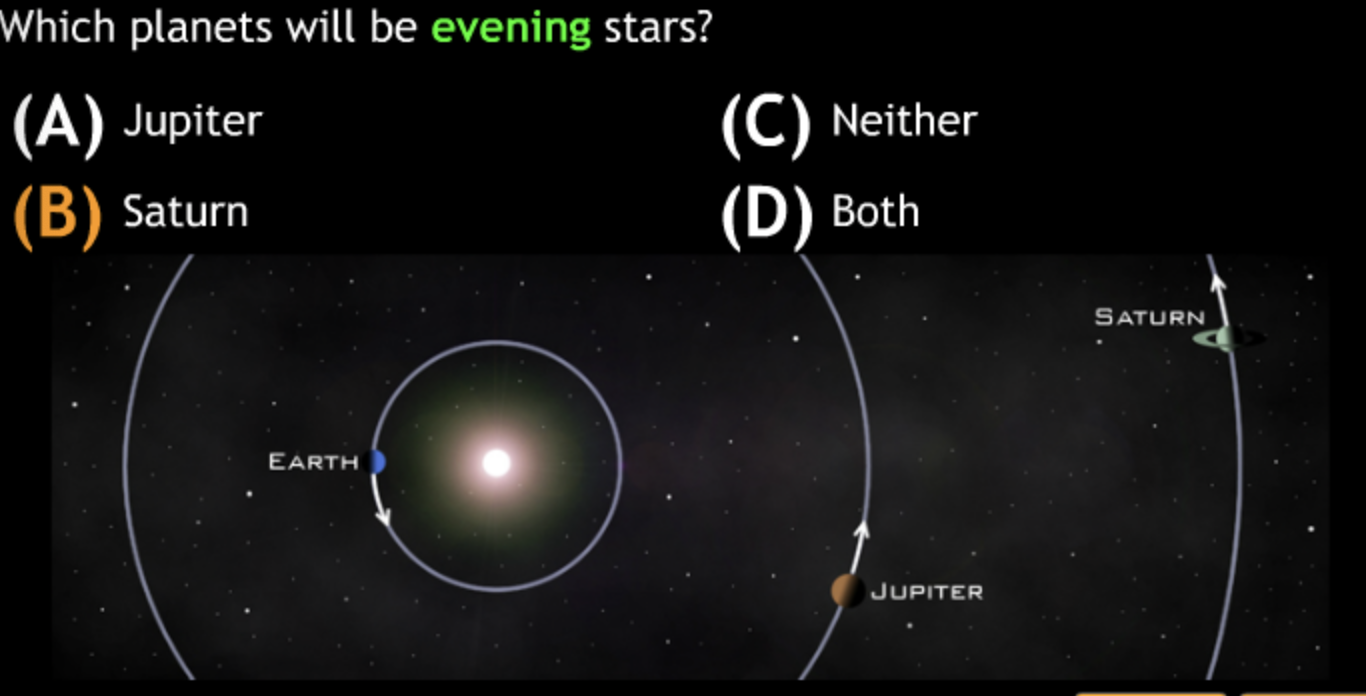

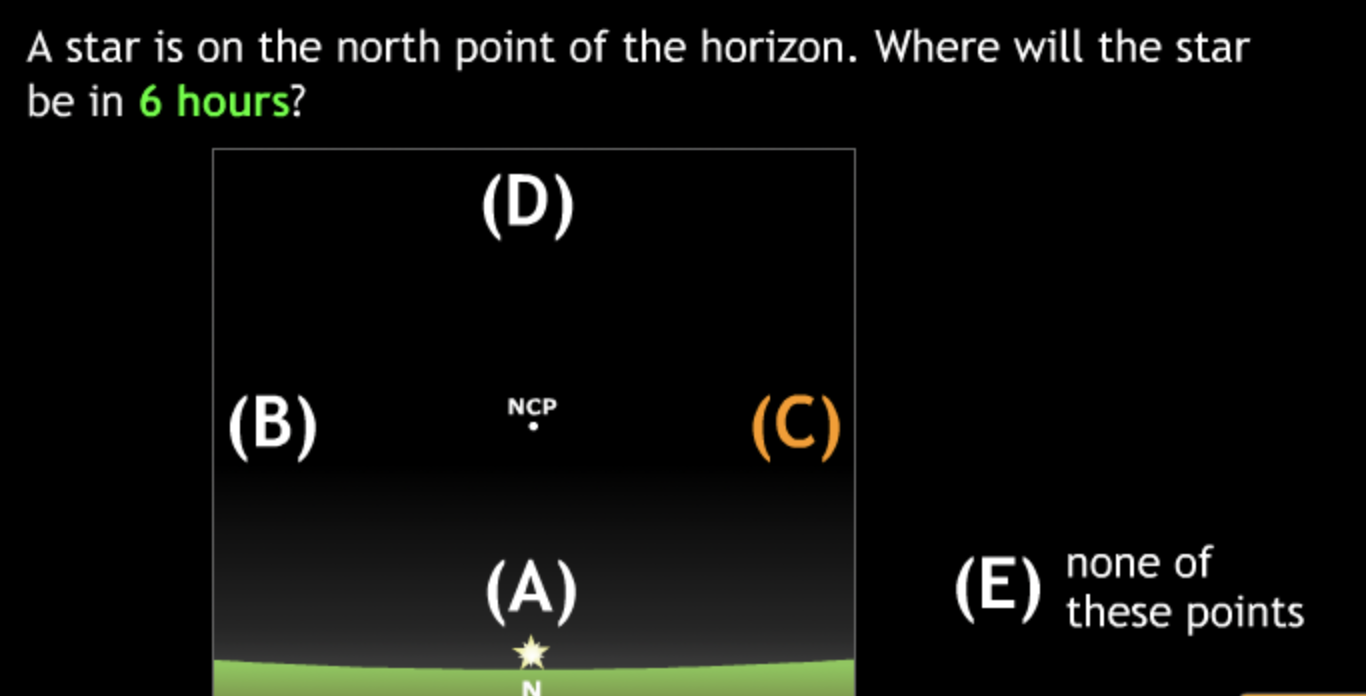




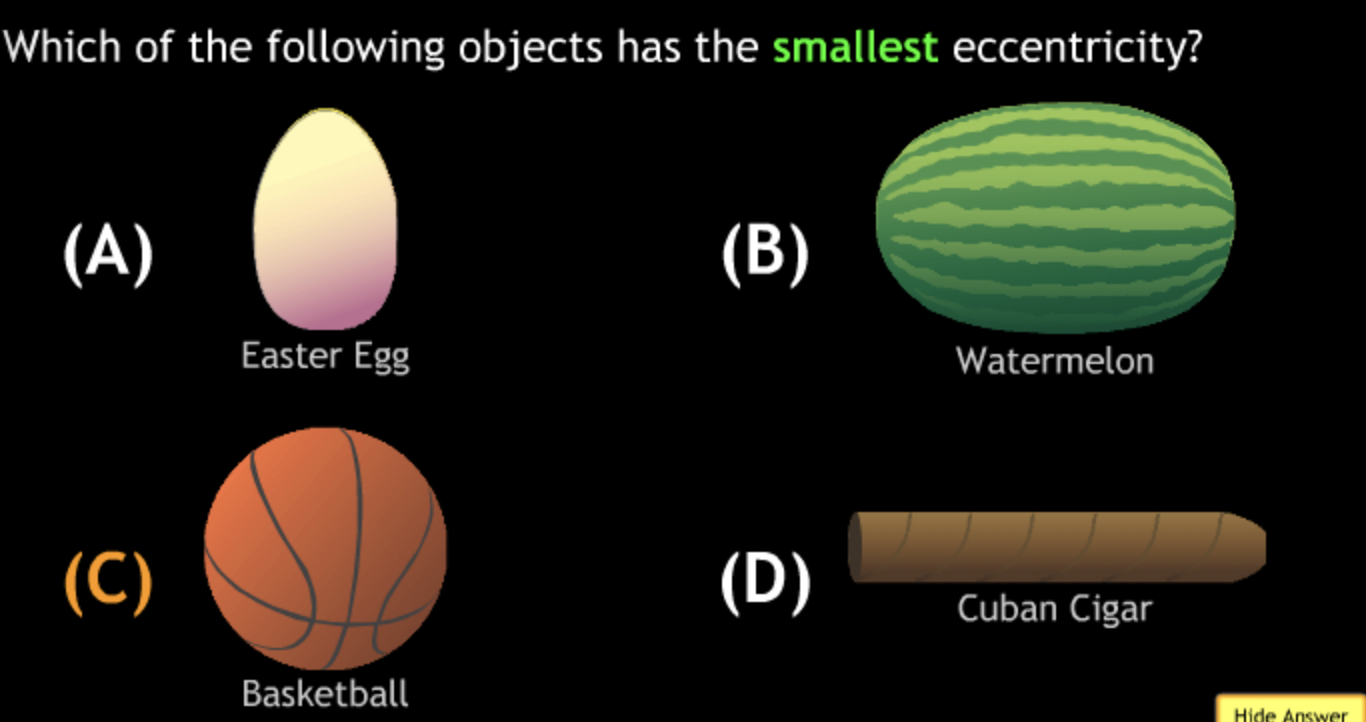
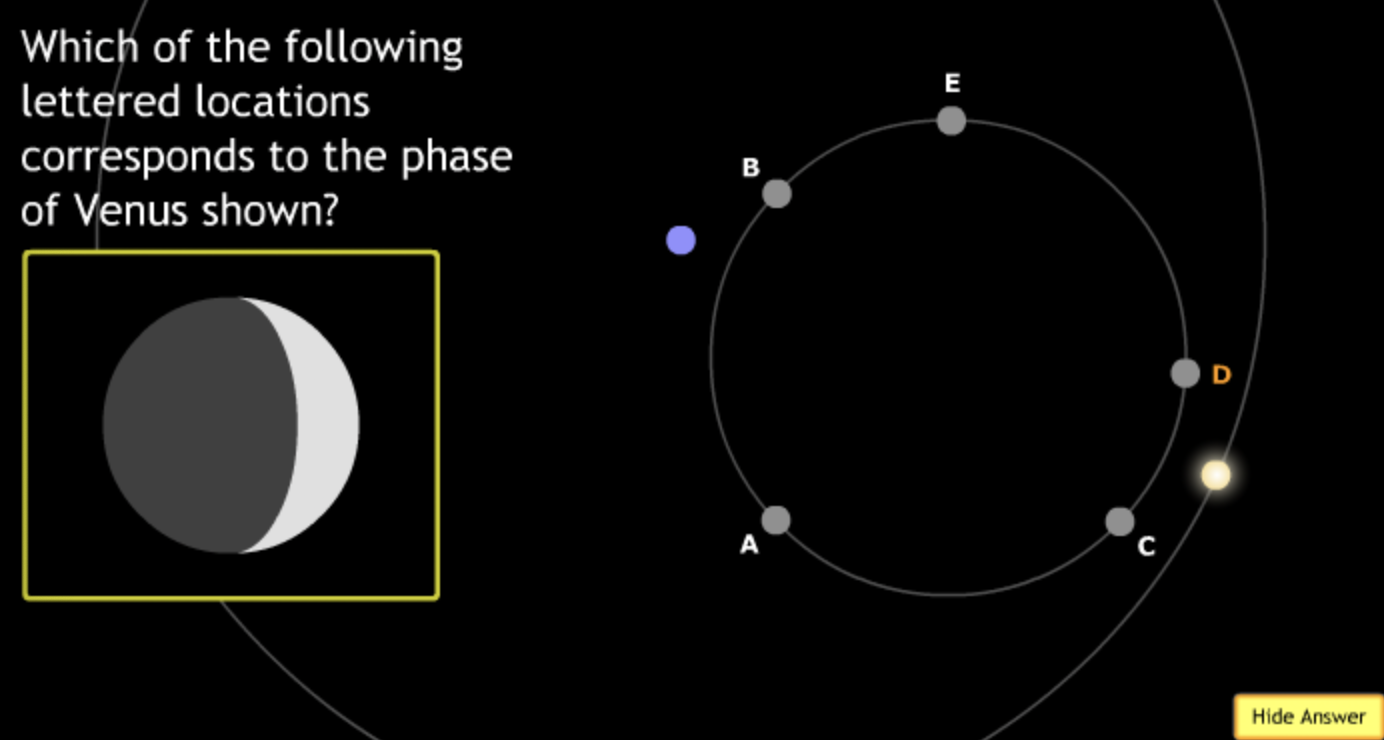
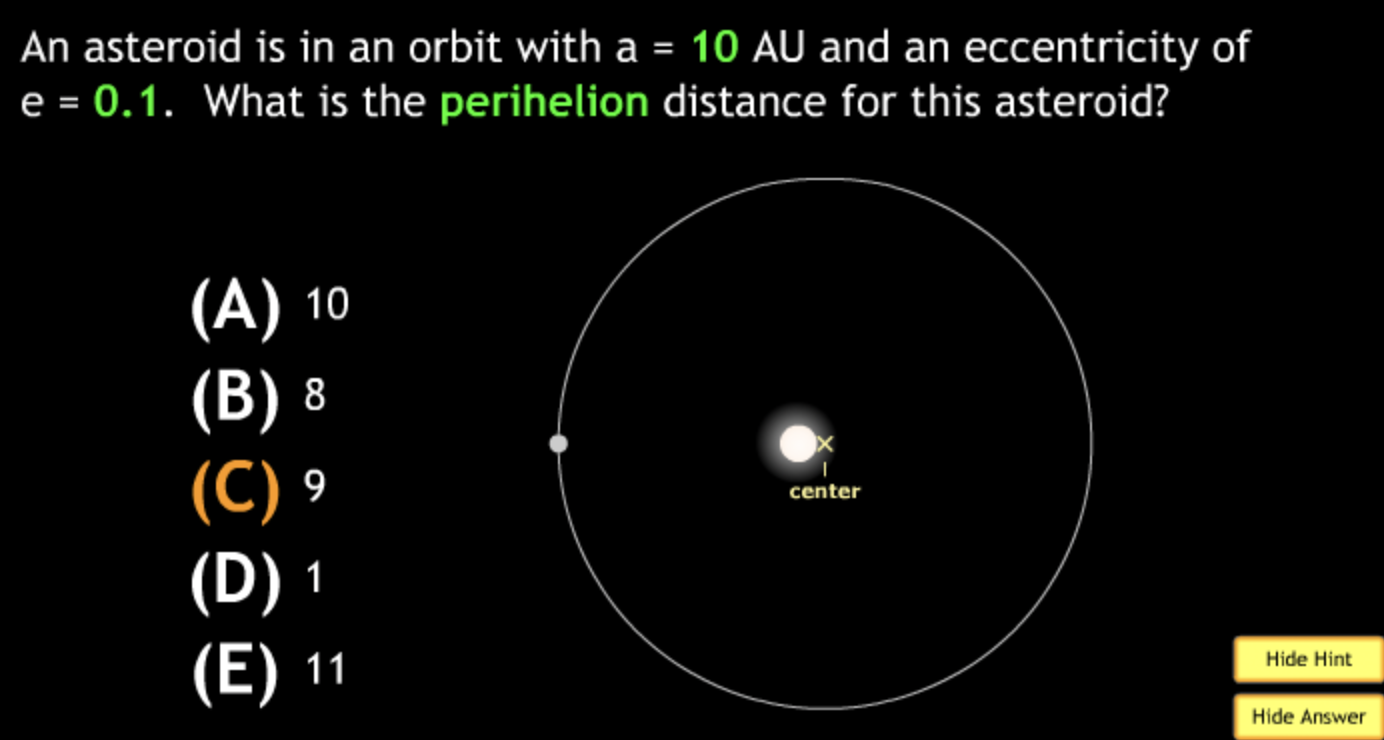
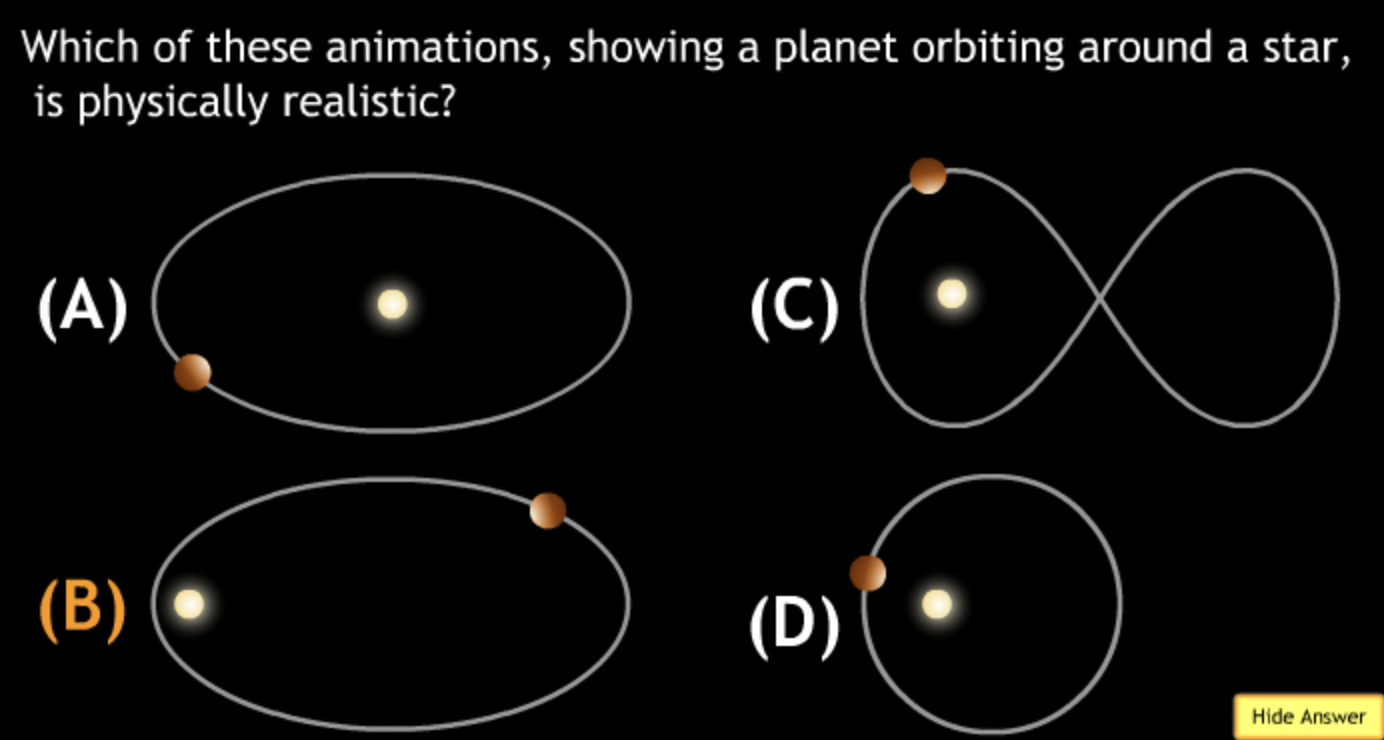
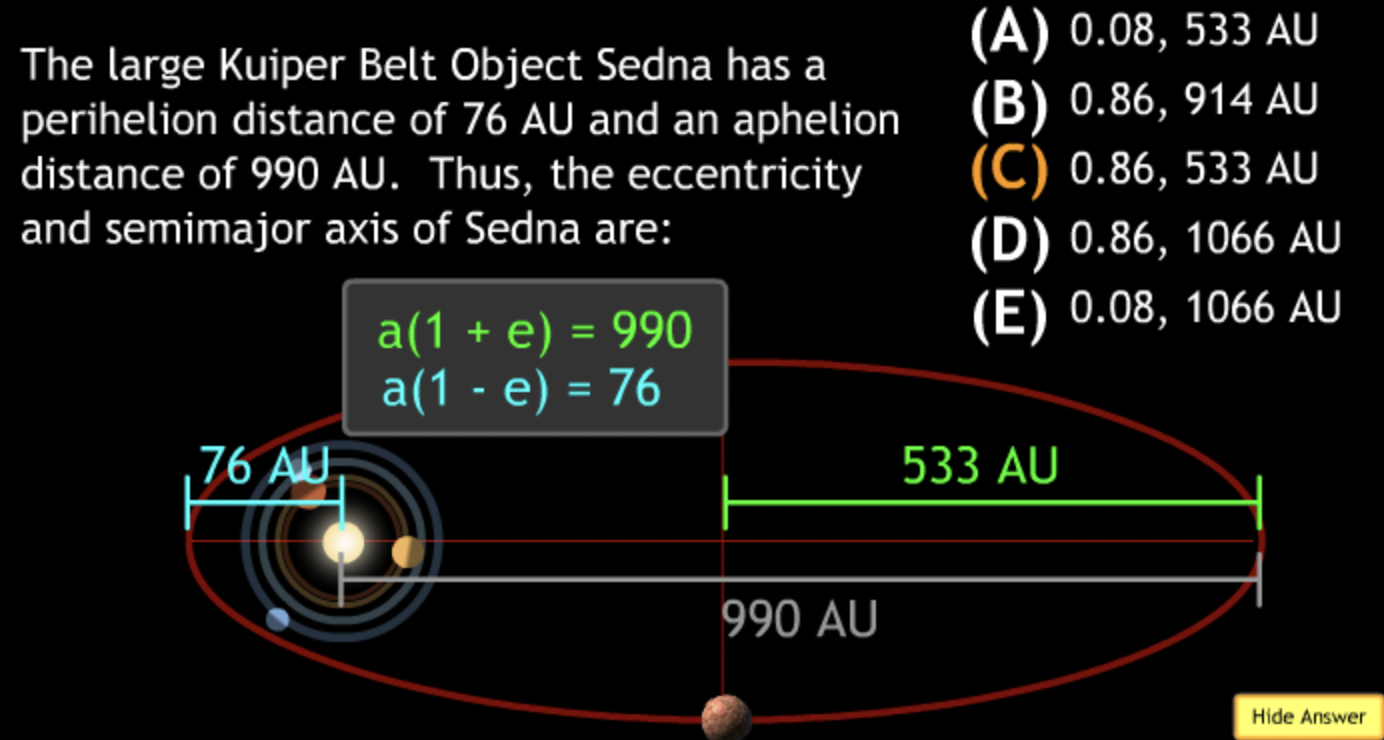
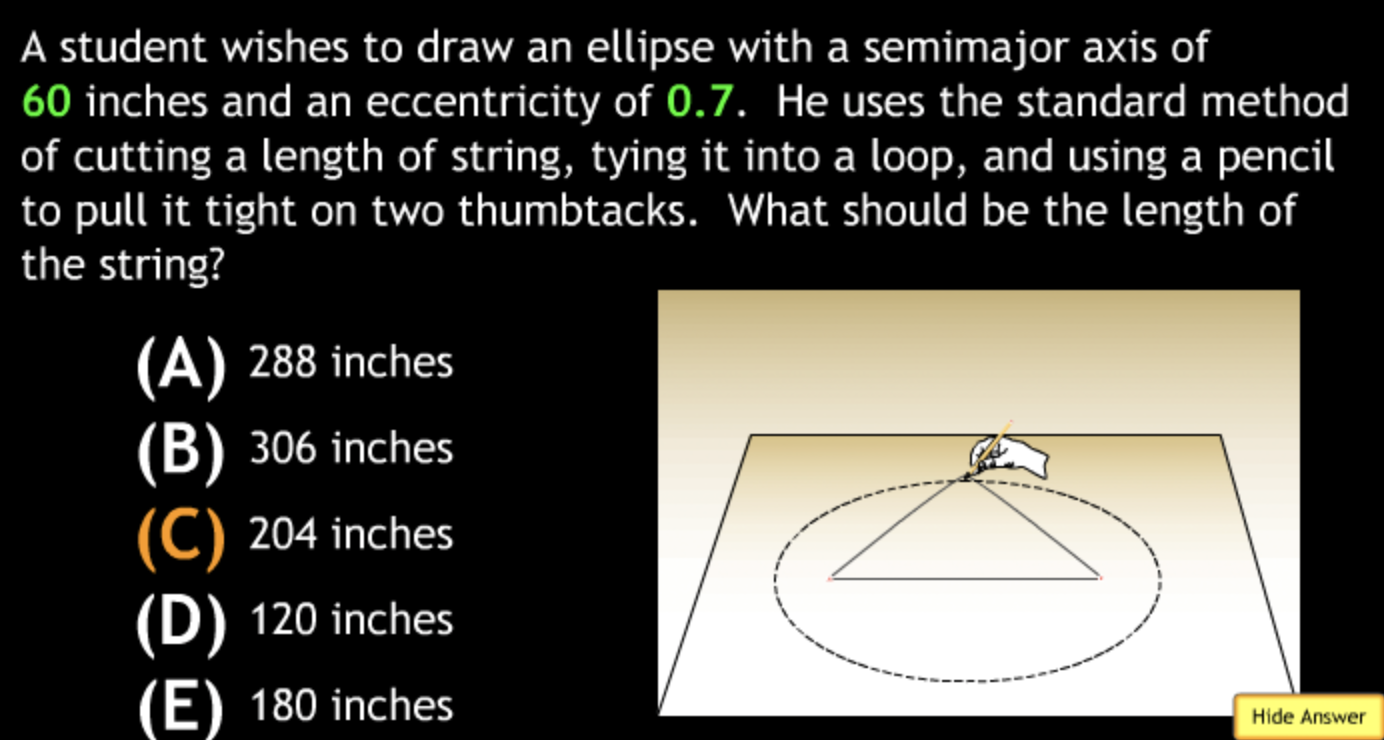
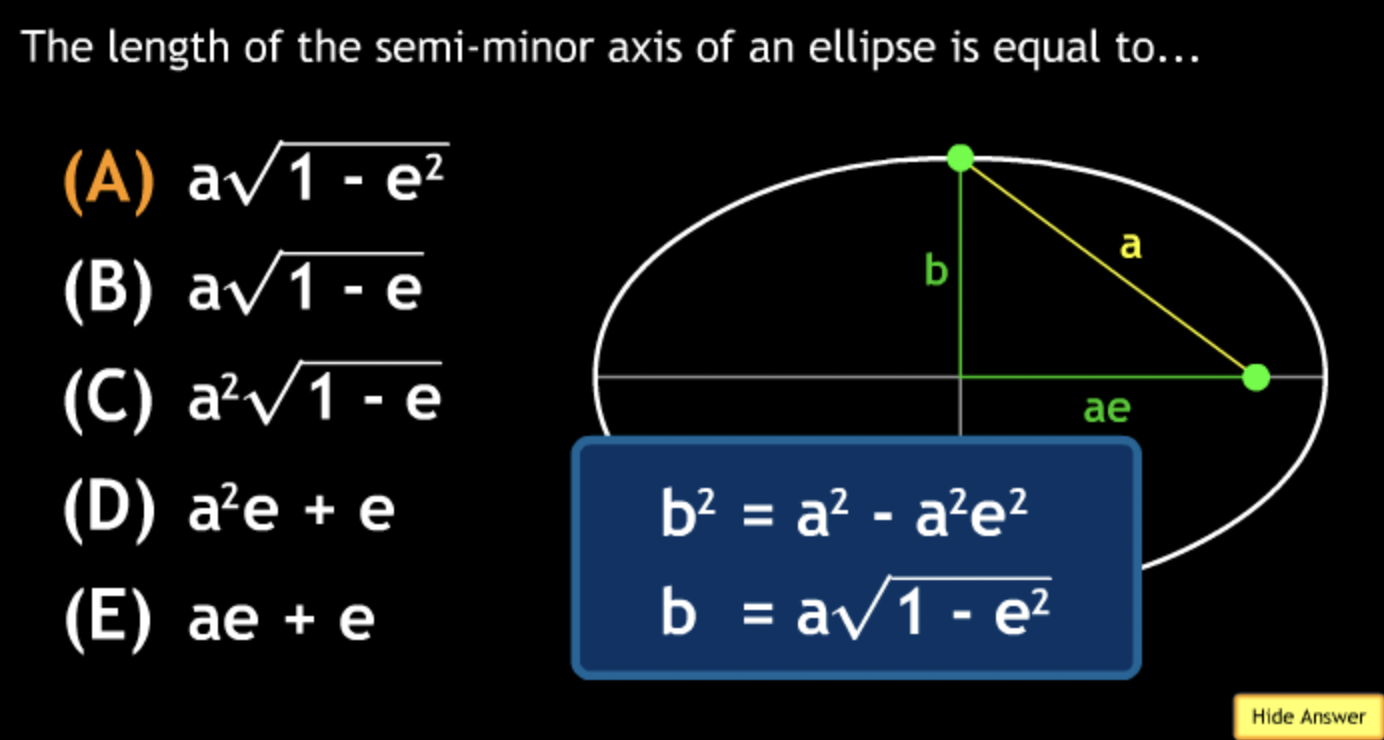
largest eccentricity → Cuban Cigar
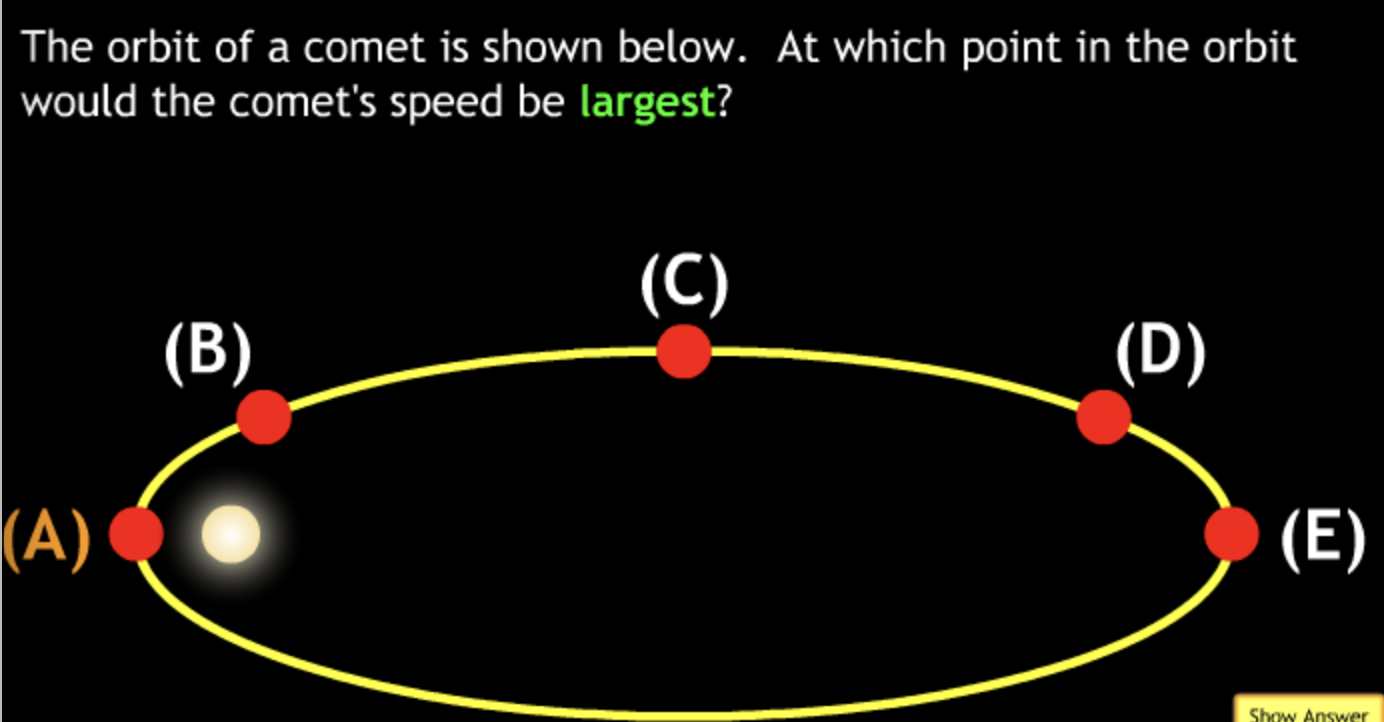
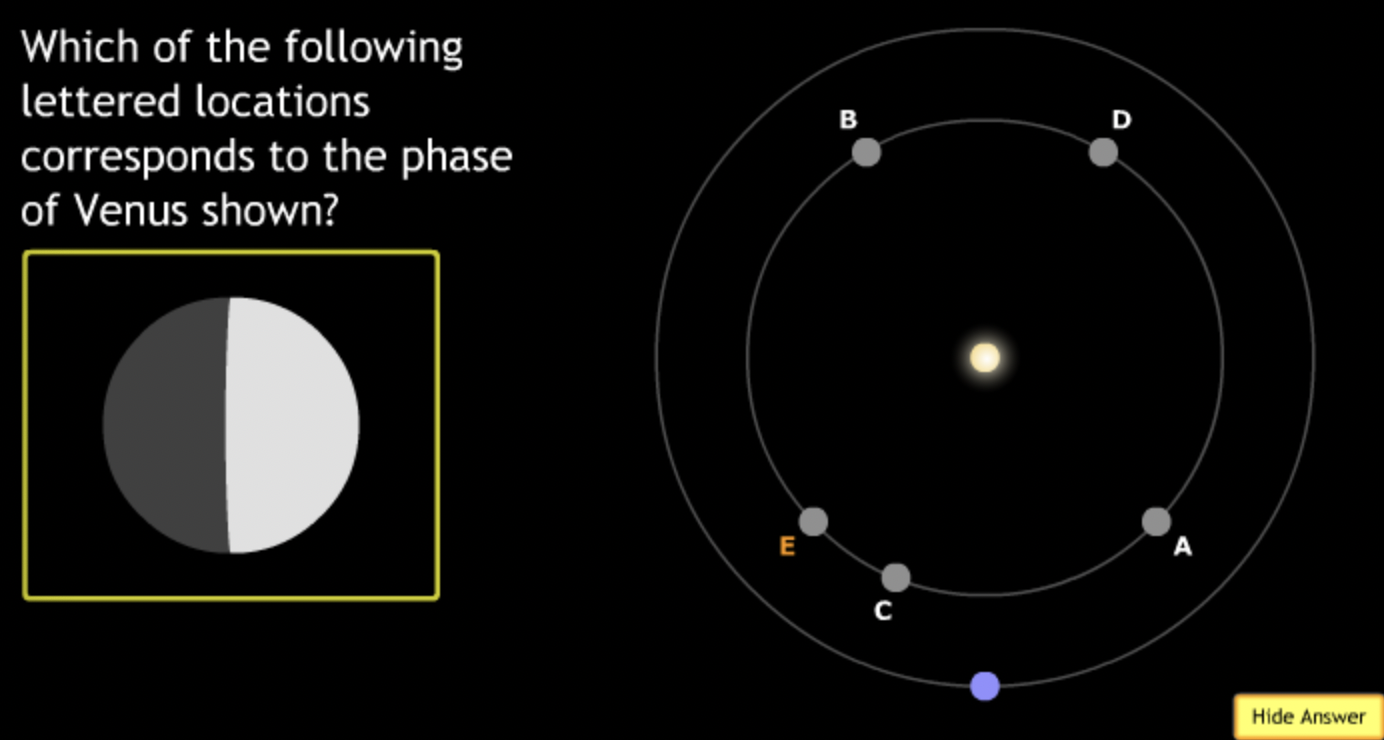
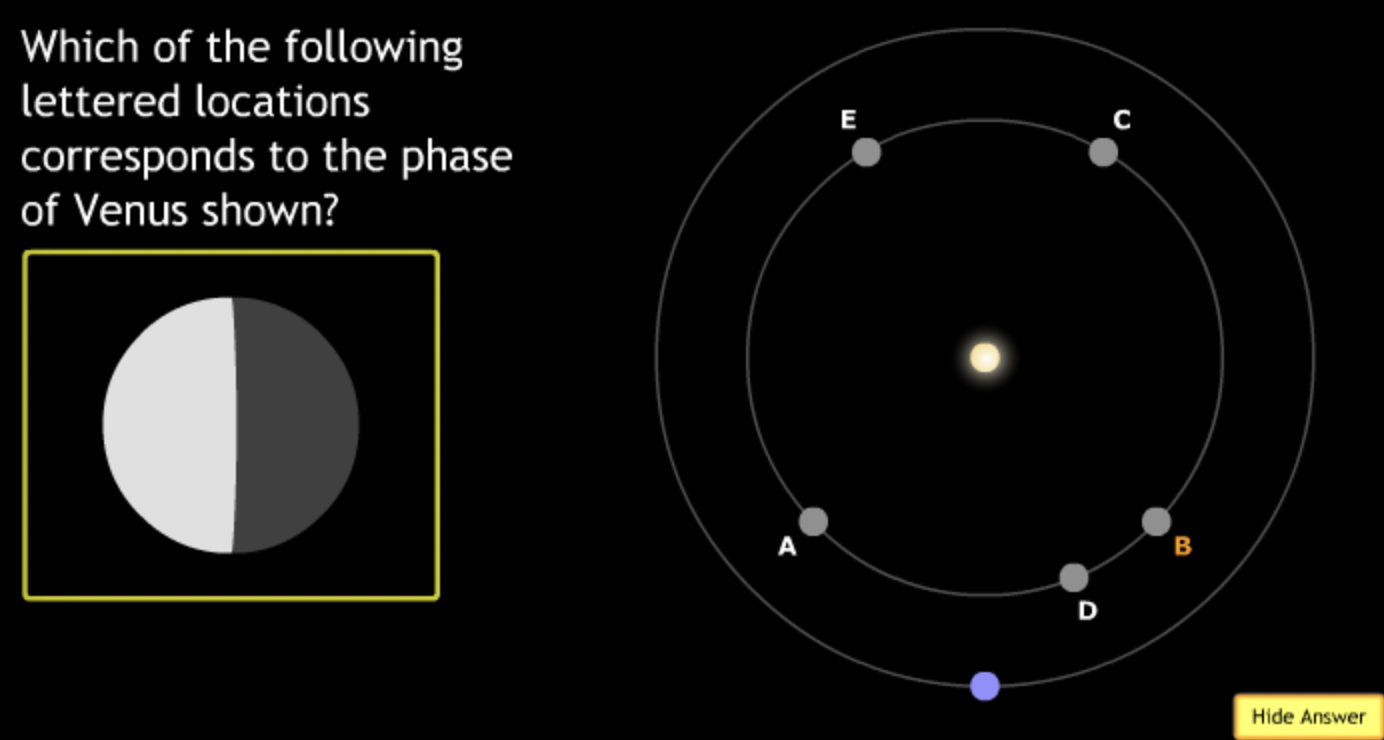
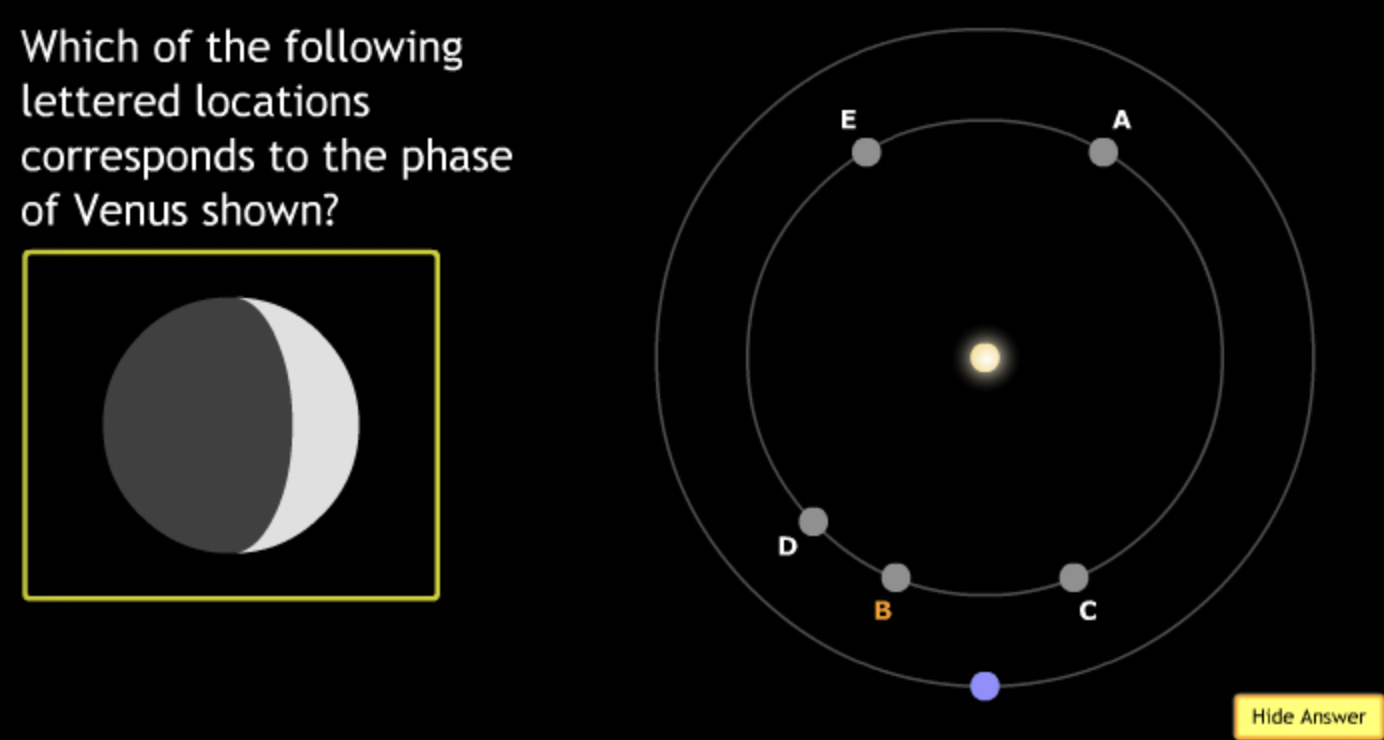
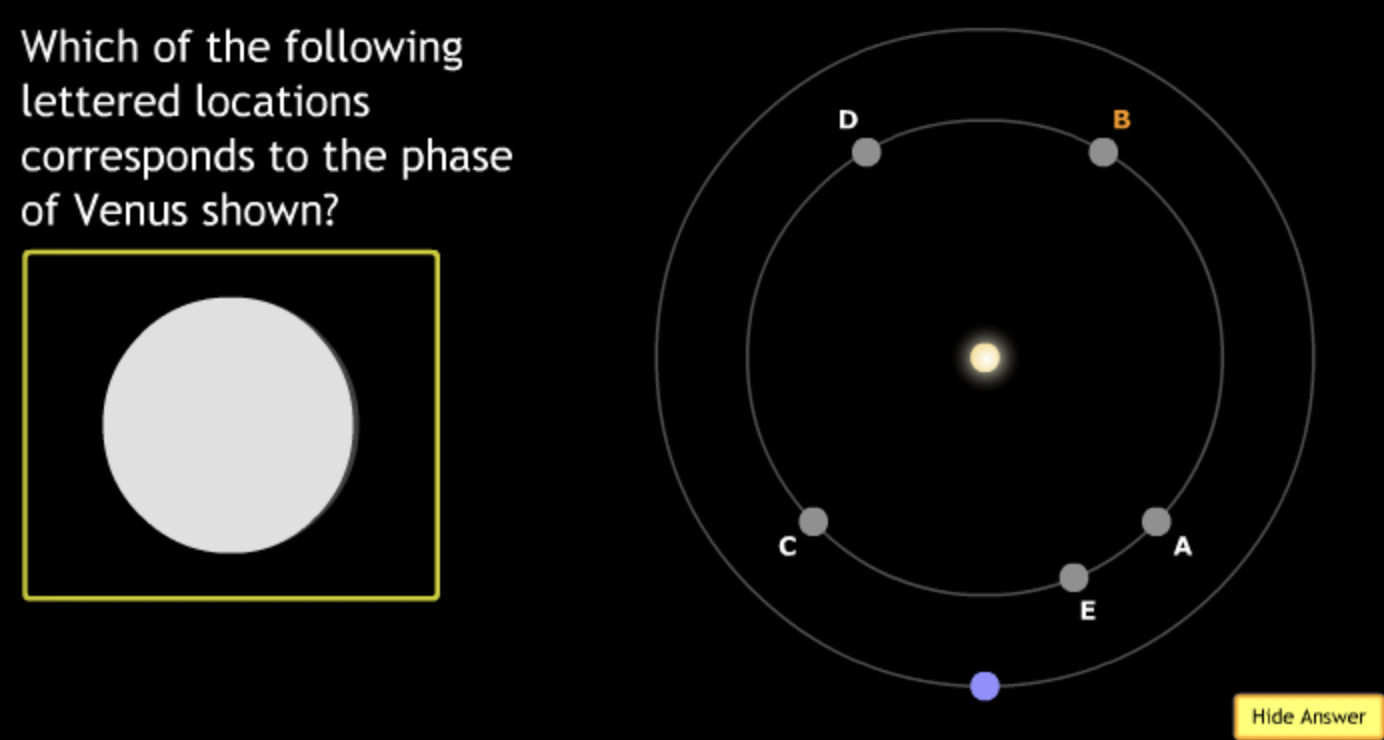
smallest → E

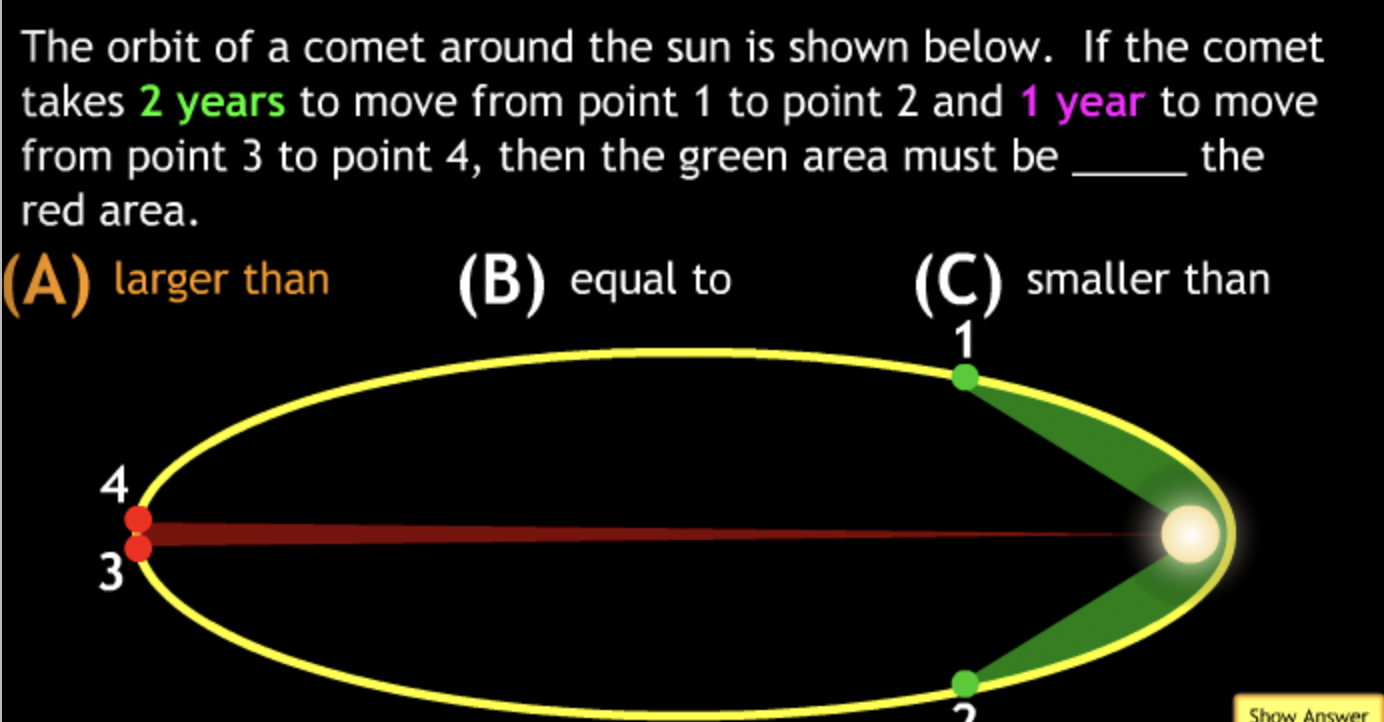

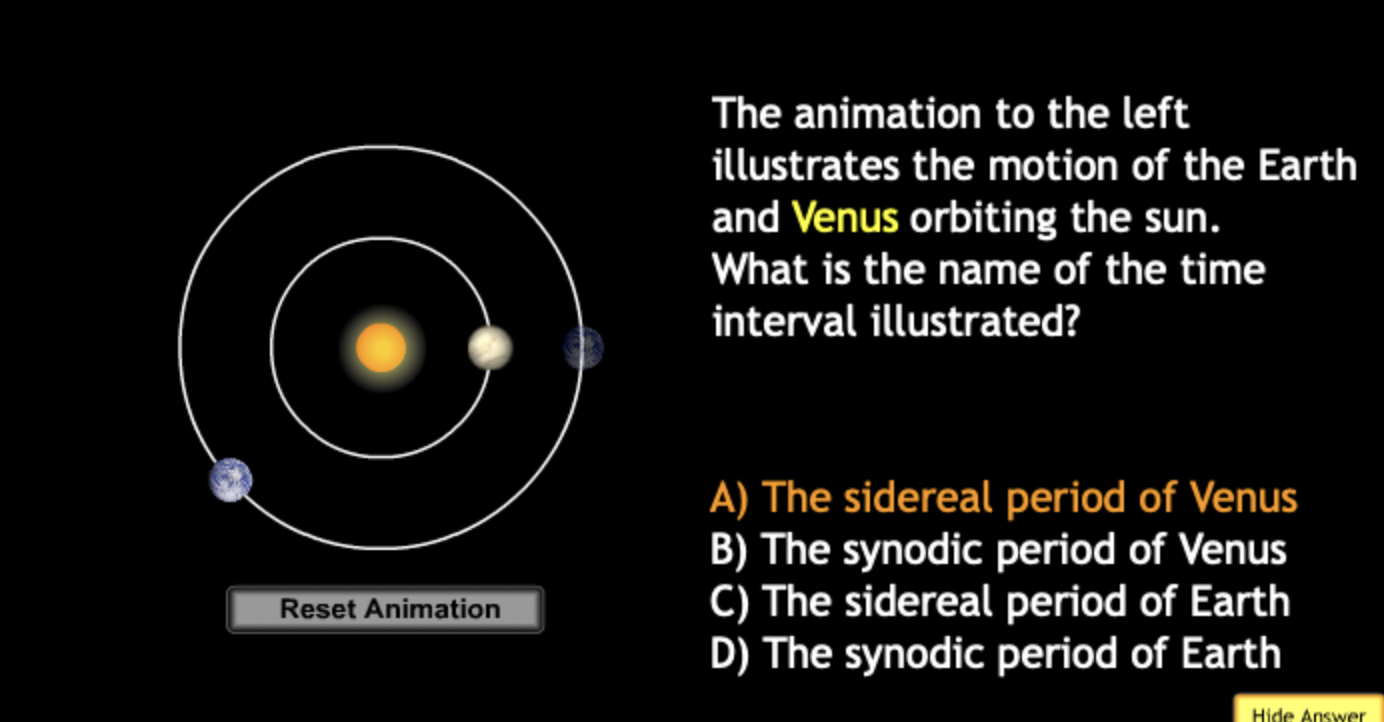
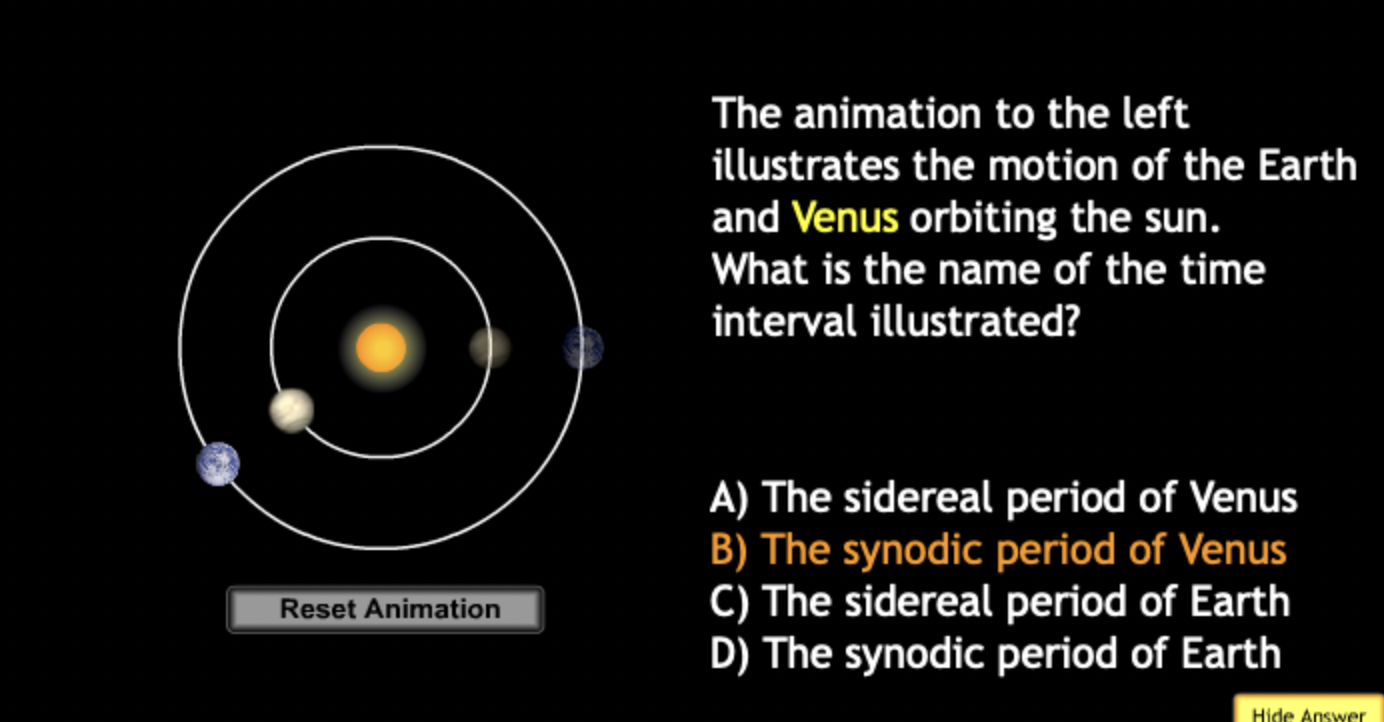
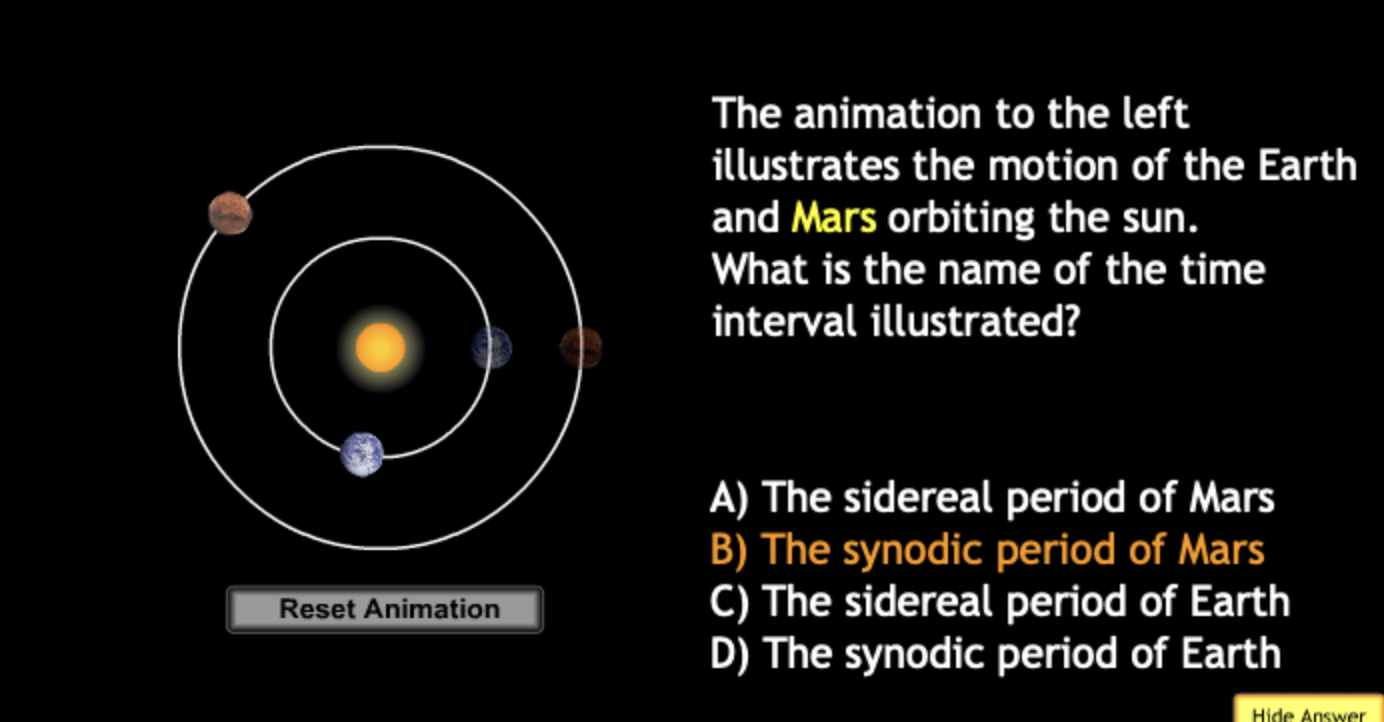
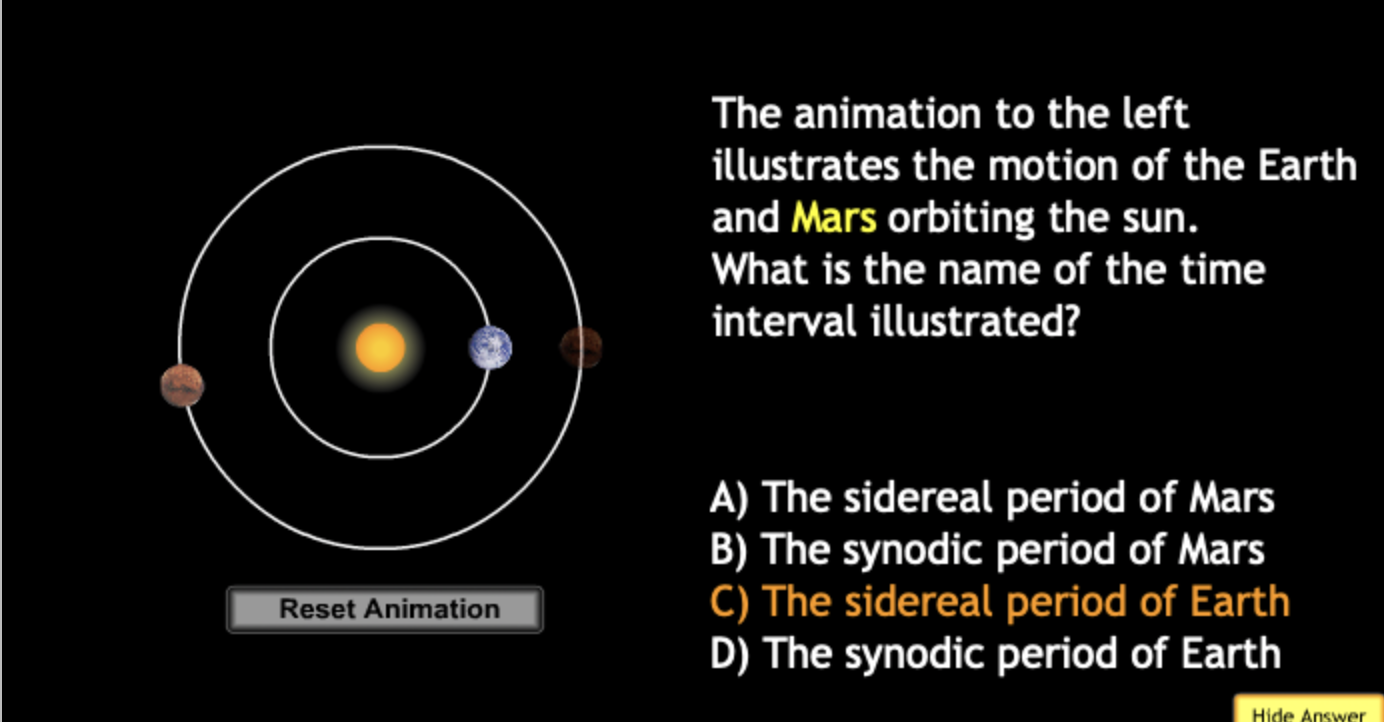
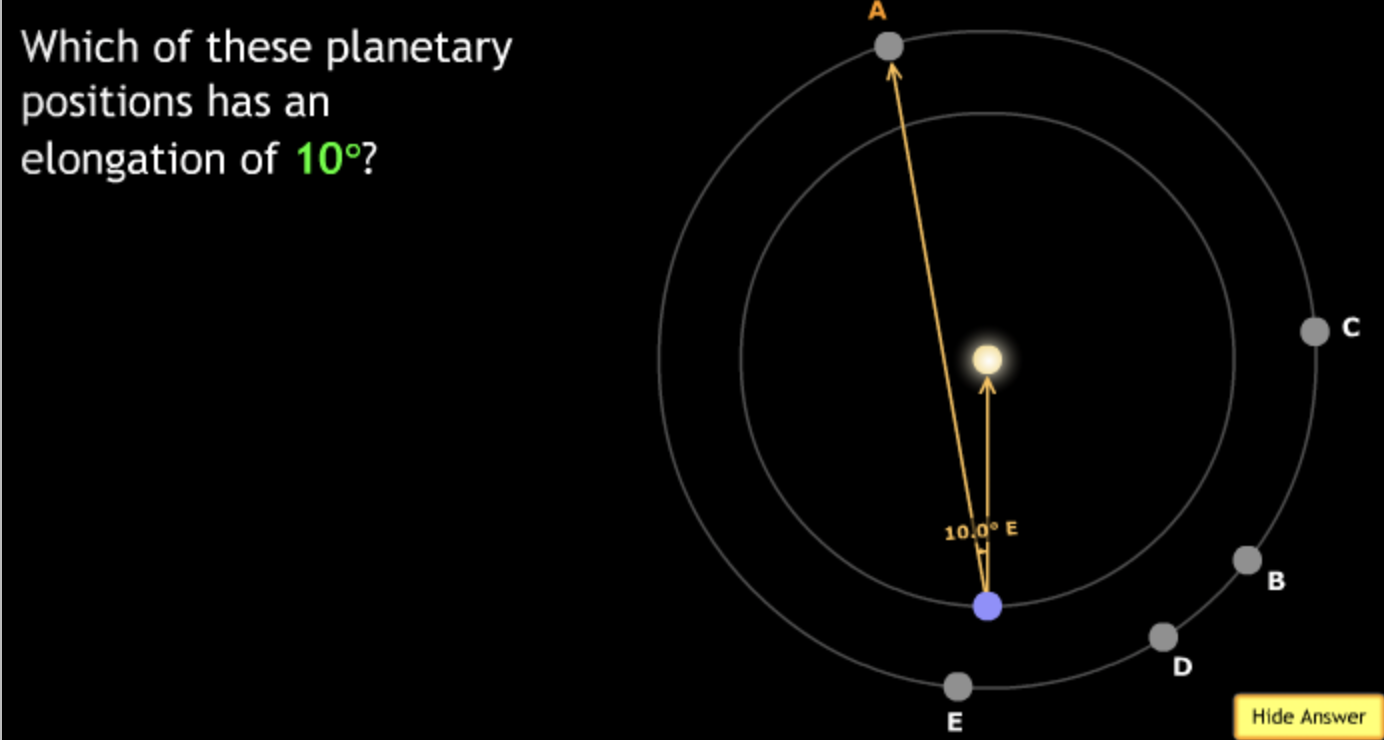
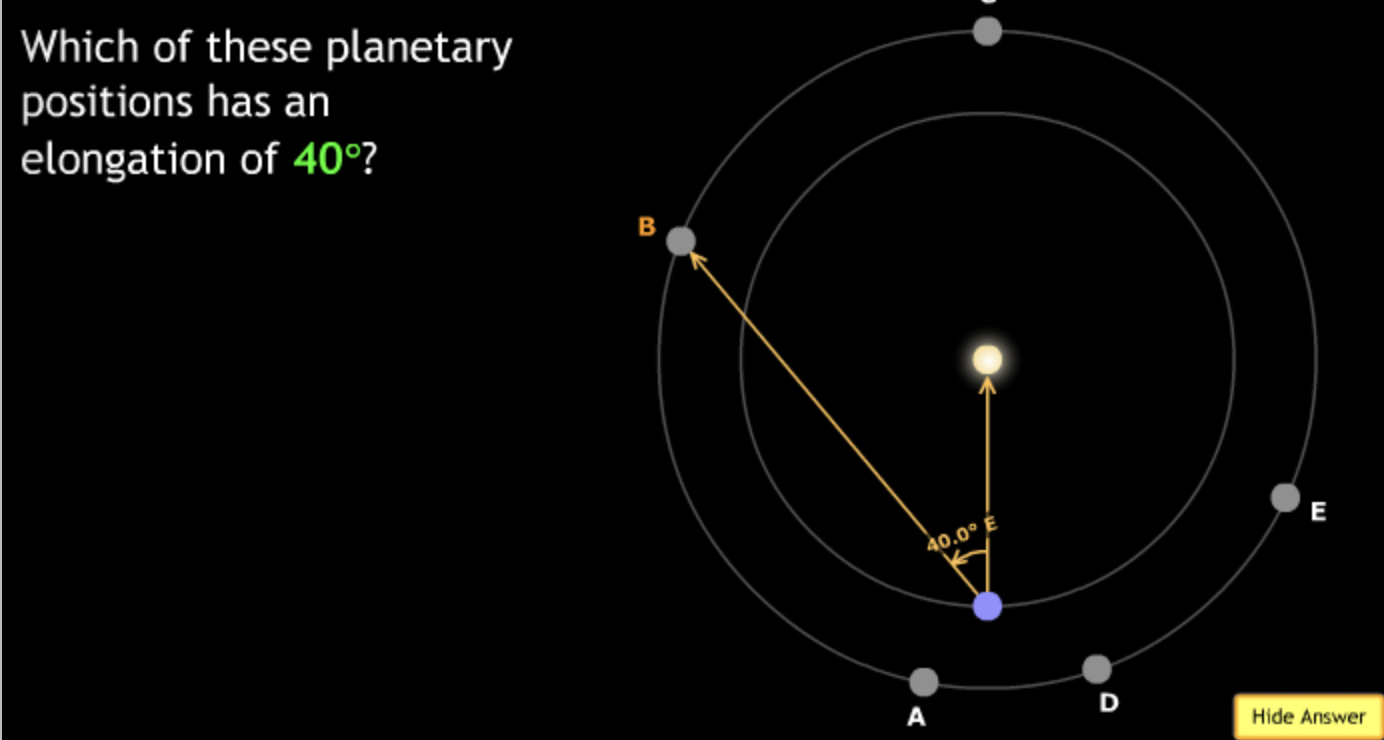
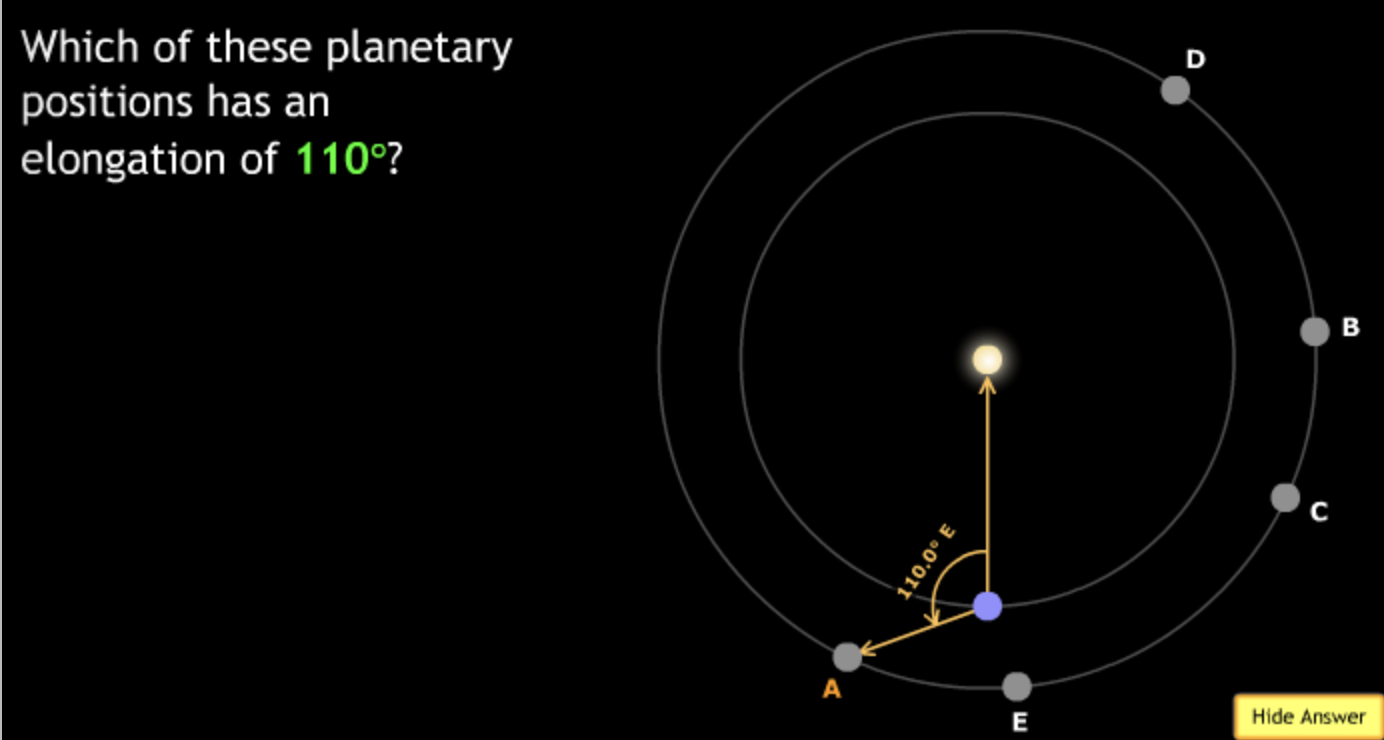
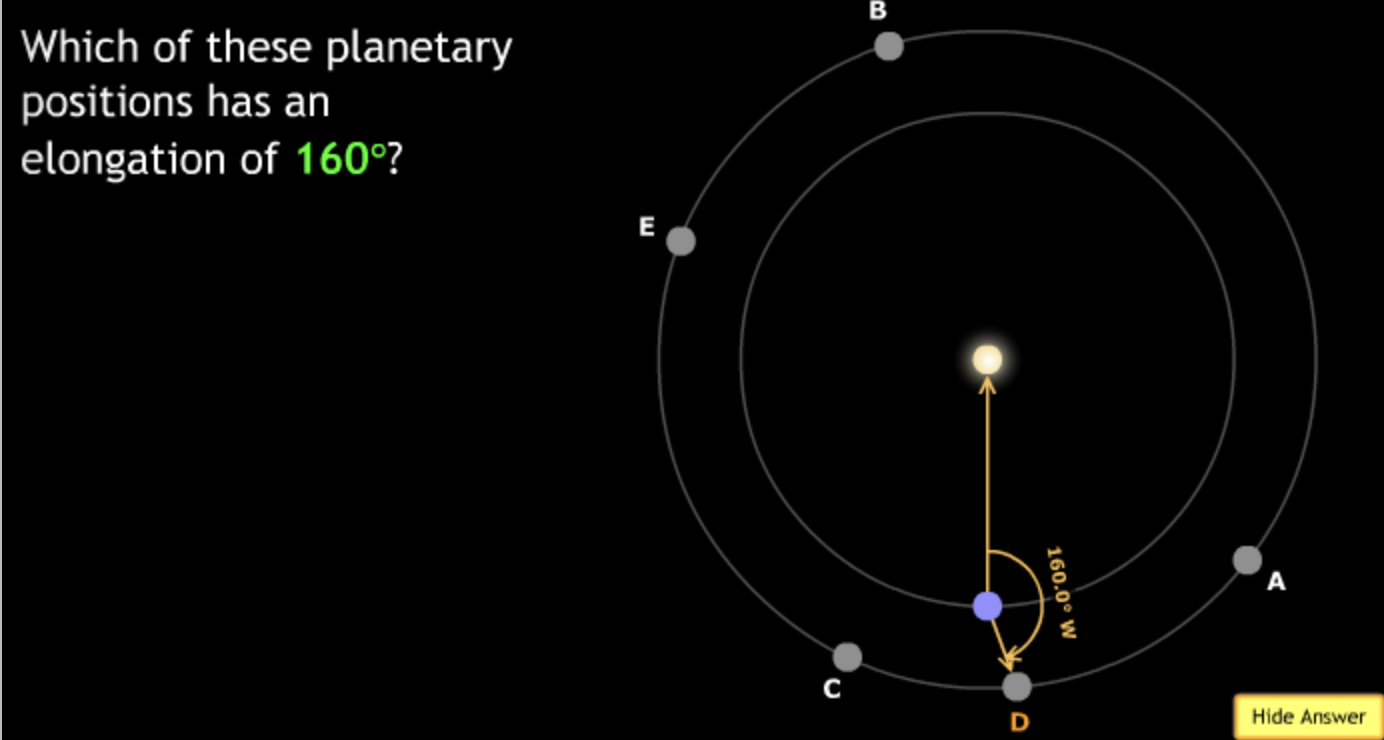
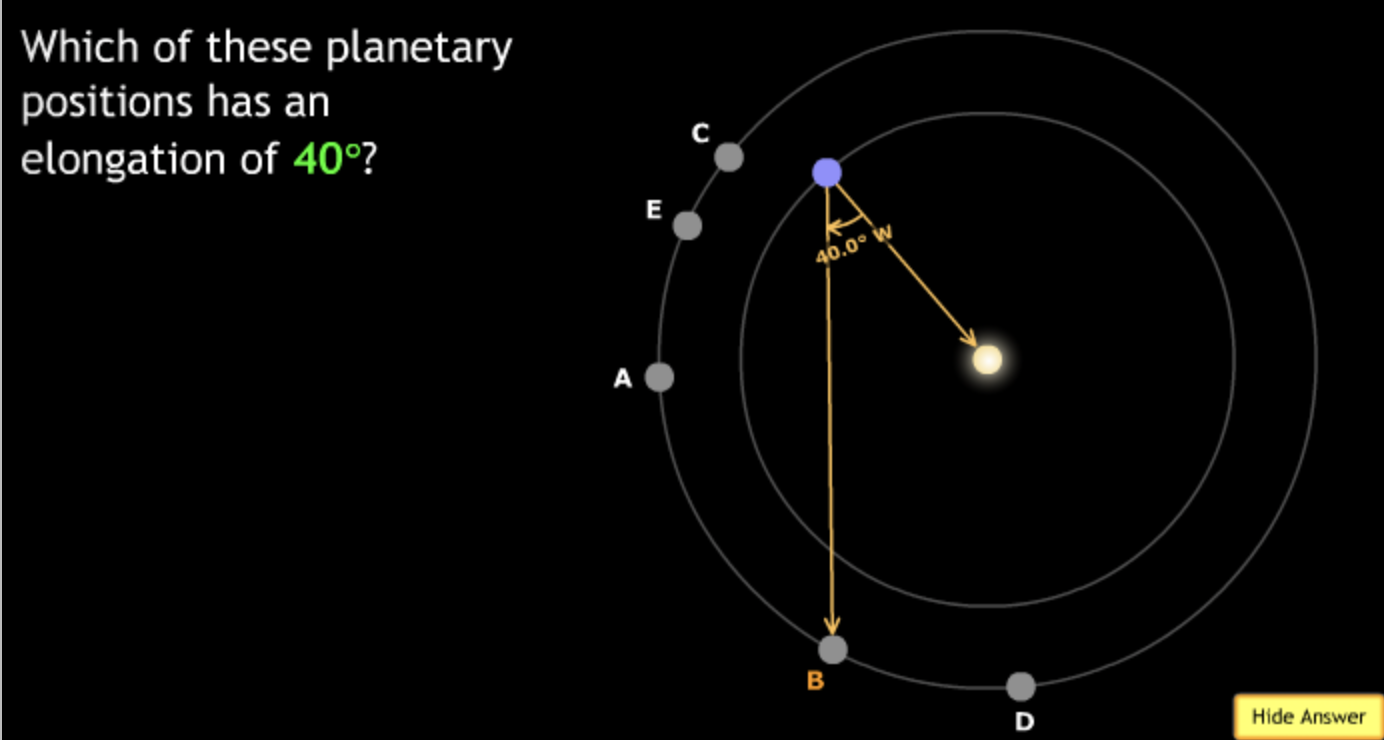

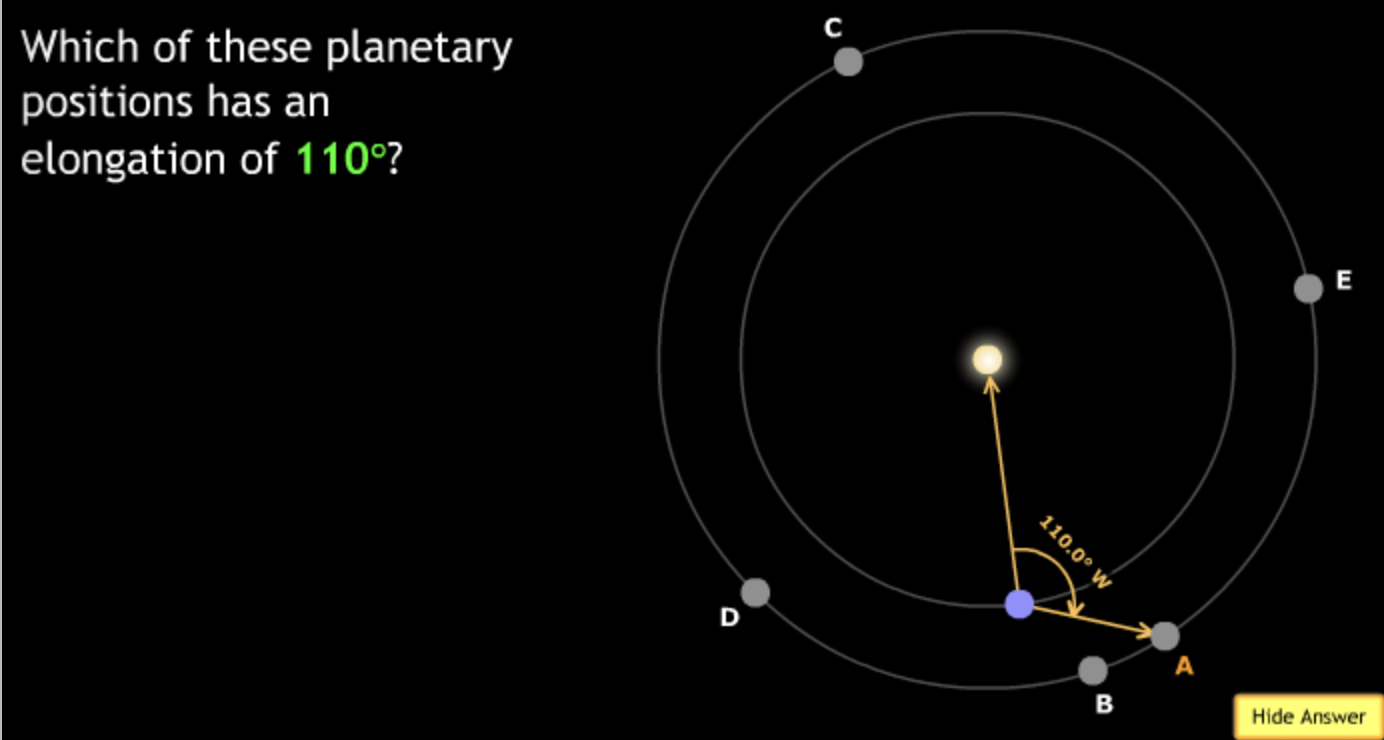
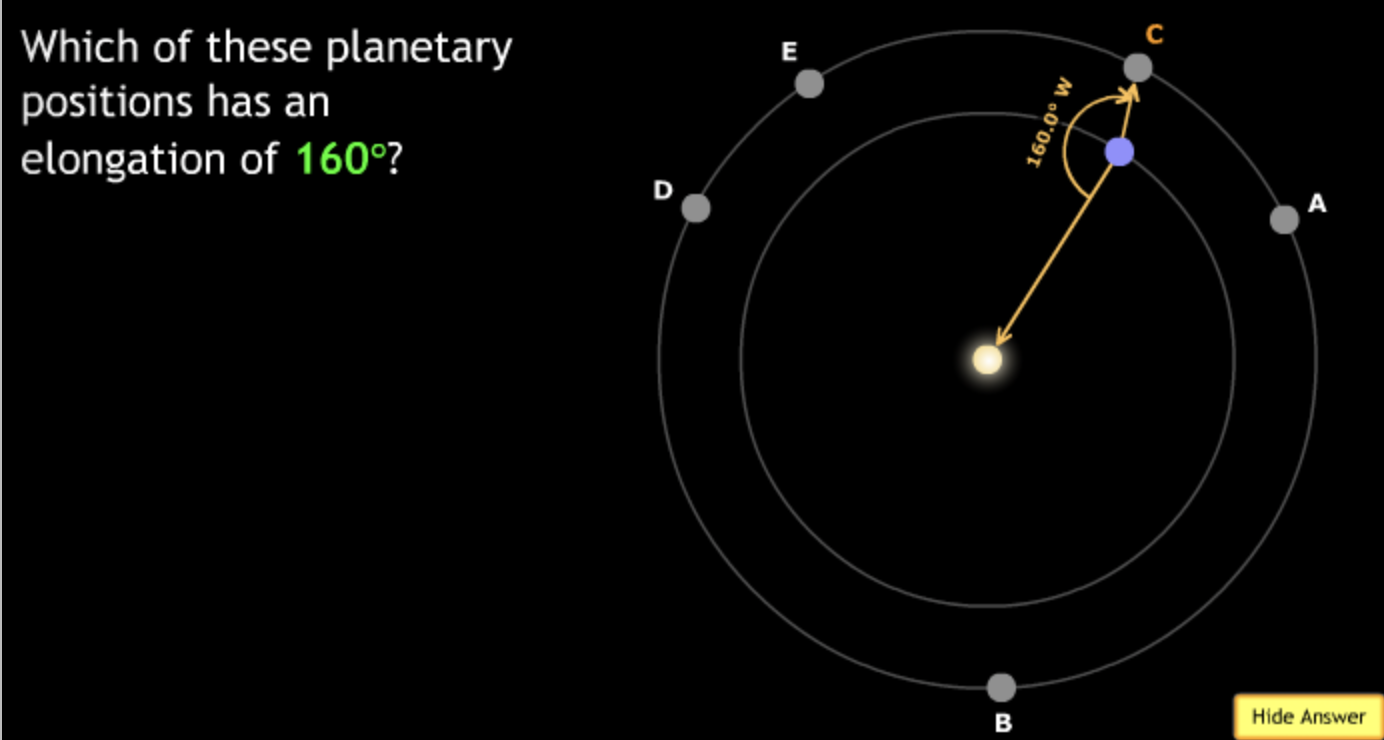
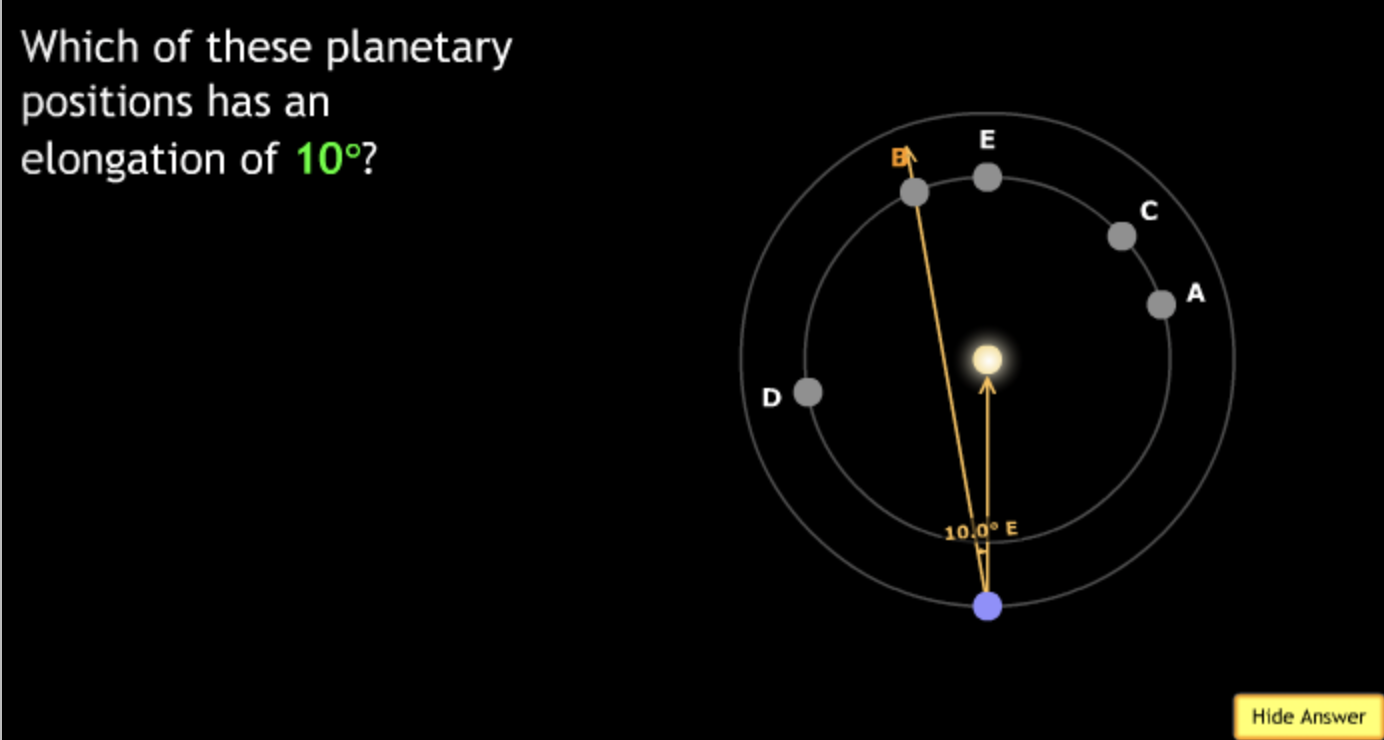

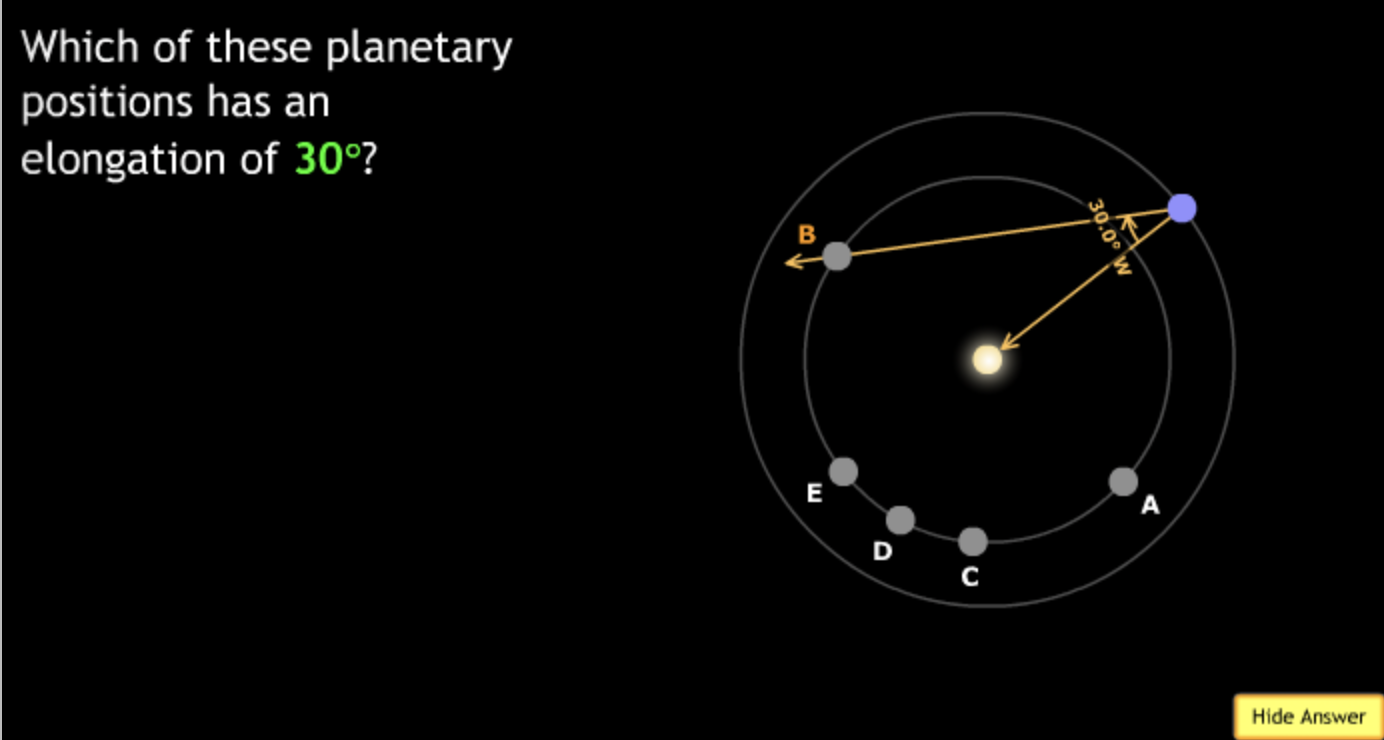
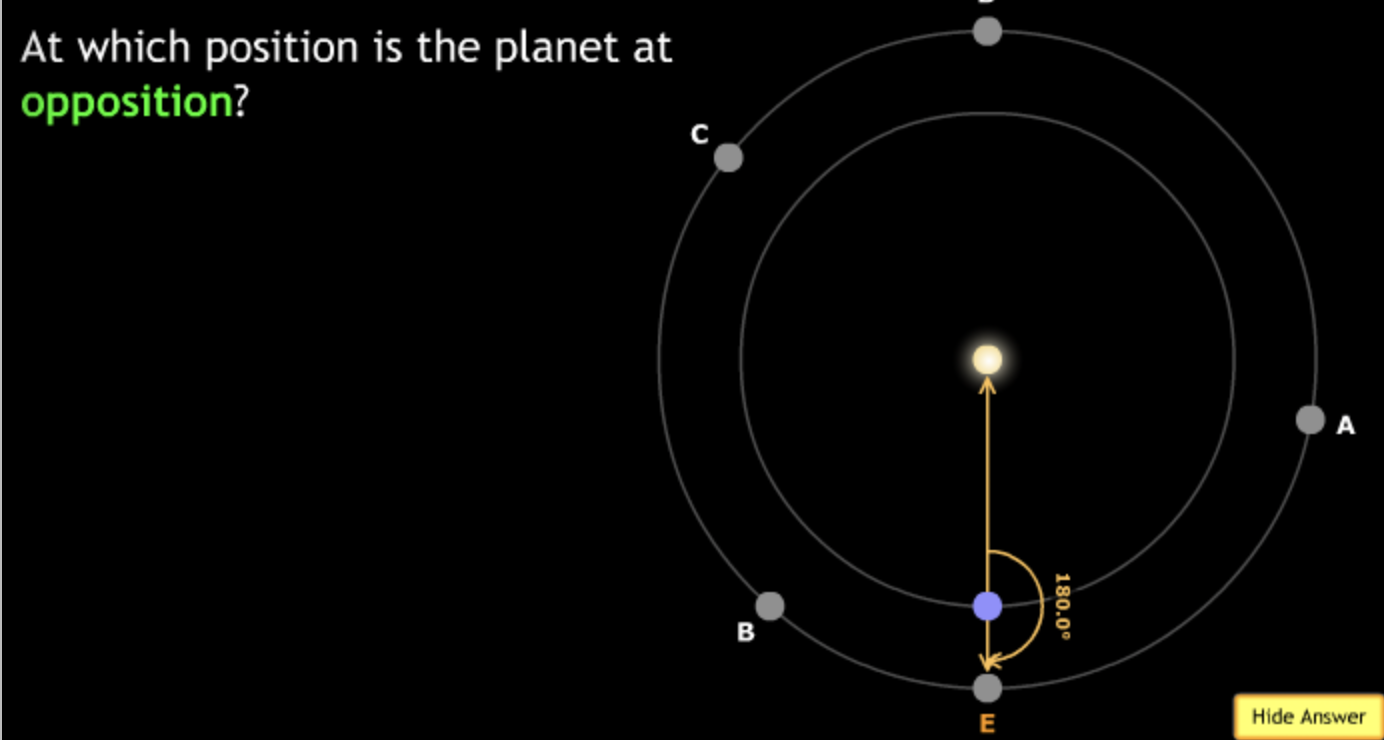
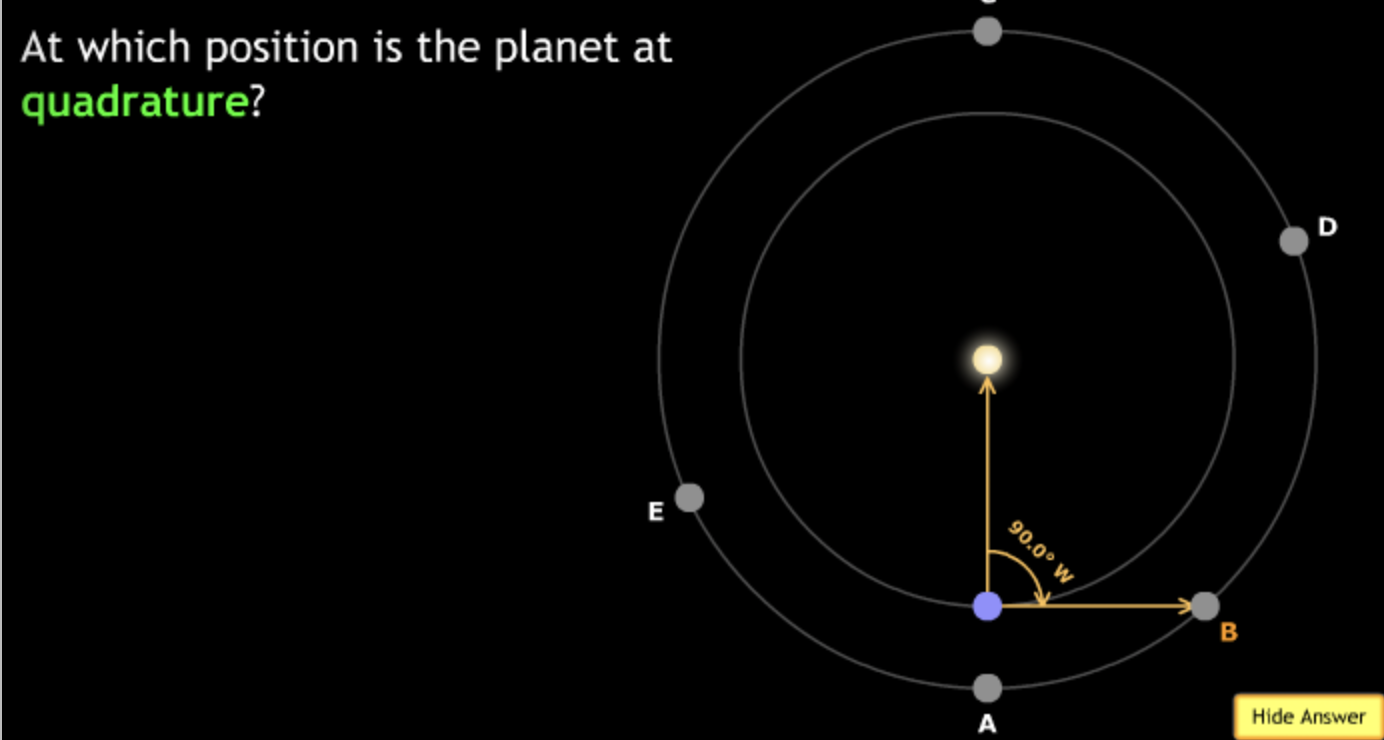
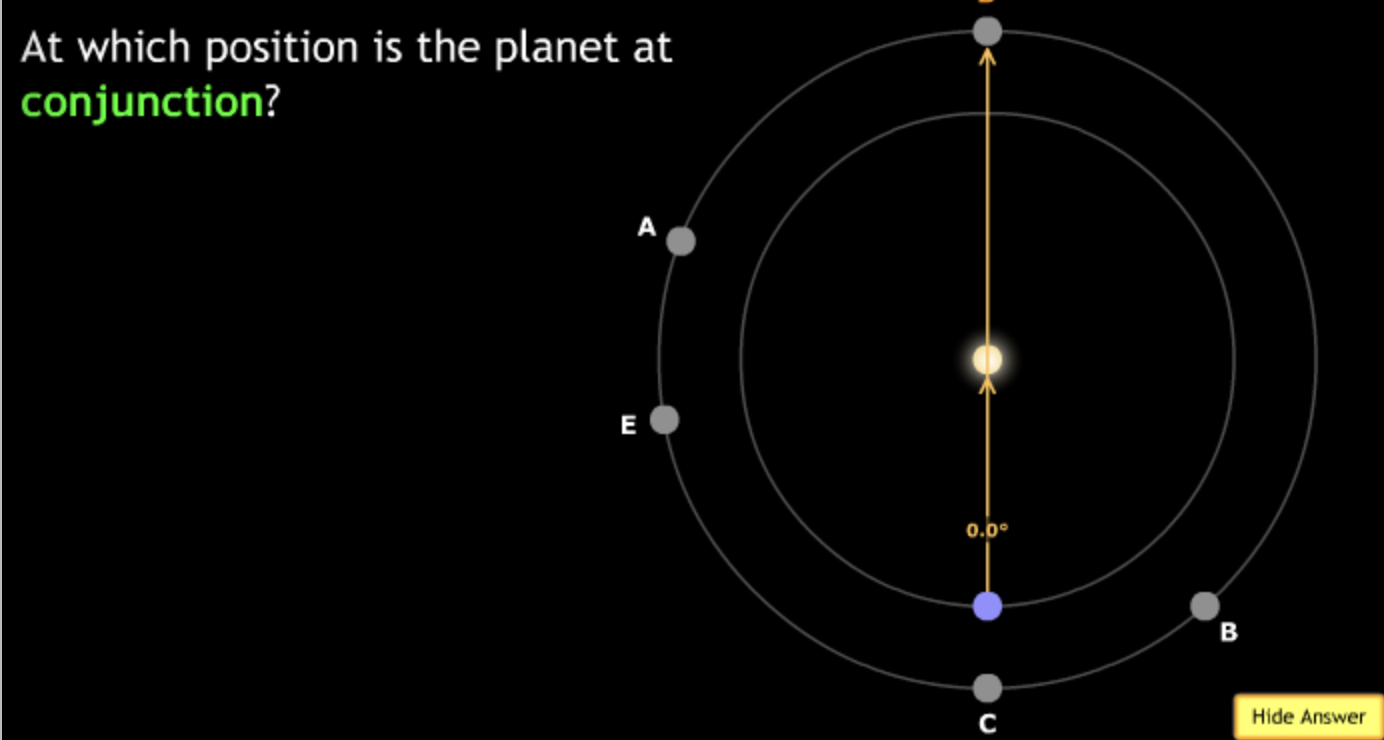
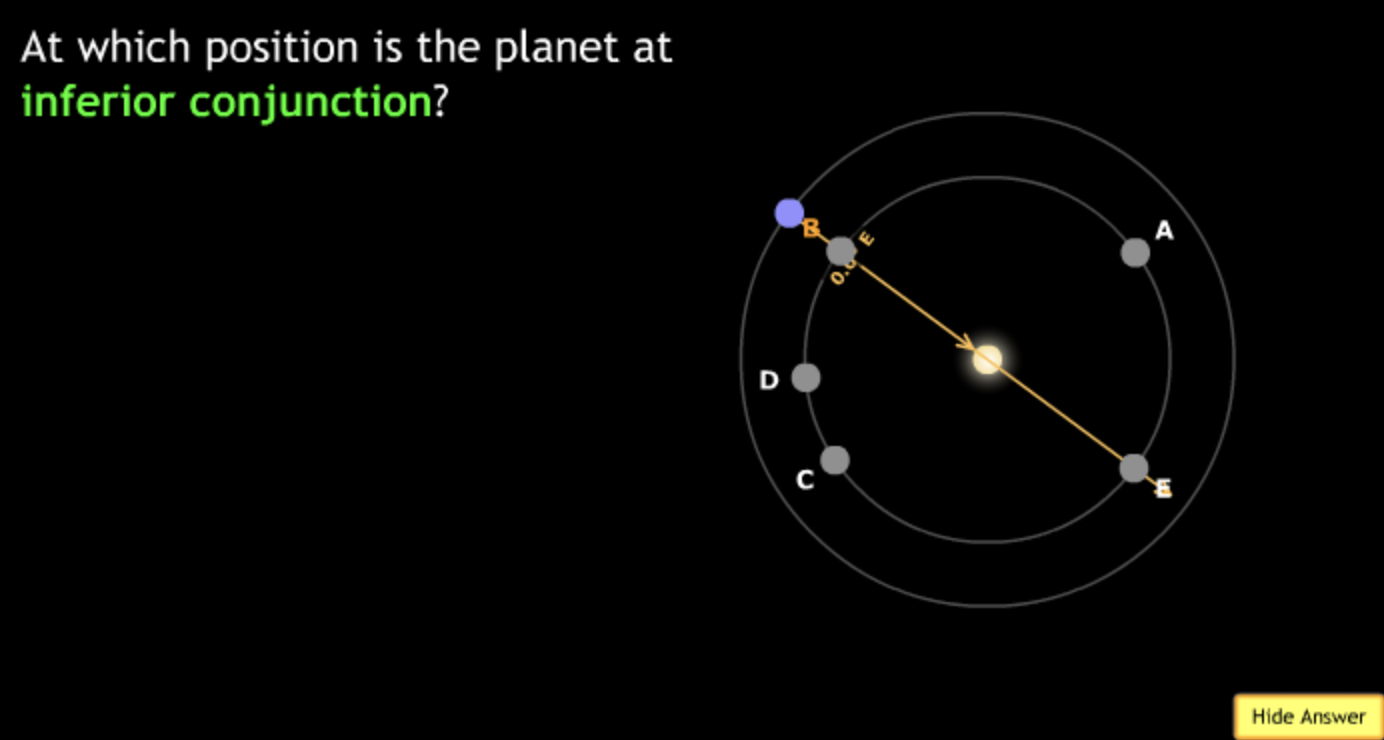
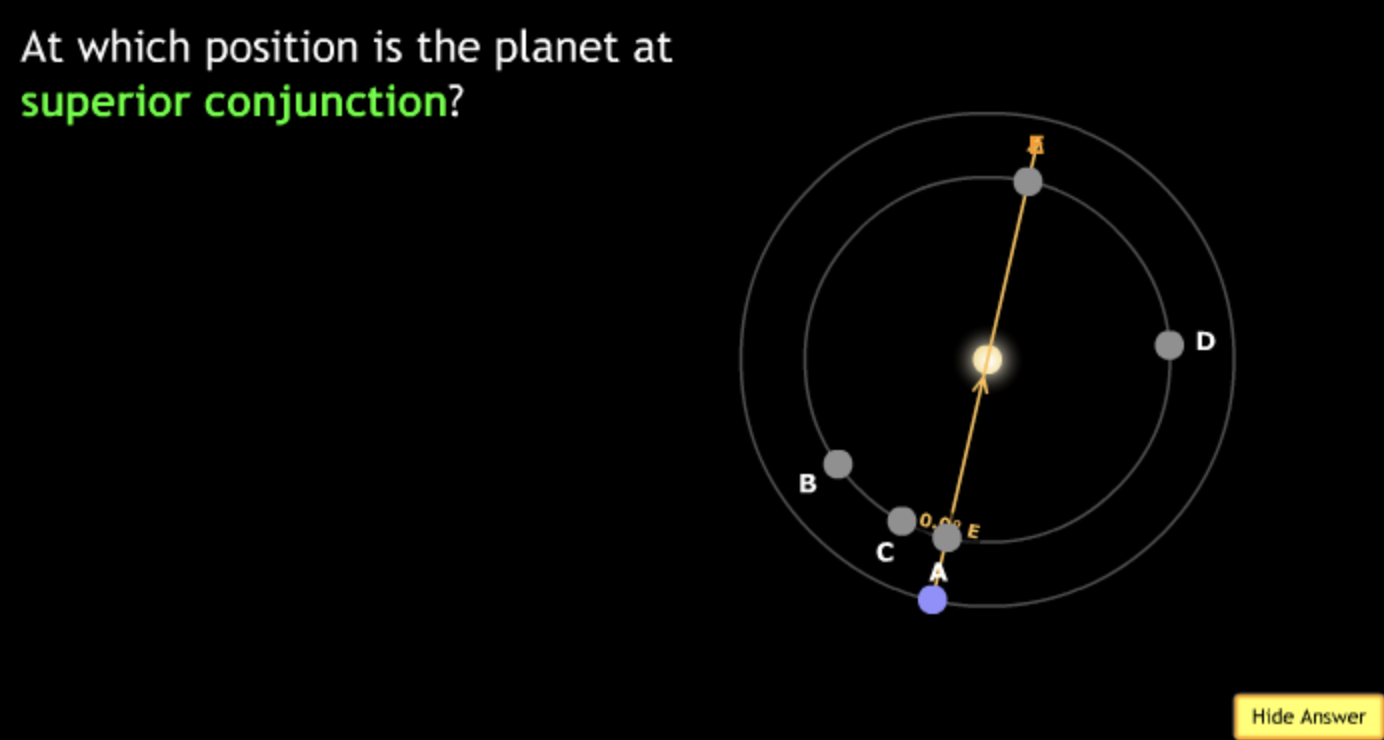
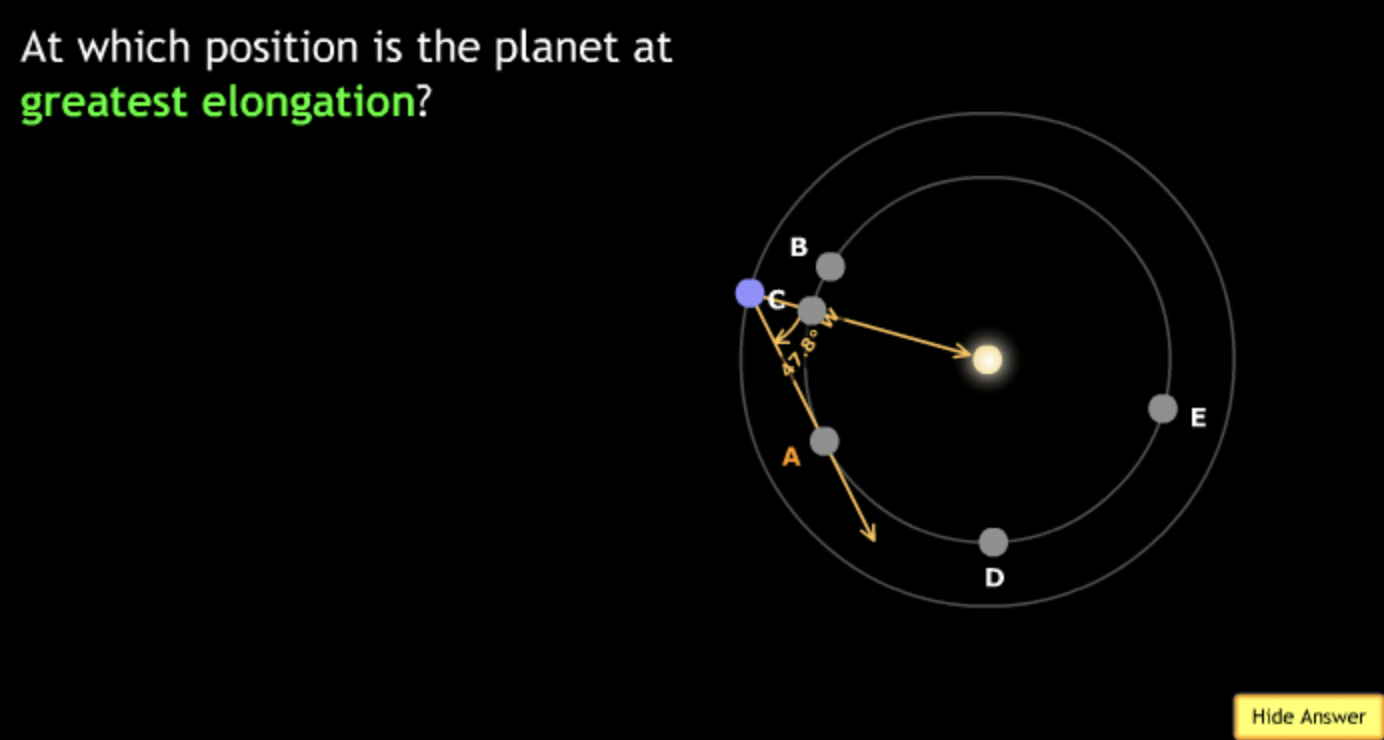

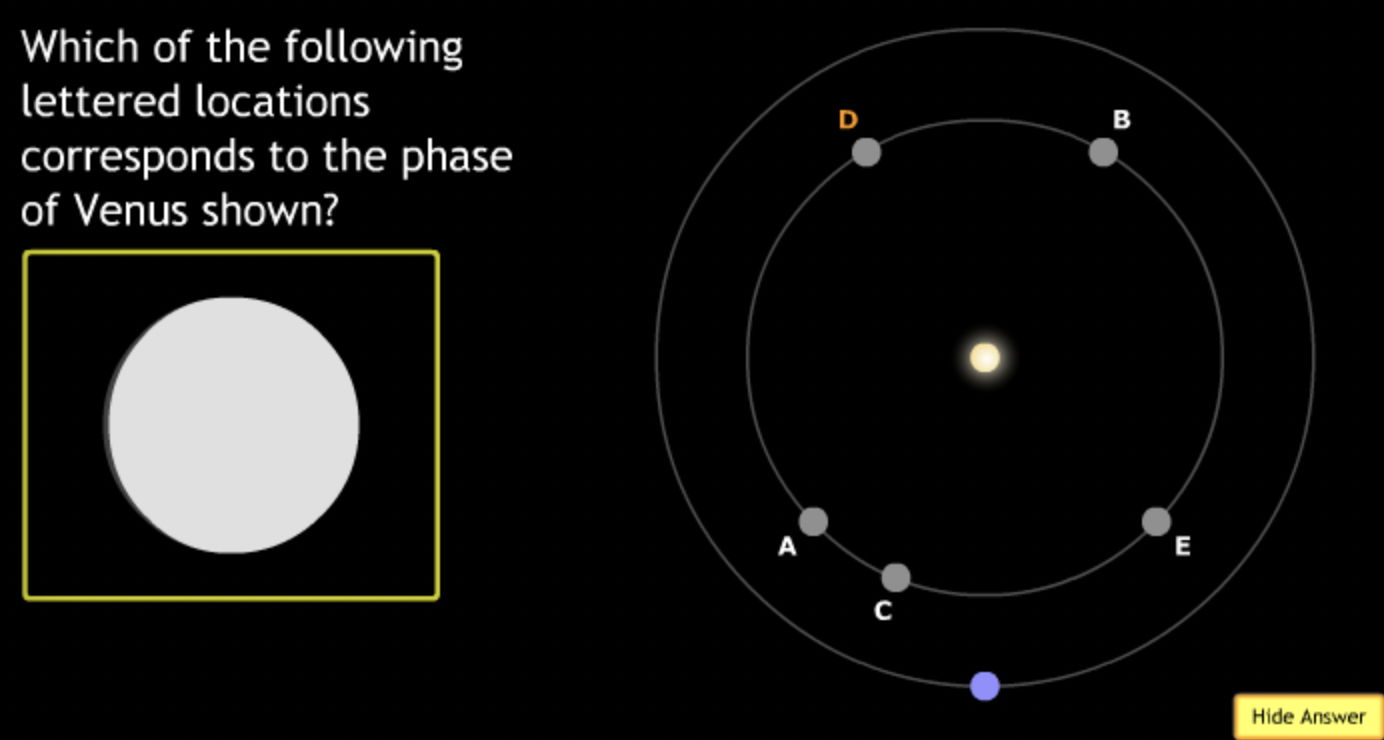
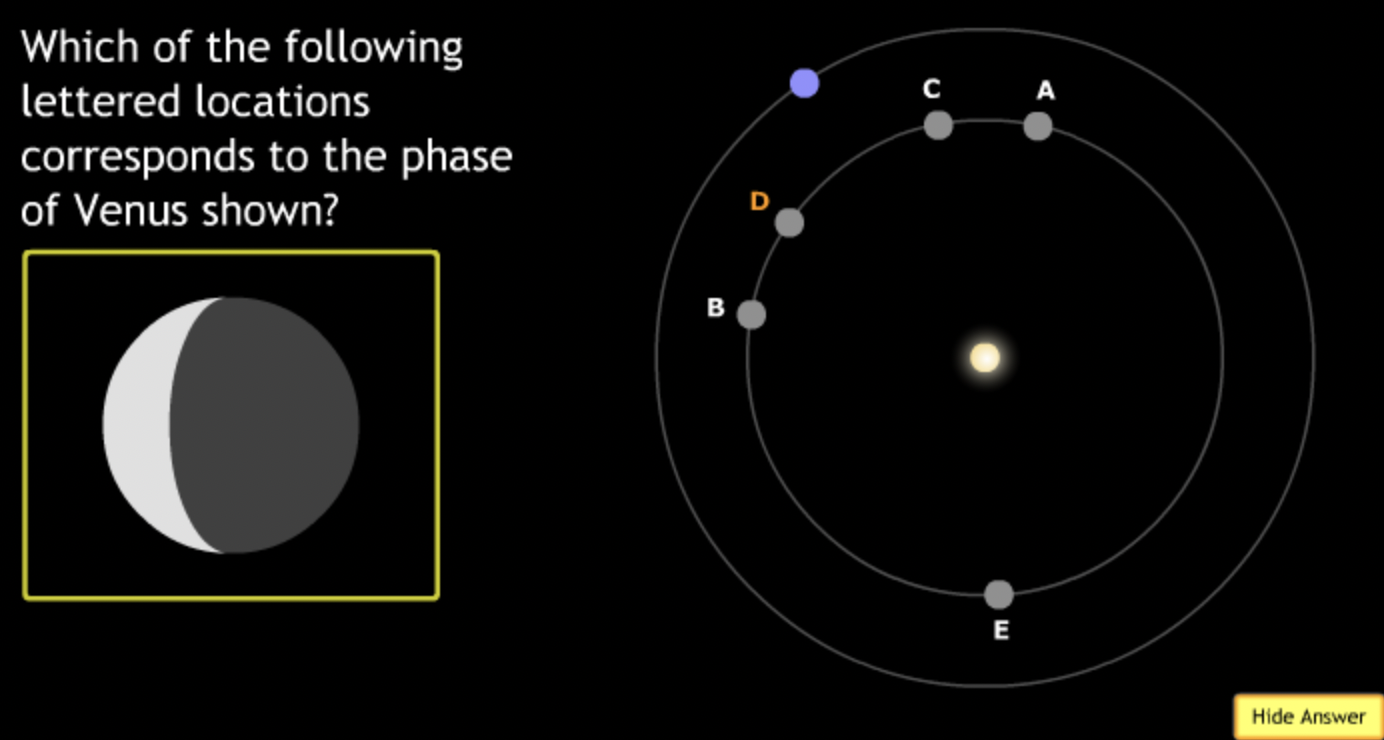
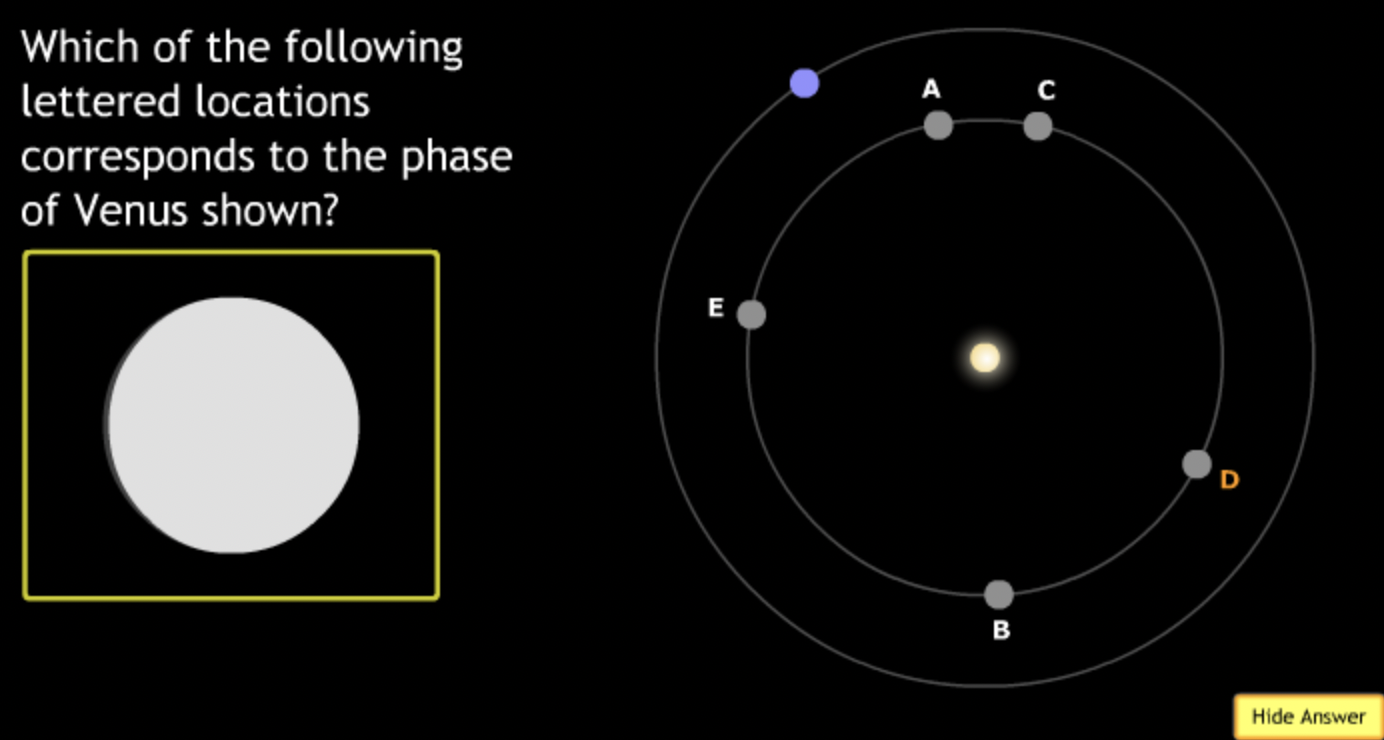
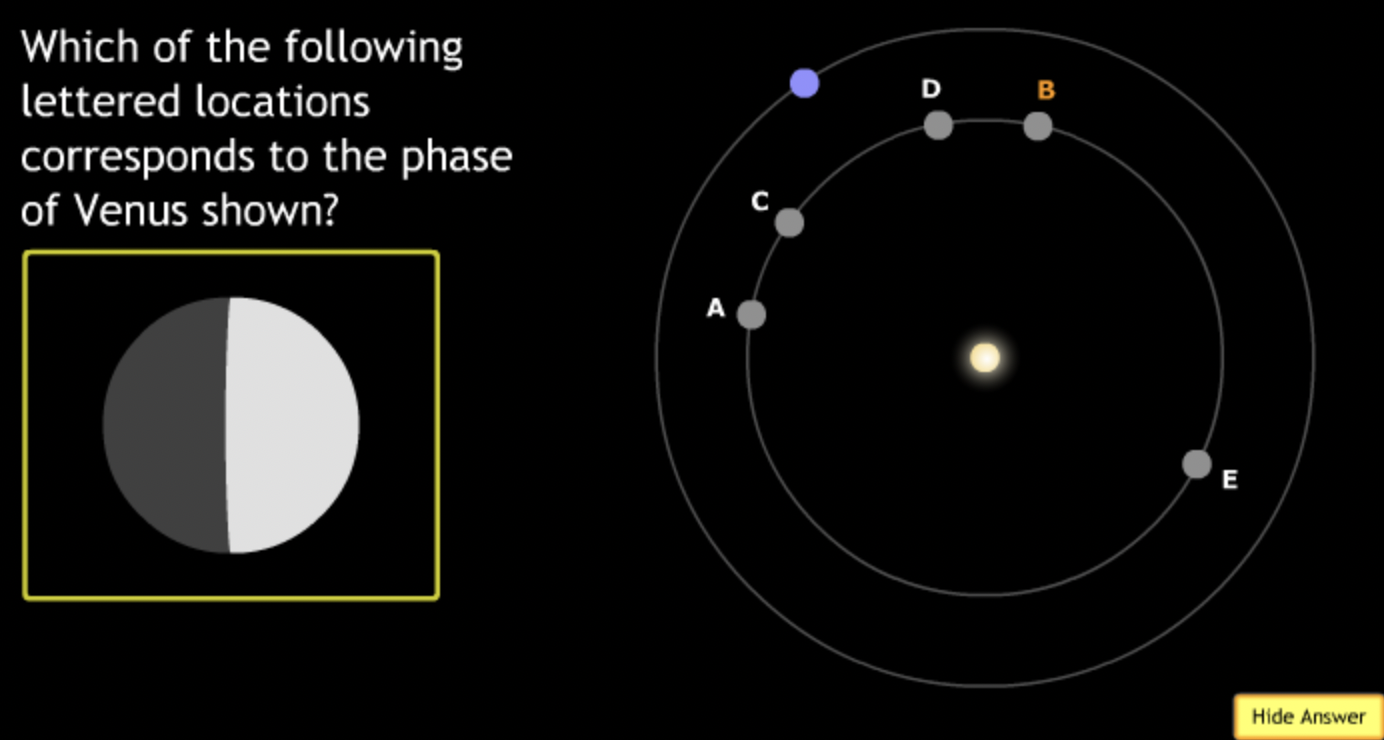
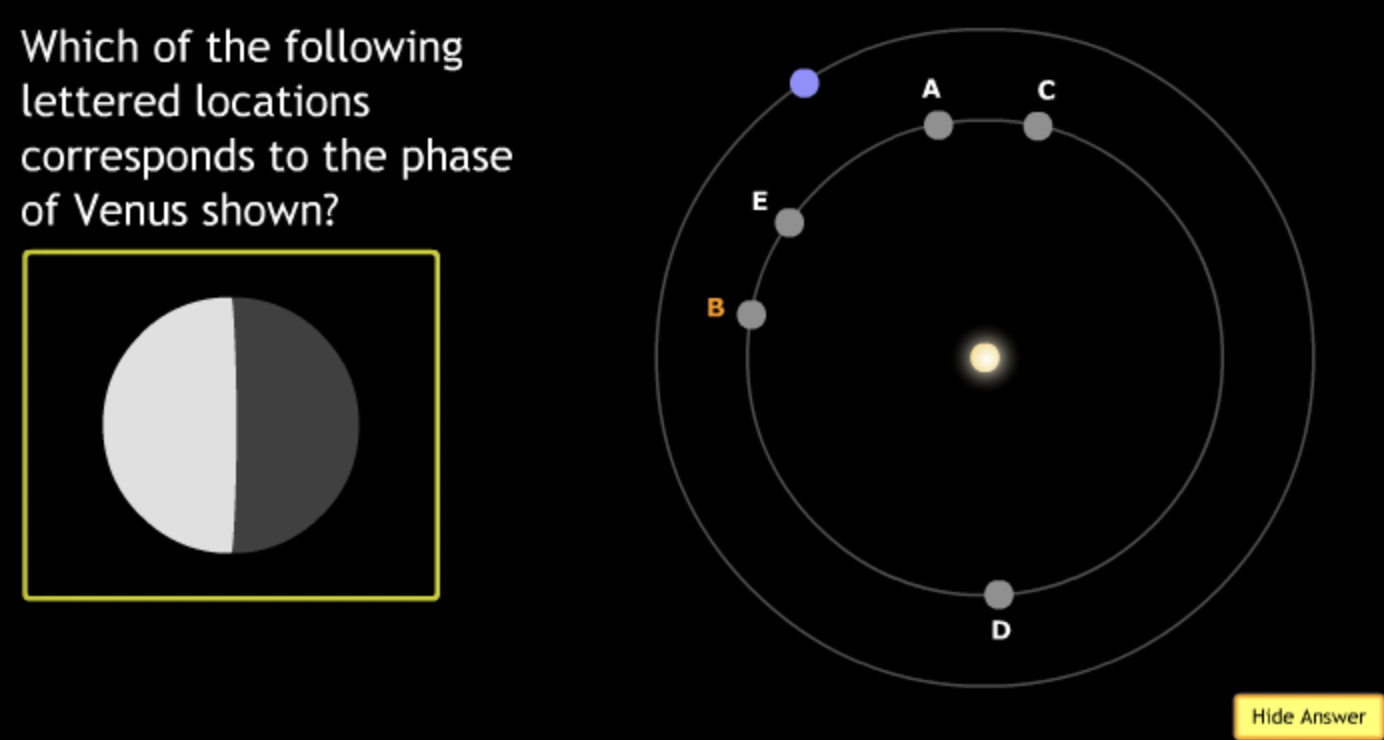
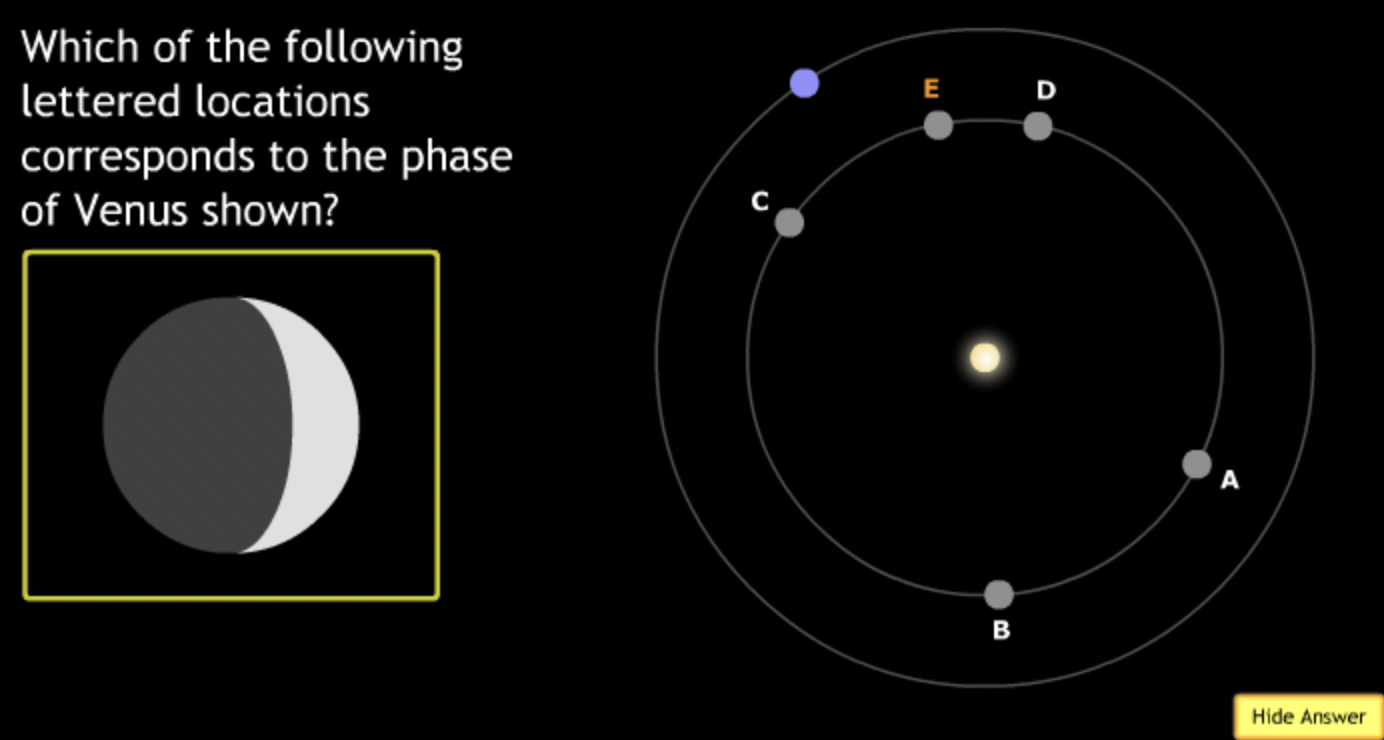
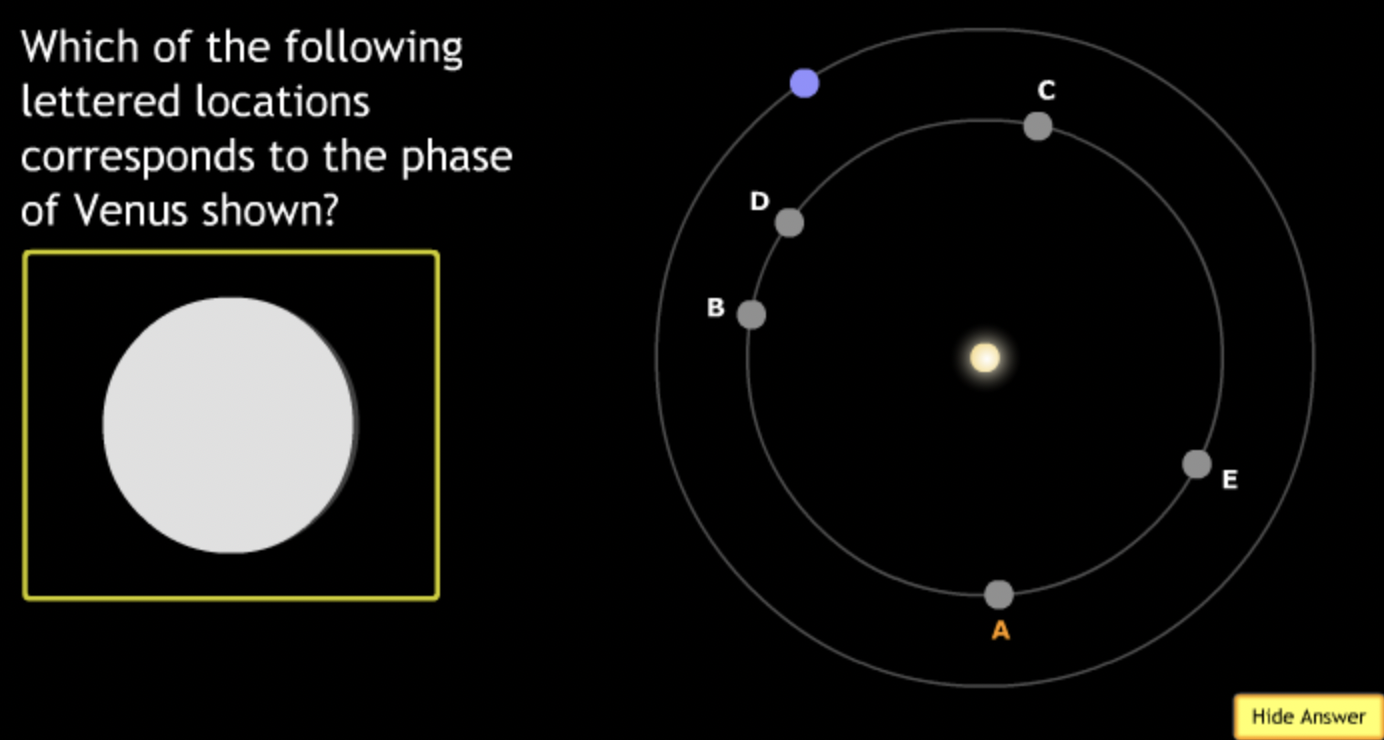
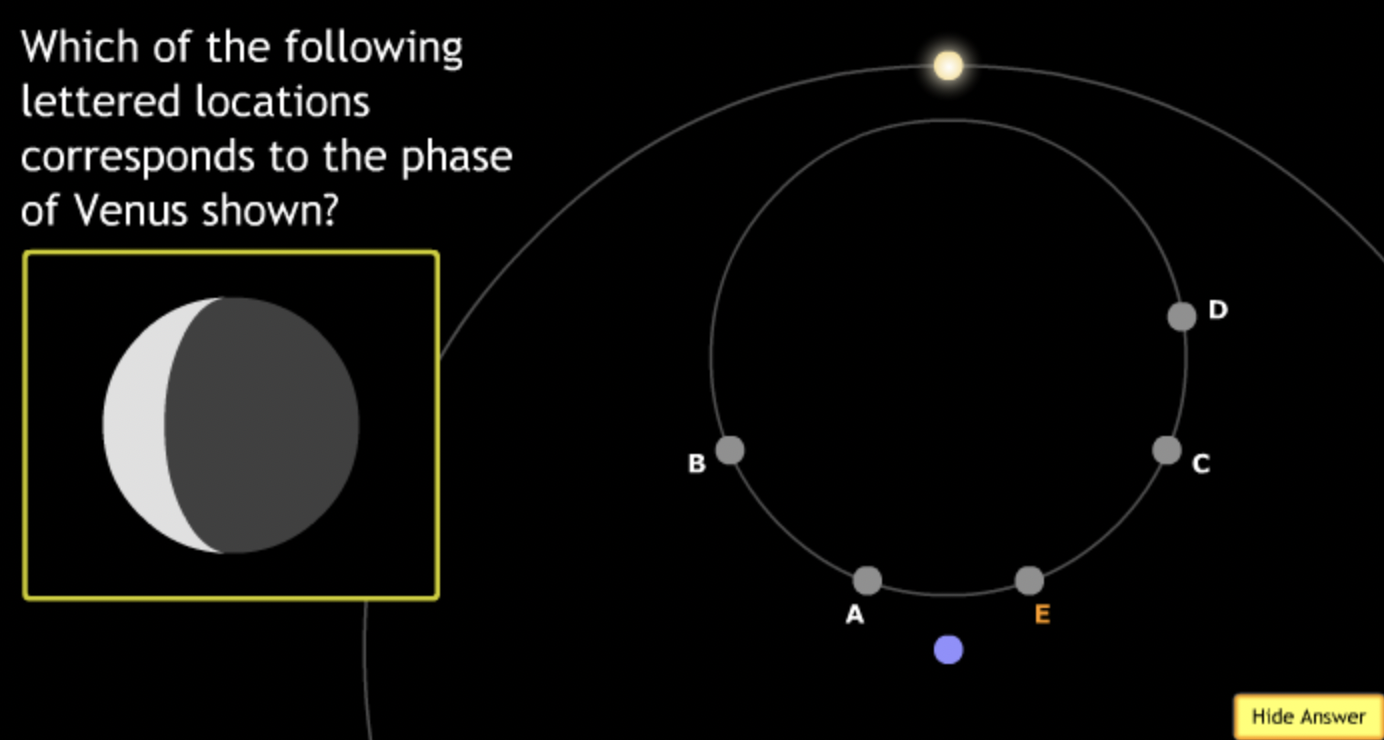
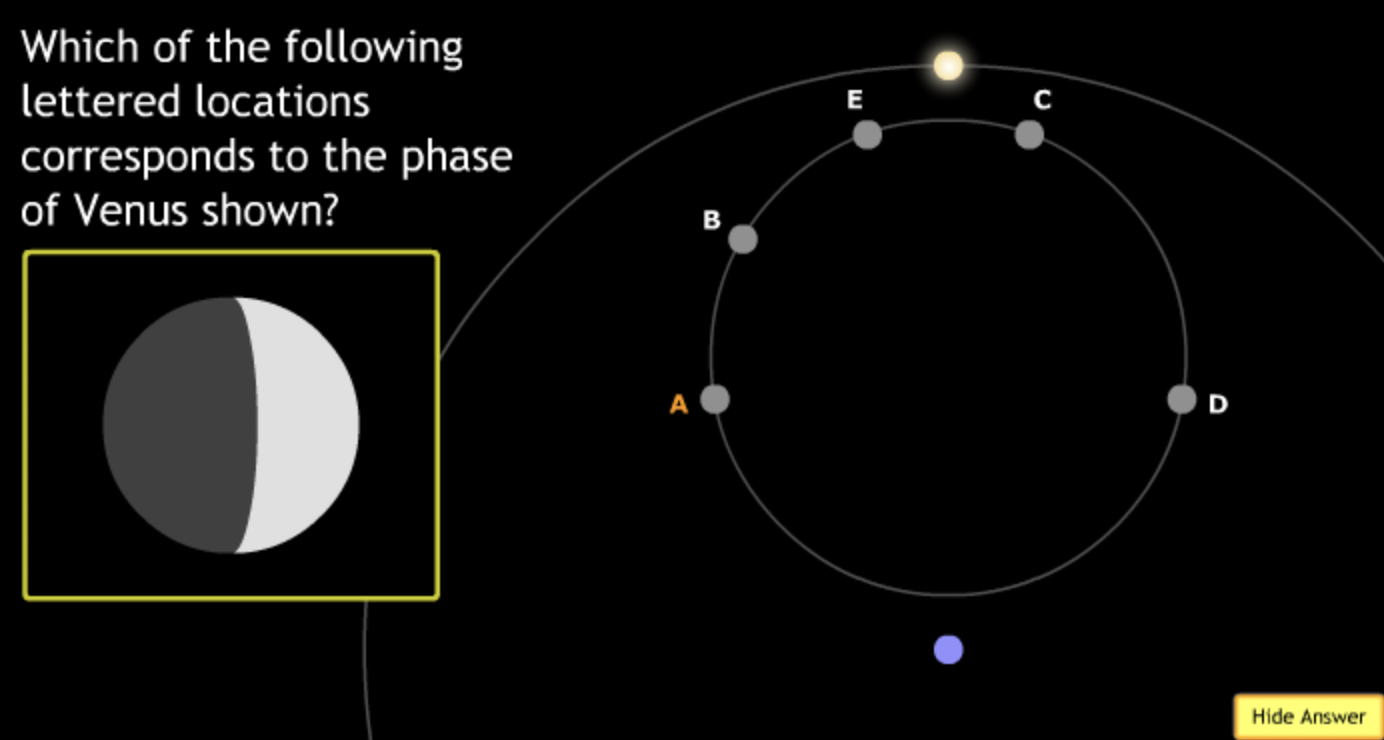
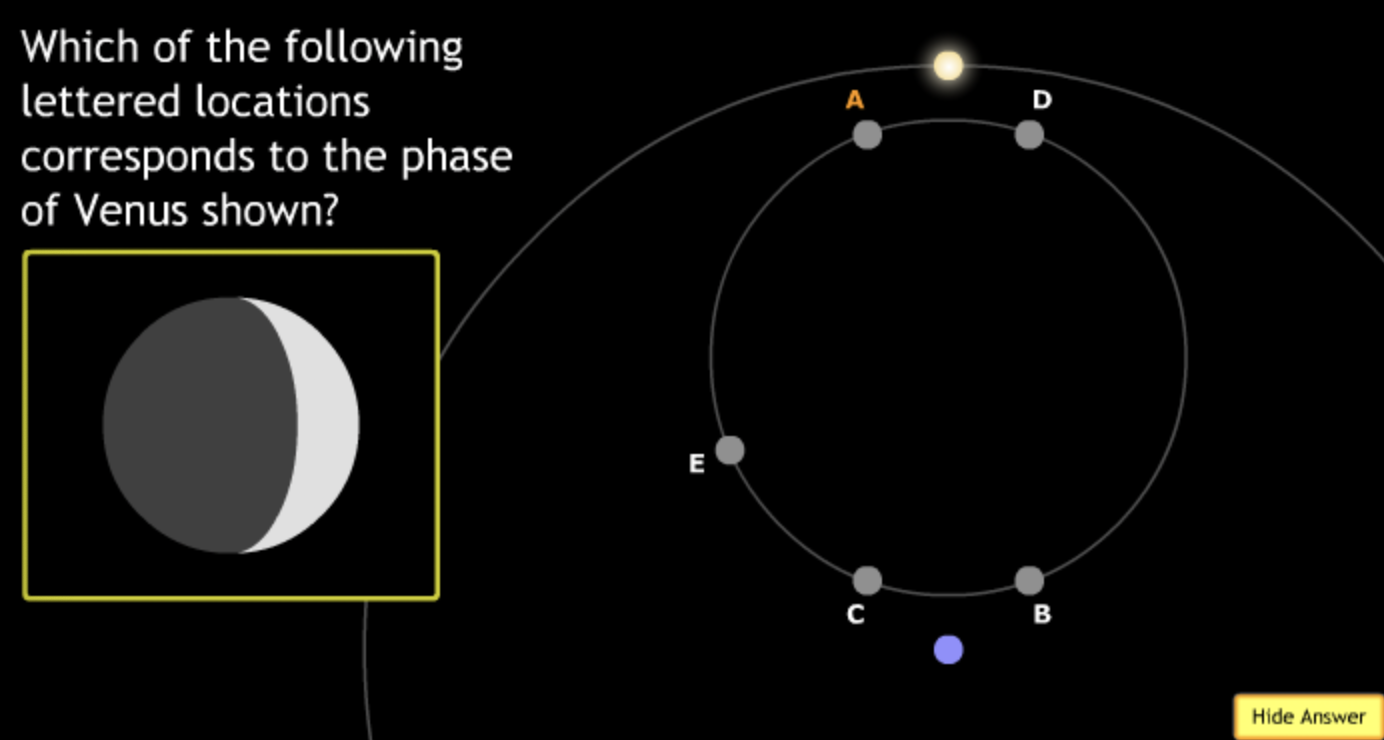
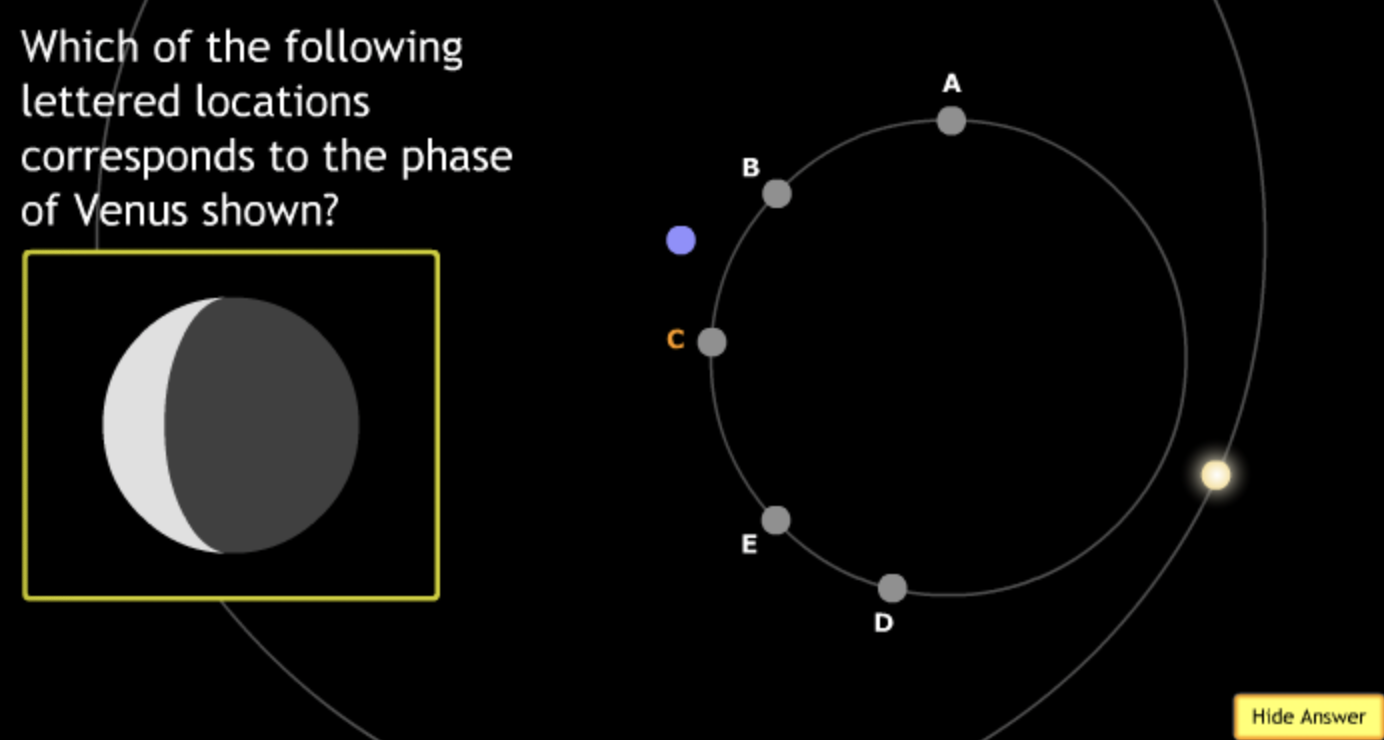
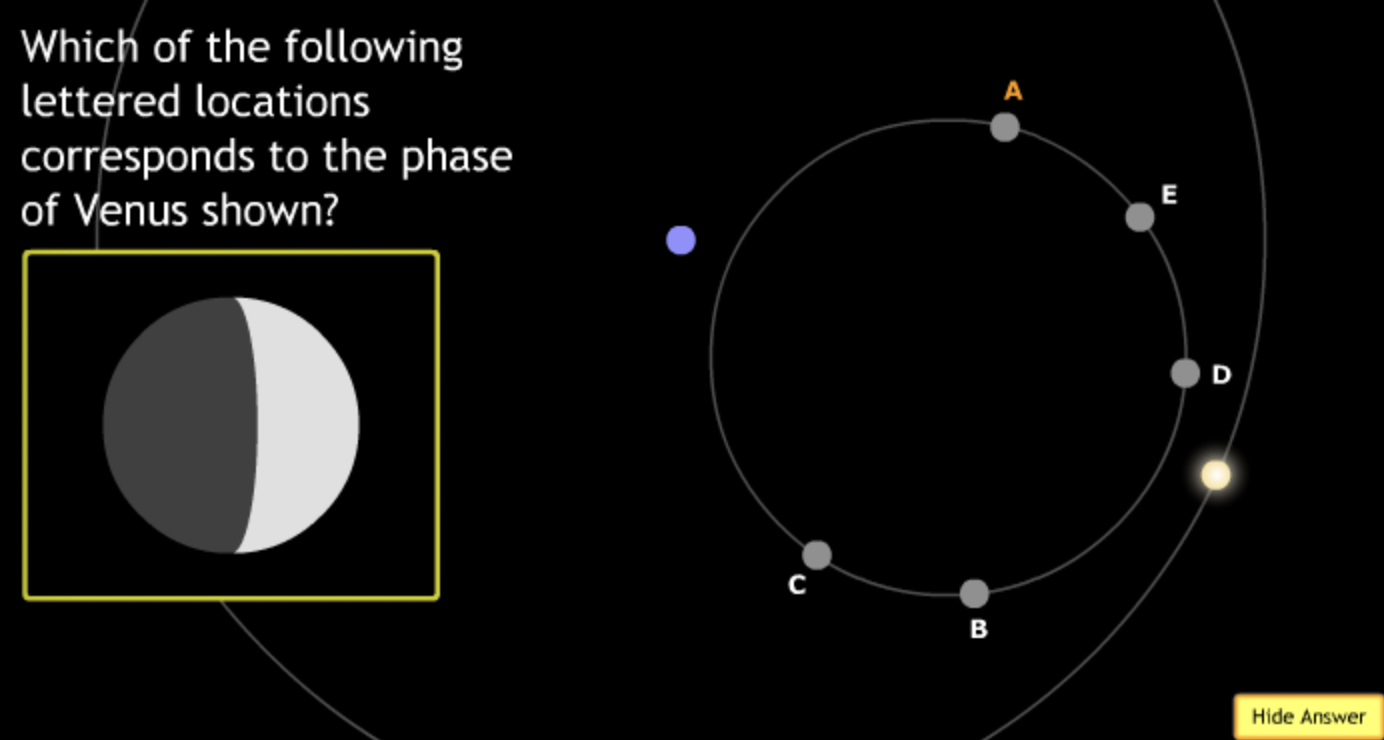
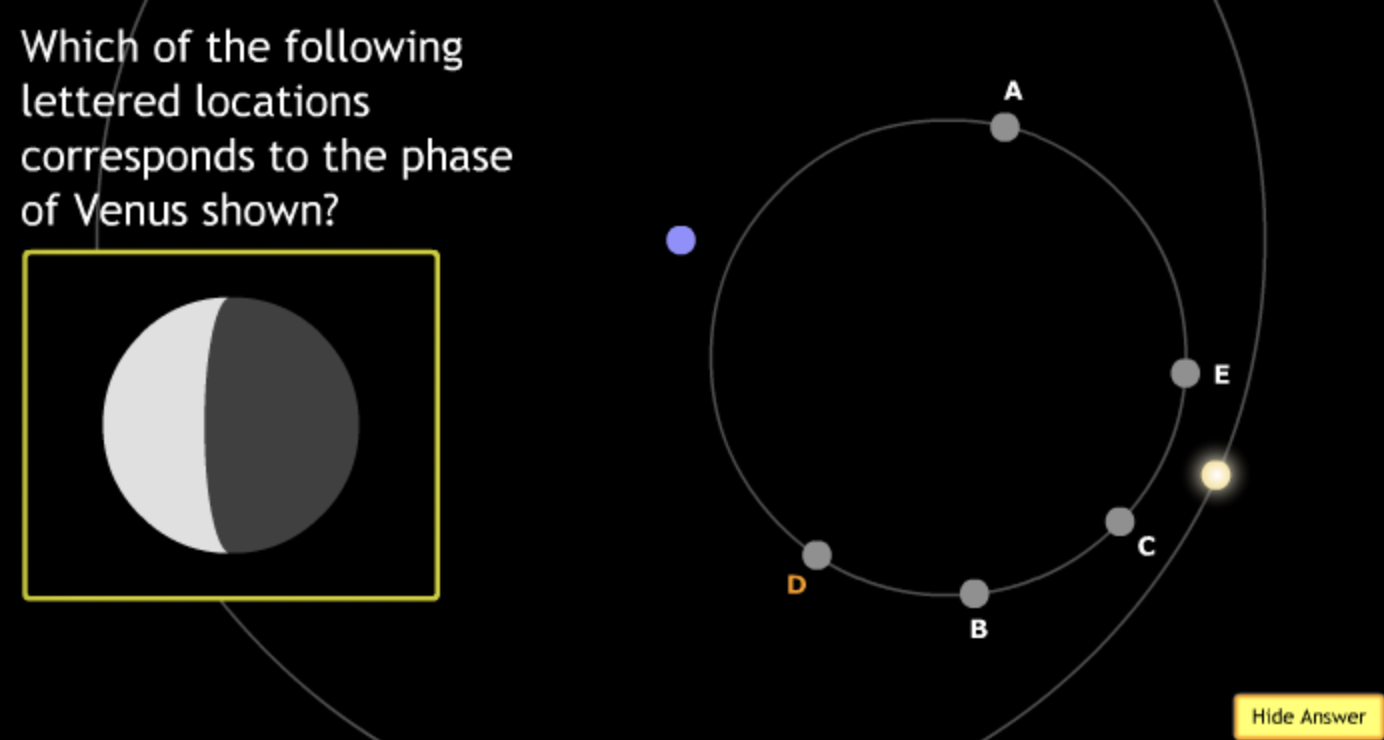
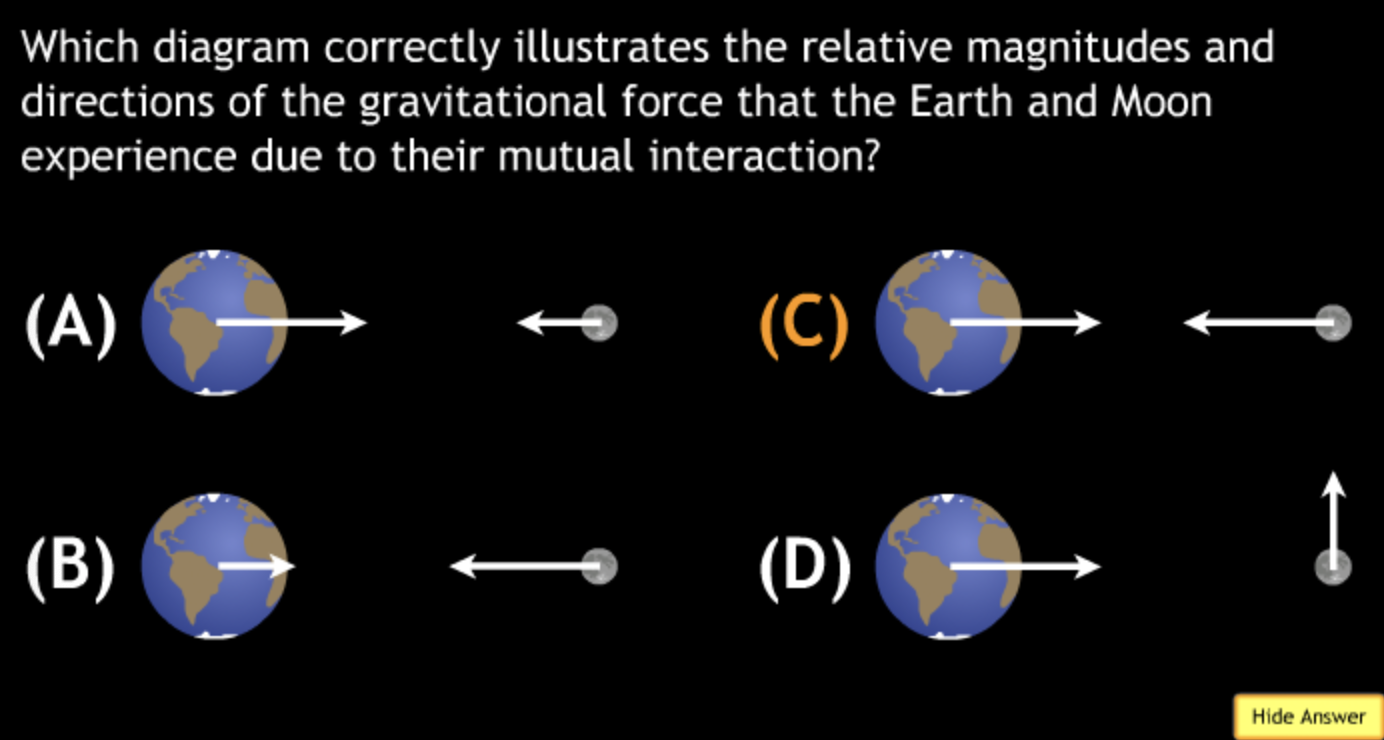
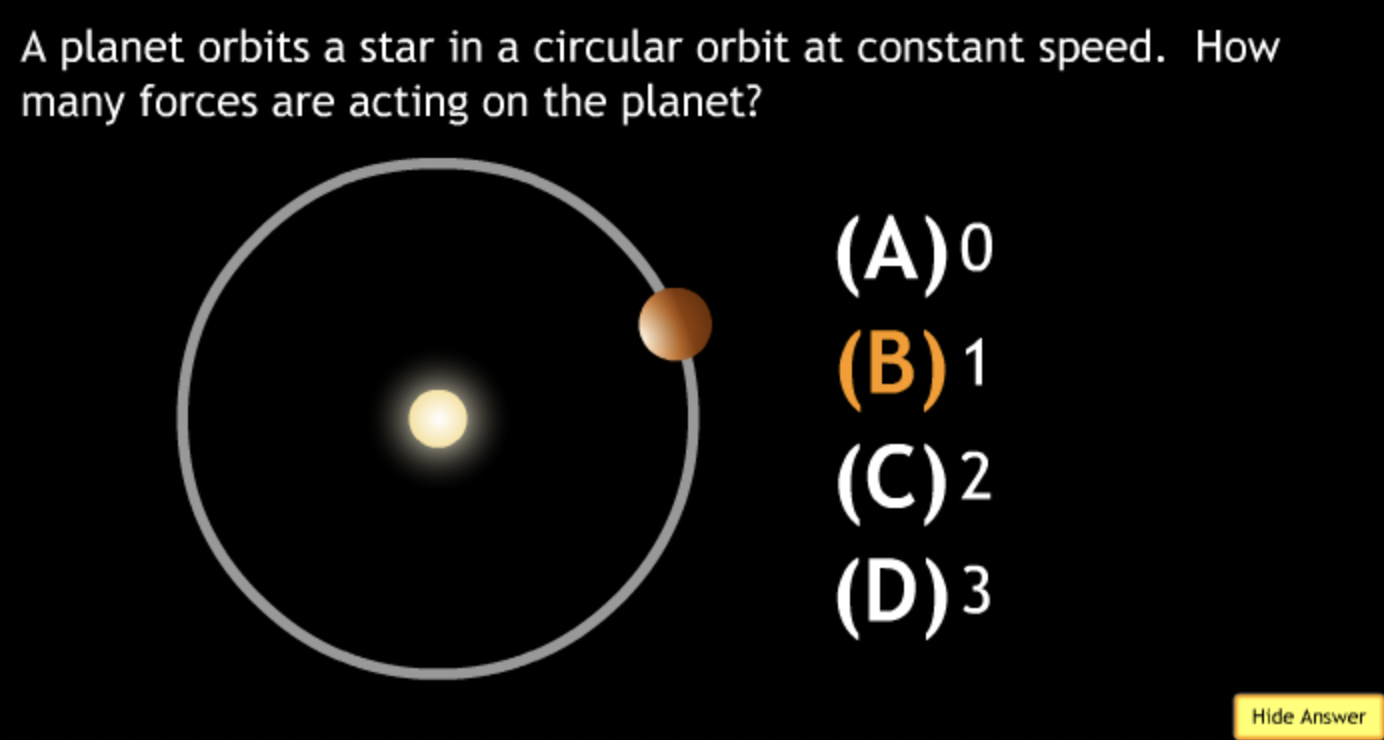
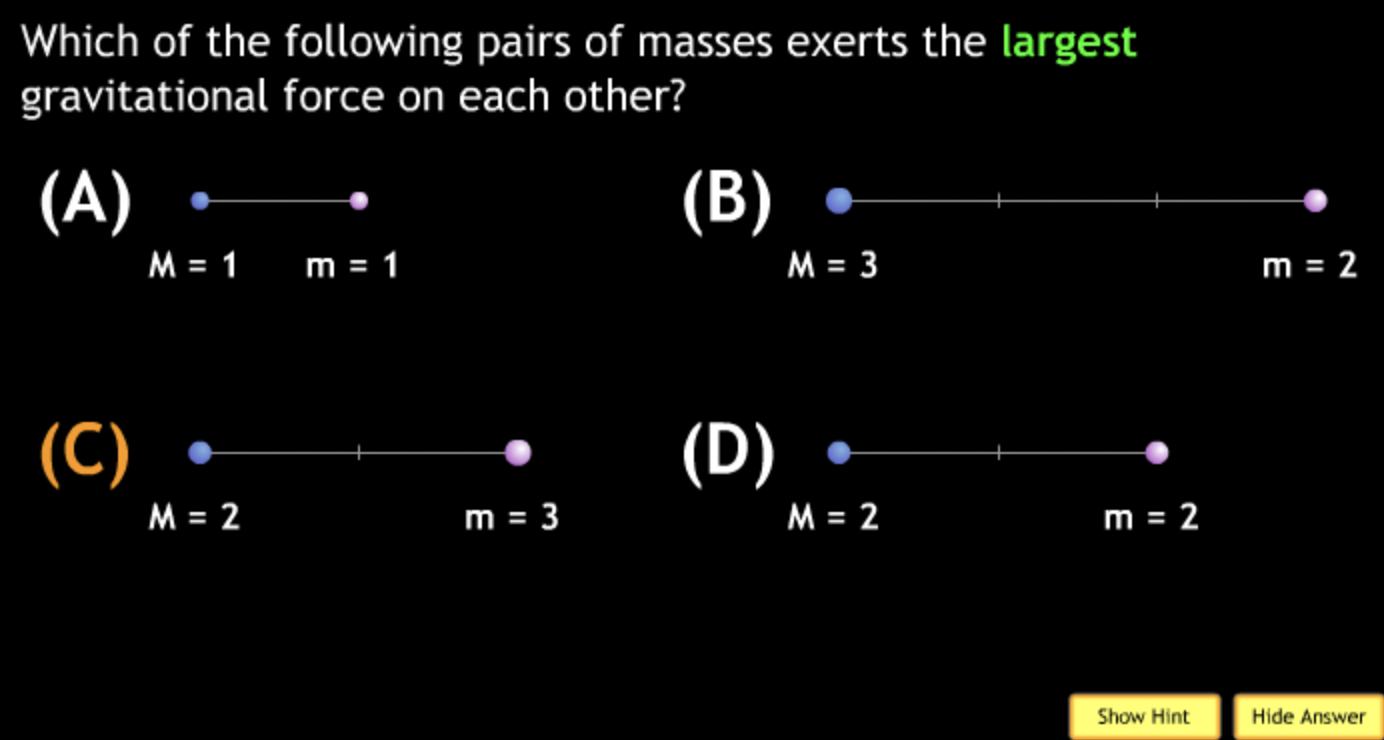
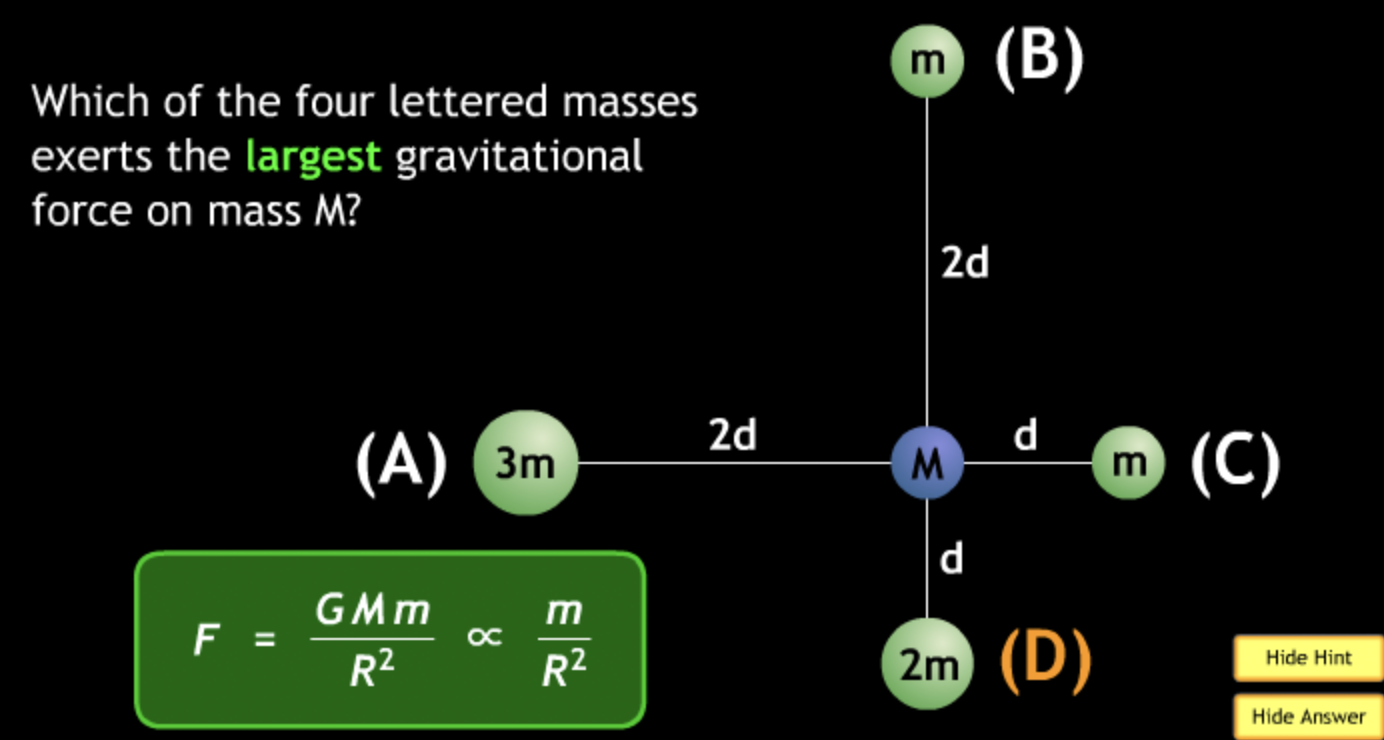
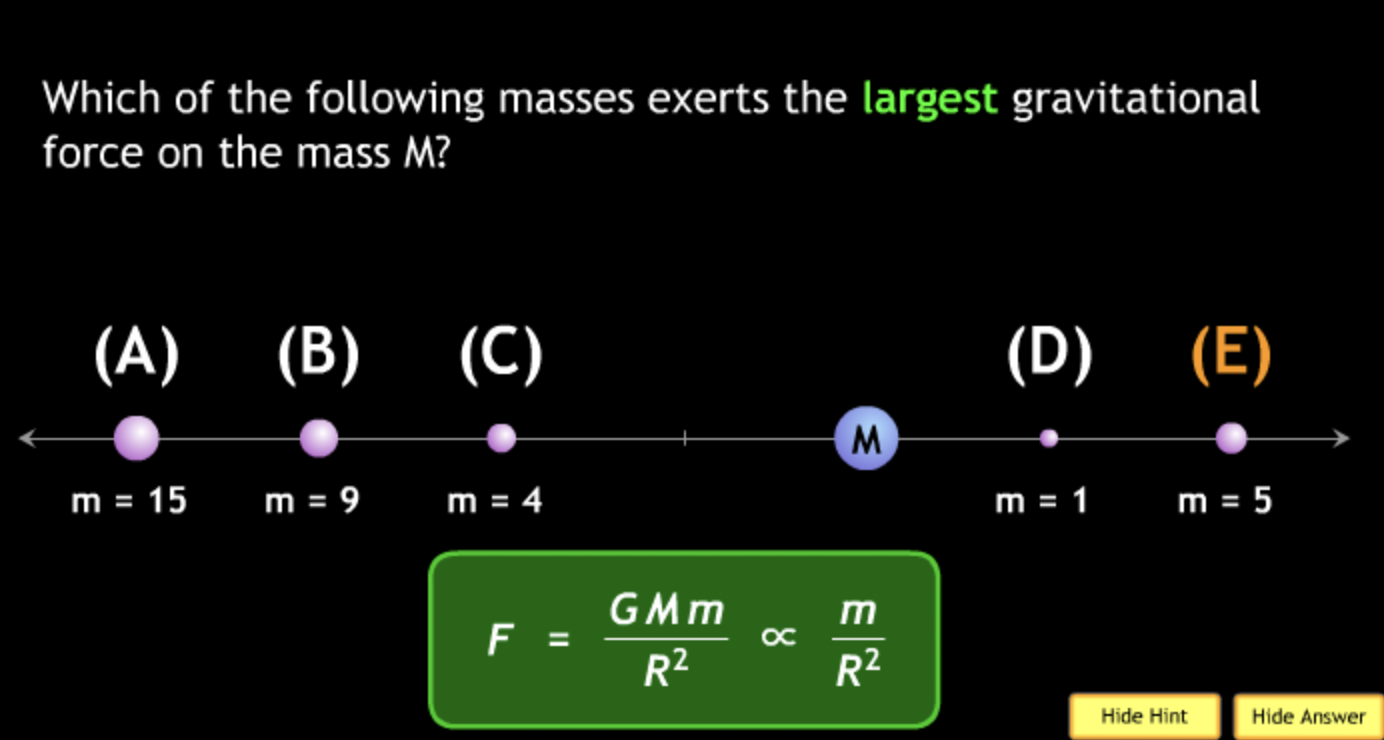
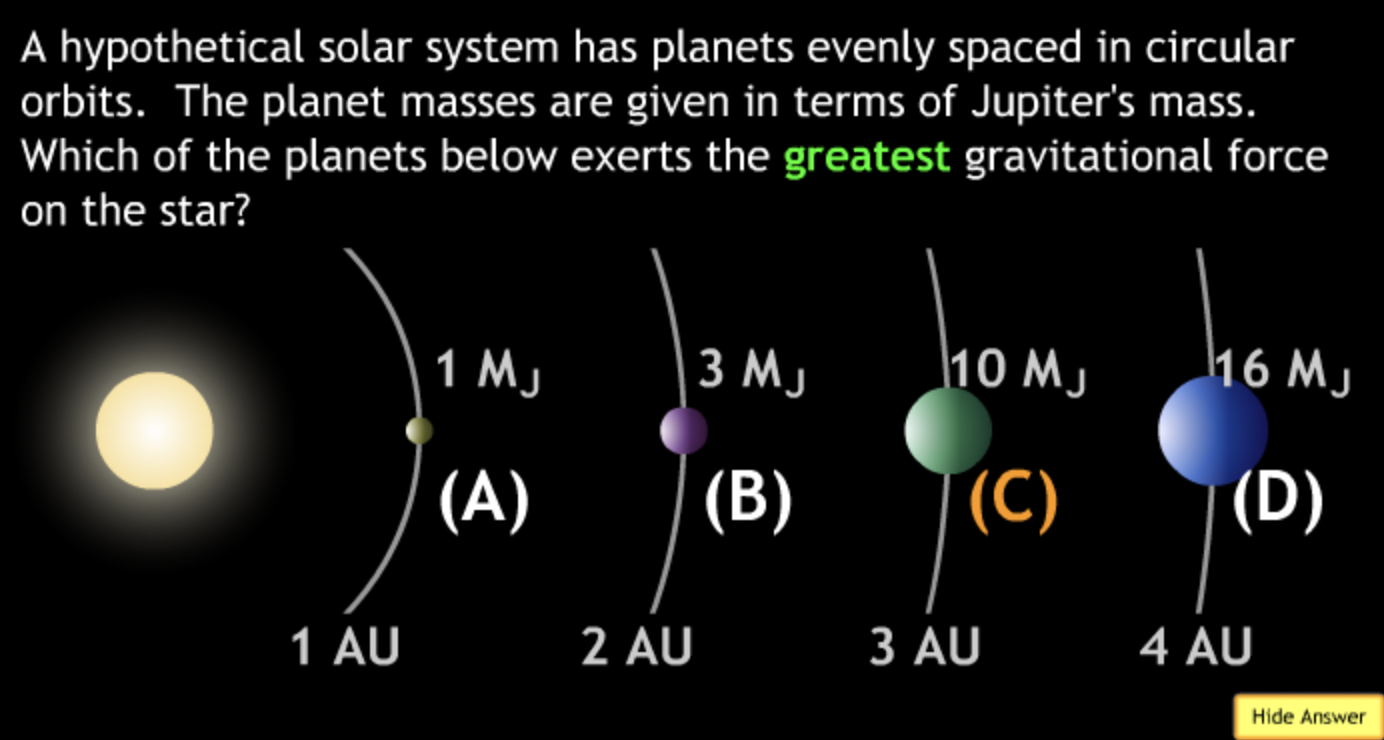
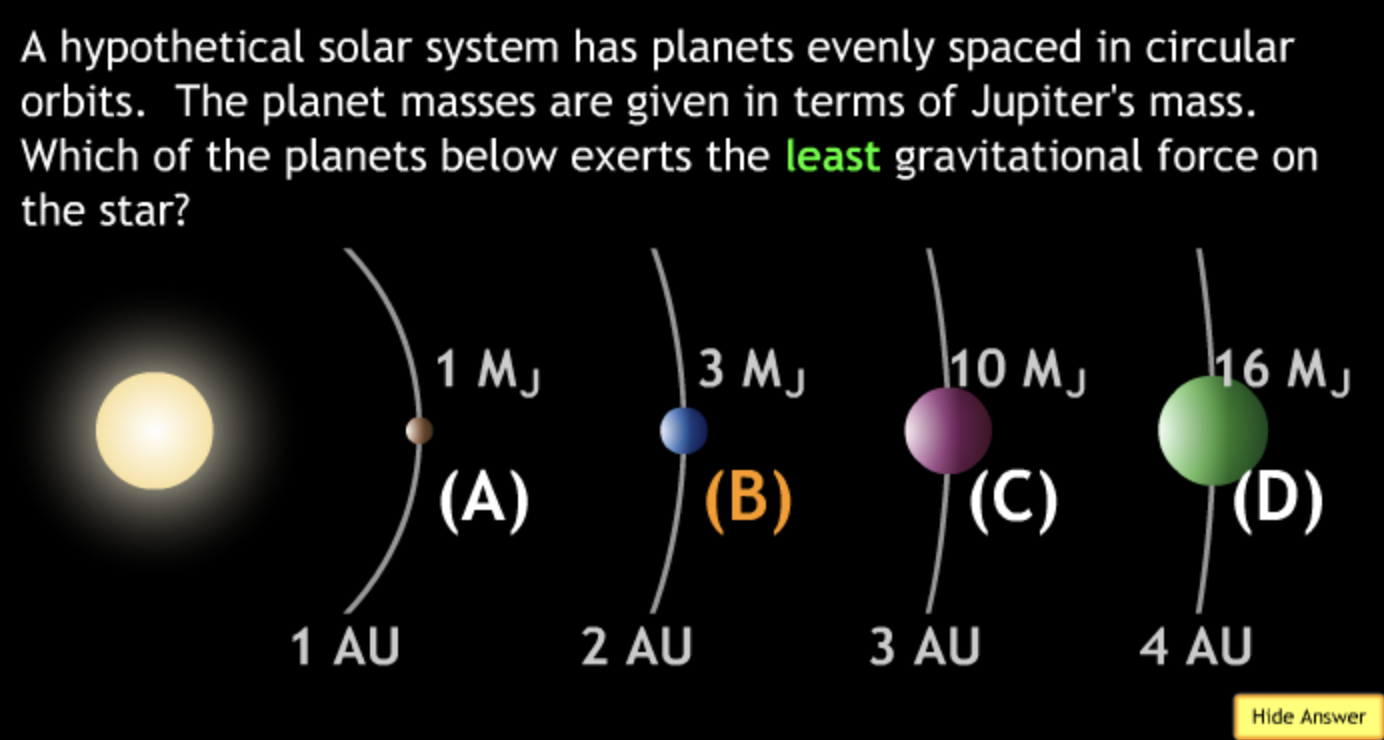
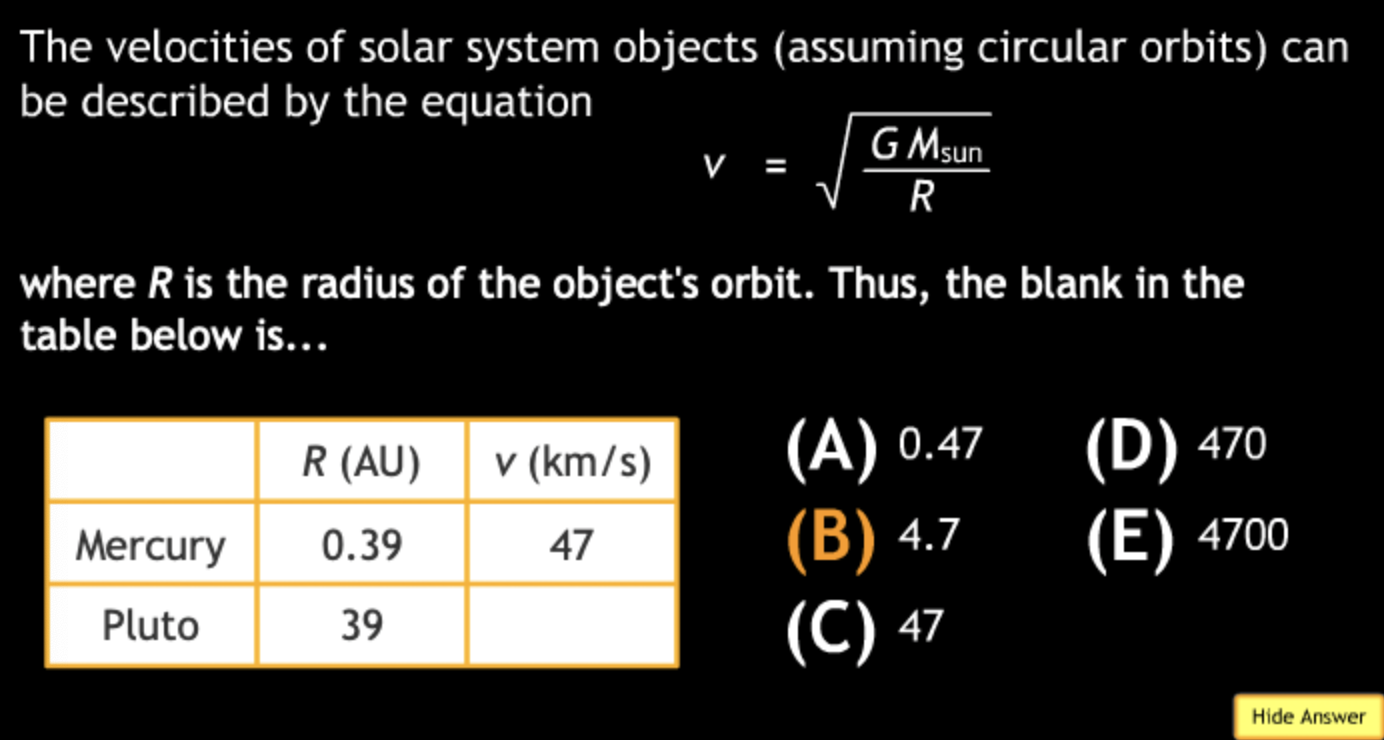
The gravitational force is an attractive force between objects that have mass.




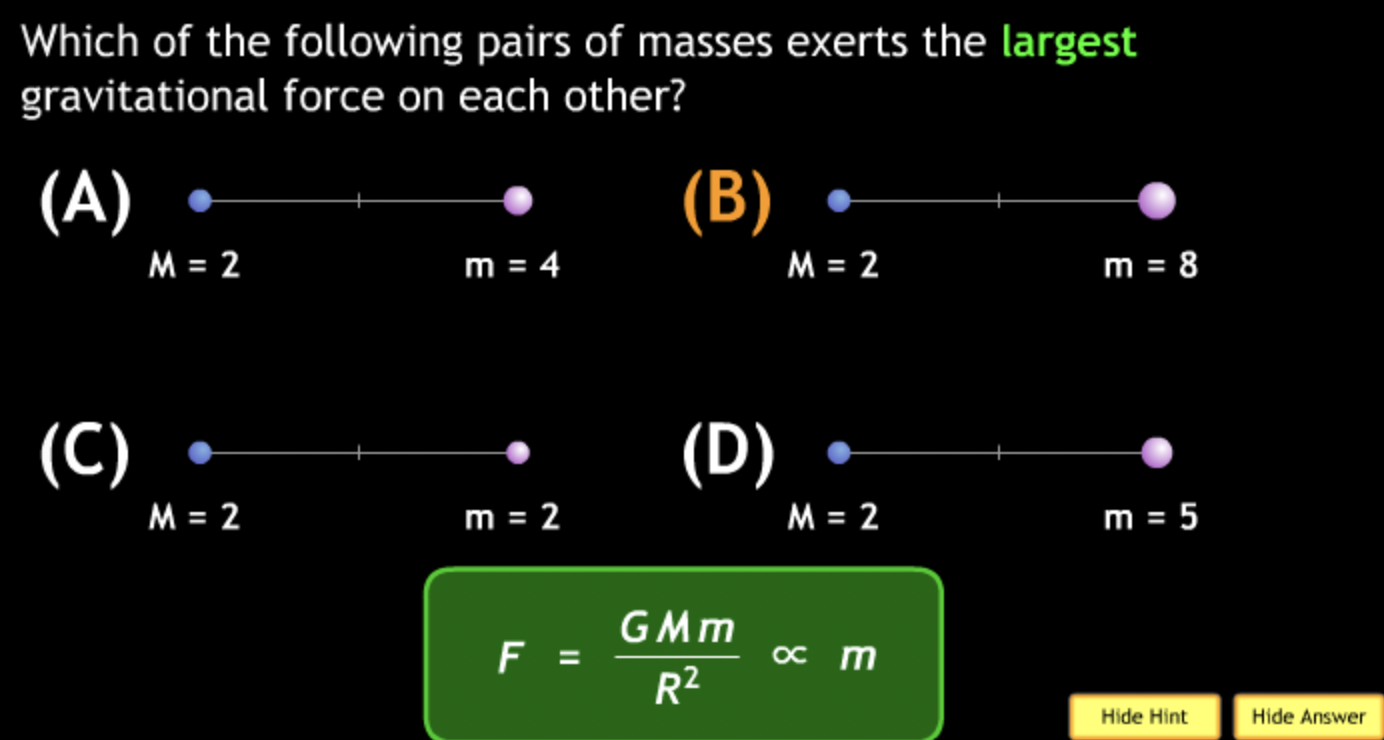
M2 were halved? → ½ F
M1 were halved and the mass of M2 were doubled? → 1F
M1 and M2 were doubled? → 4F
separation R were doubled? → 1/4F
m1 and separation R were both doubled? → 1/2F
M1 and M2, and the separation R were all doubled? → 1F
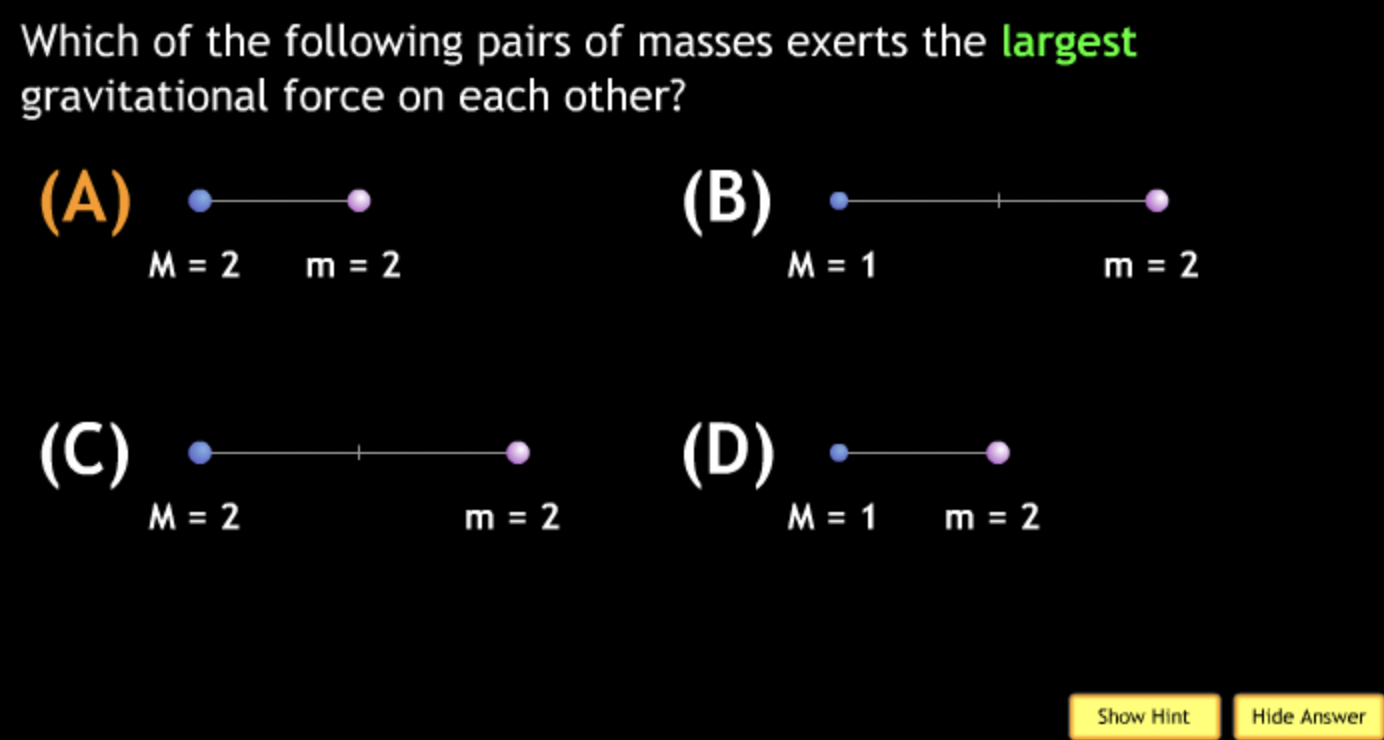
smallest? → C. M = 2. m = 2.

smallest? → C. M = 5. m = 2.
smallest? → B. M = 1. m = 2.
smallest? → B.
smallest? → B
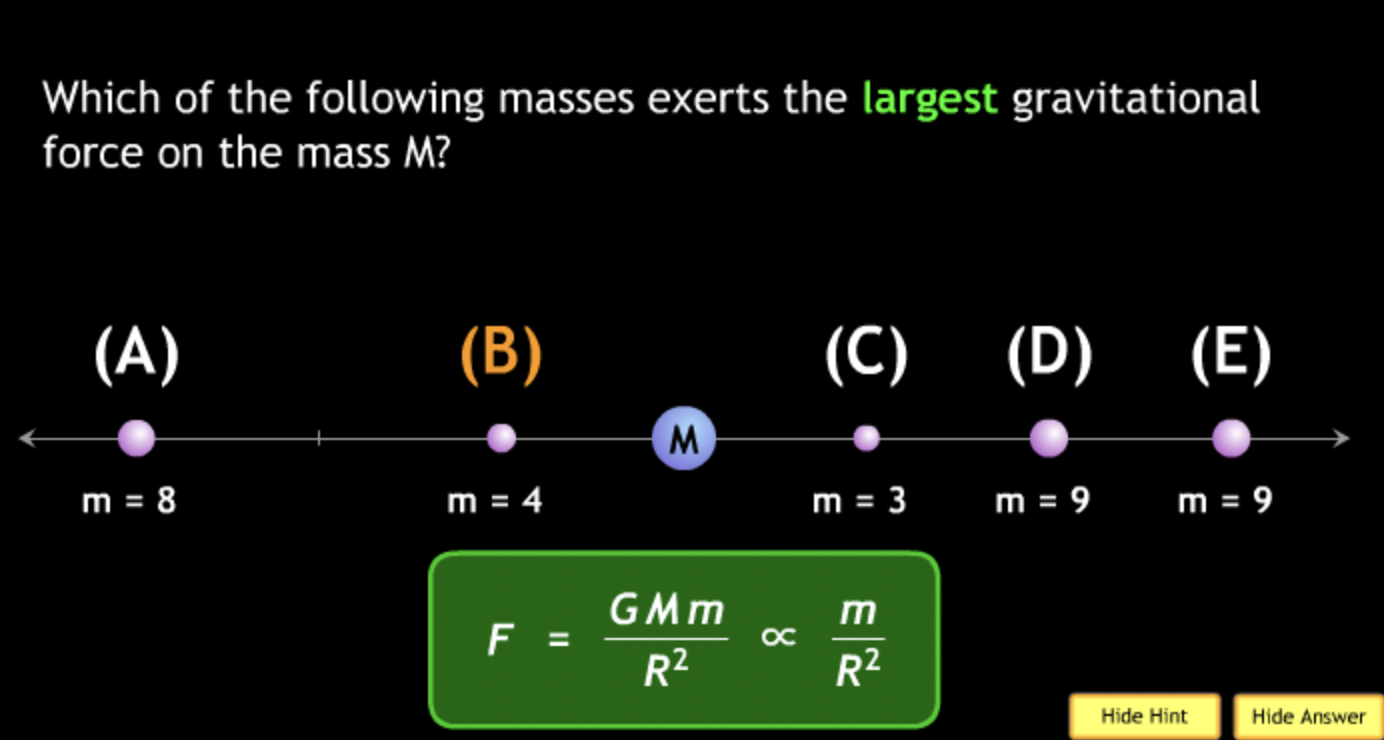
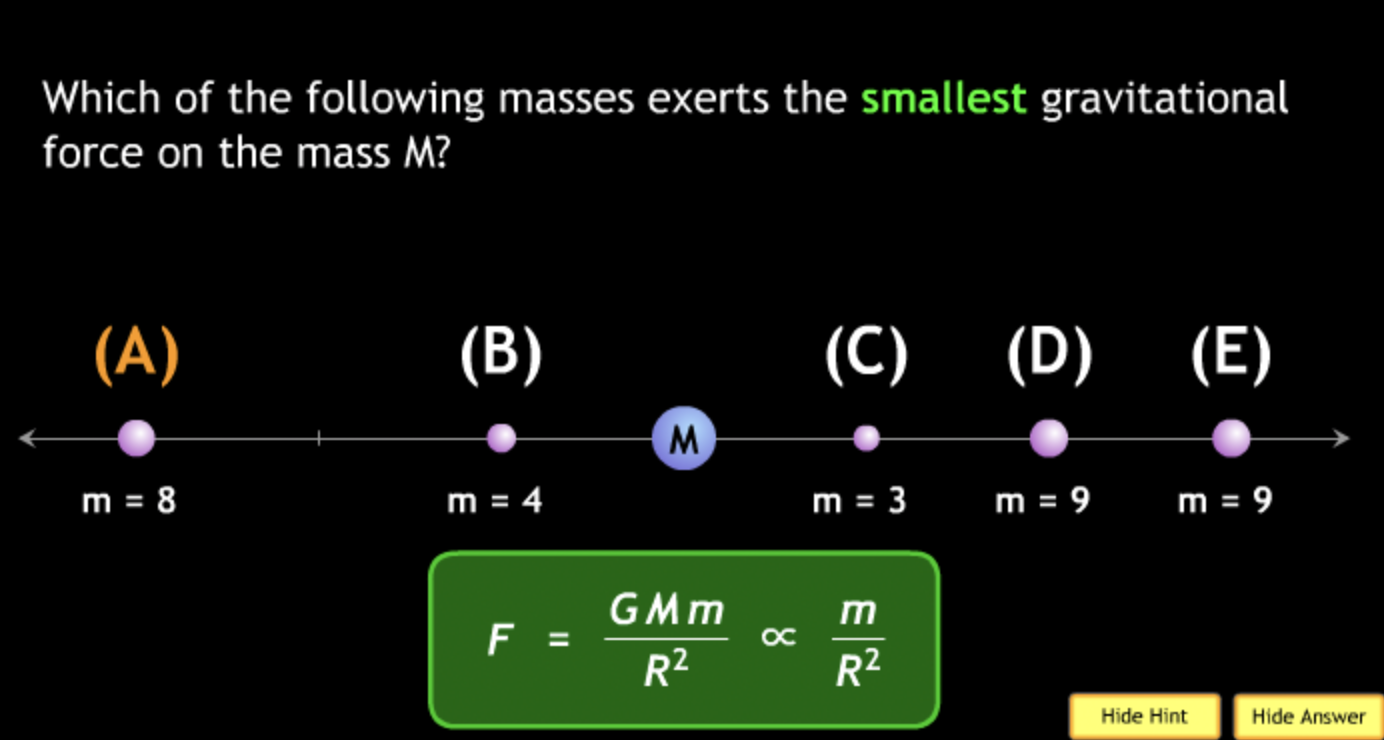
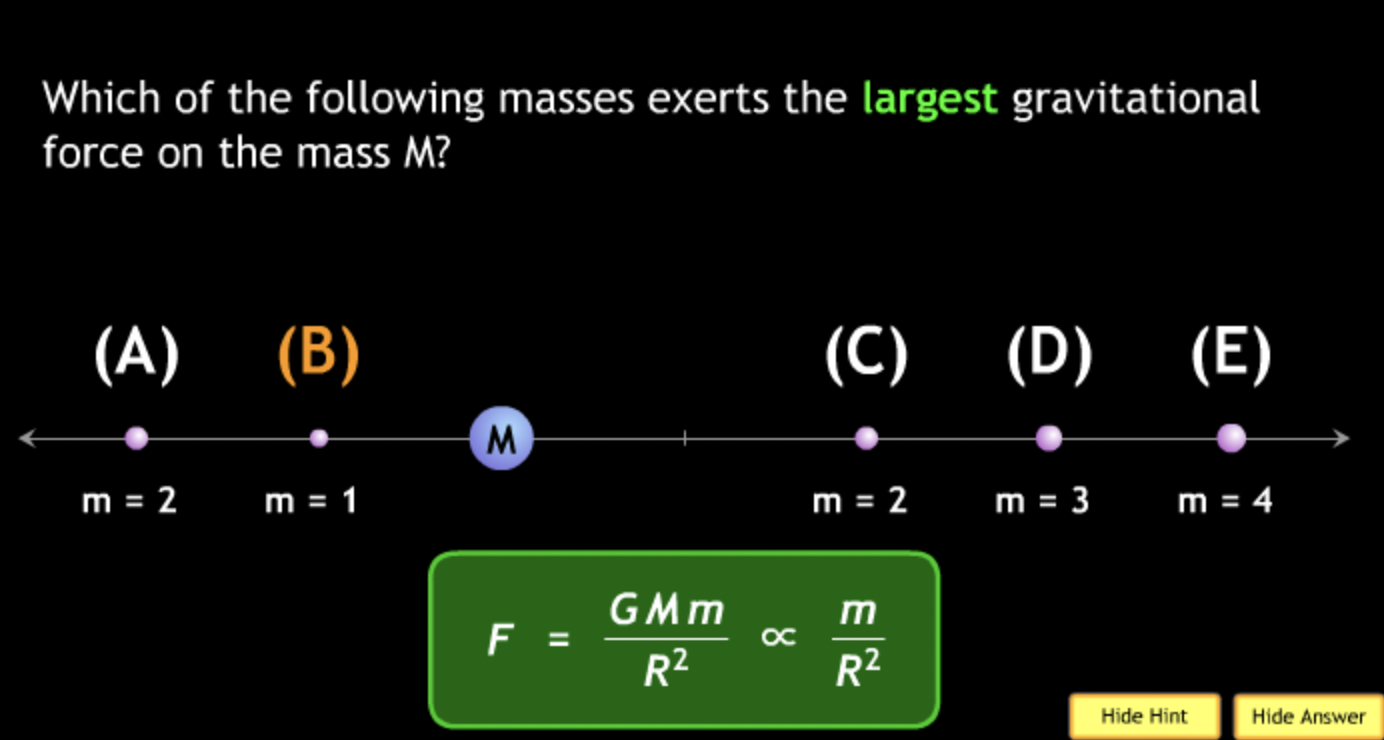
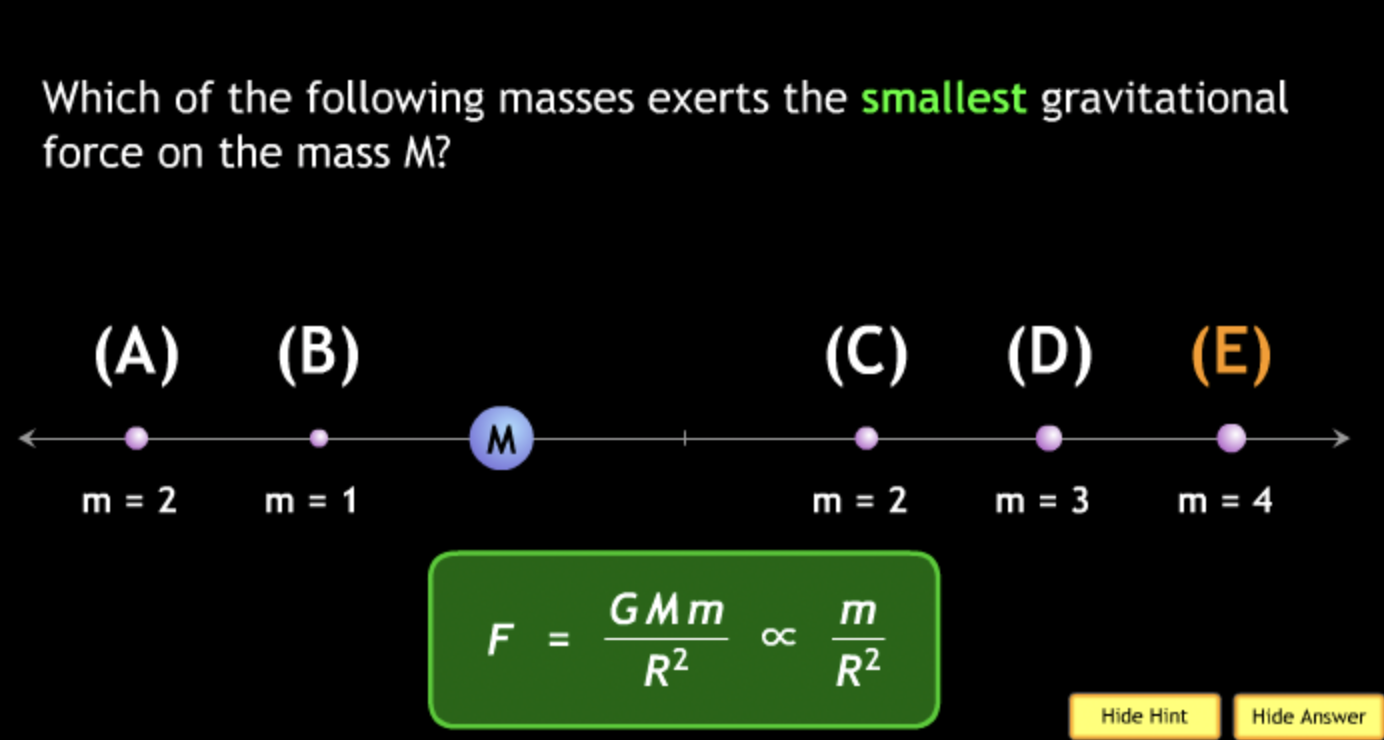
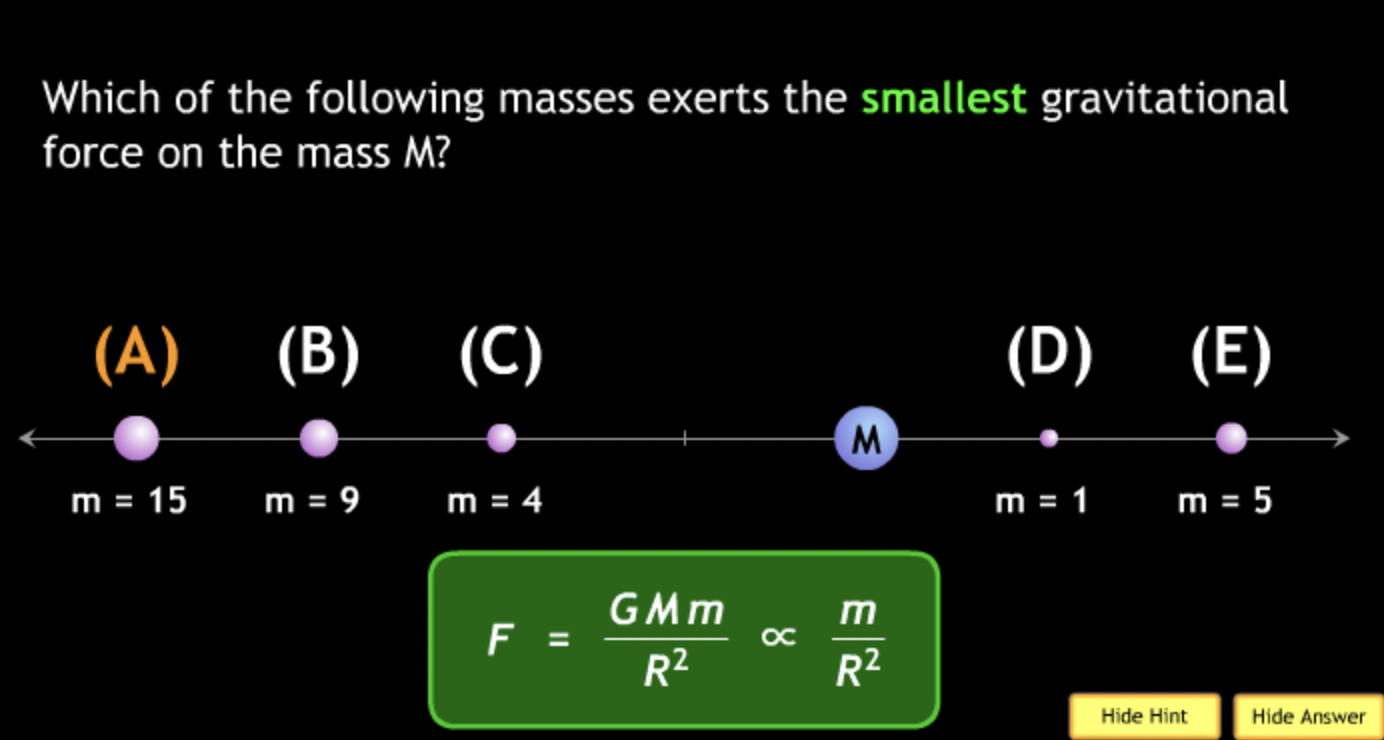















longest wavelength? → C

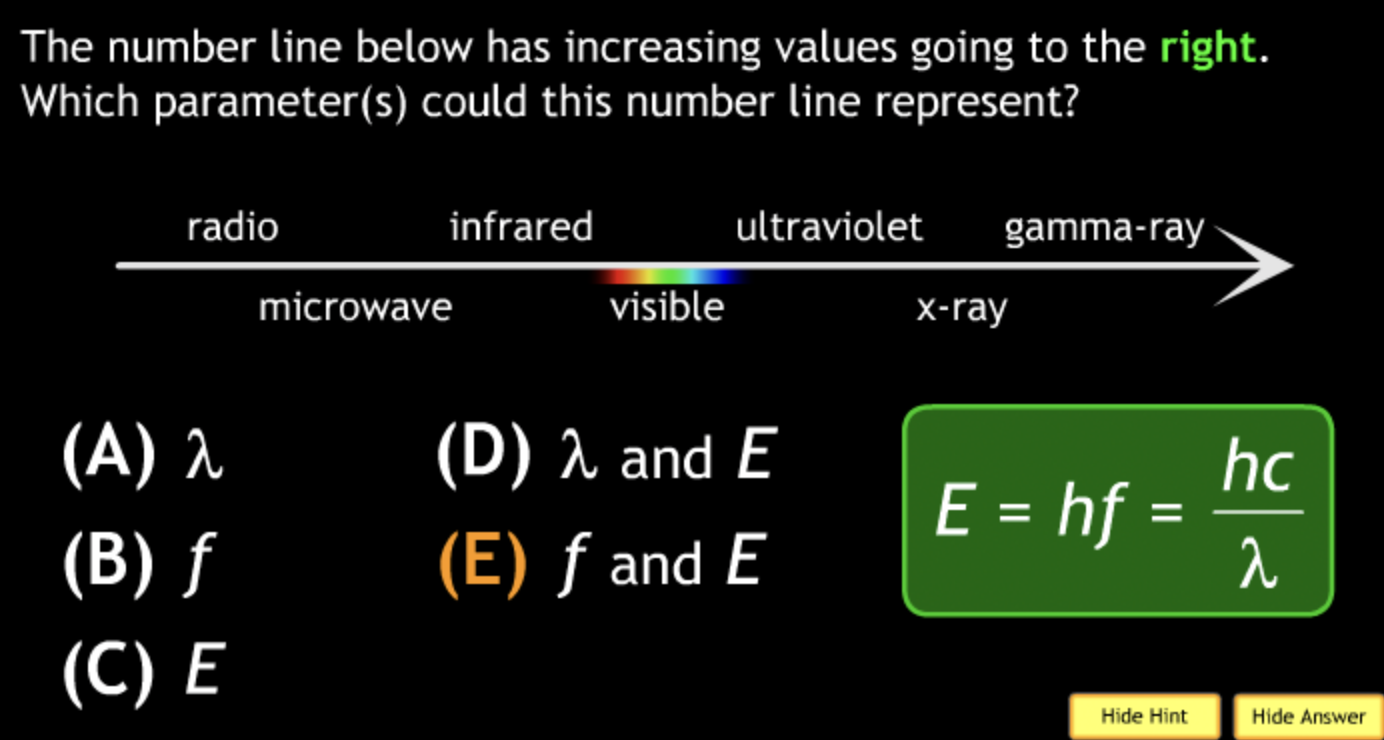
radio waves → D. a sky-scraper
gamma rays → A. an atomic nucleus
microwaves → C. a fingertip

a small bacterium → A. visible light
a mountain → C. radio waves

largest frequency? → X-Rays smallest energy? → Microwave
largest wavelength? → Microwave. smallest frequency? → Microwave
largest velocity in space? → all have the same velocity in space
smallest velocity in space? → all have the same velocity in space

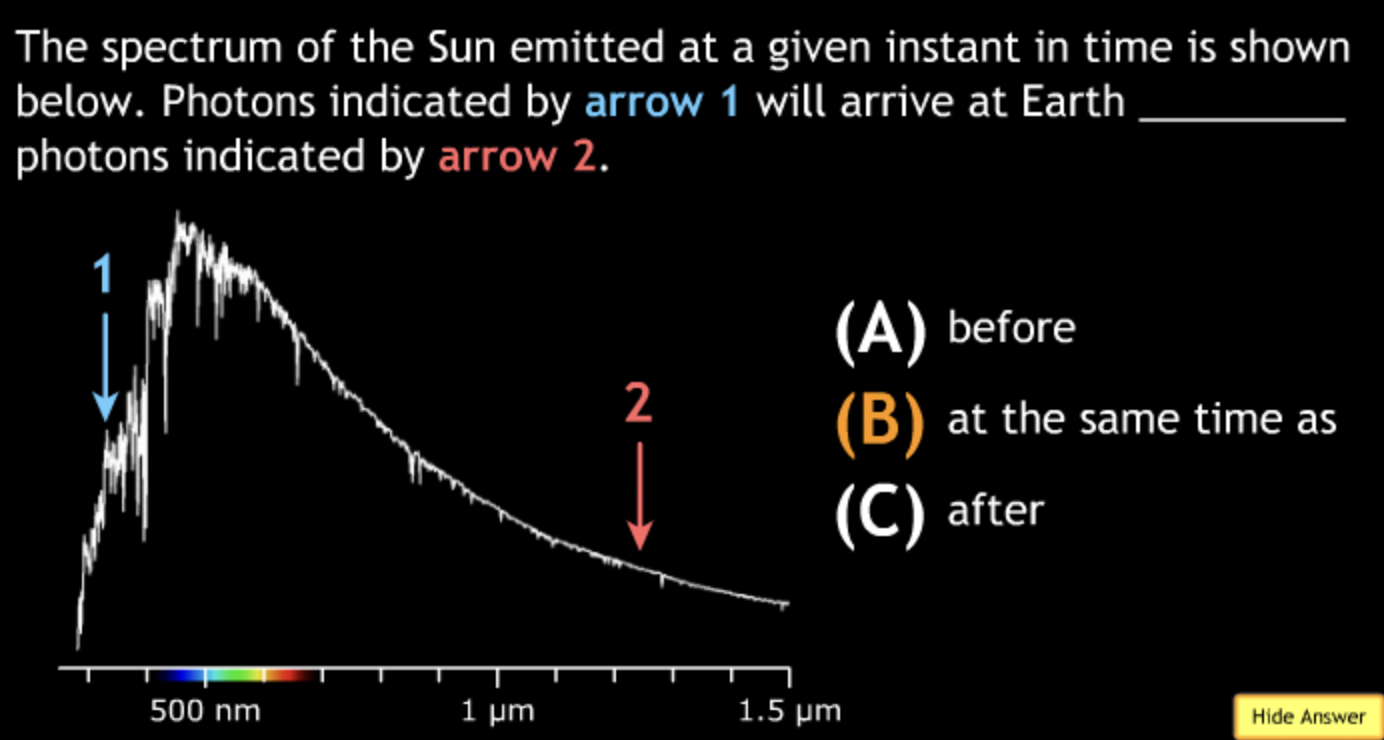
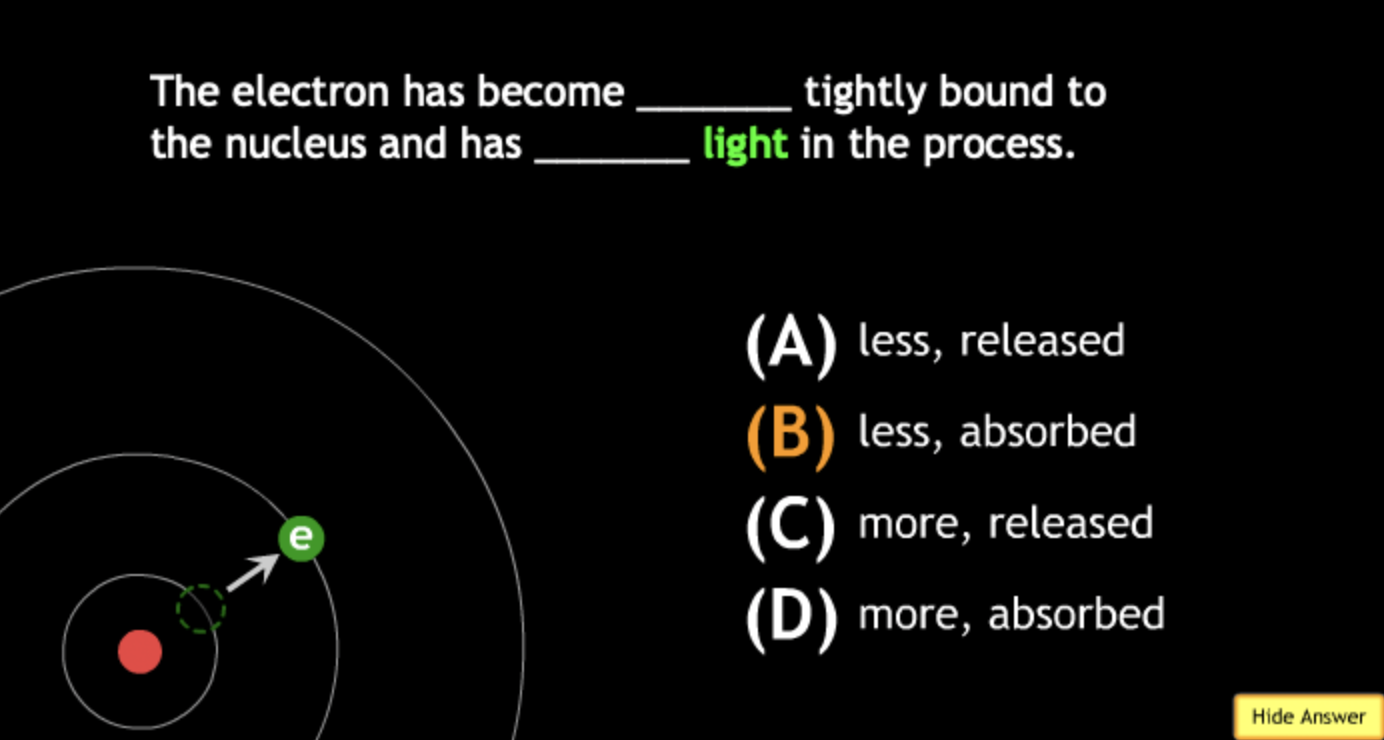
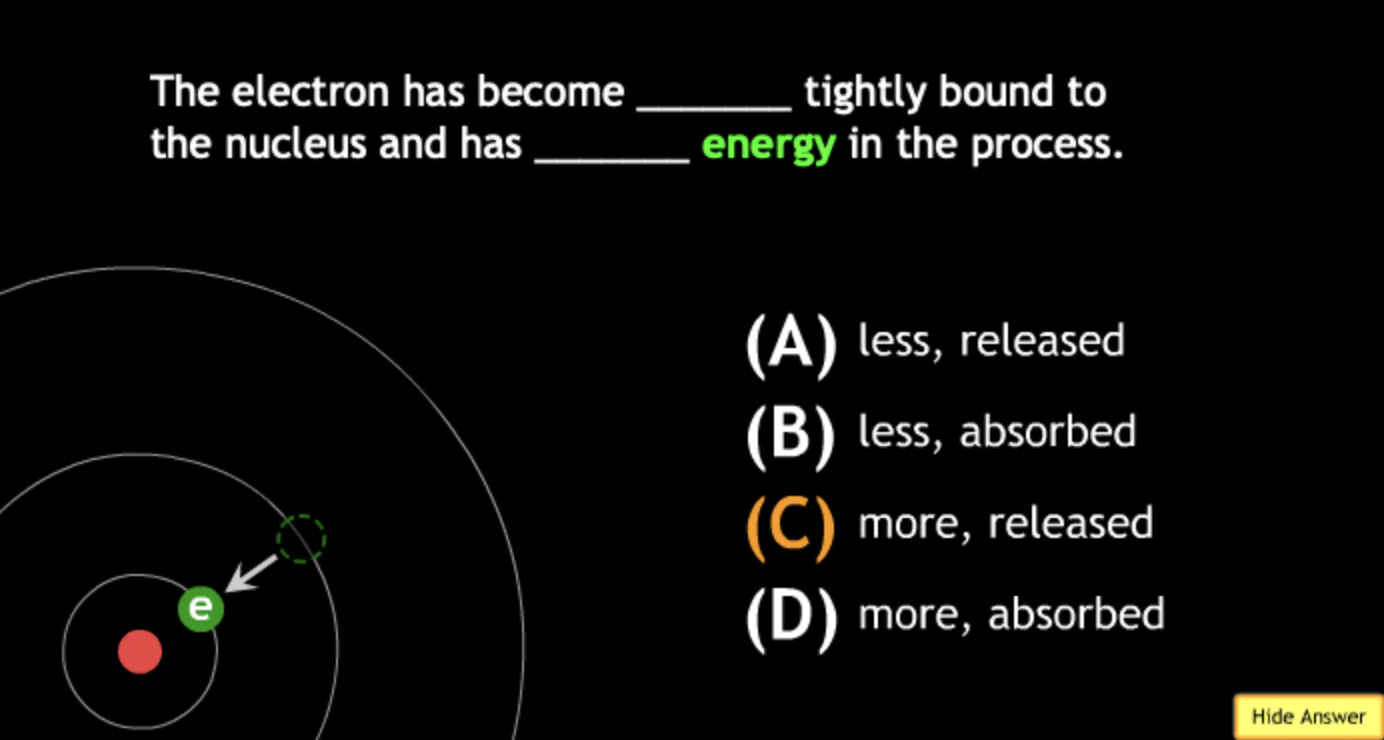
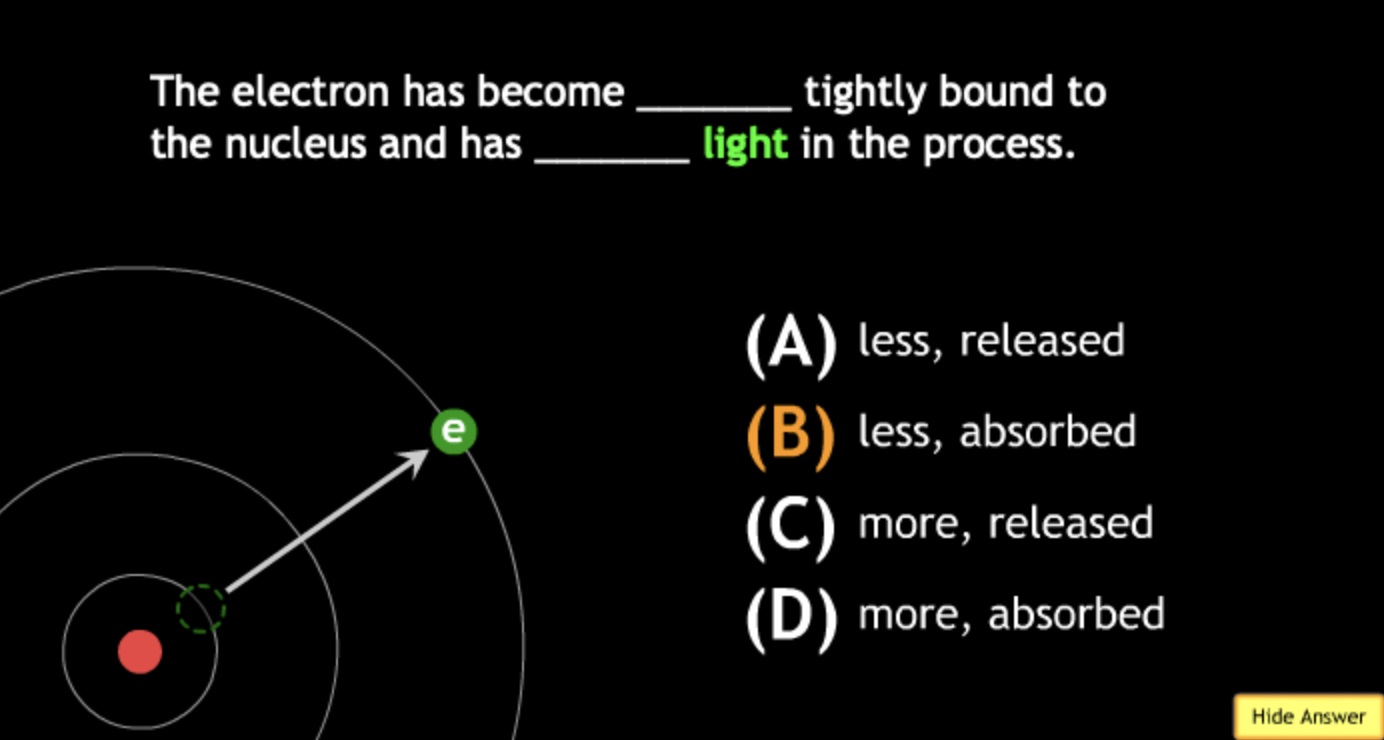
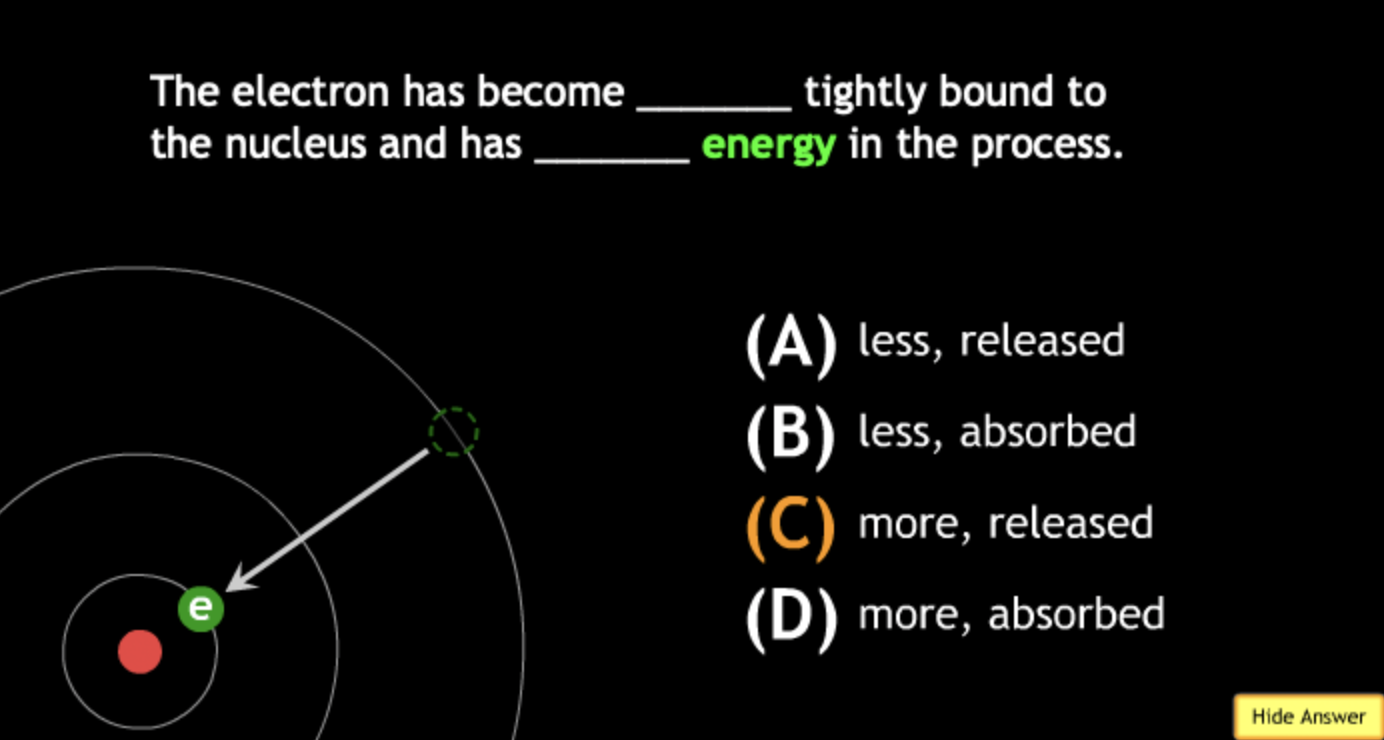
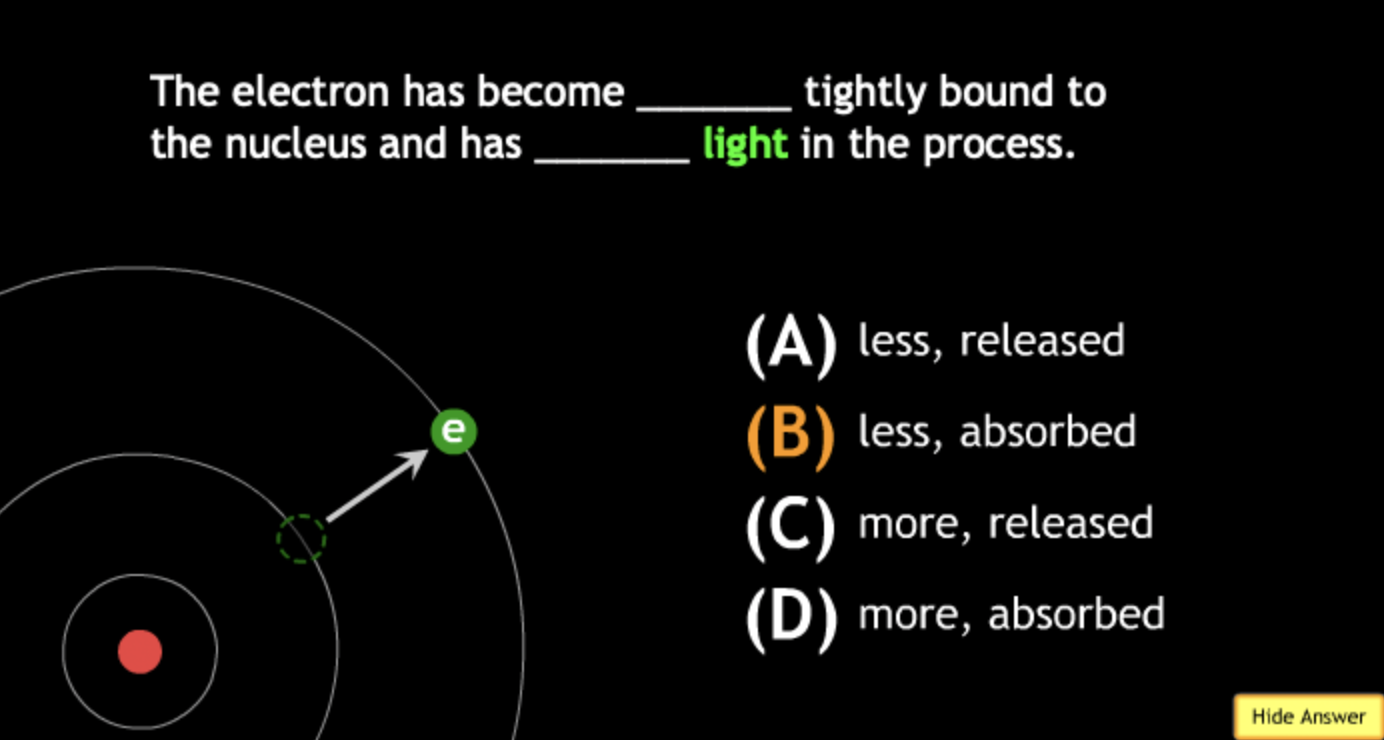
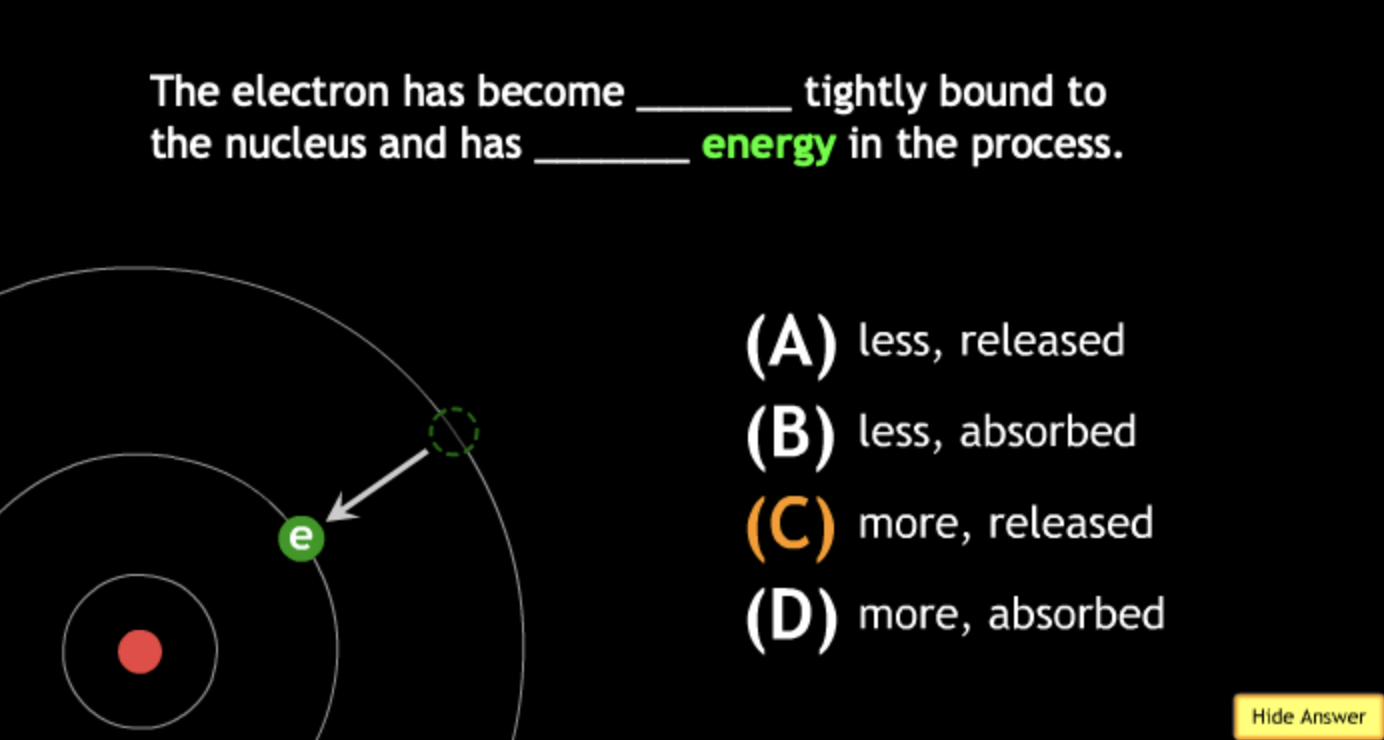
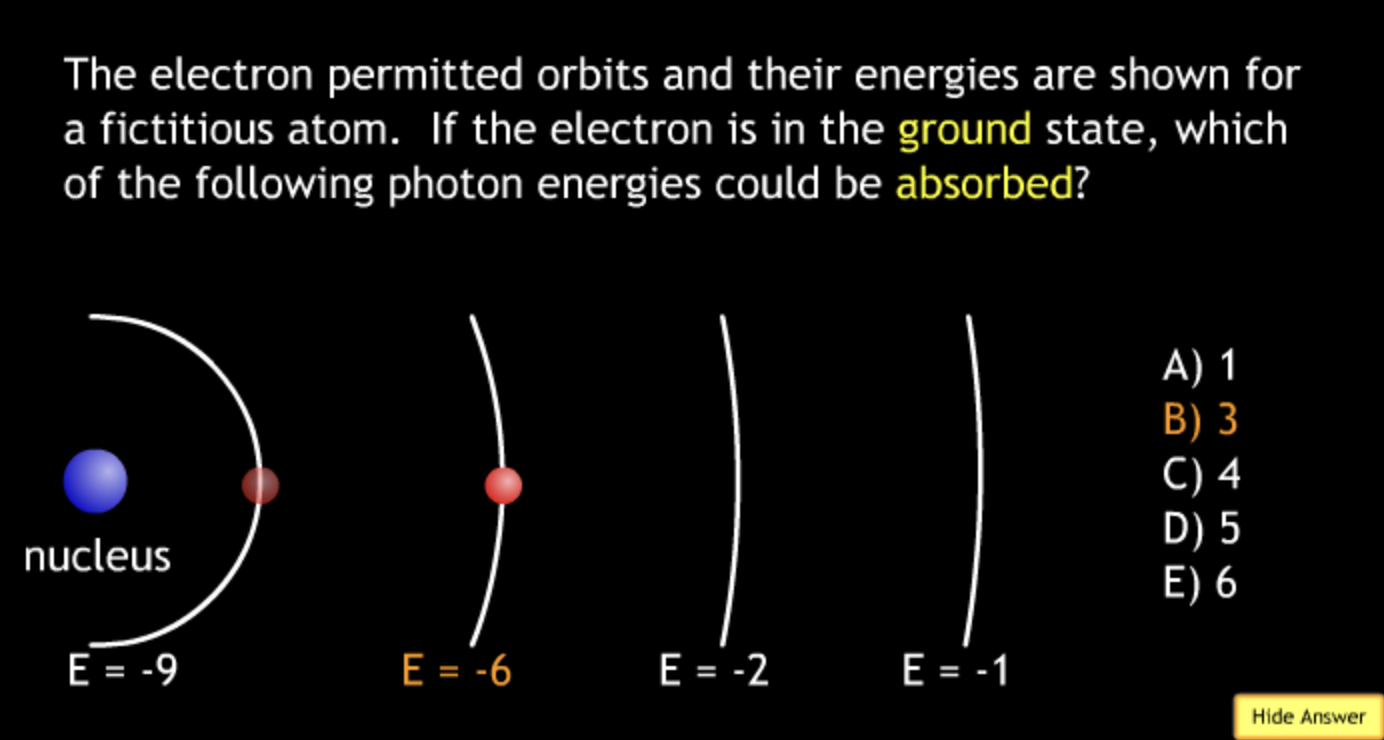


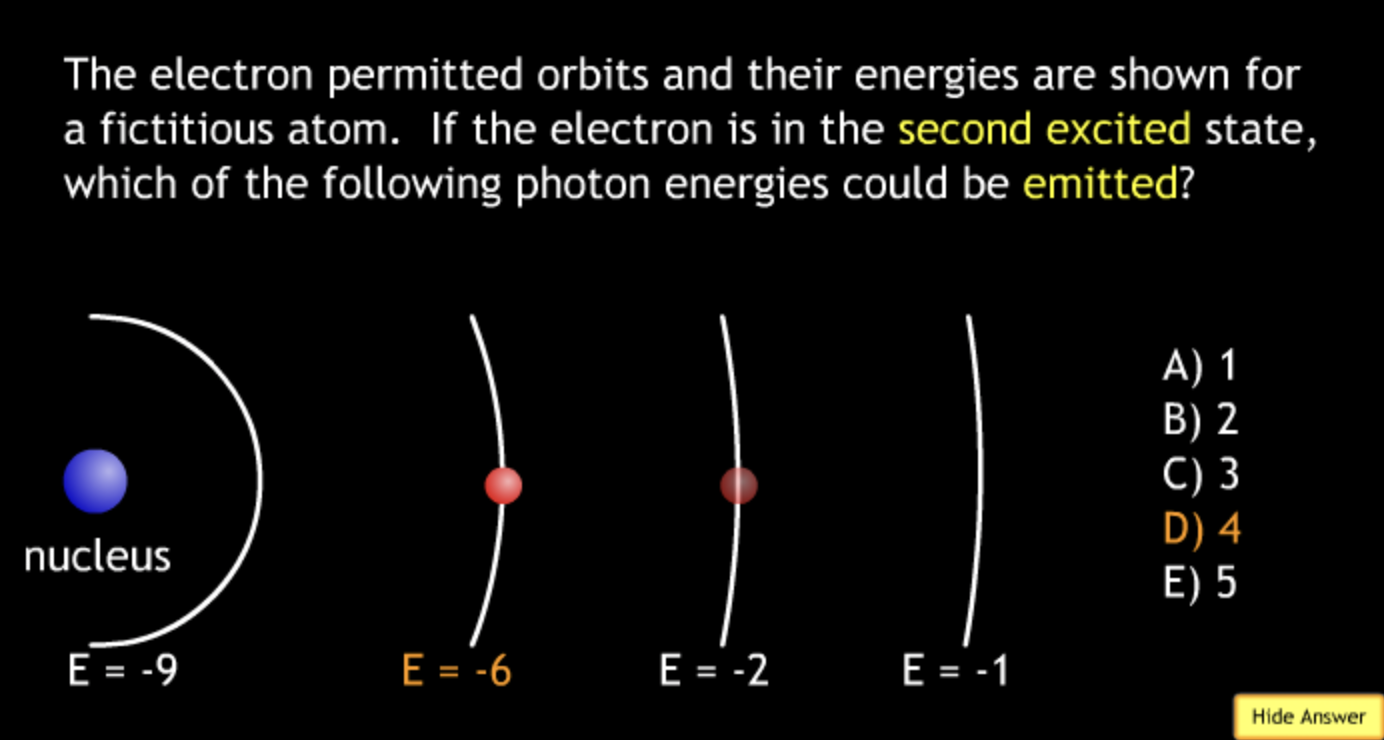
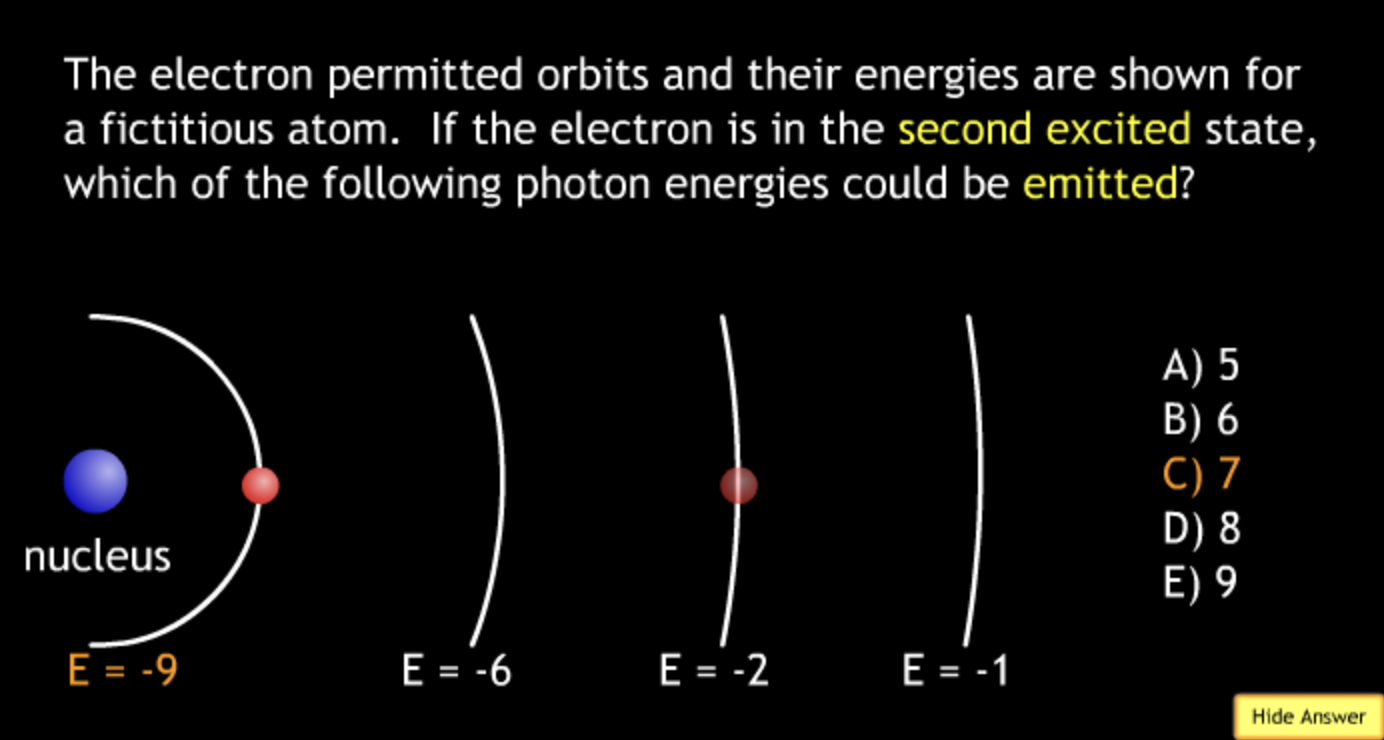
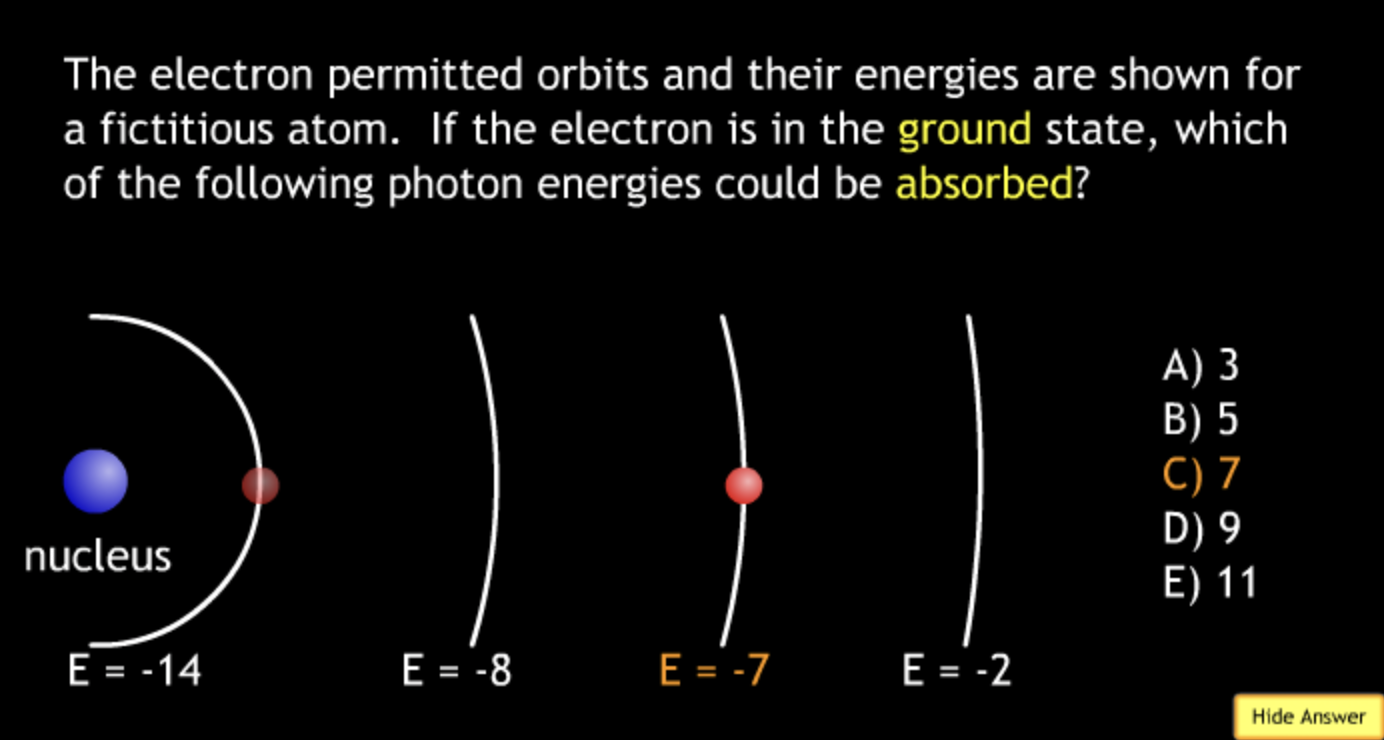
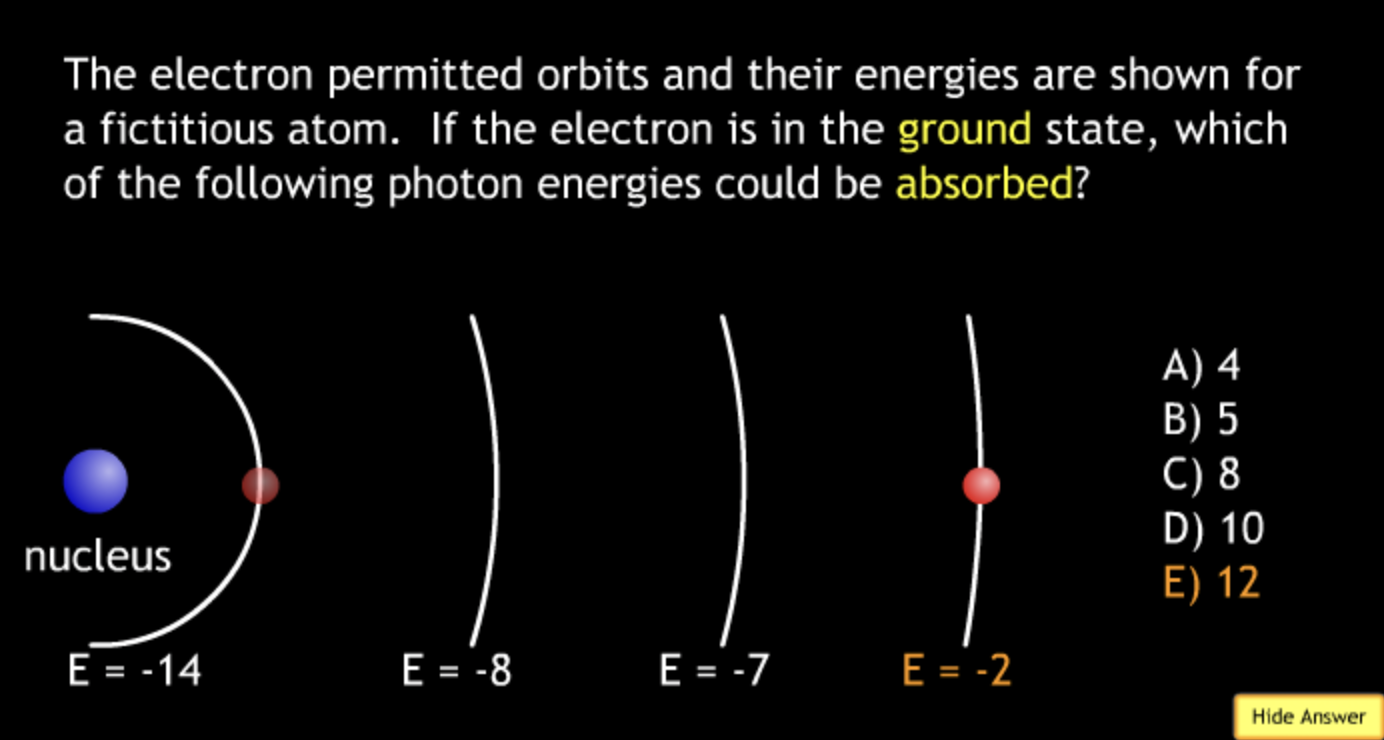
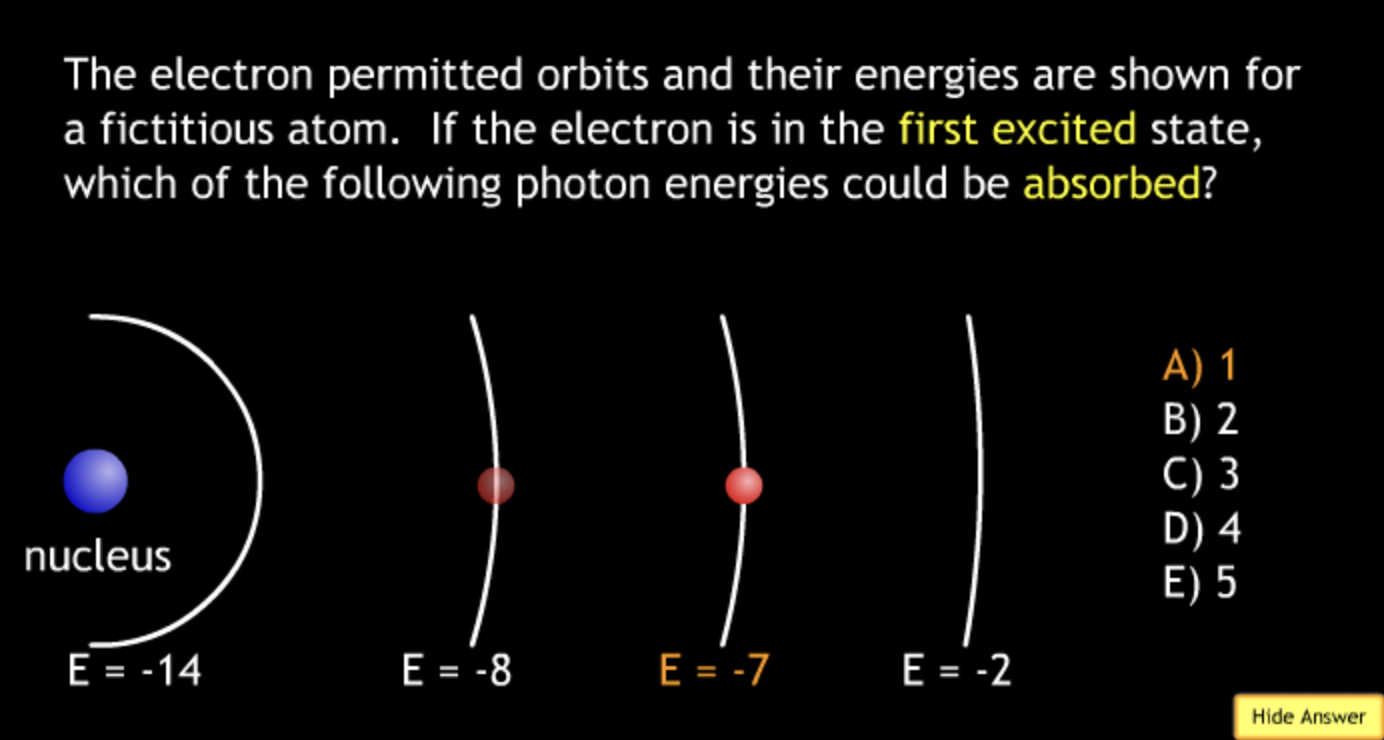

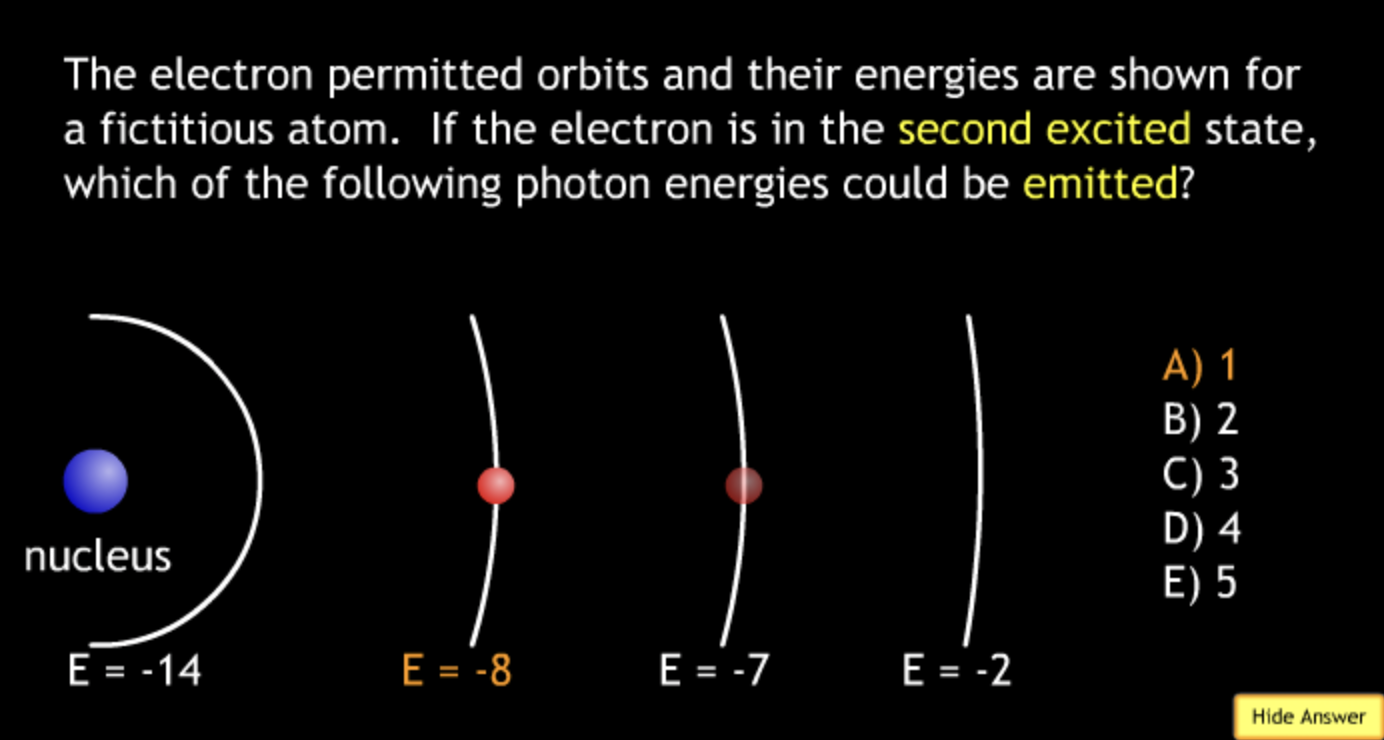

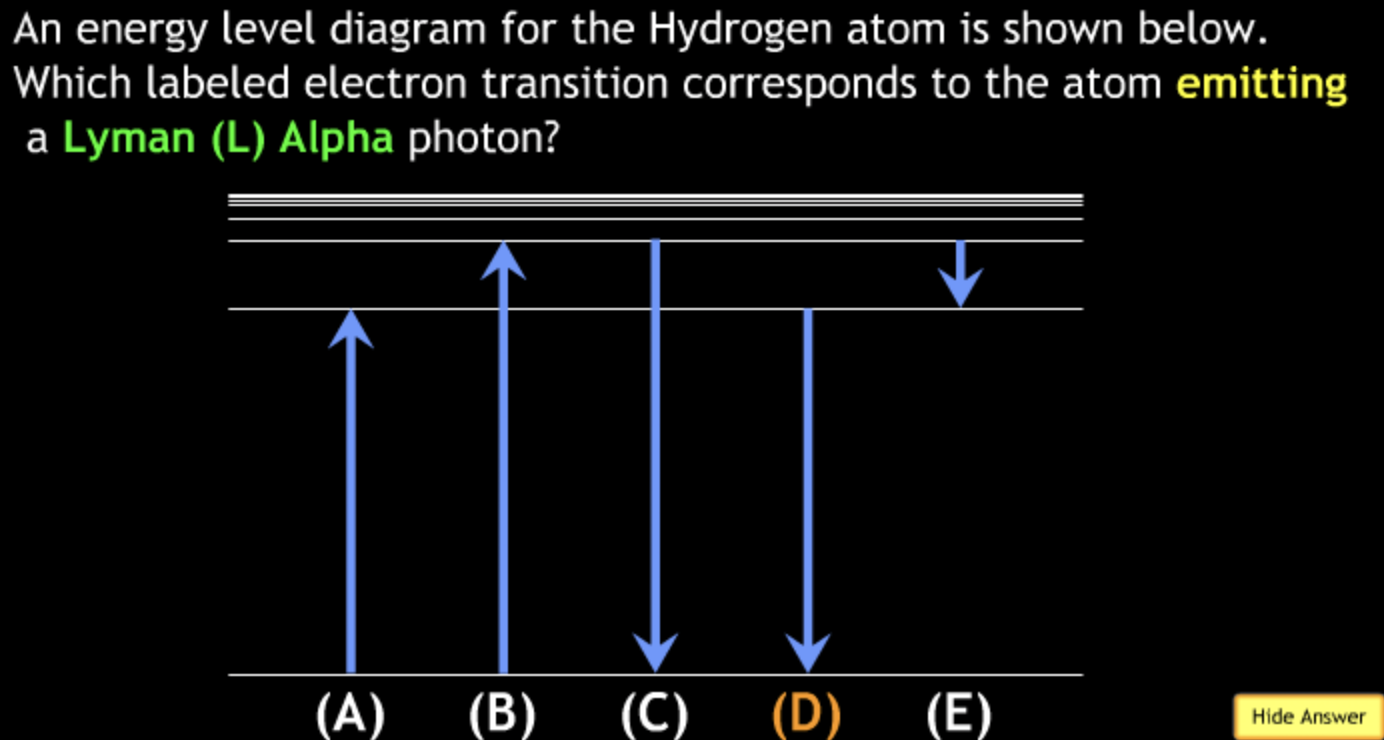
absorbing? → A.
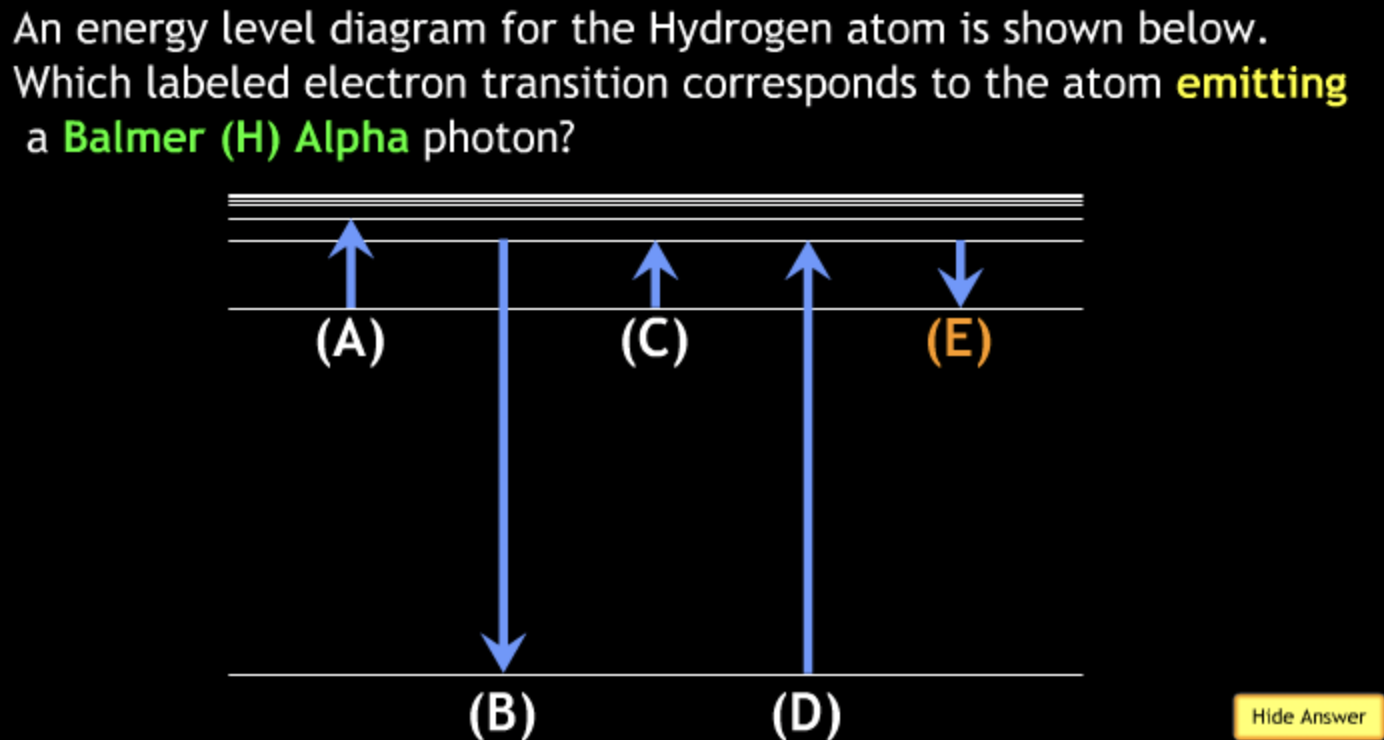
absorbing? → C
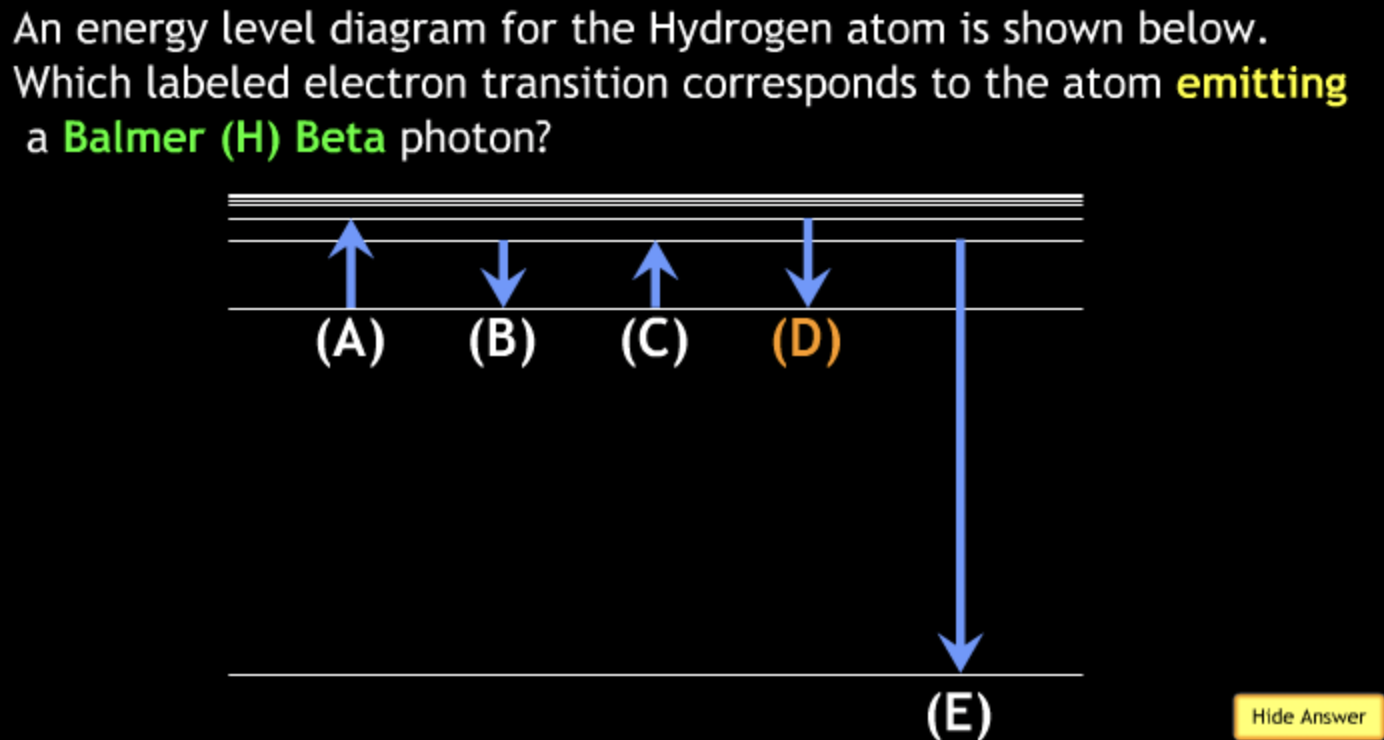
absorbing/ → A
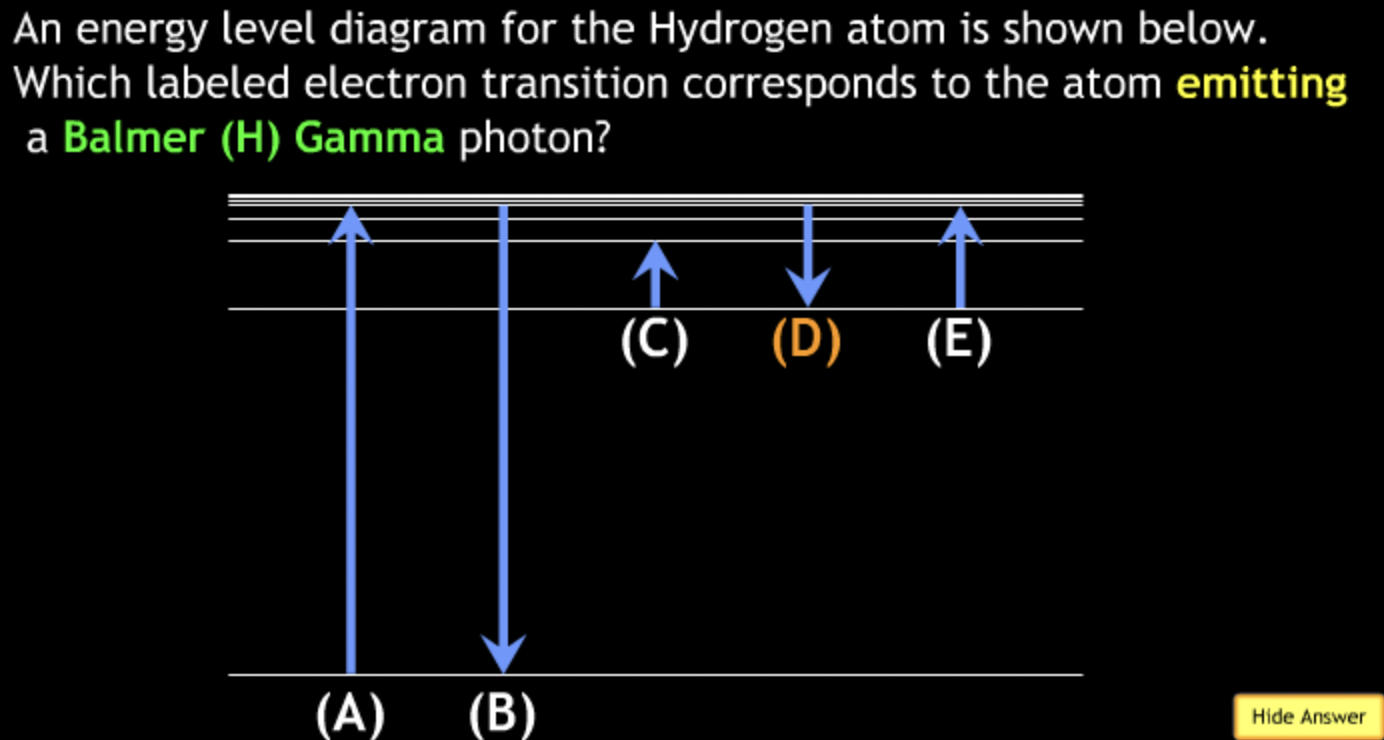
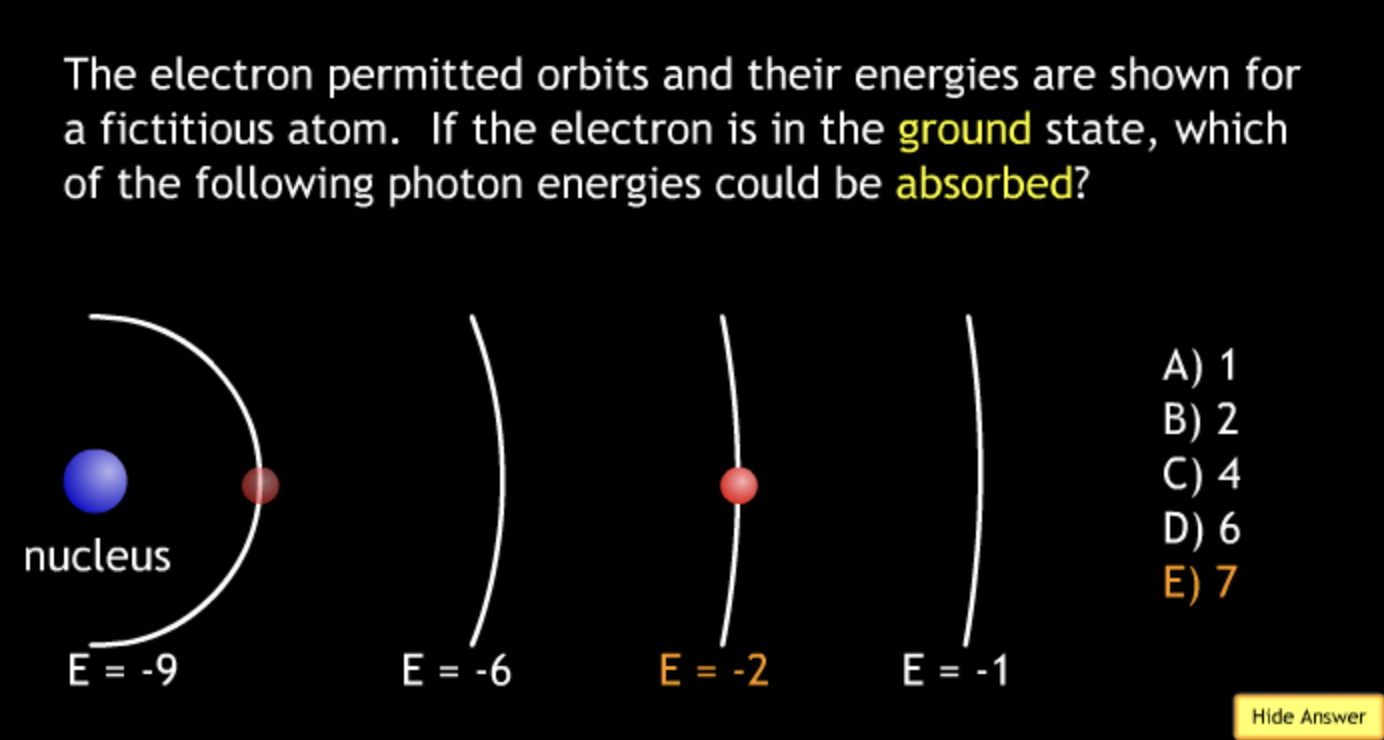
absorbing? → E
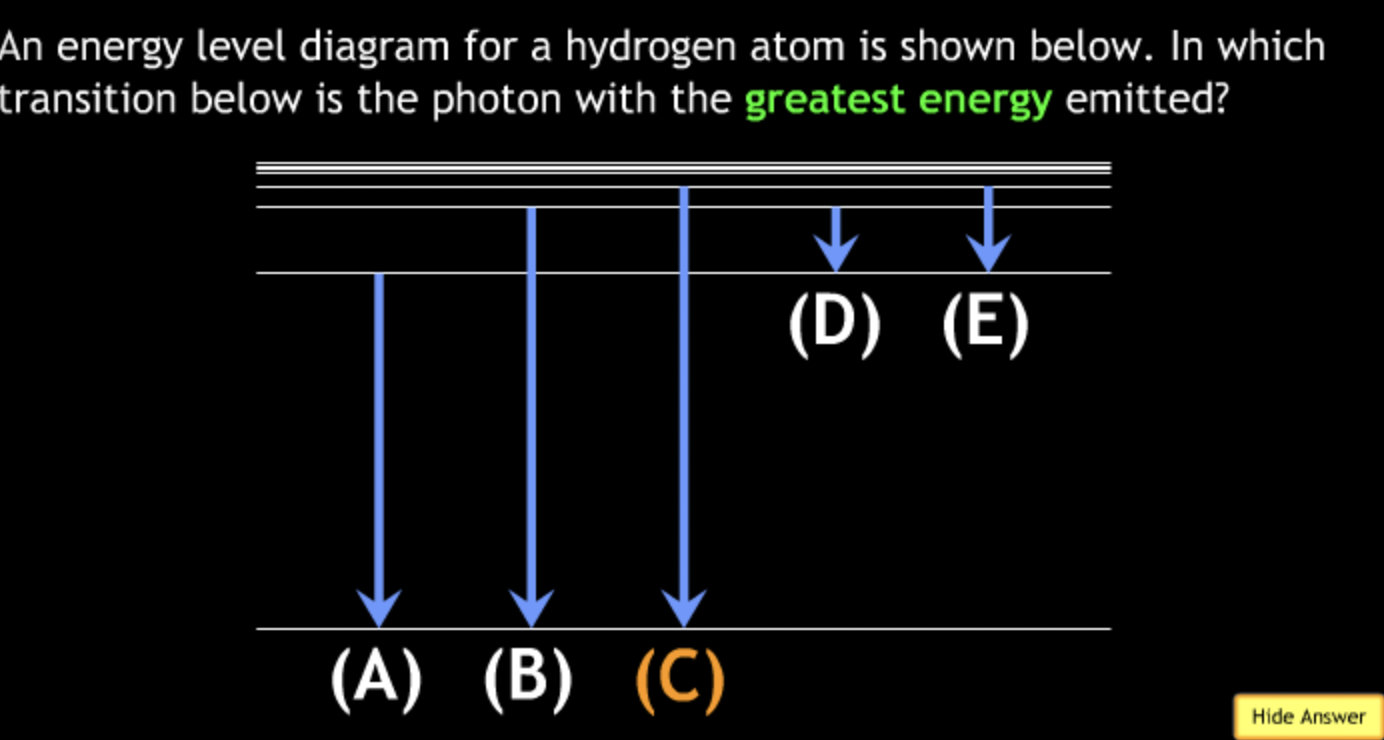





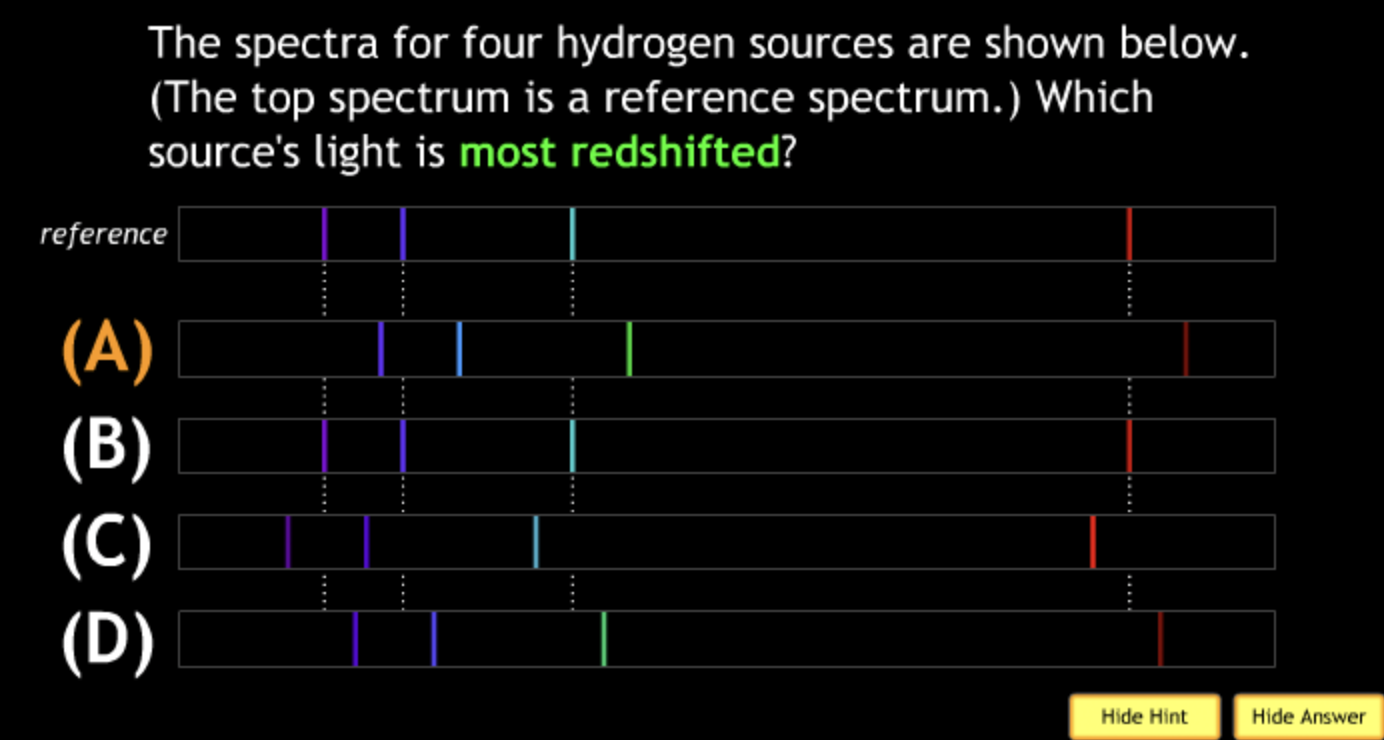
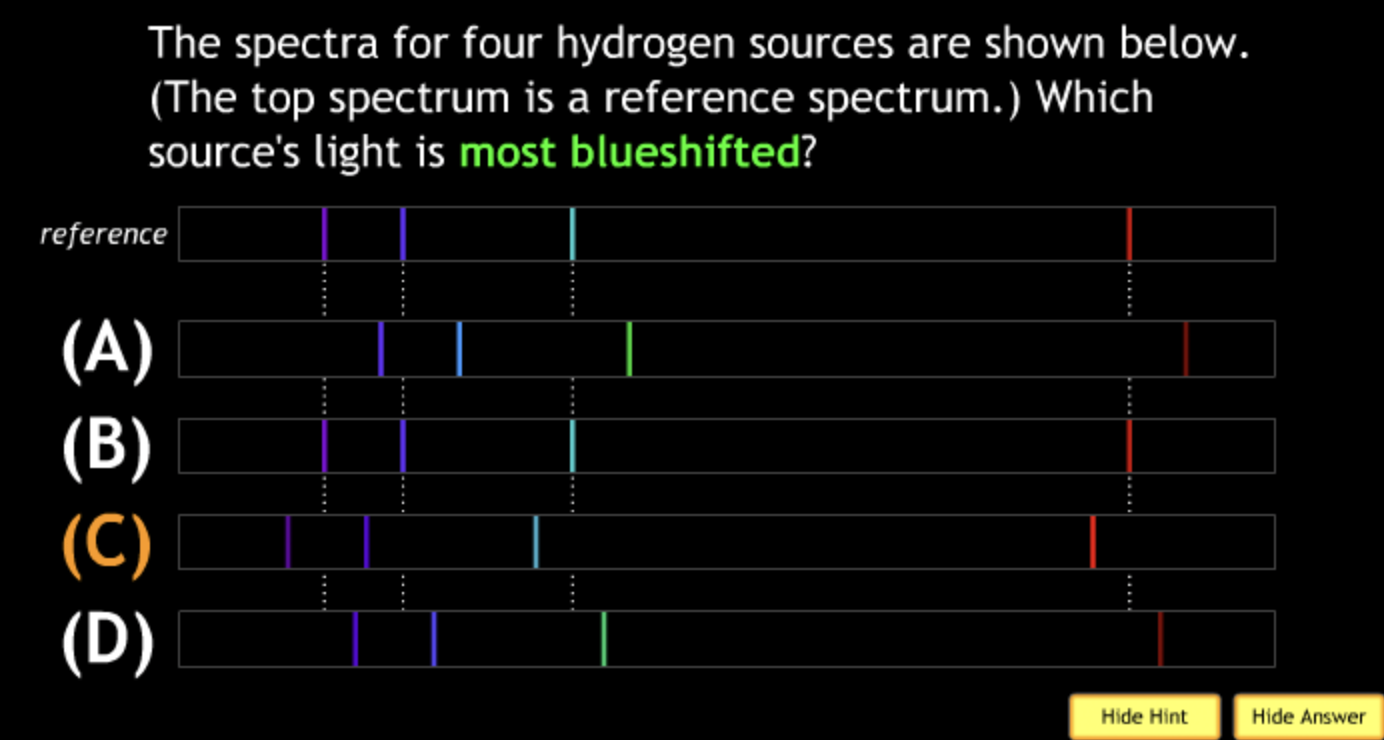
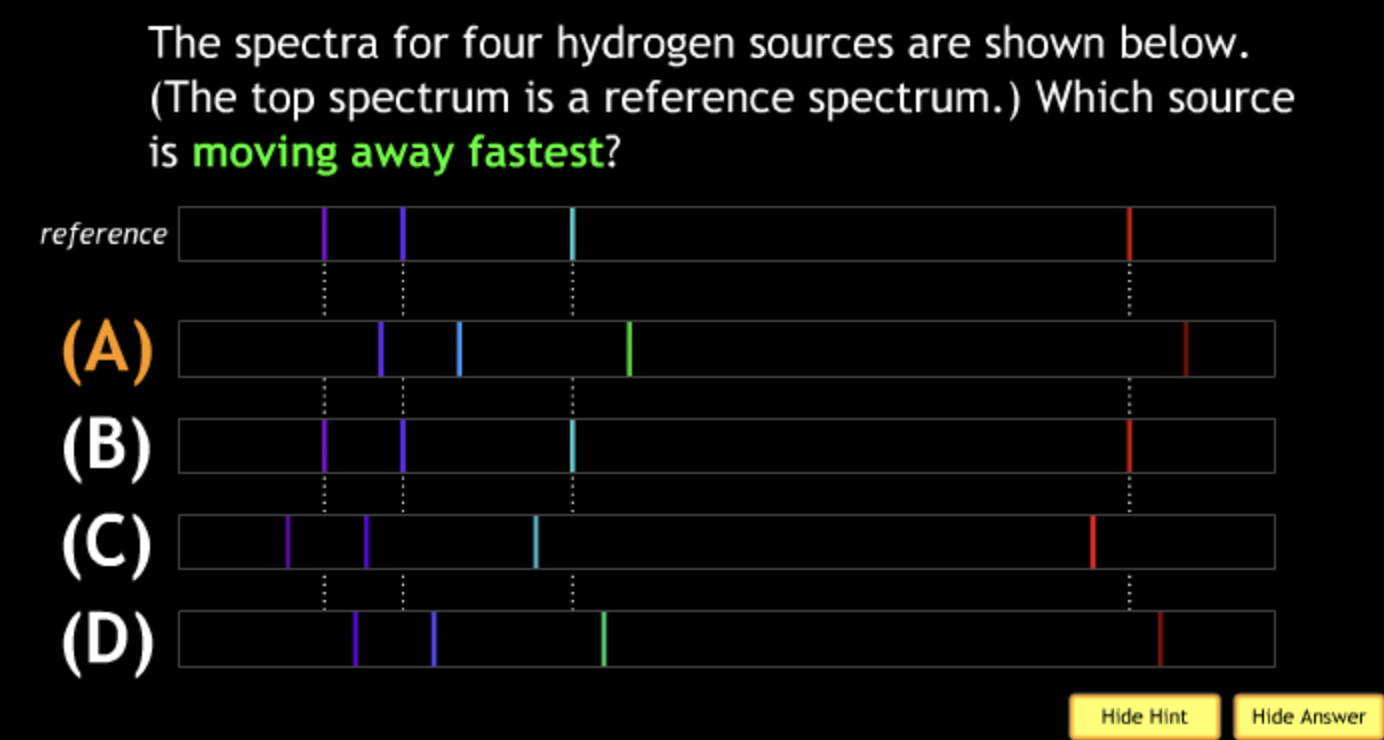
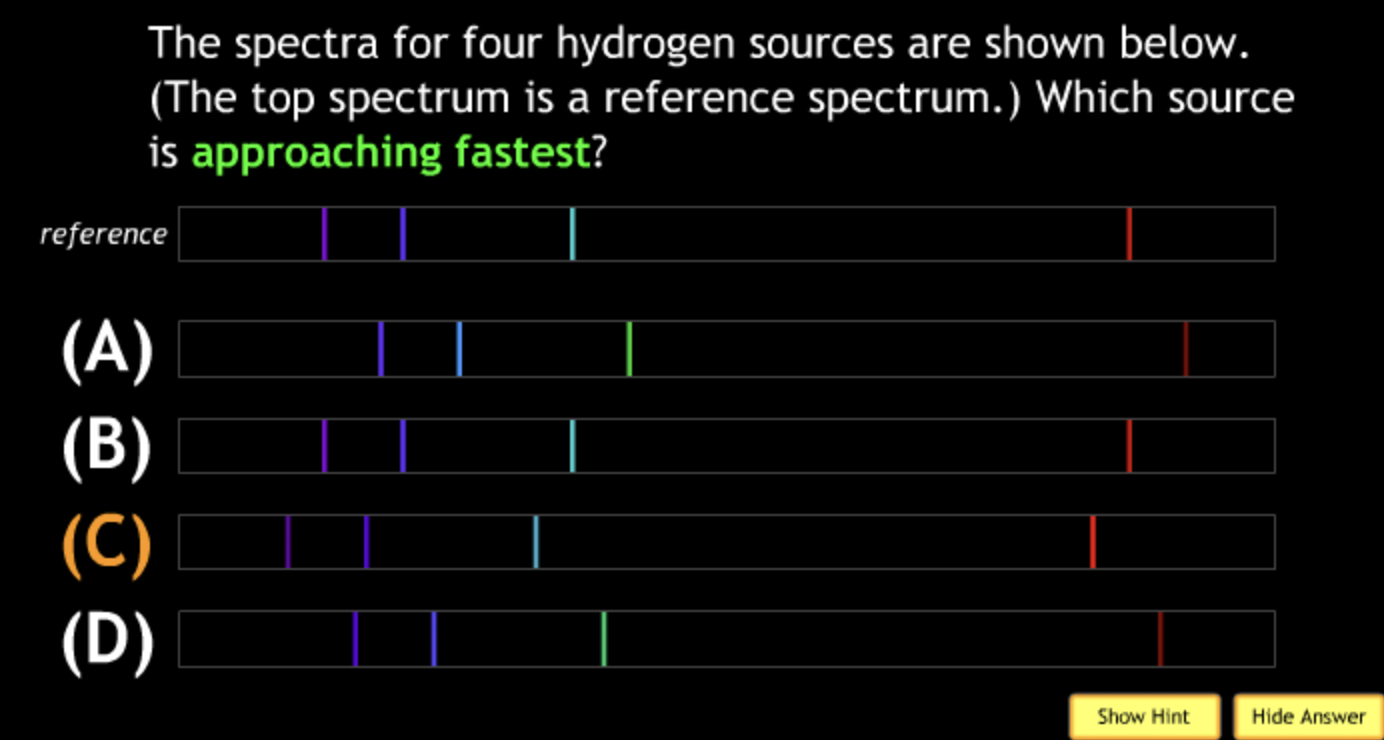
lowest speed? → A






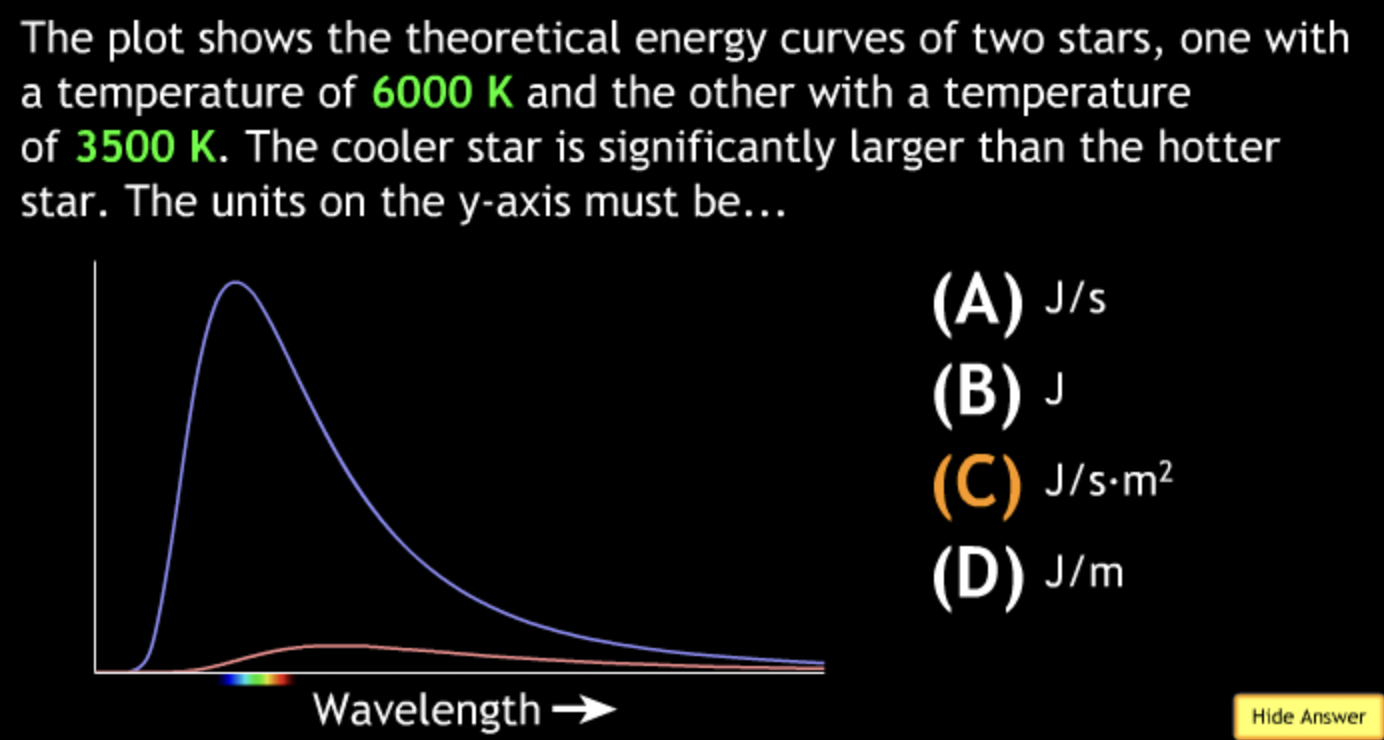
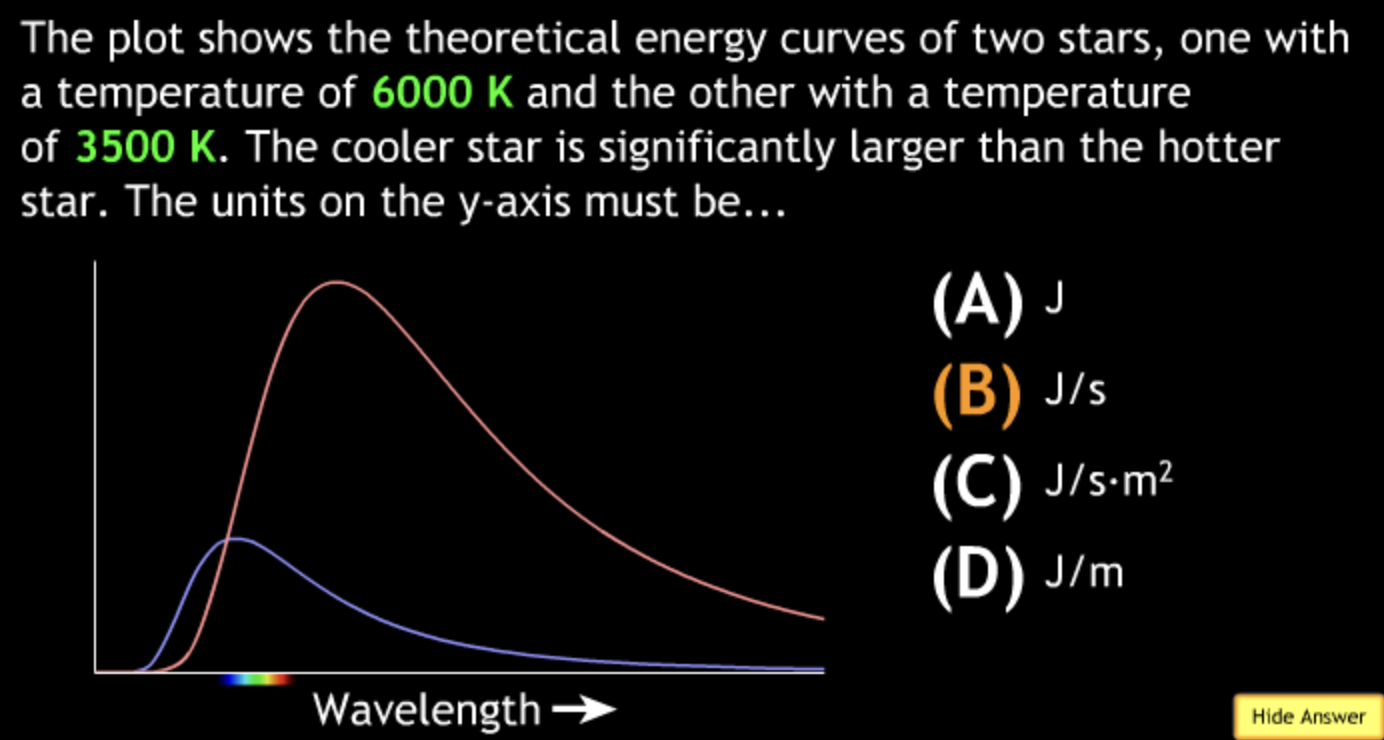
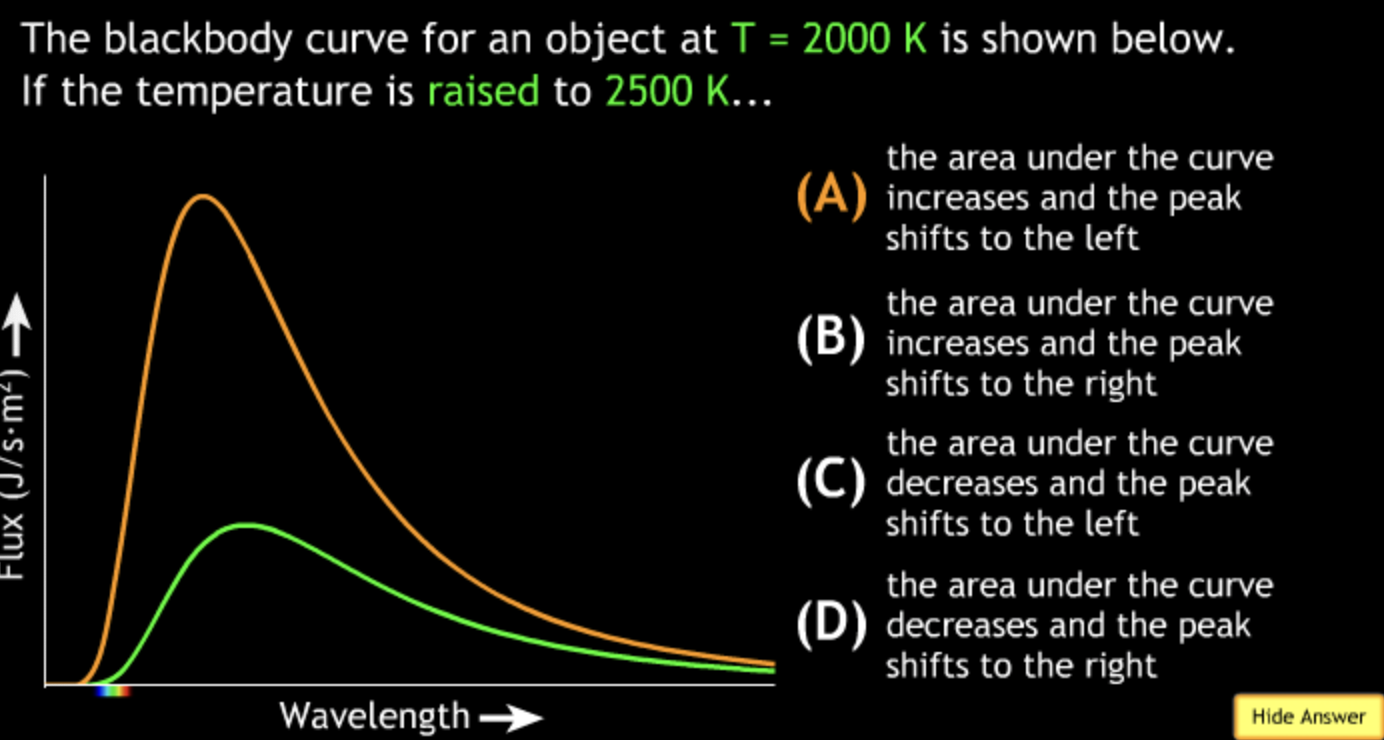
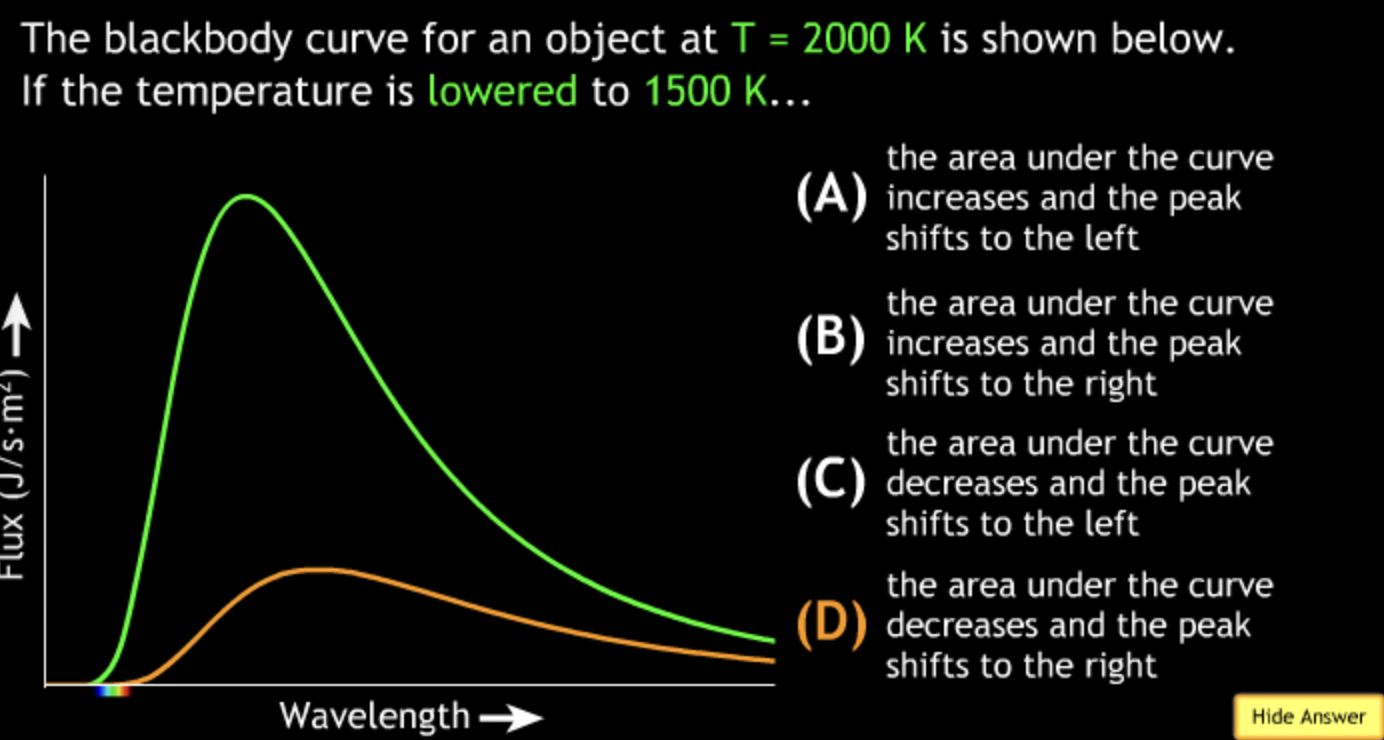
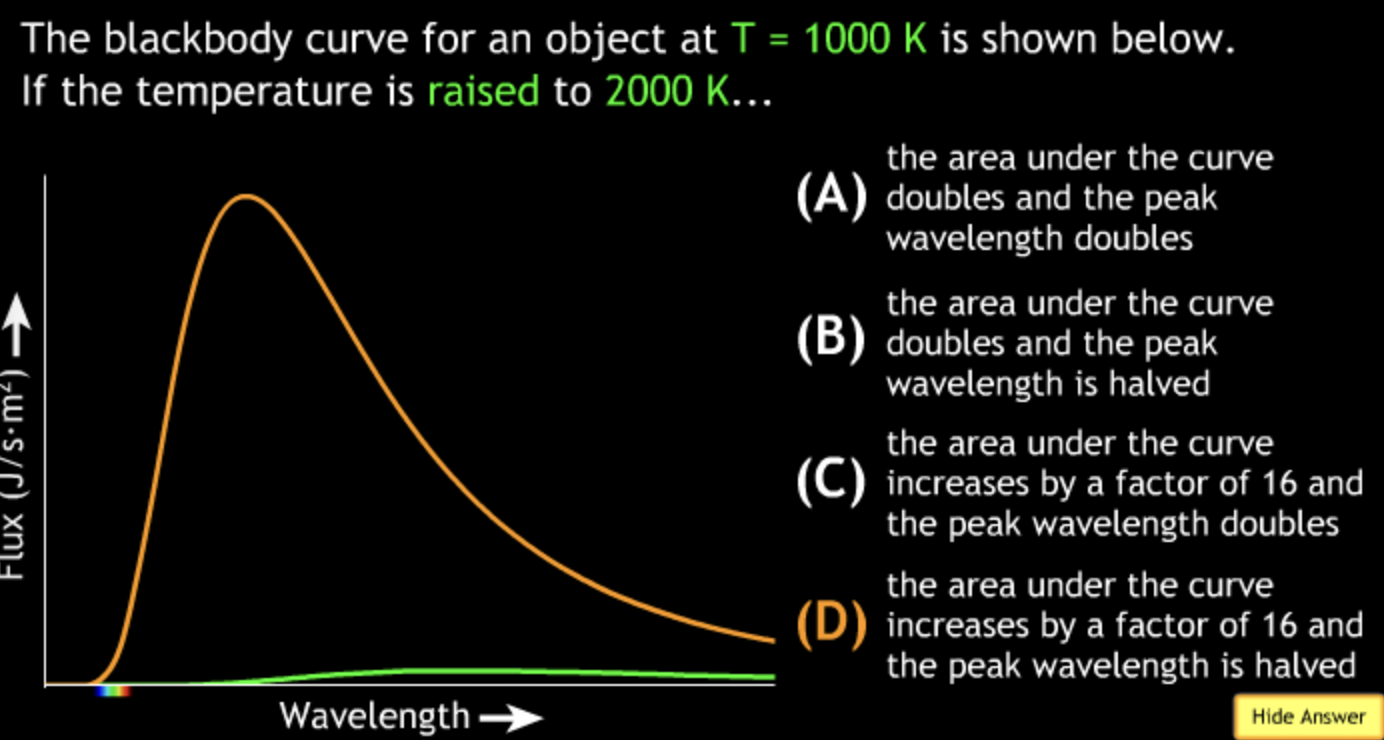
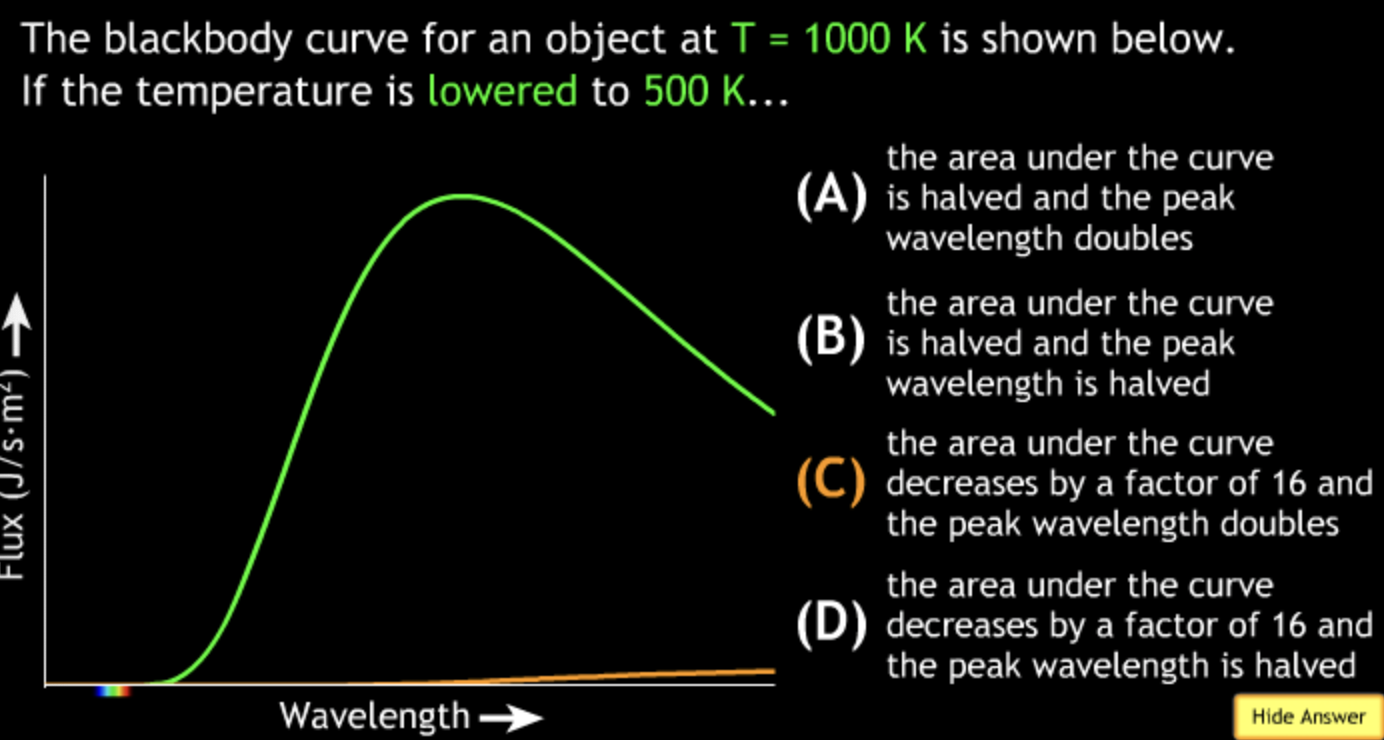
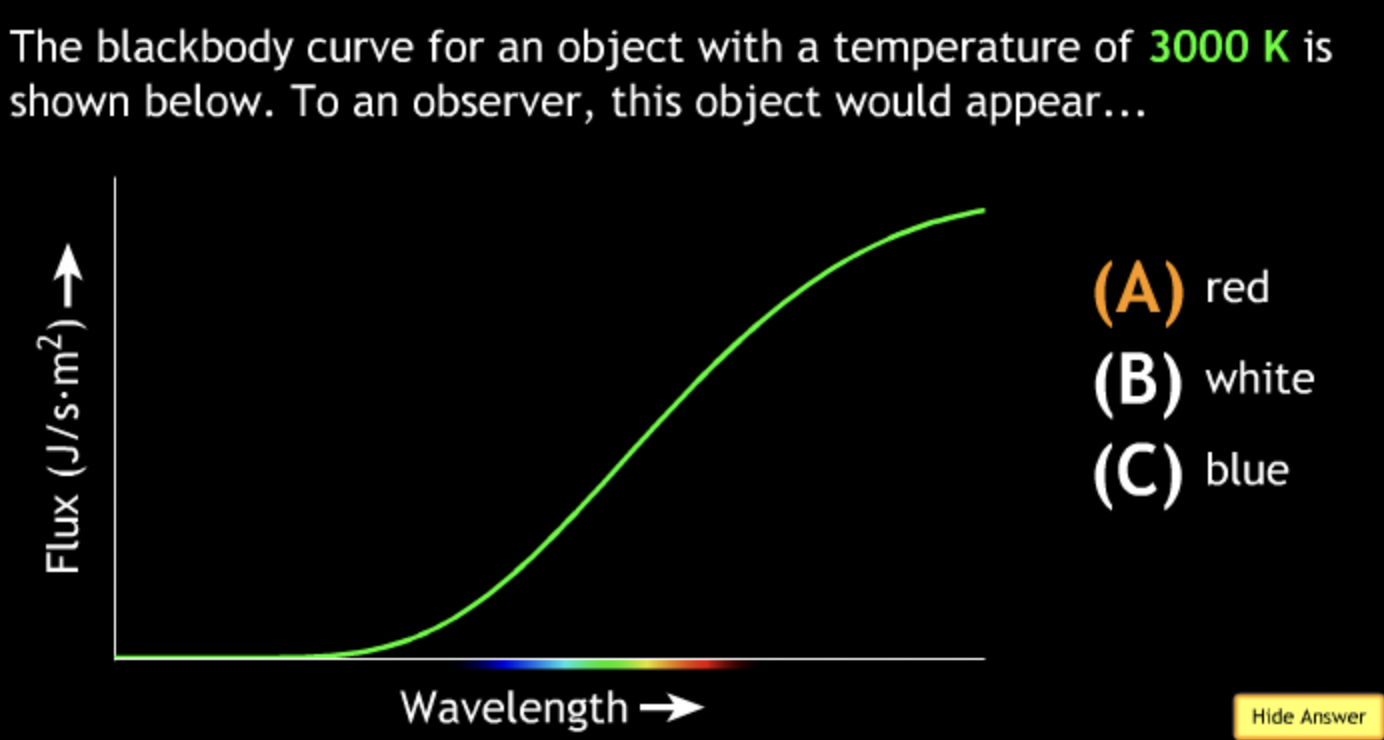
8000K → white
30000K? → blue
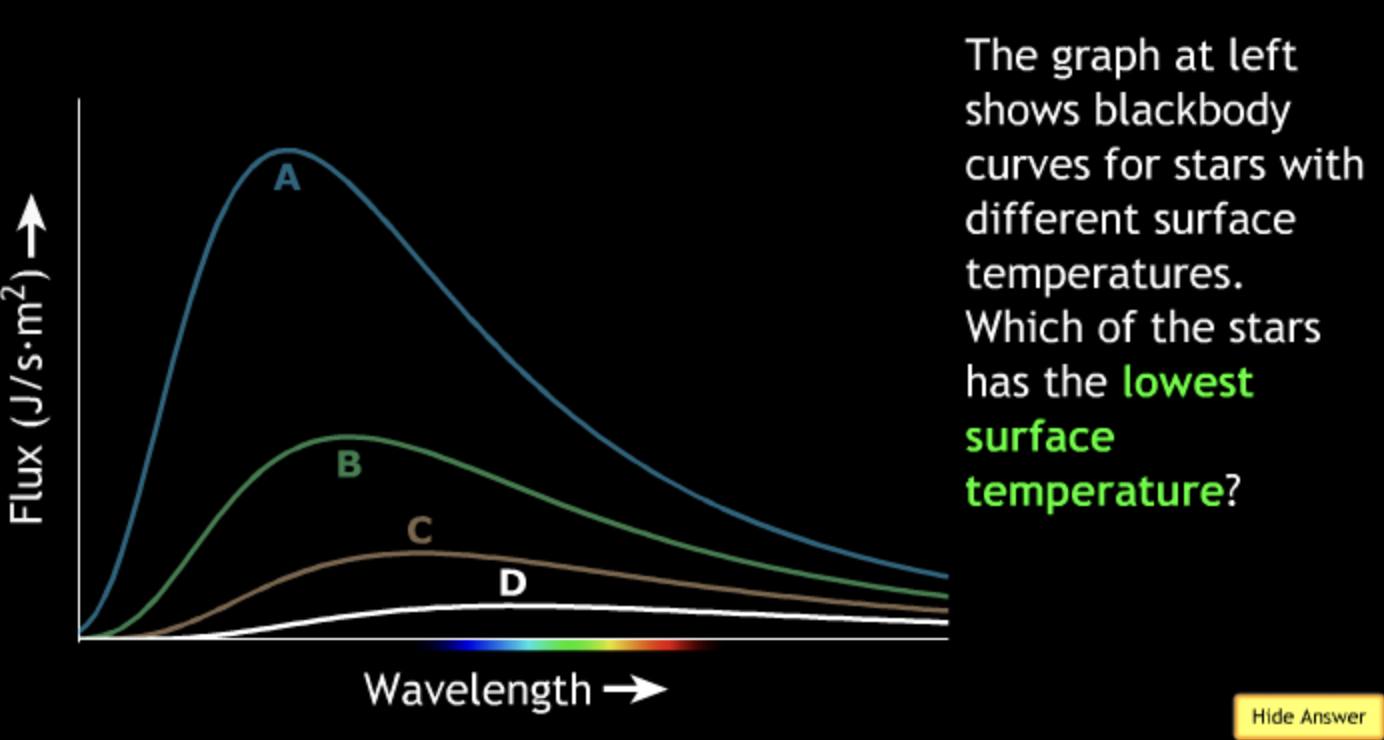
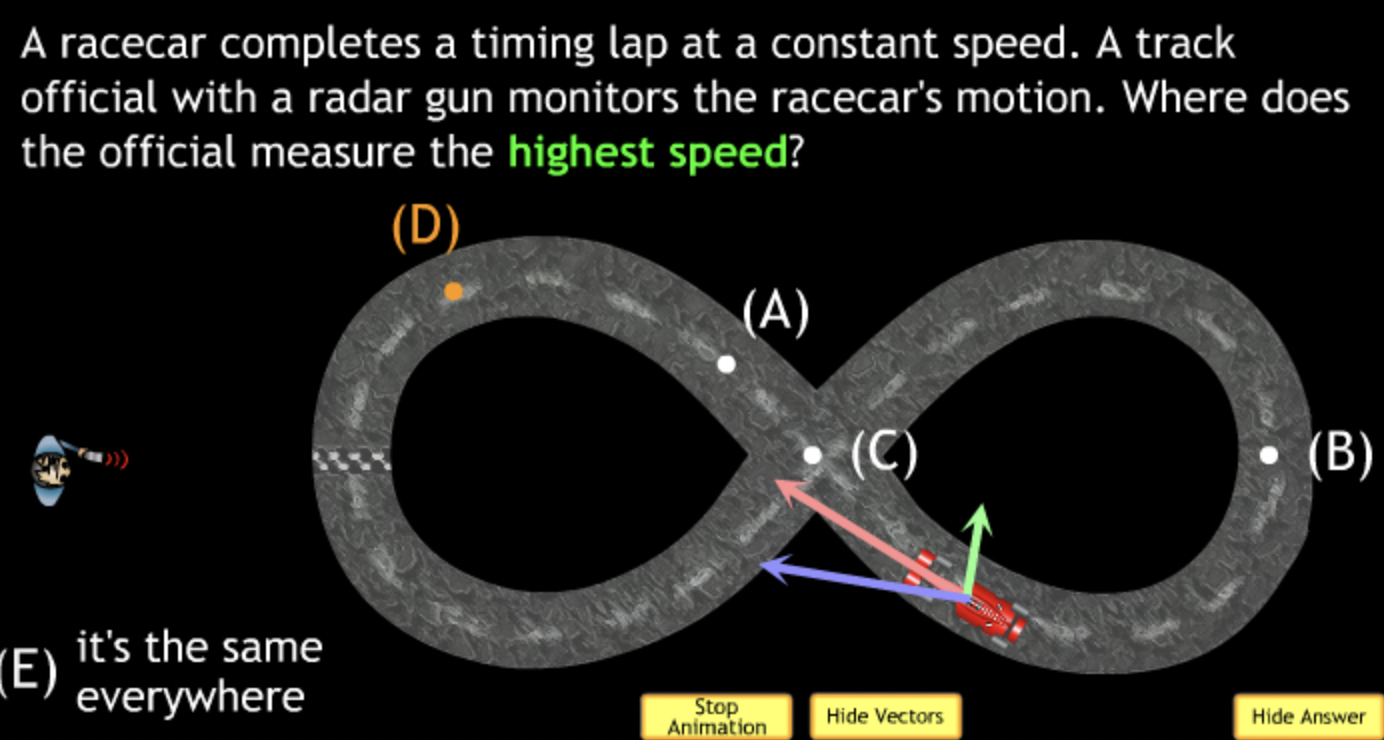
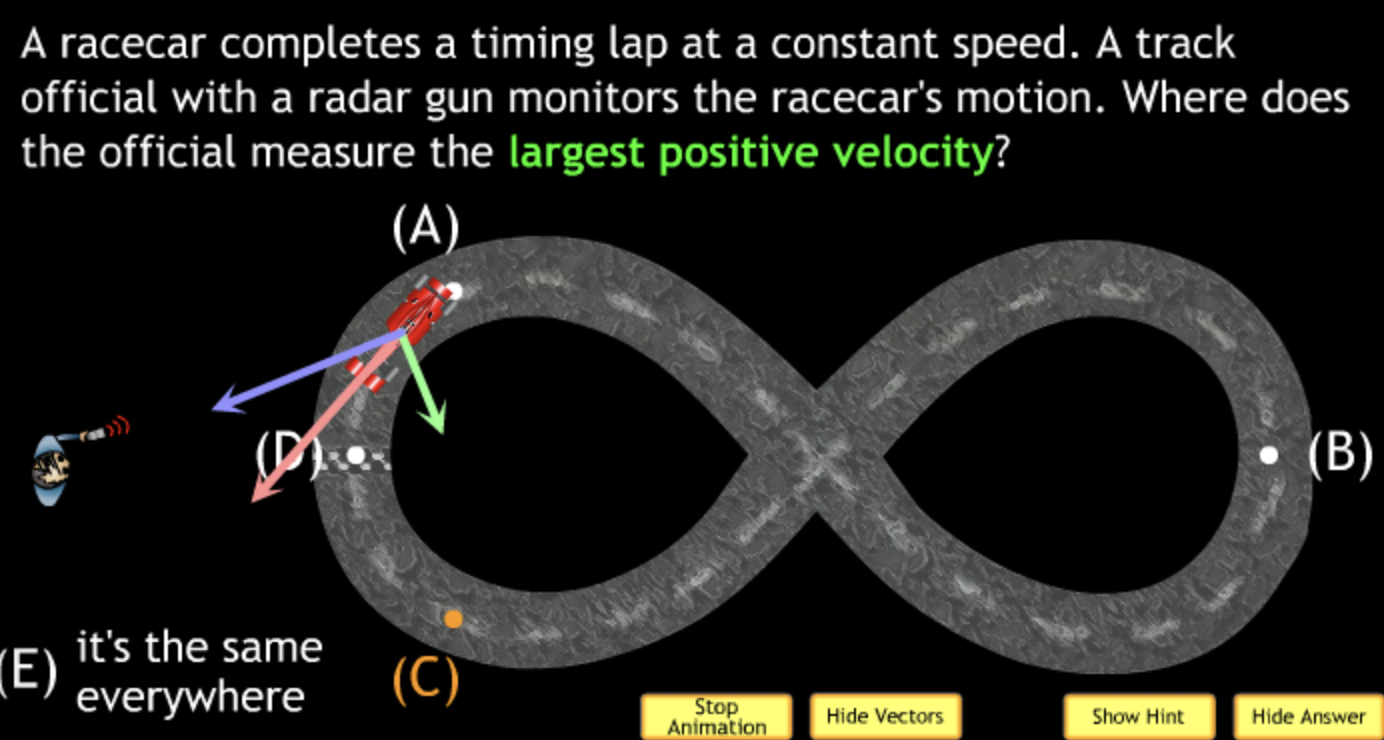
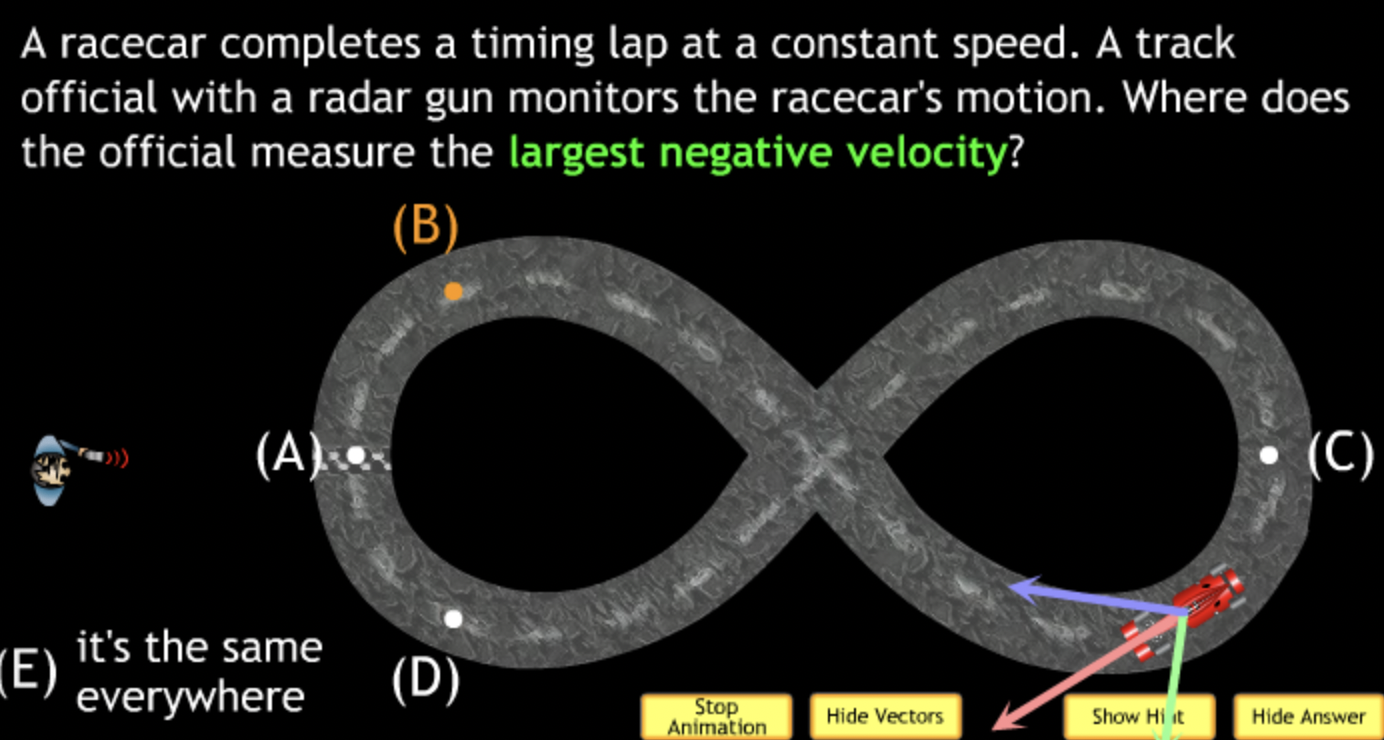
highest? → A
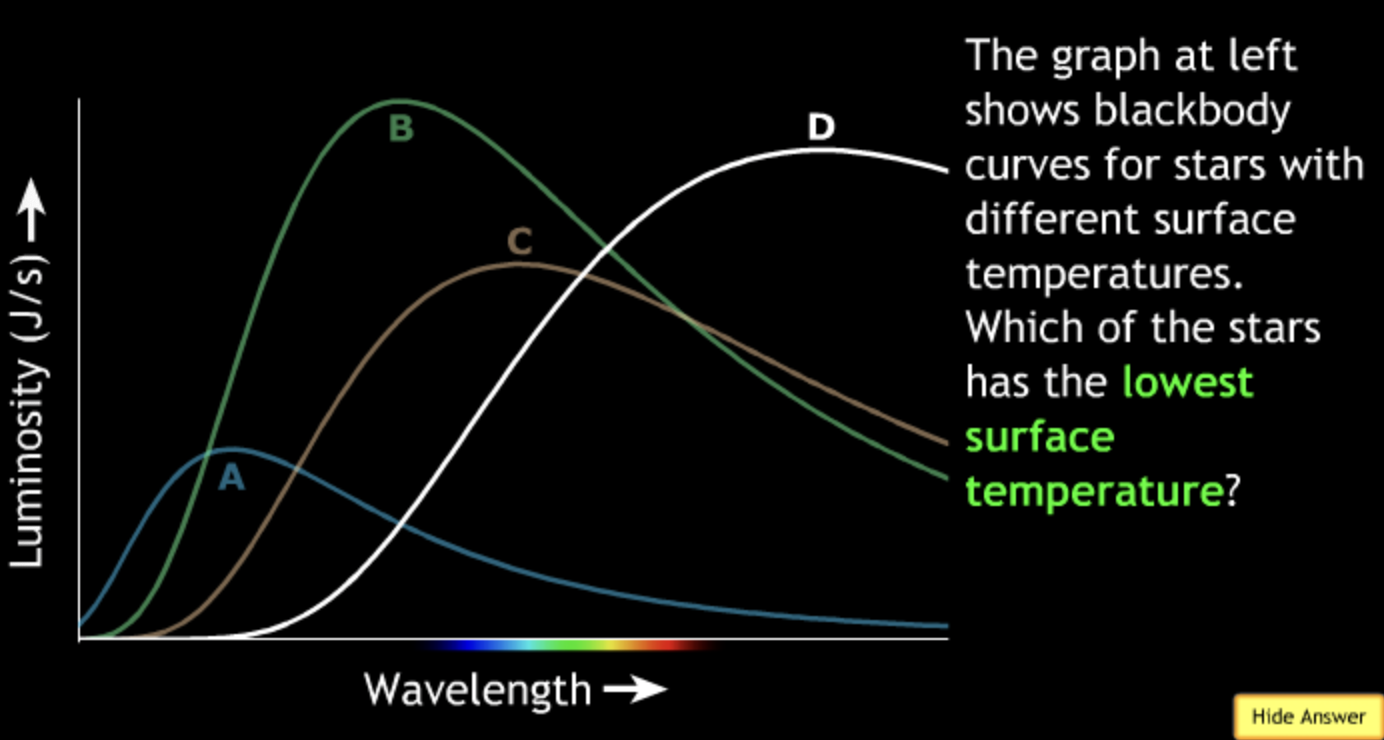
highest? → A
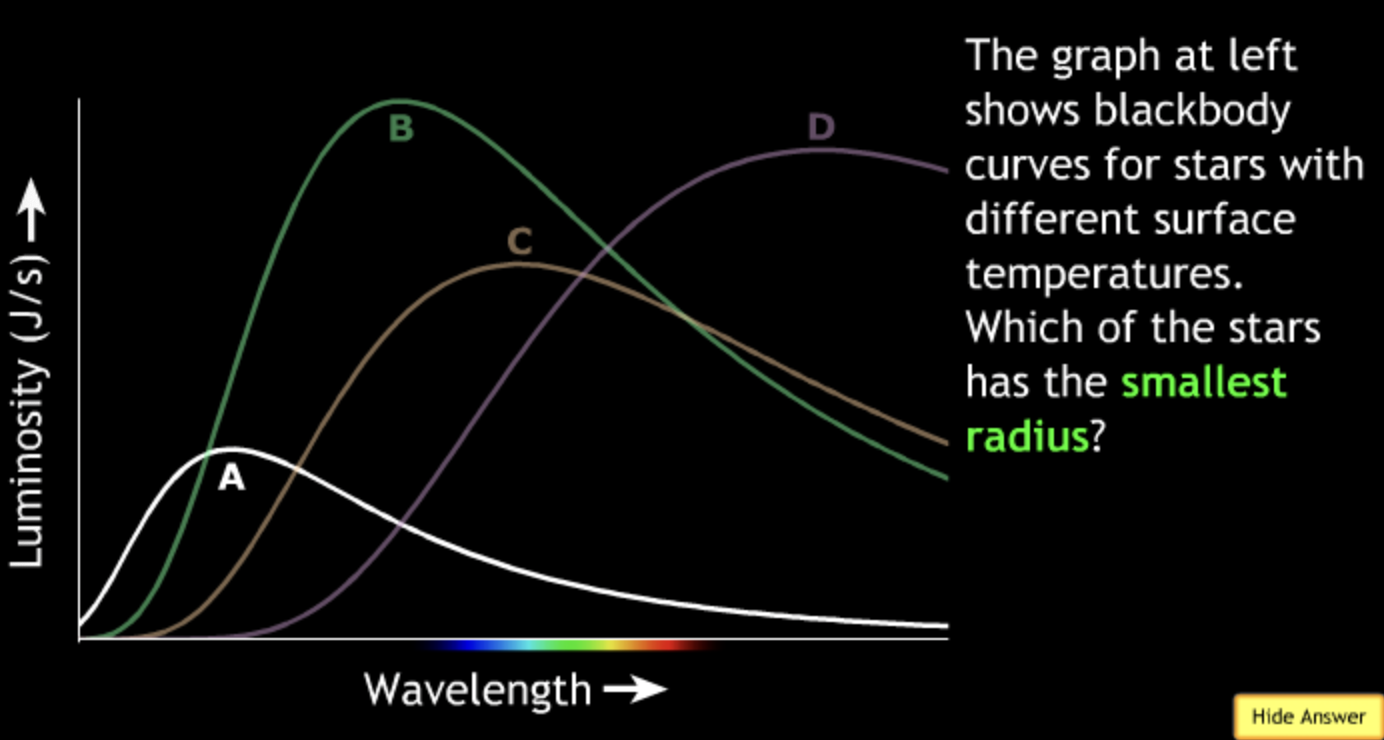
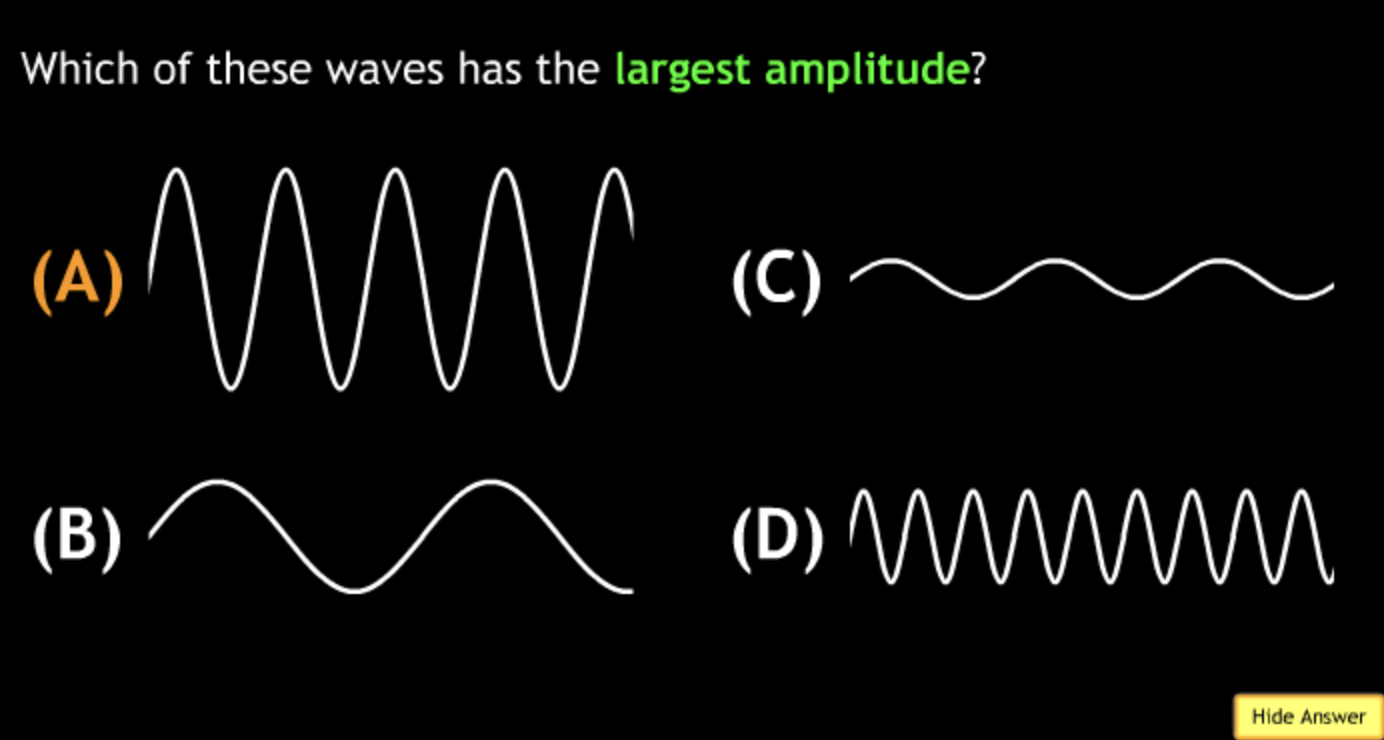
largest? → D

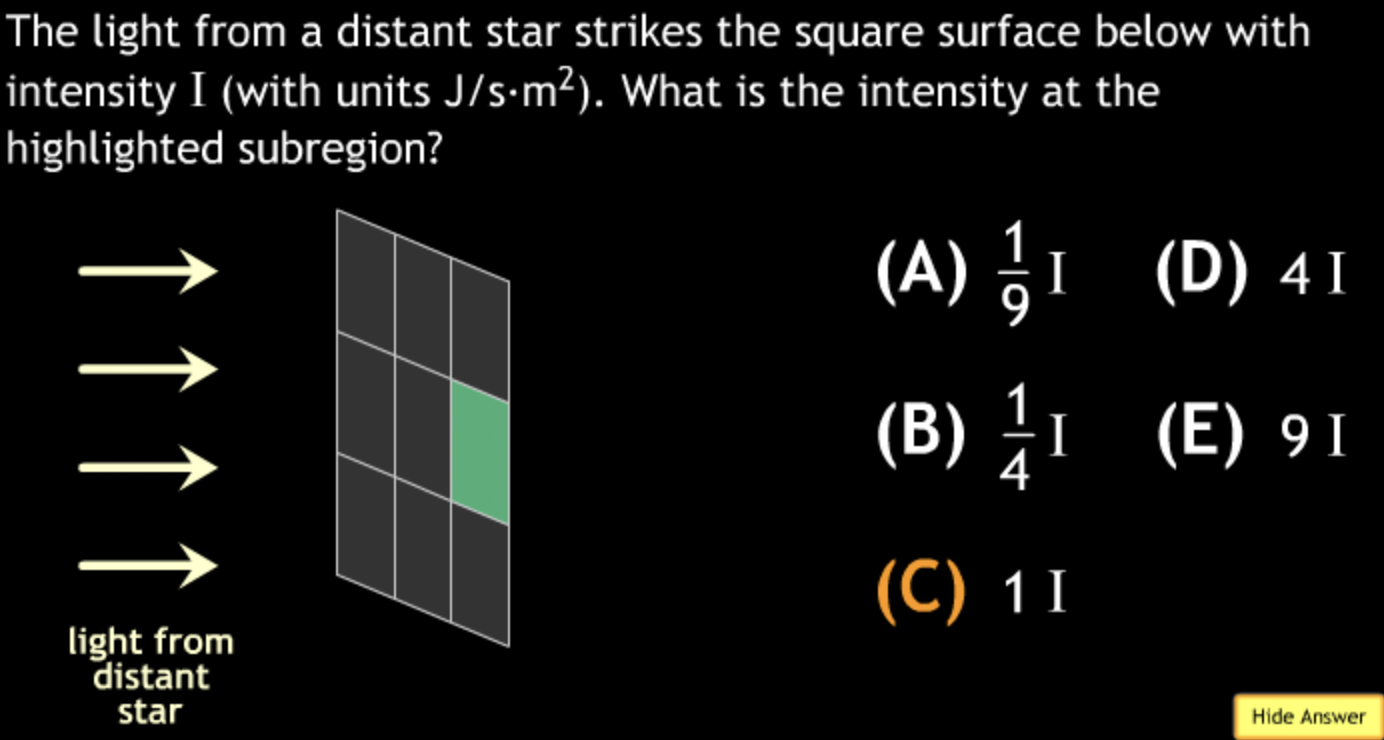
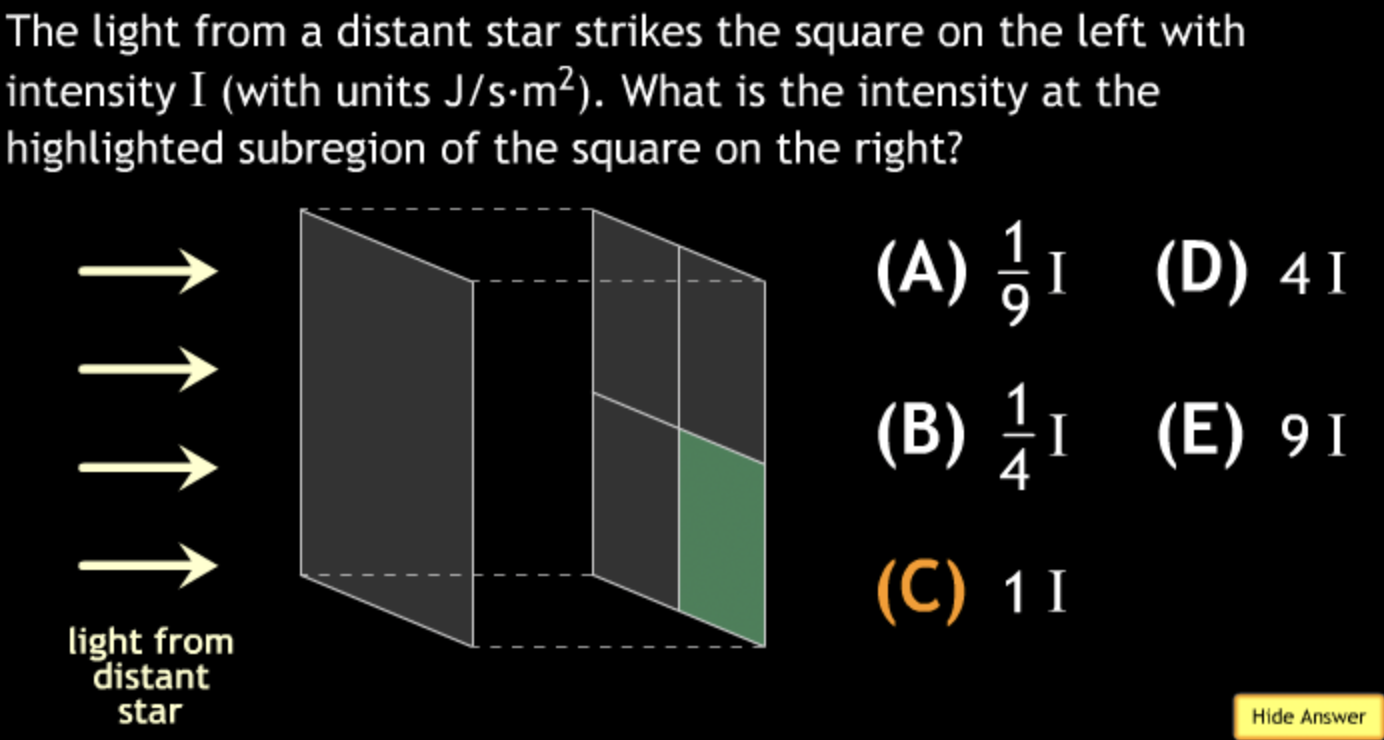
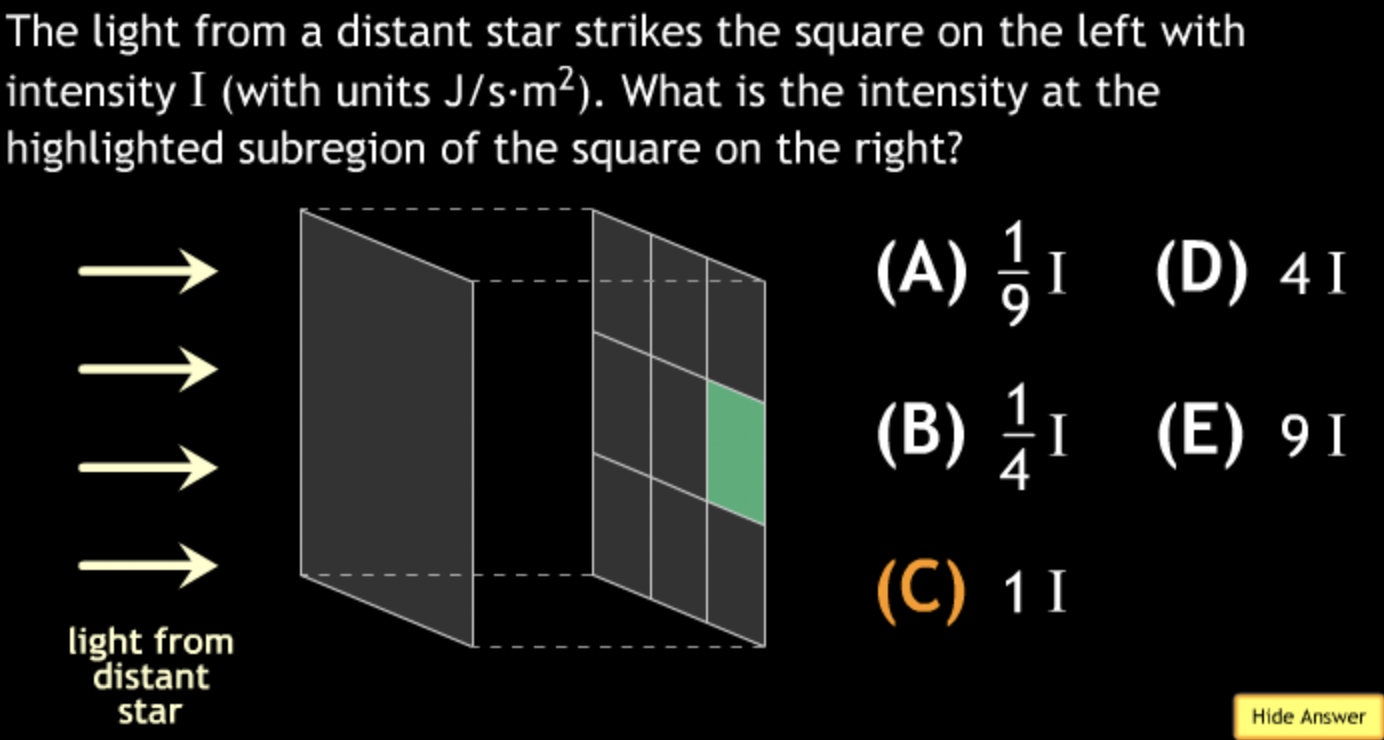
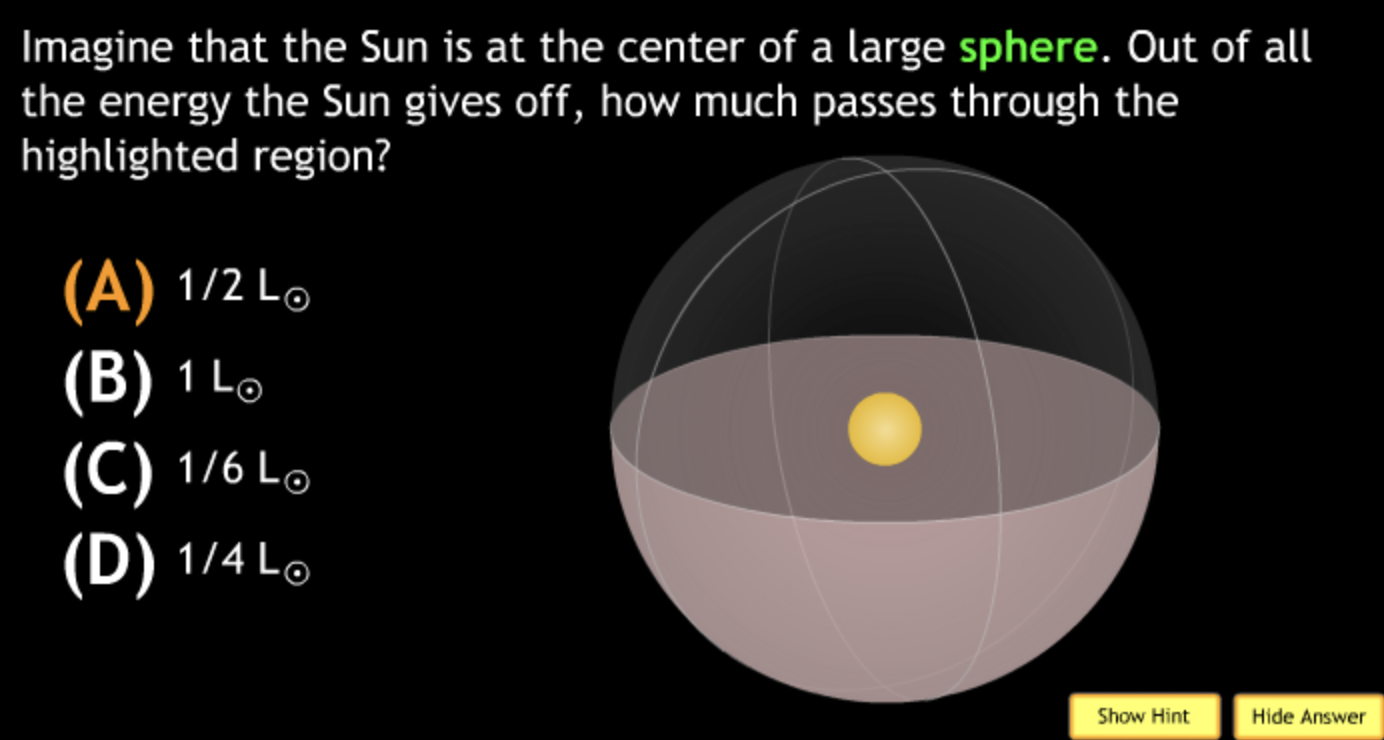
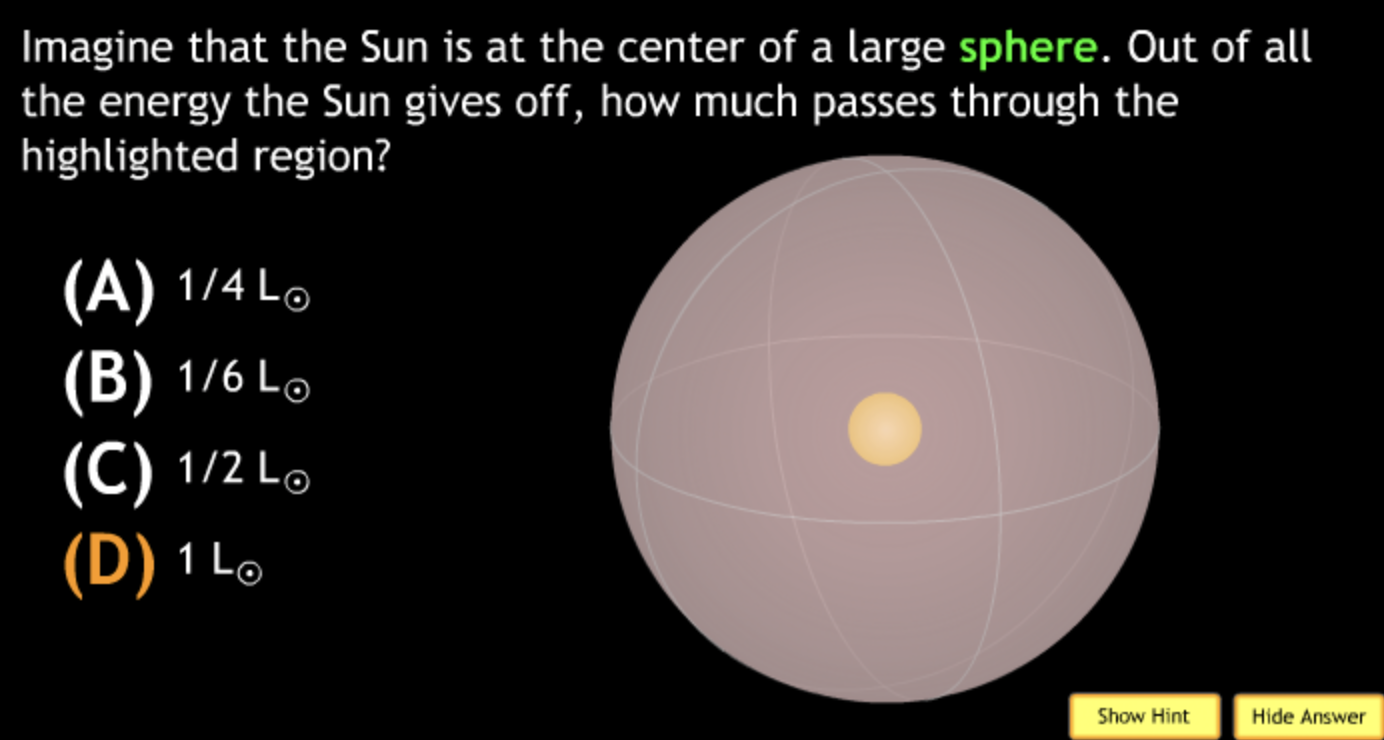
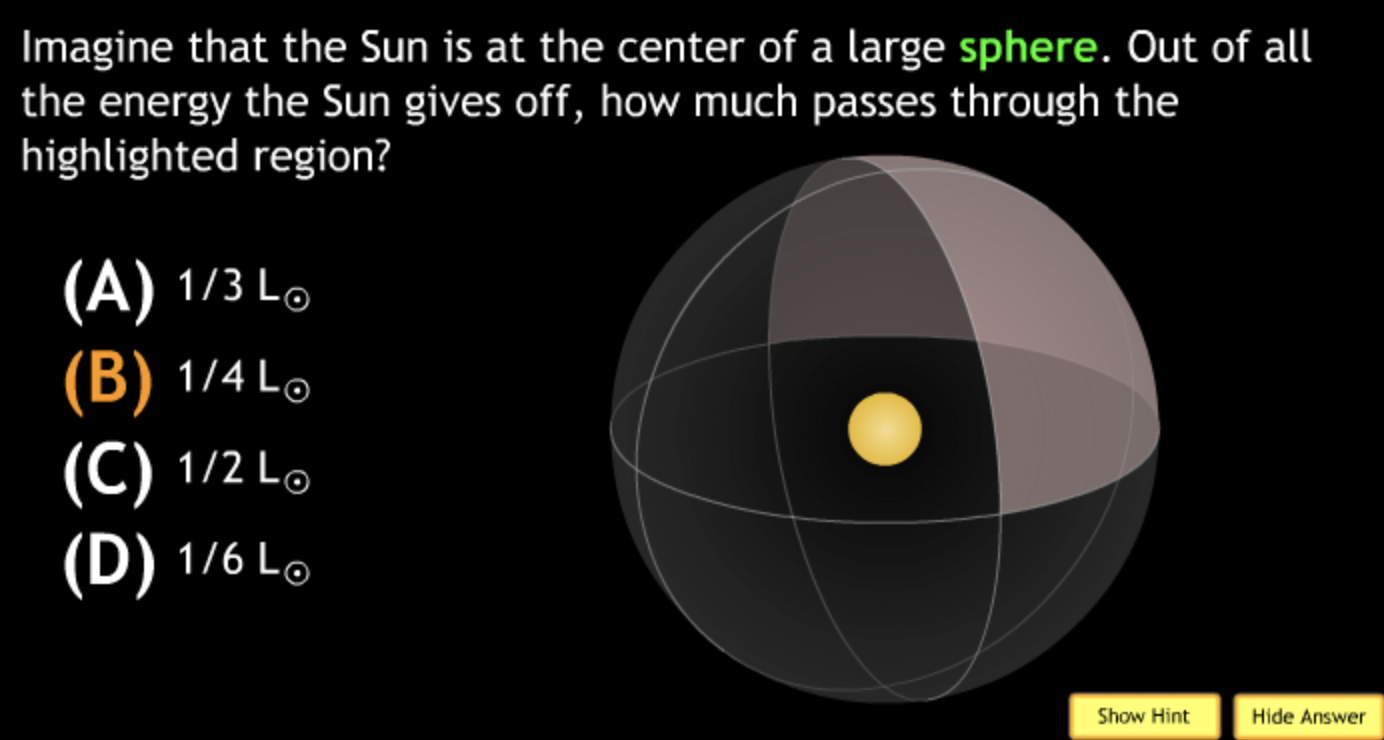
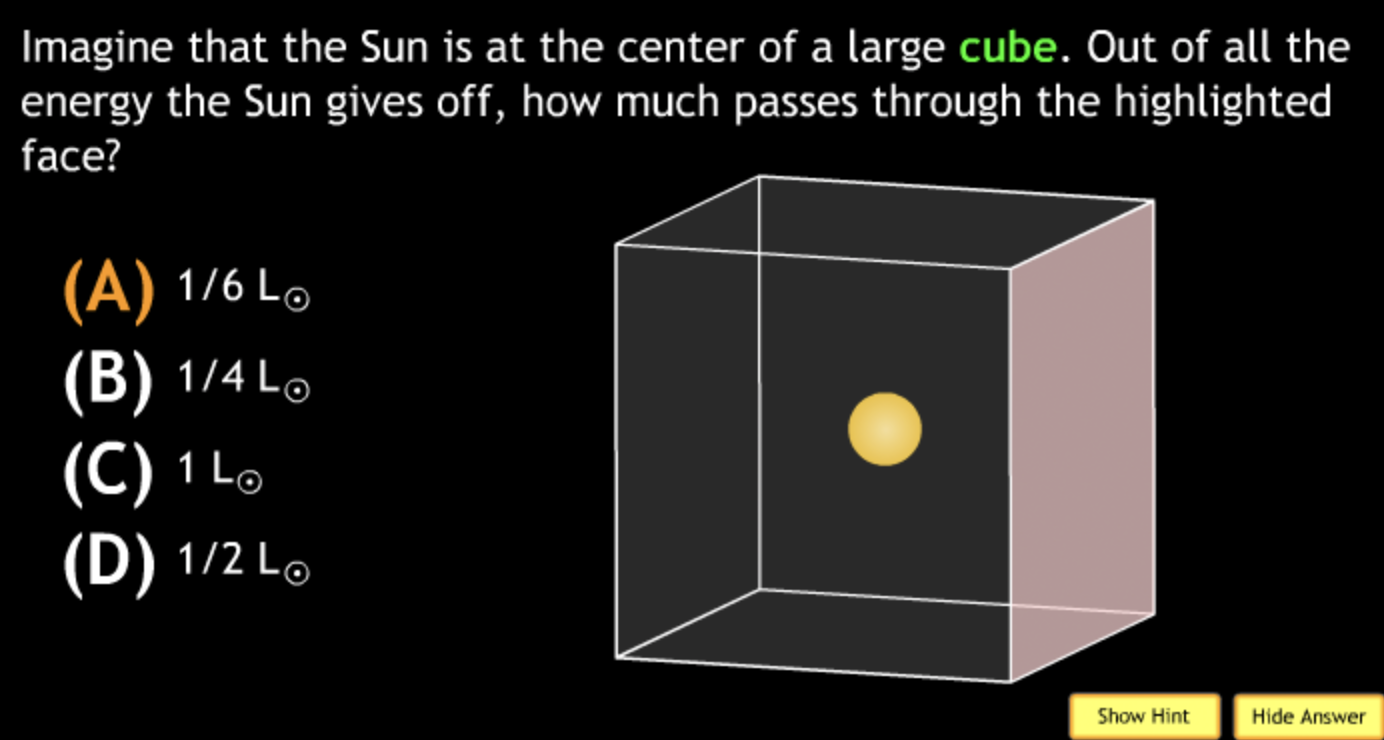
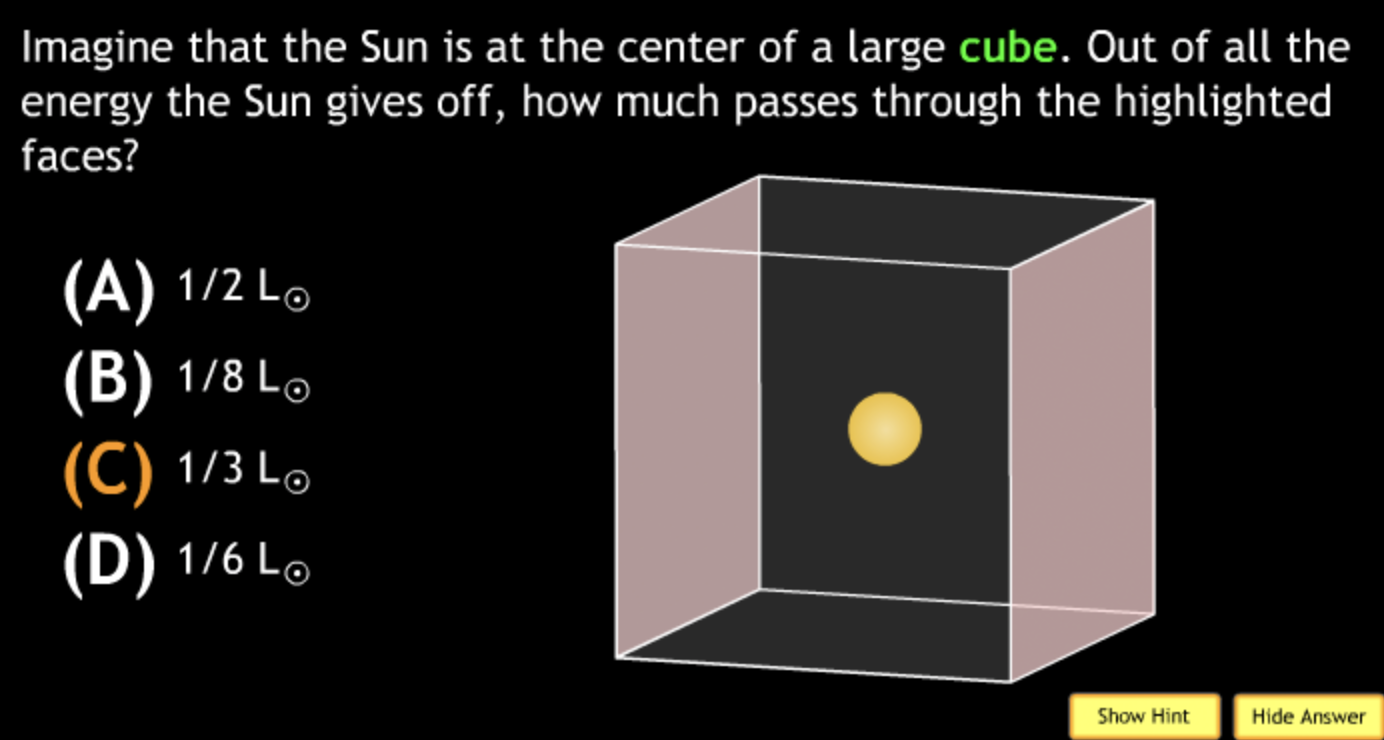

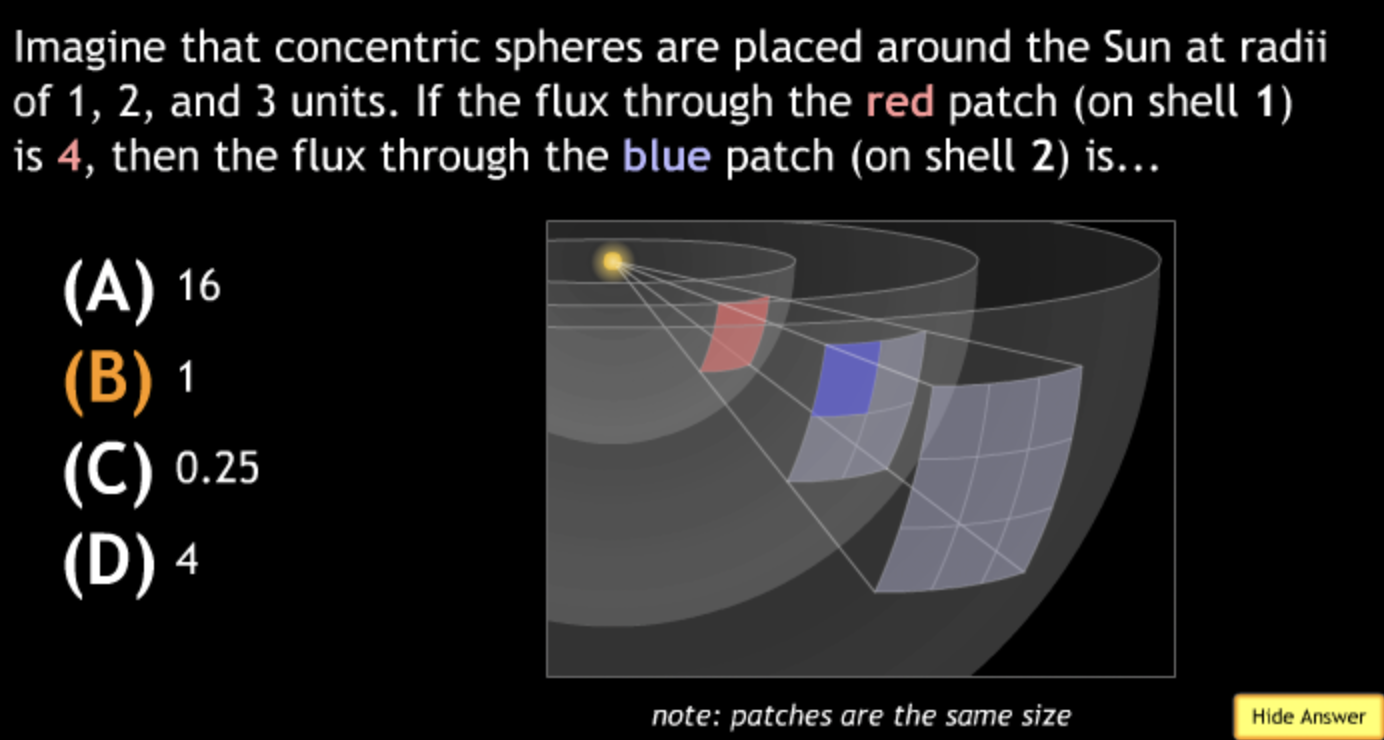
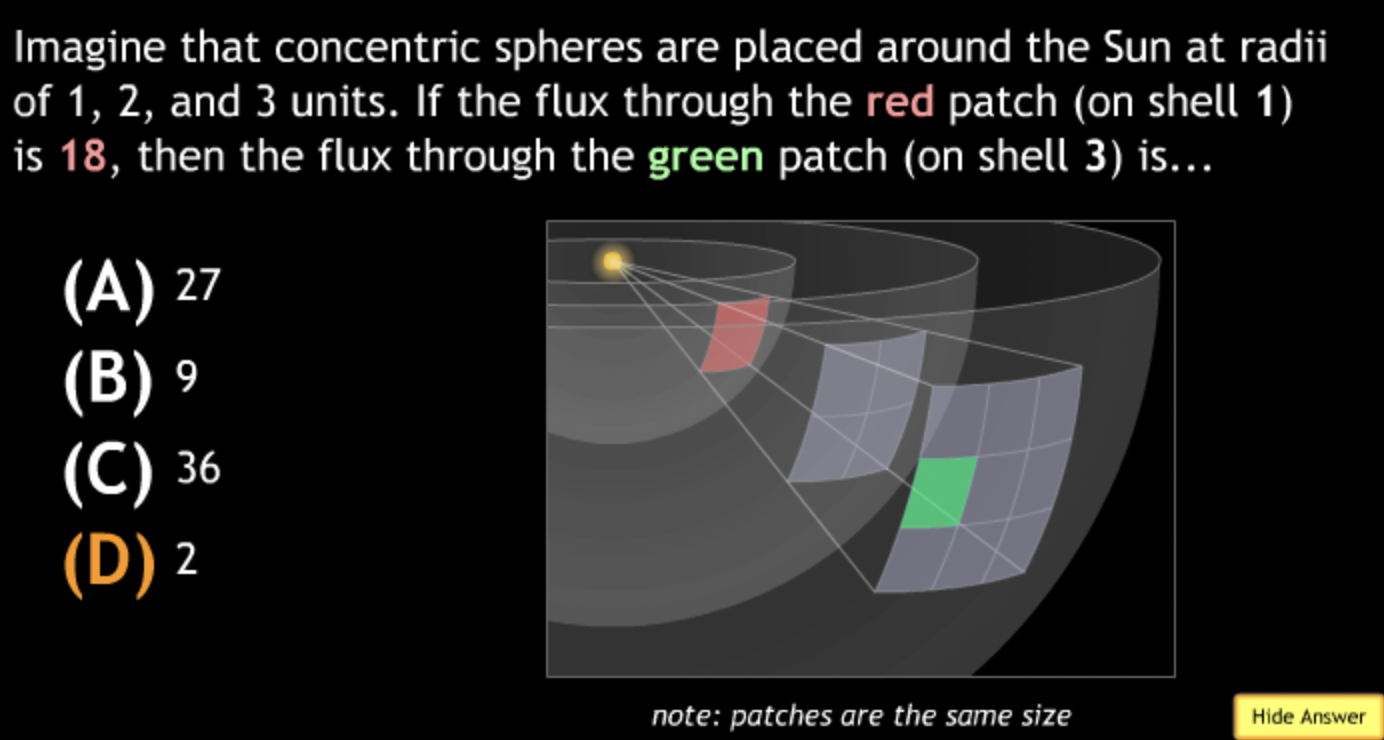
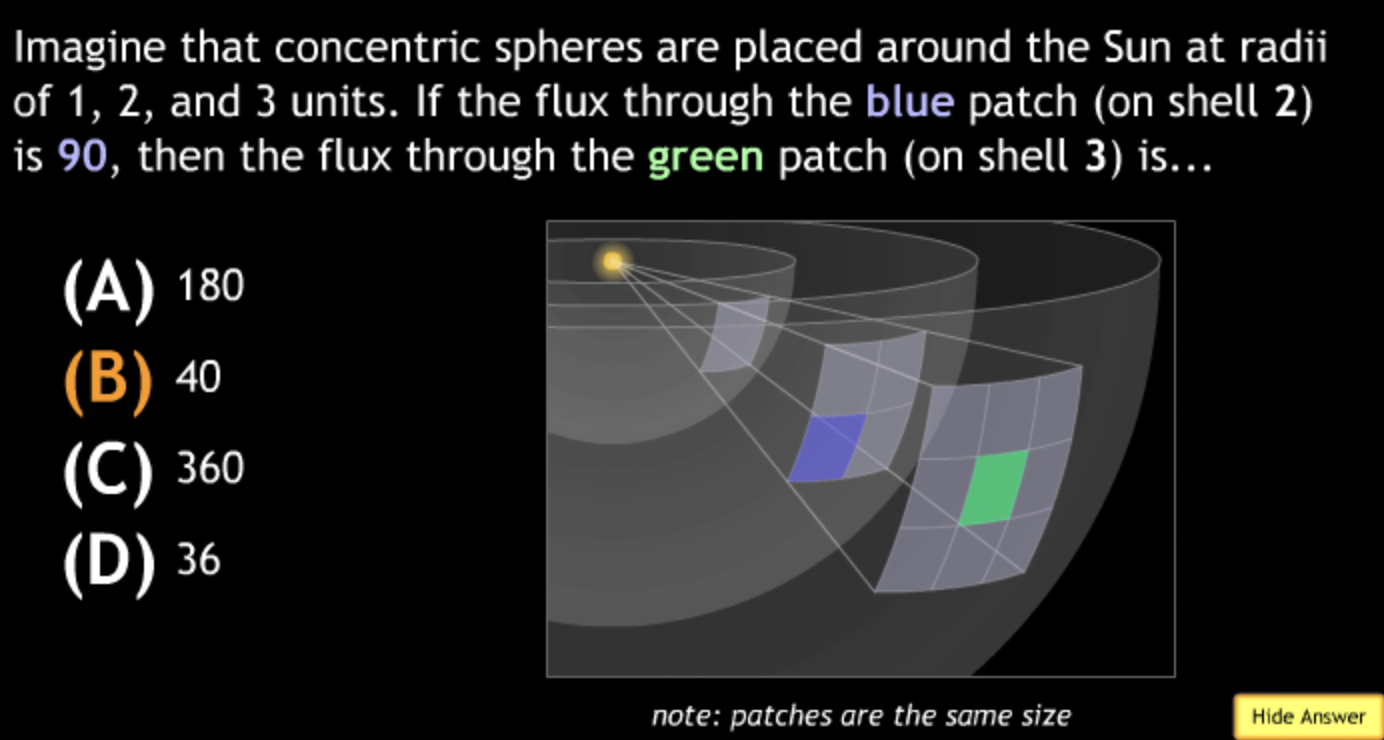
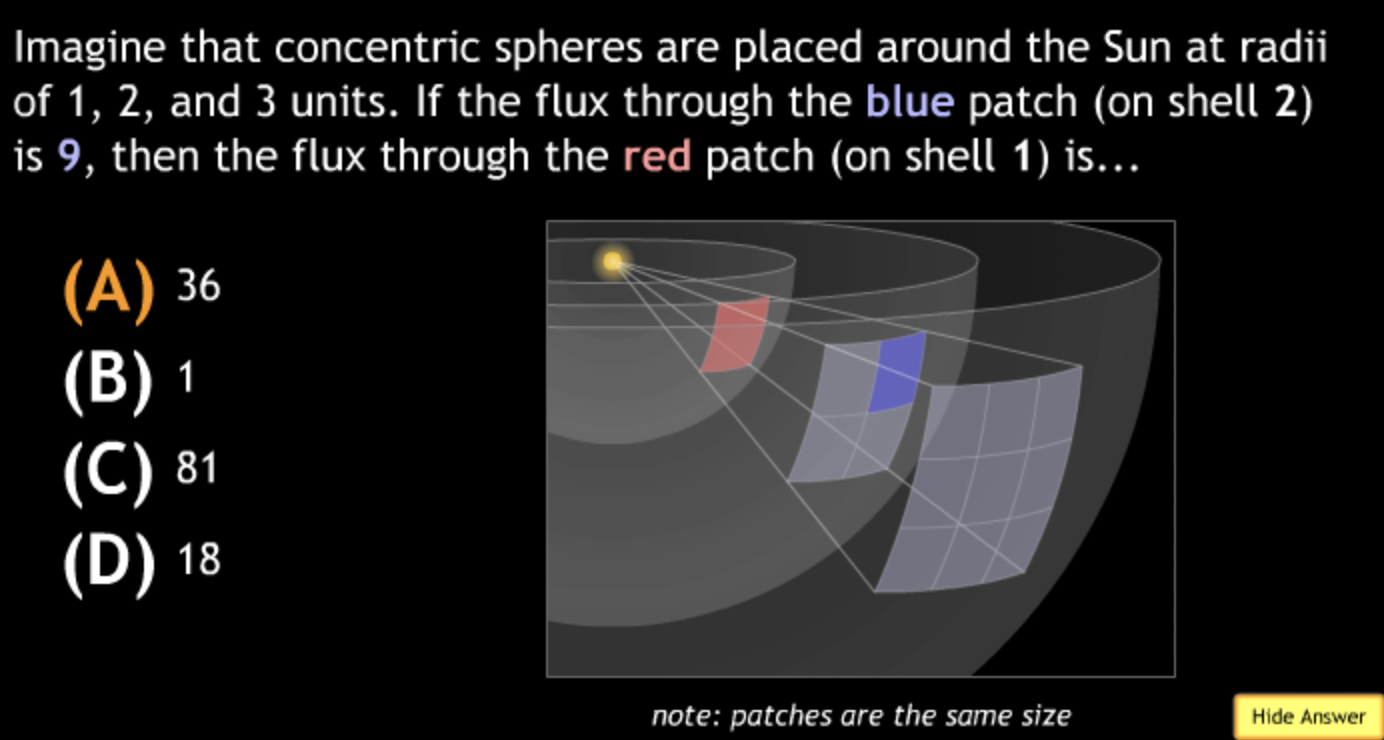
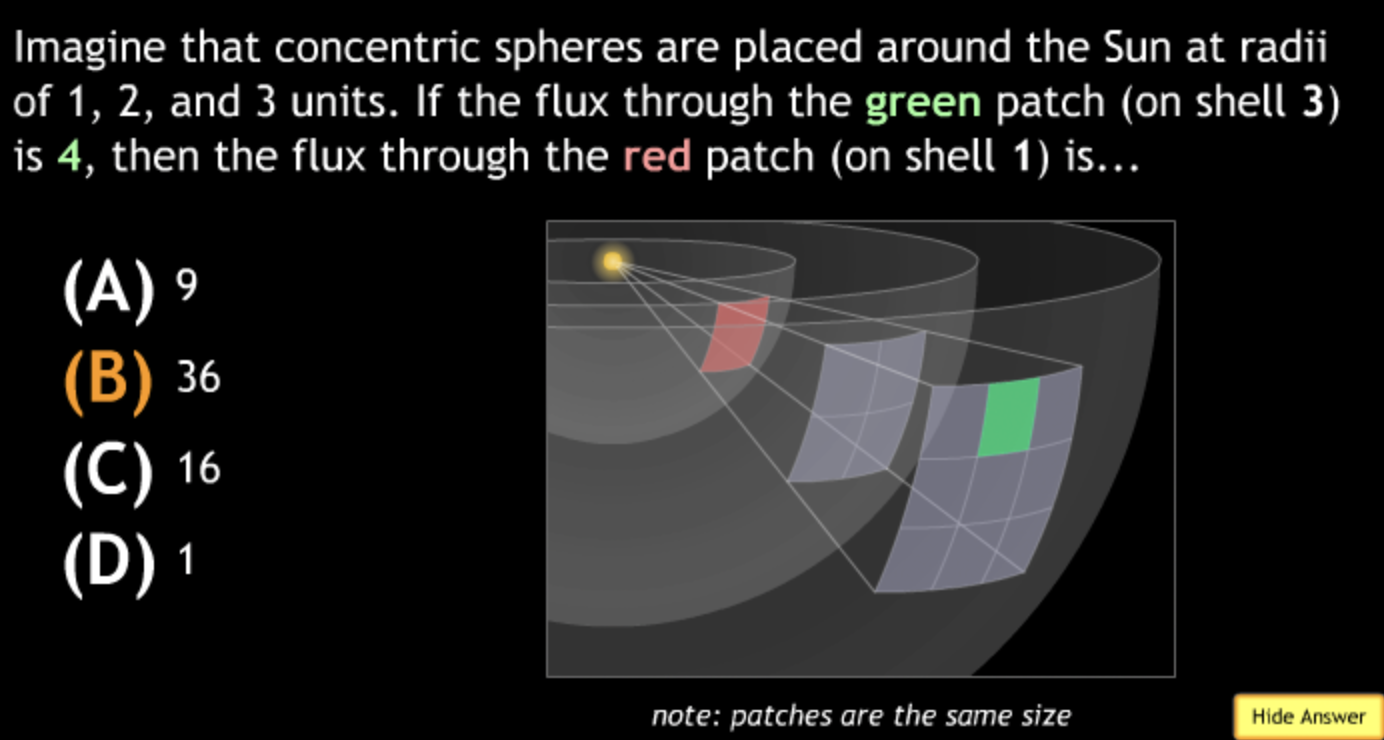
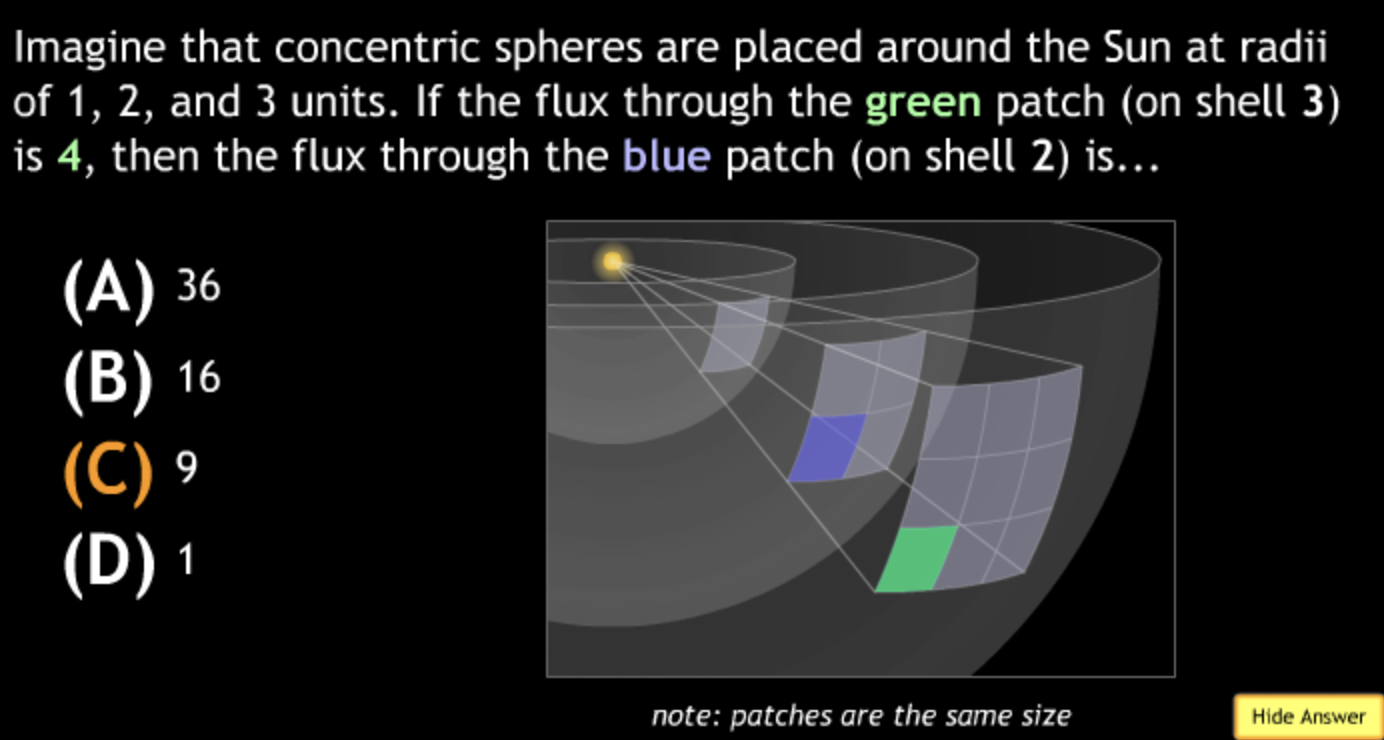
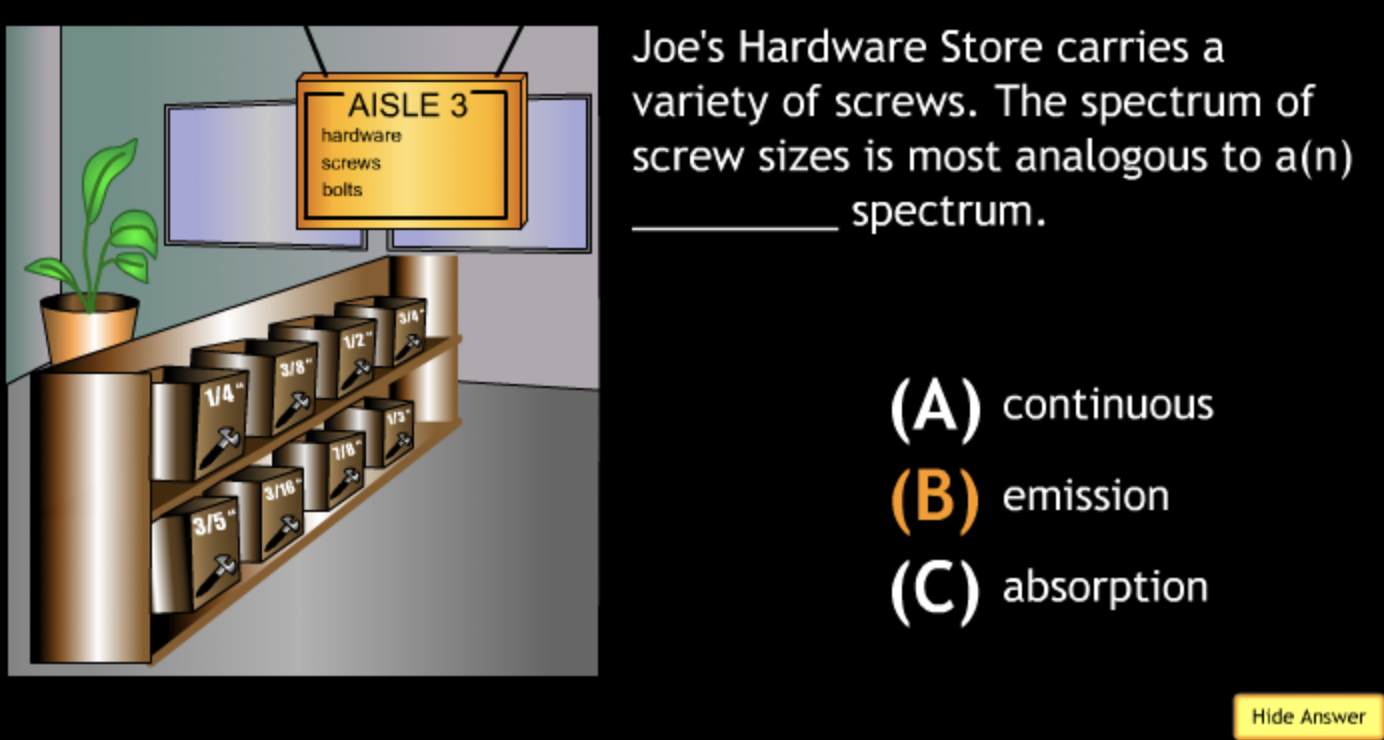


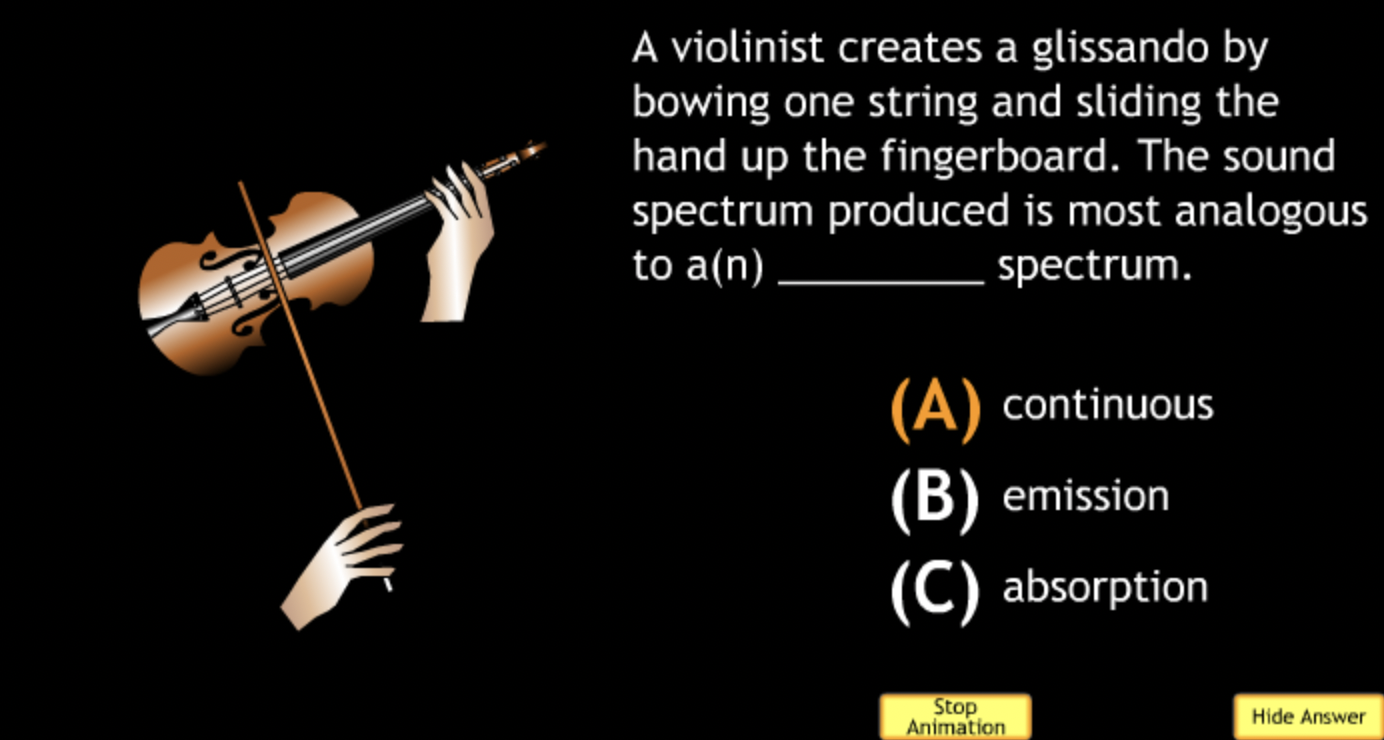
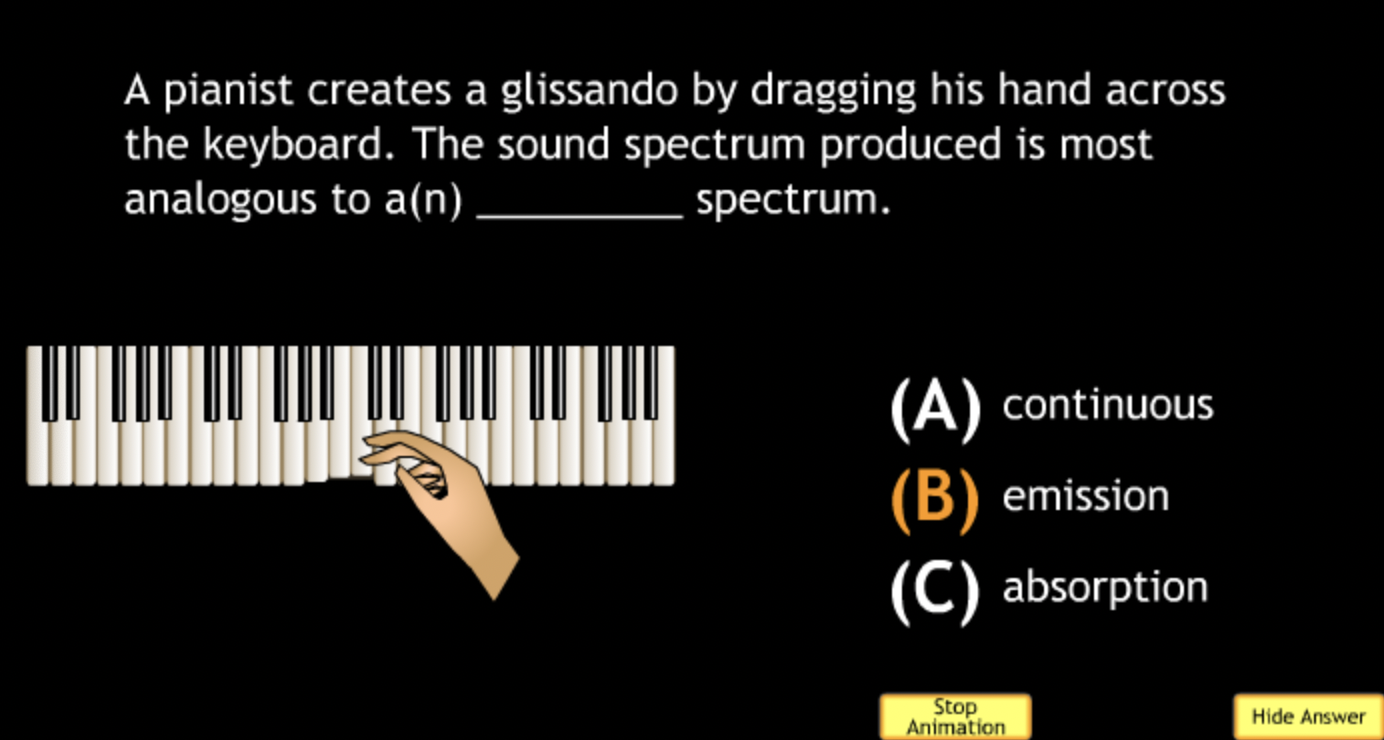
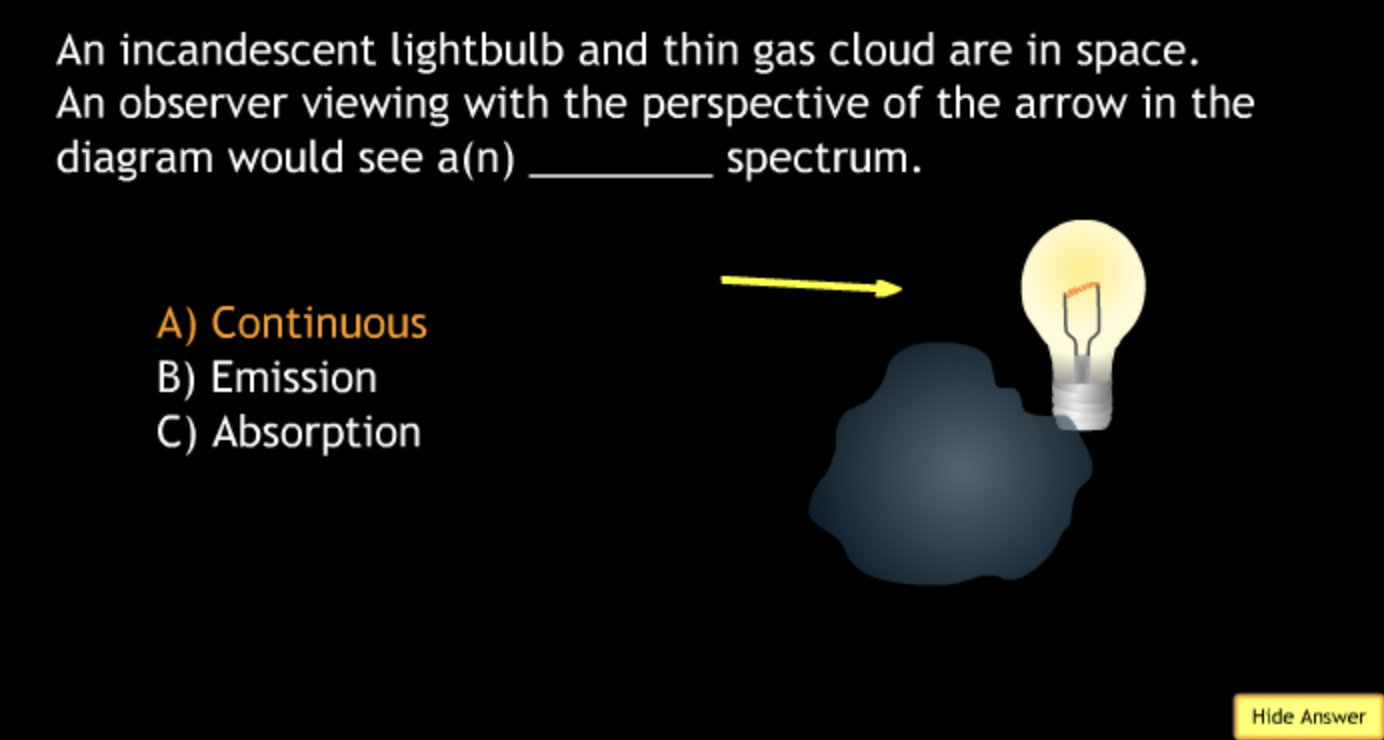
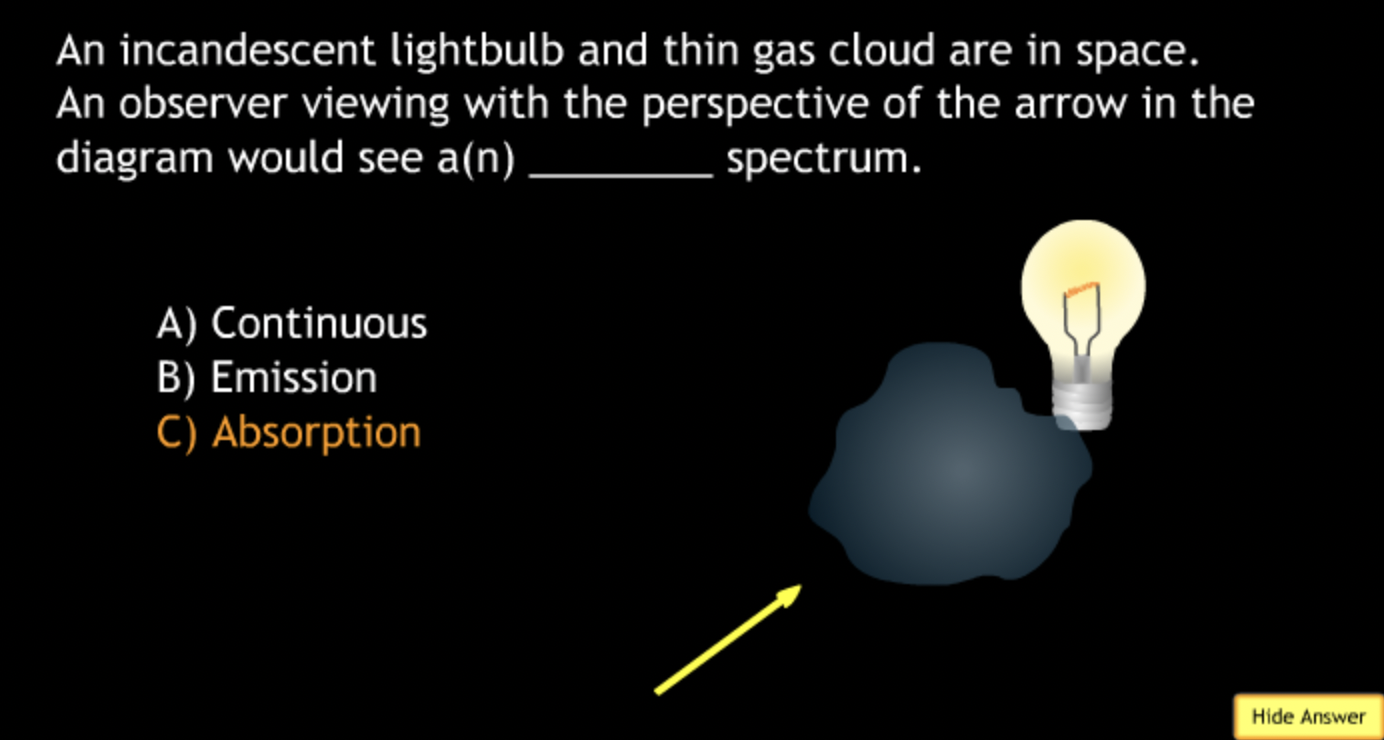
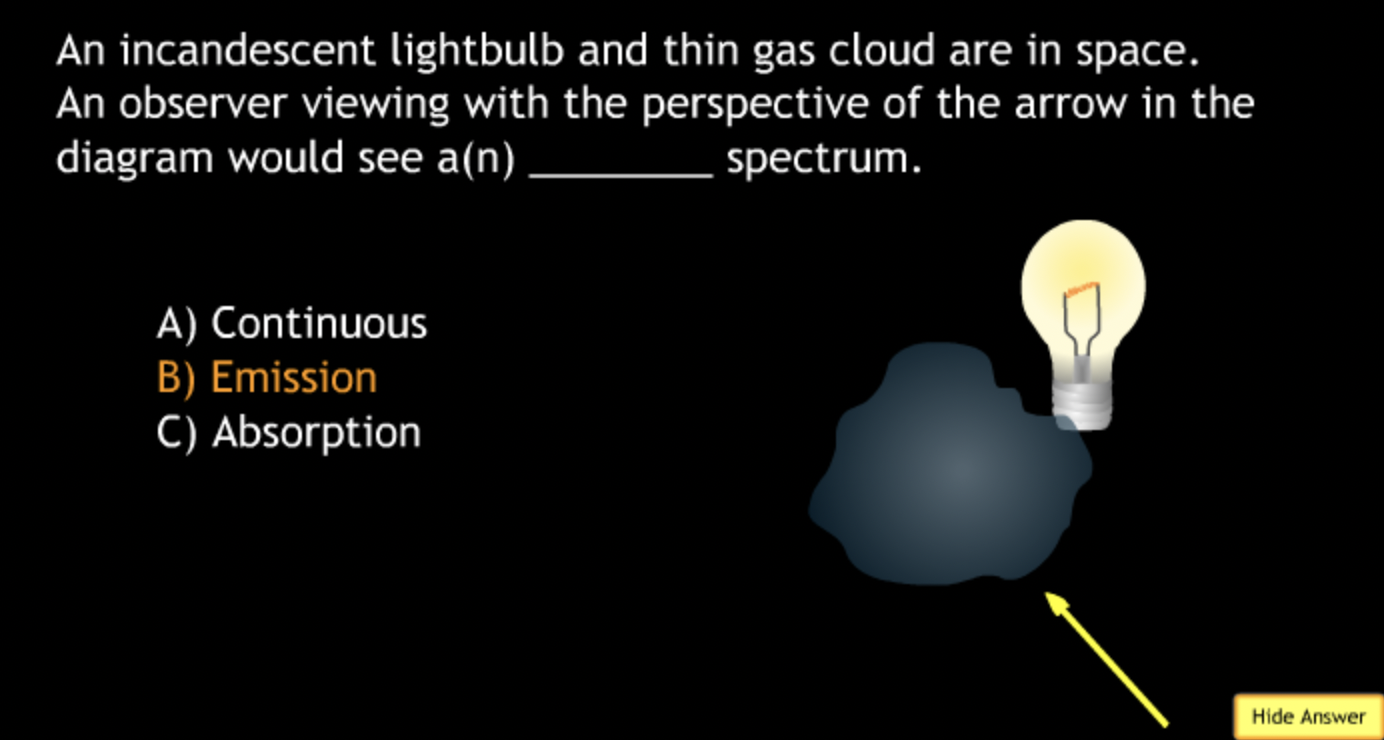
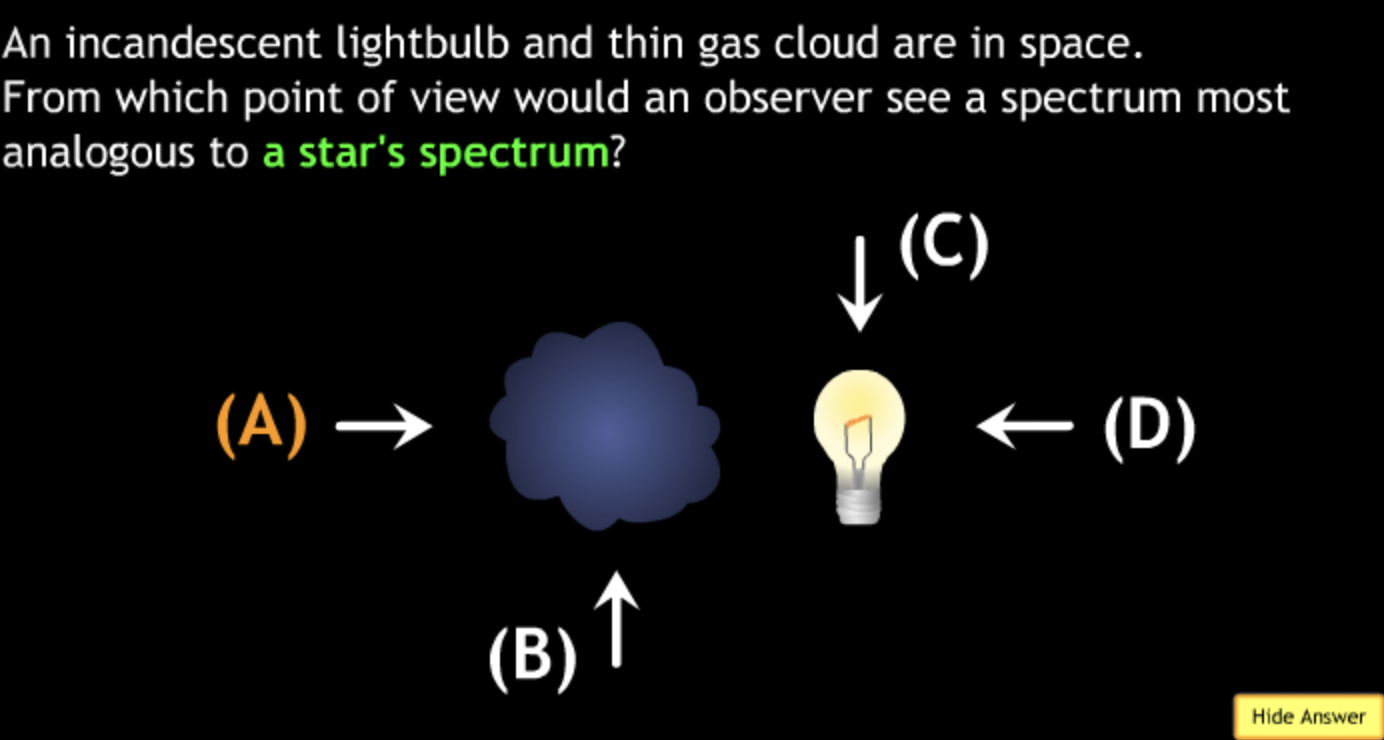
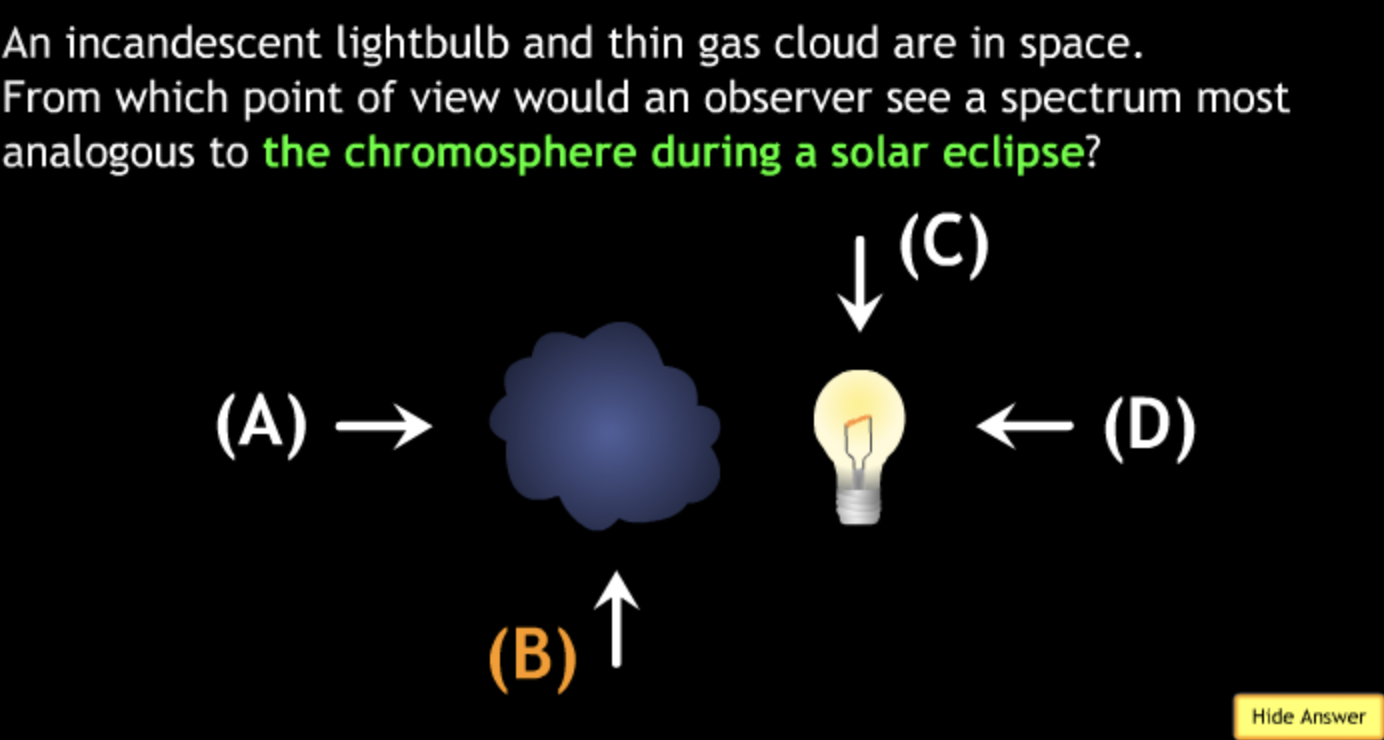

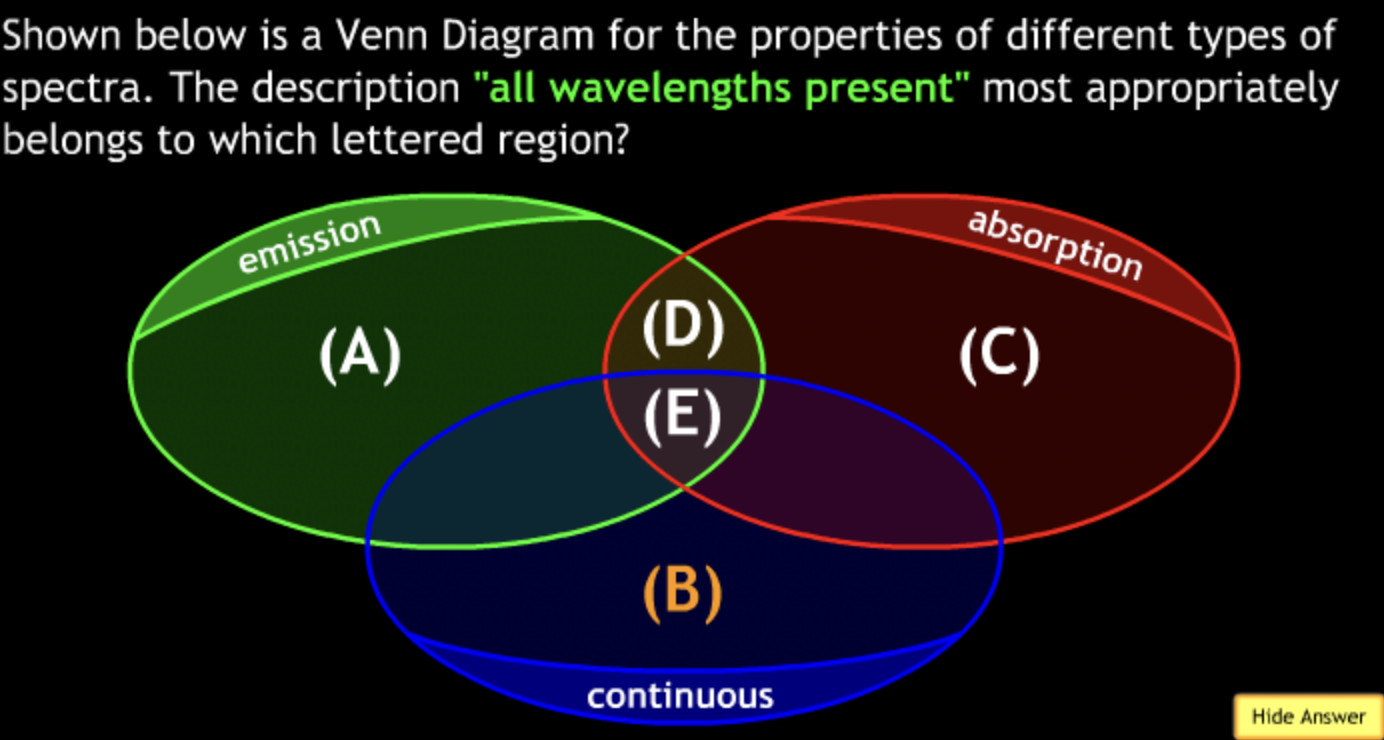
not all wavelengths present? → D
produced by the chromosphere (as seen during eclipse)? → A
described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law? → B
described by Kirchoff’s Laws? → E
produced by a hot dense substance? → B
produced by typical stars? → C
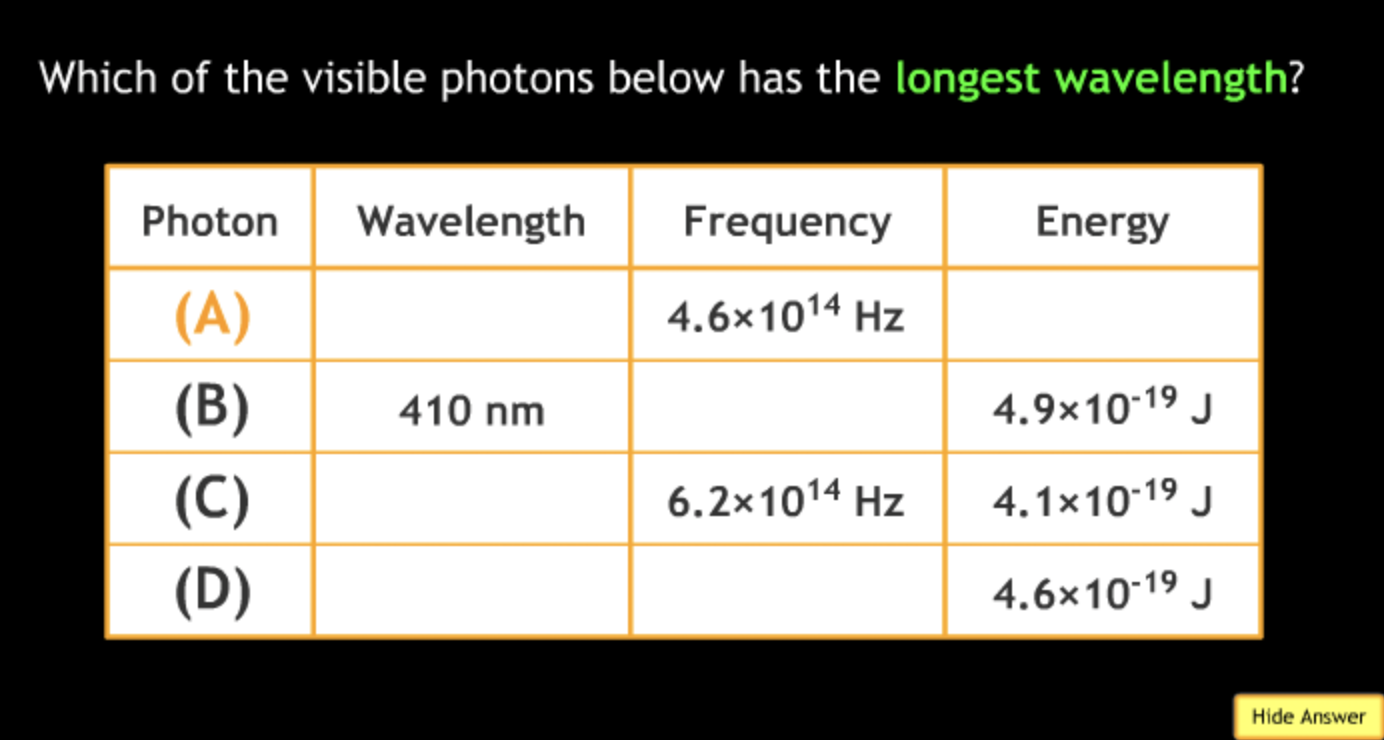
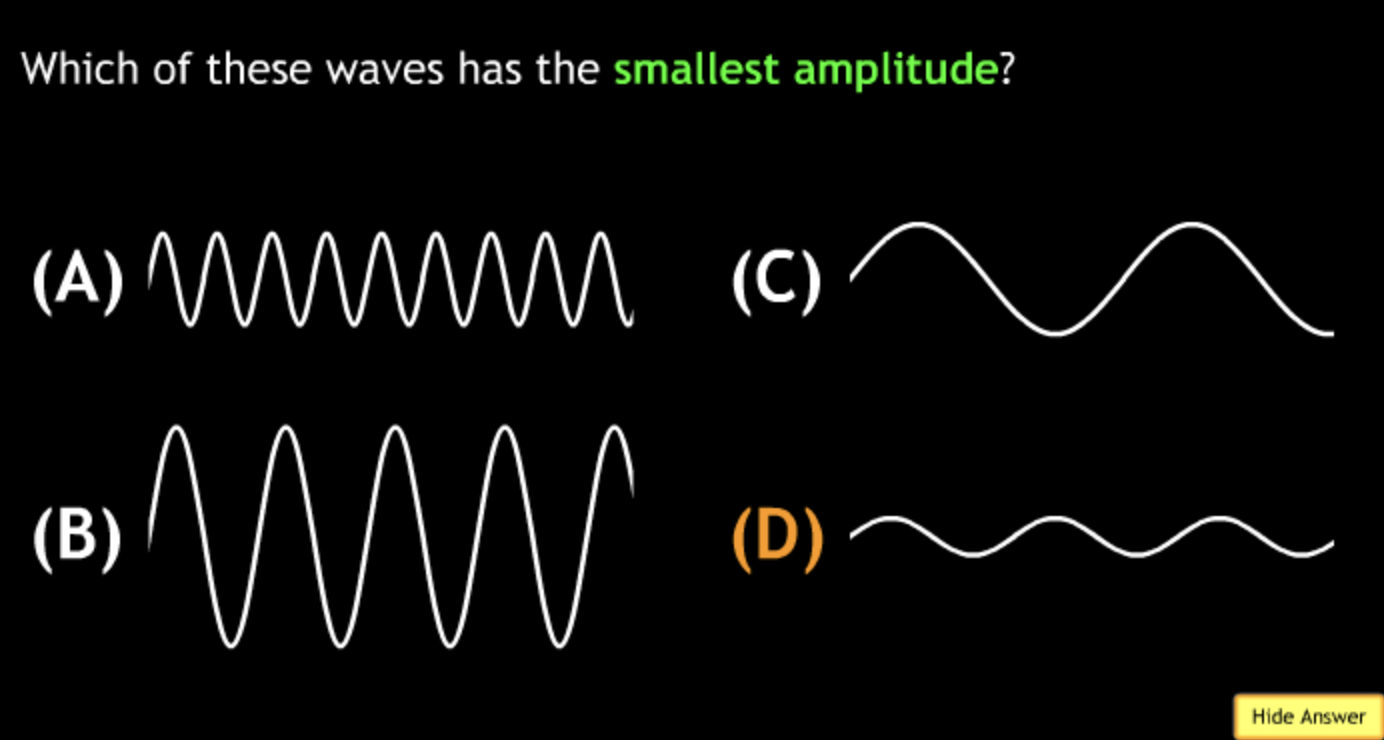
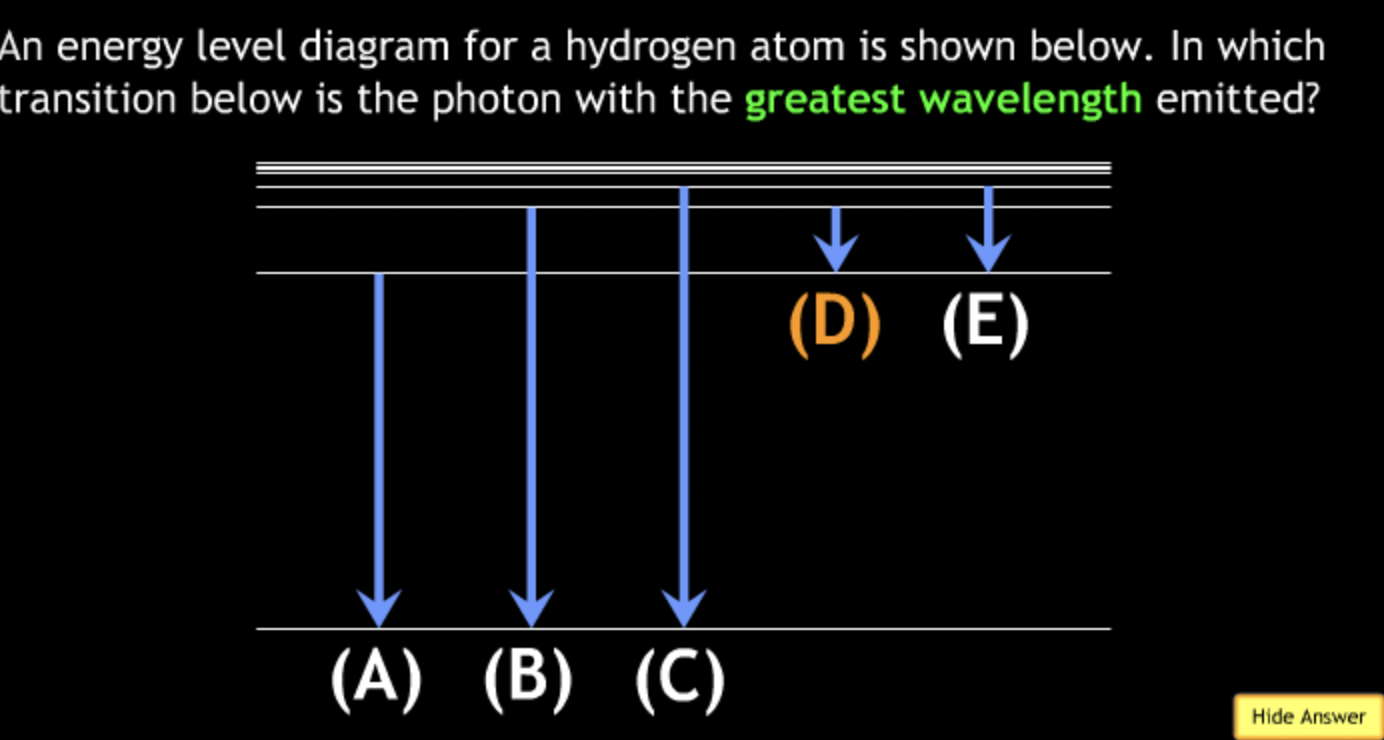
shortest? → B
highest frequency? → B
lowest frequency? → A
greatest energy? → B
least energy? → A
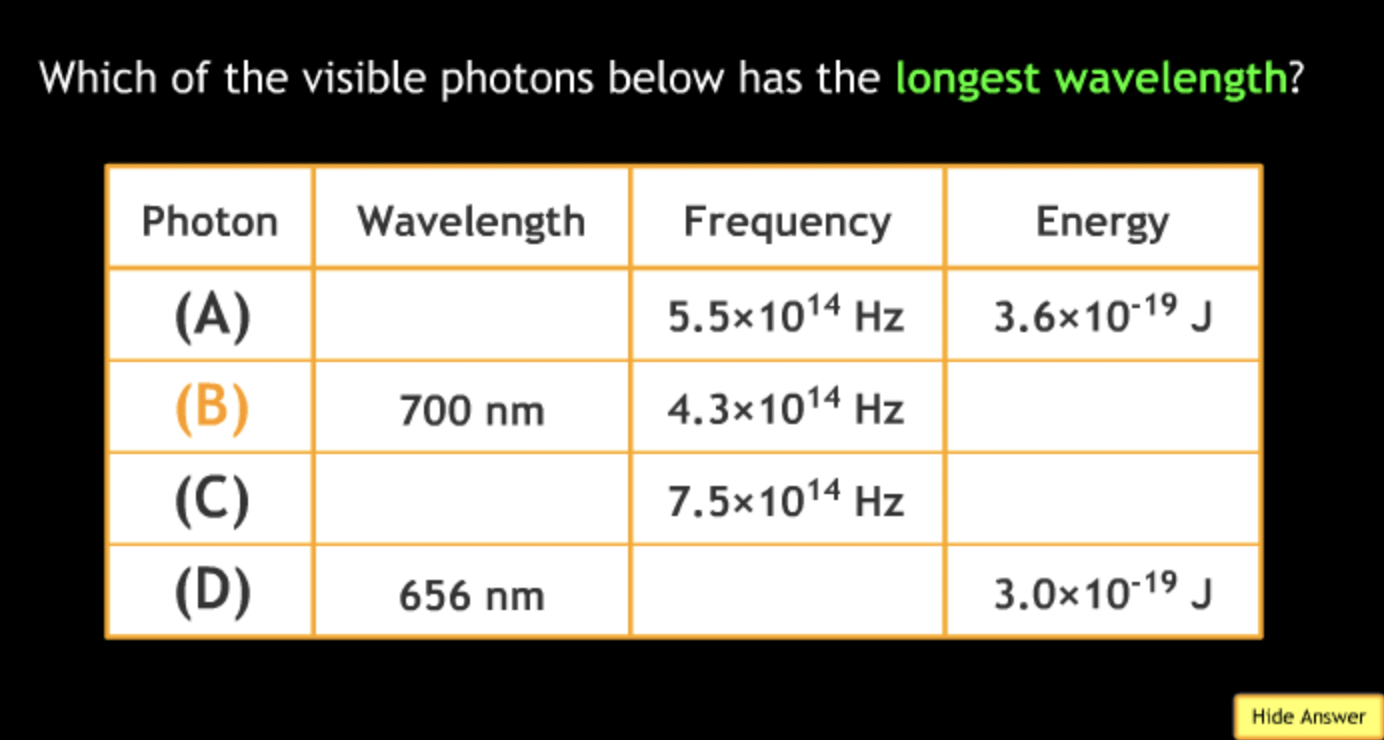
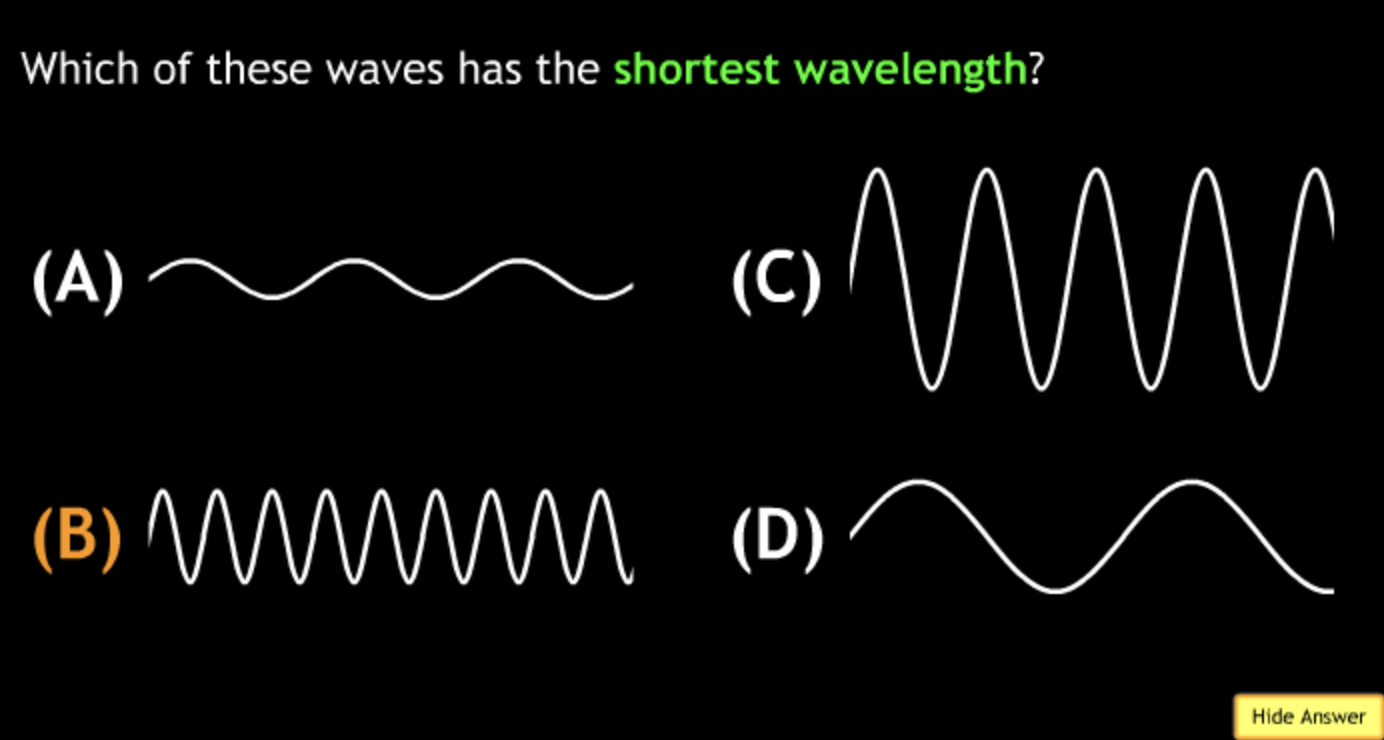
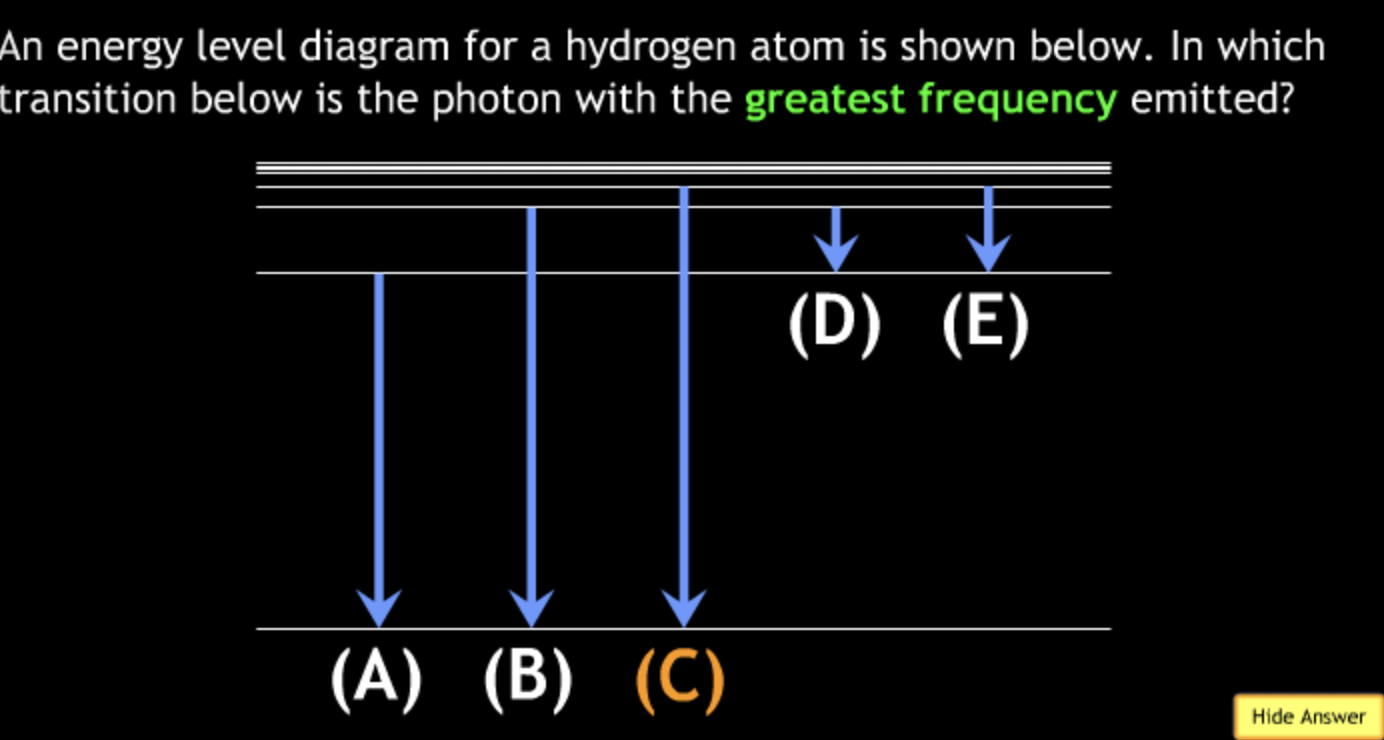
shortest? → C
highest frequency? → C
lowest frequency? → B
greatest energy? → C
least energy? → B

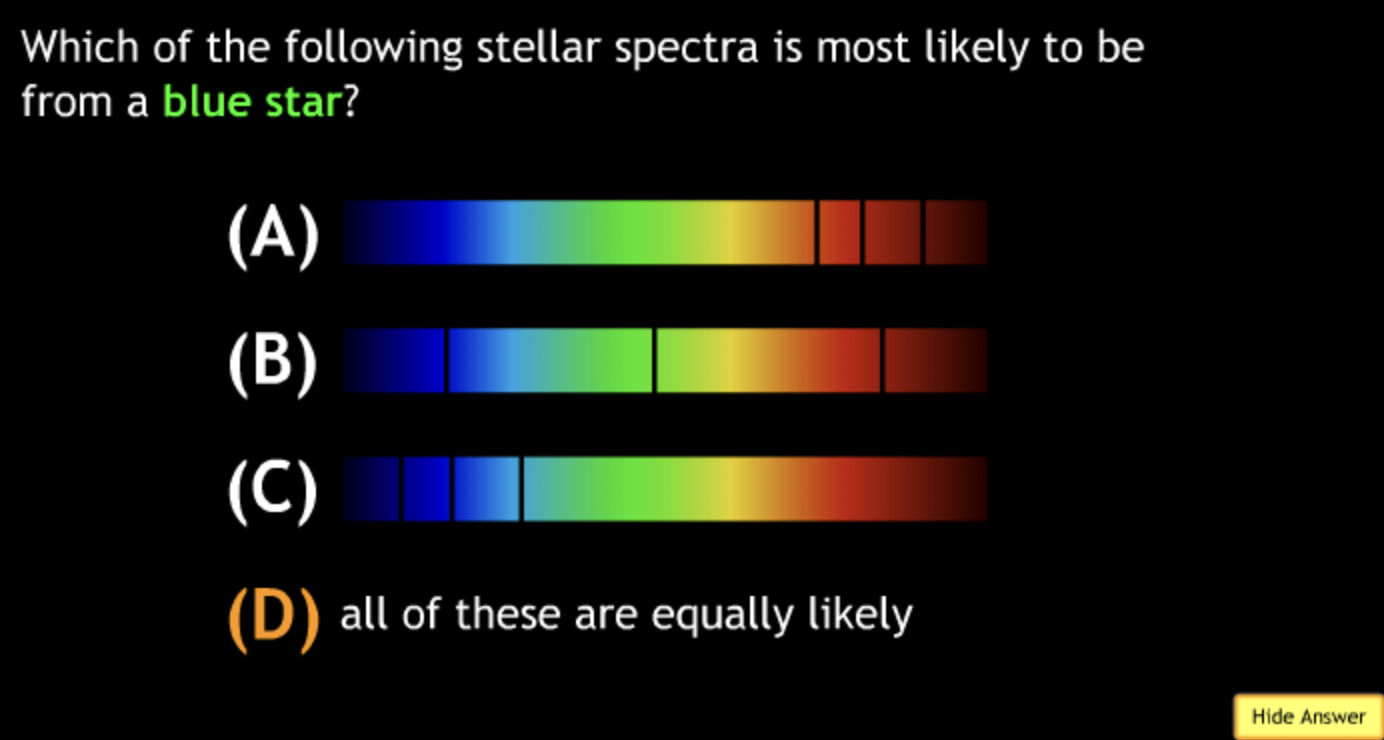
ultraviolet? → D
visible light? → C
x-rays? → E
radio? → A






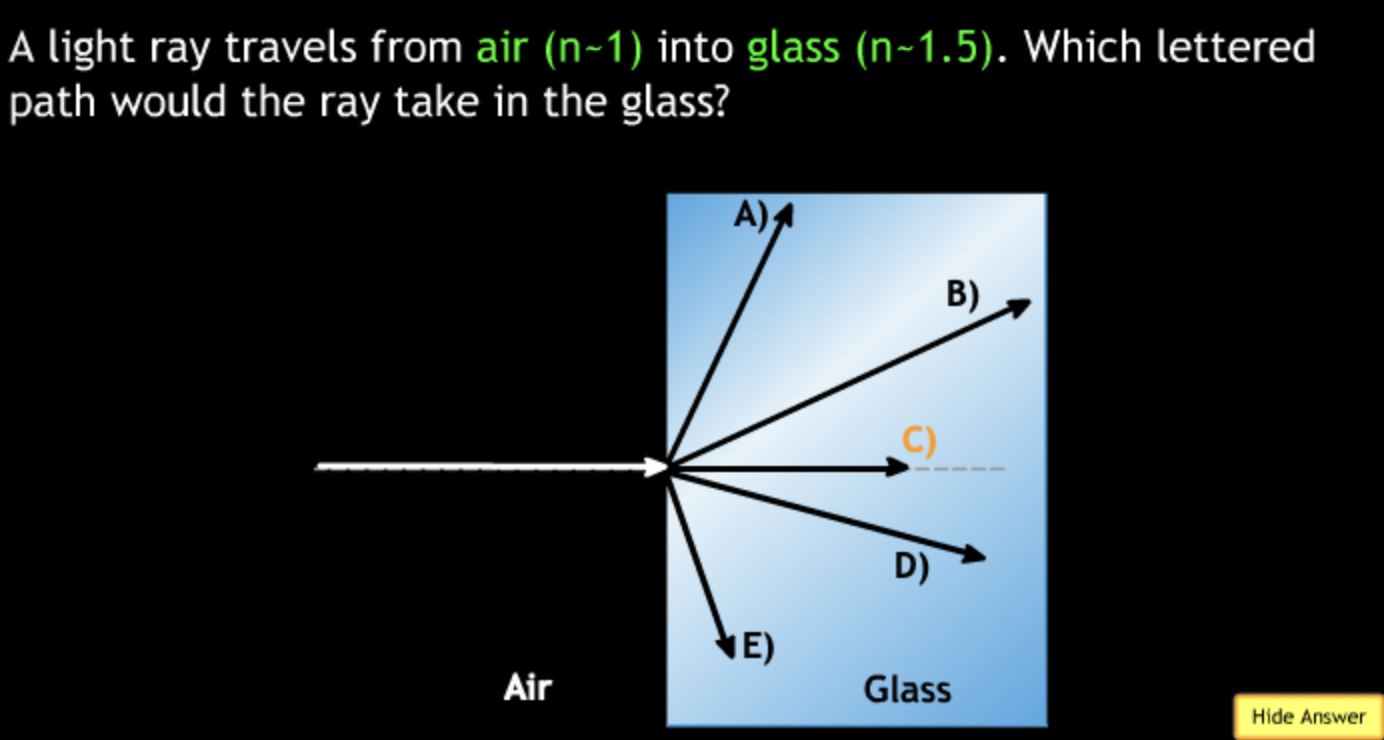
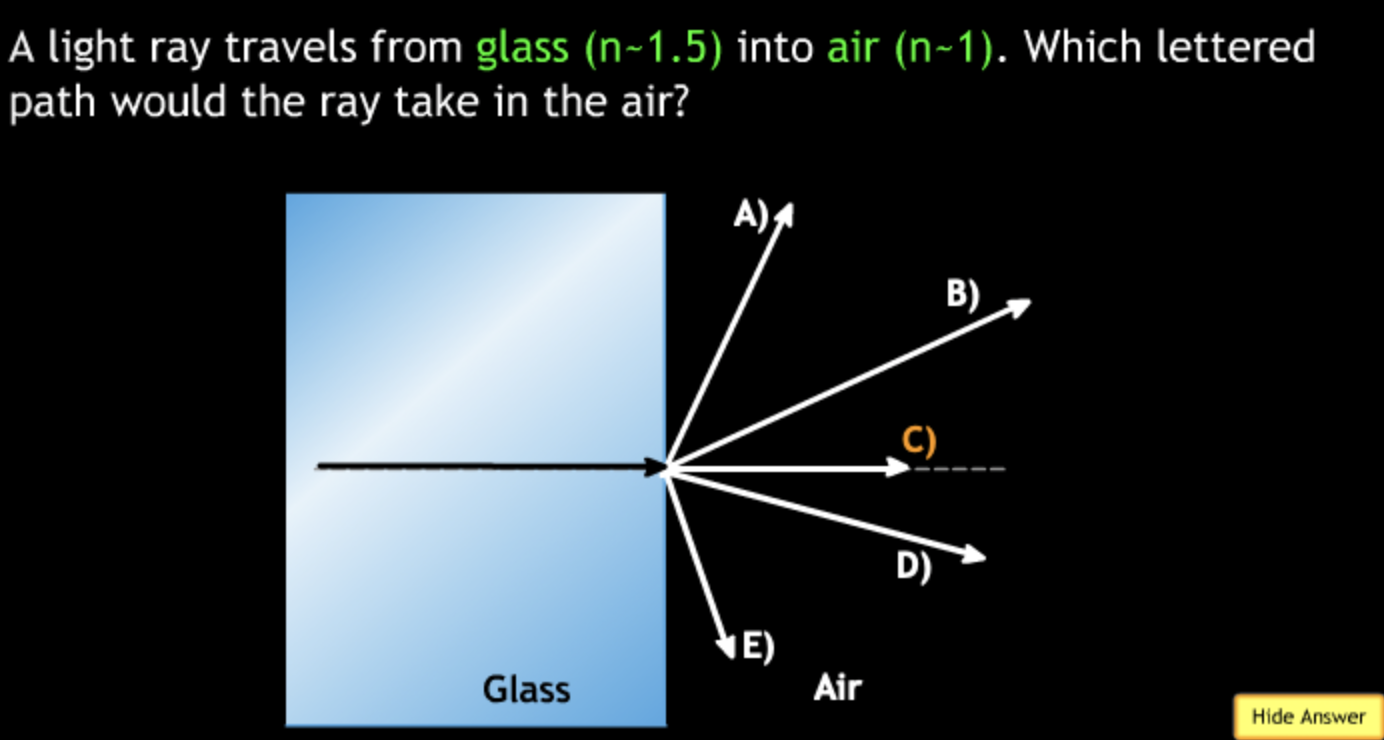
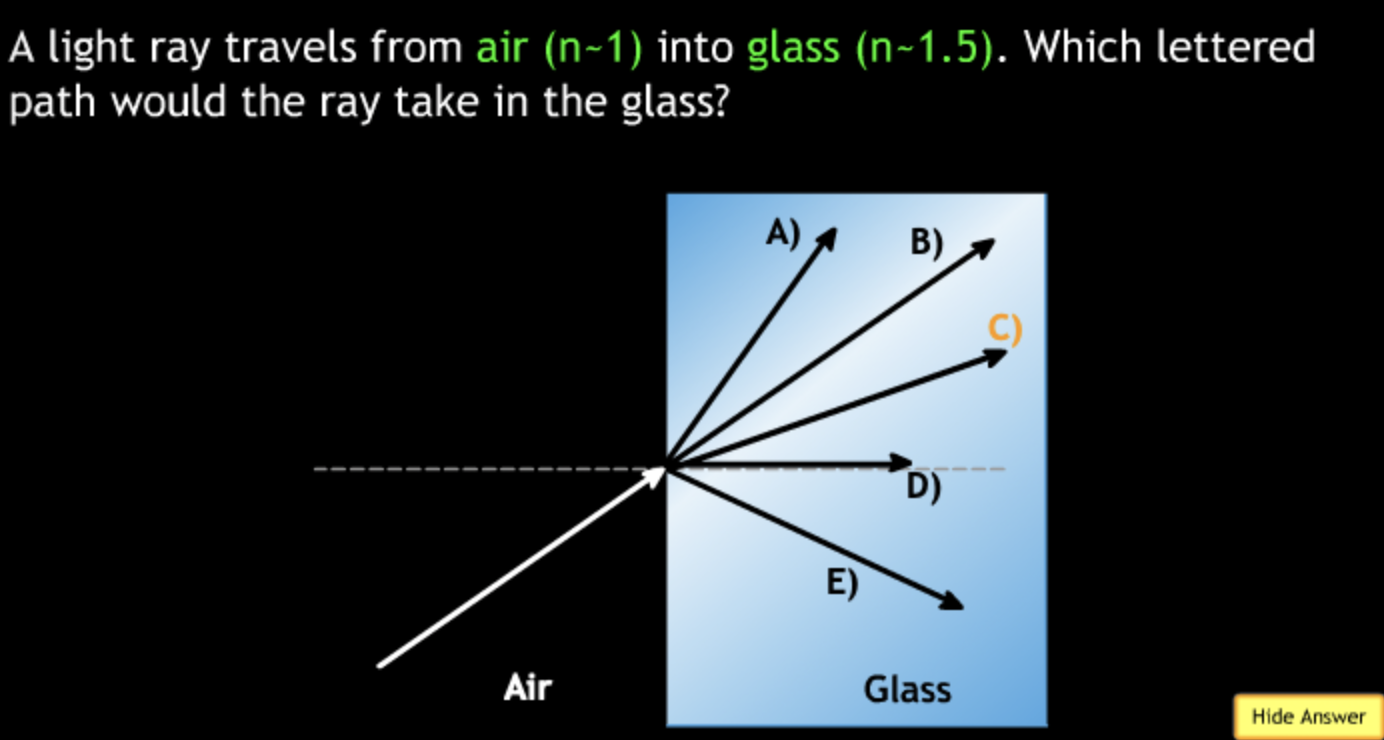
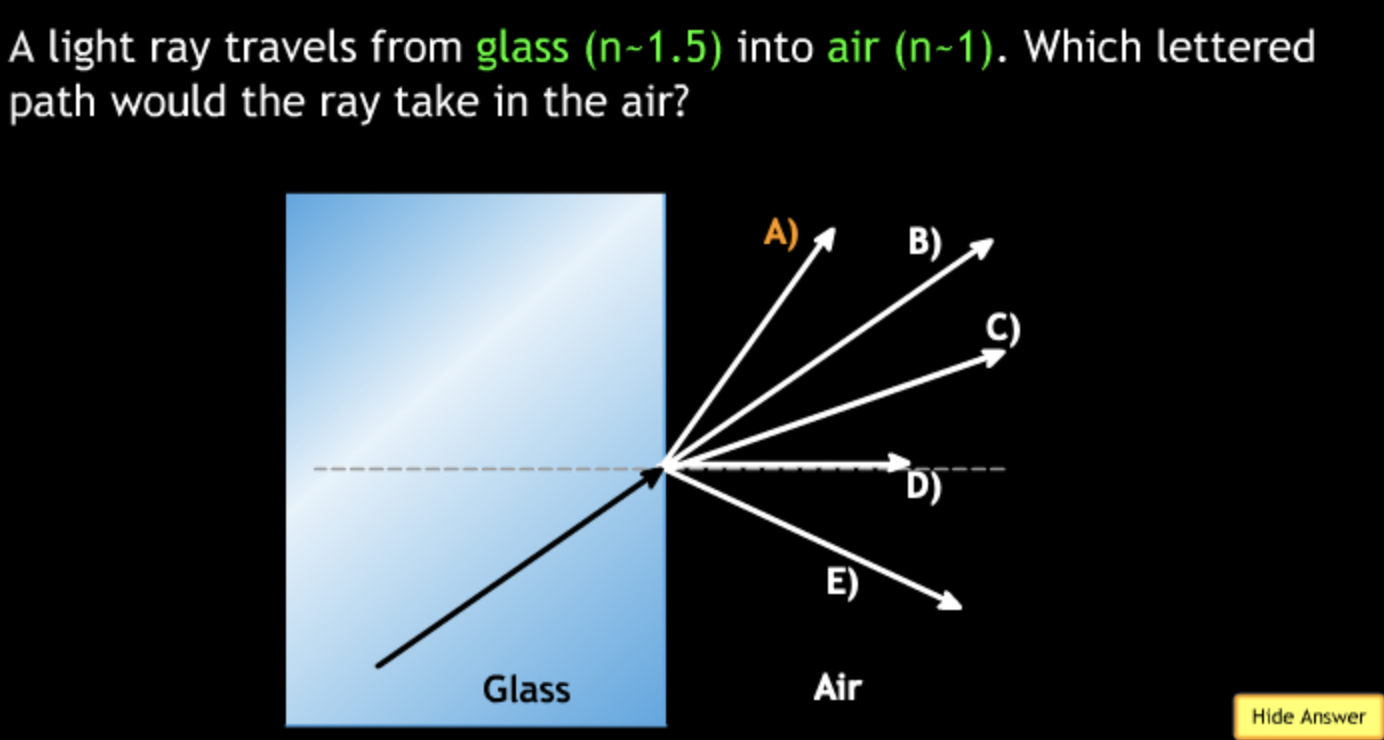
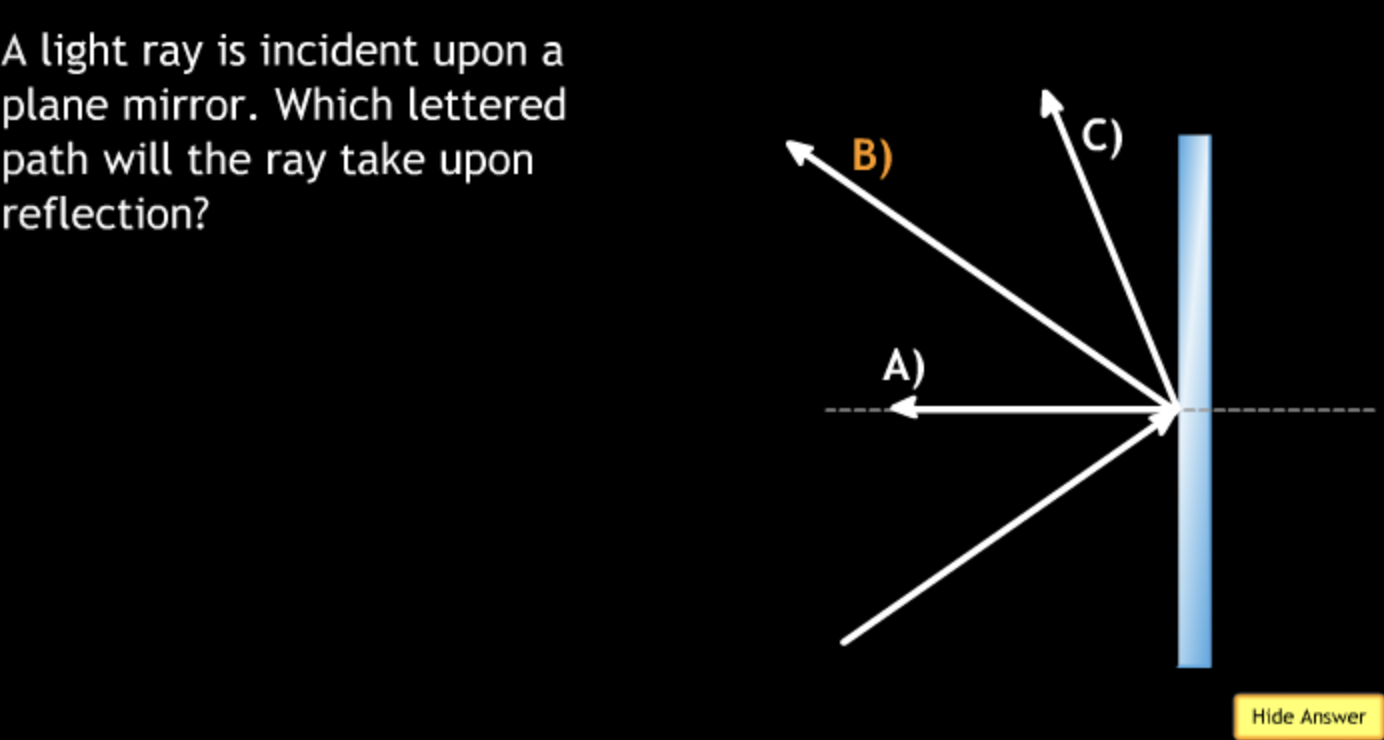

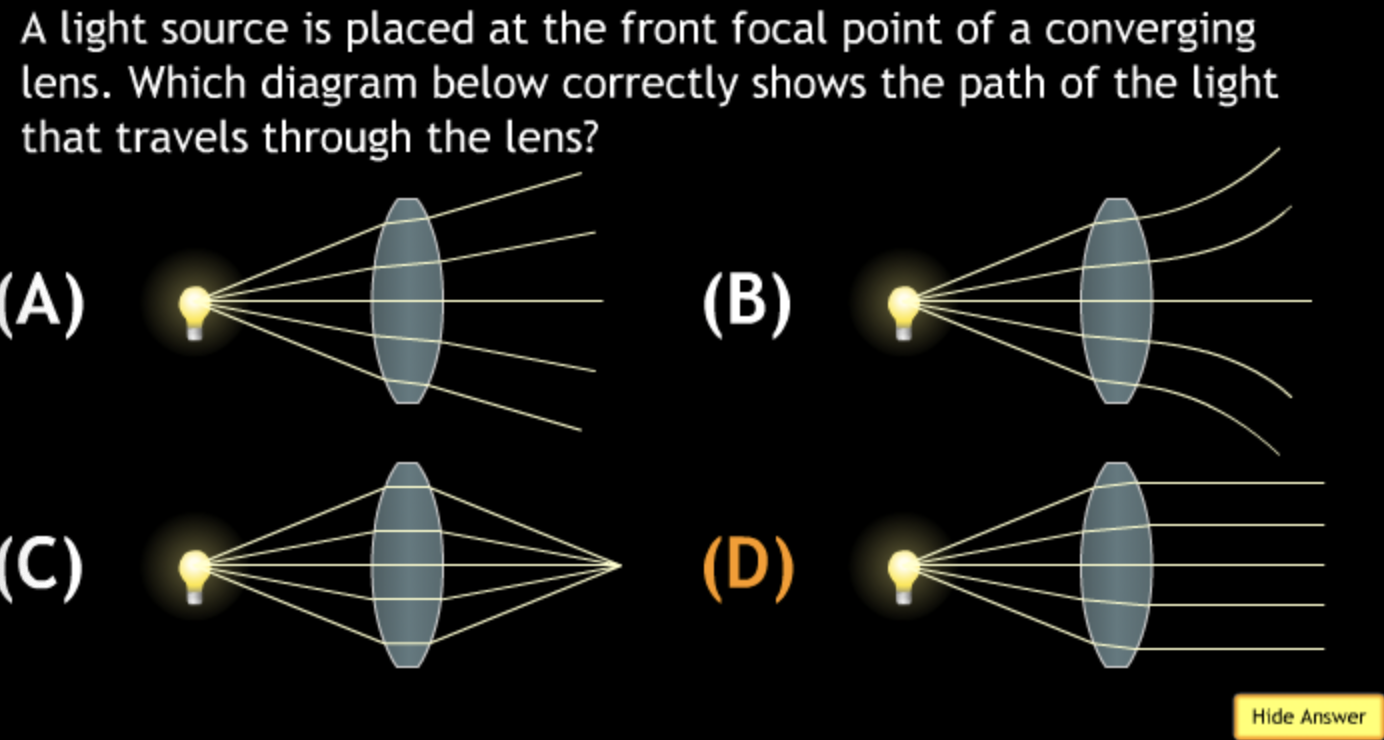
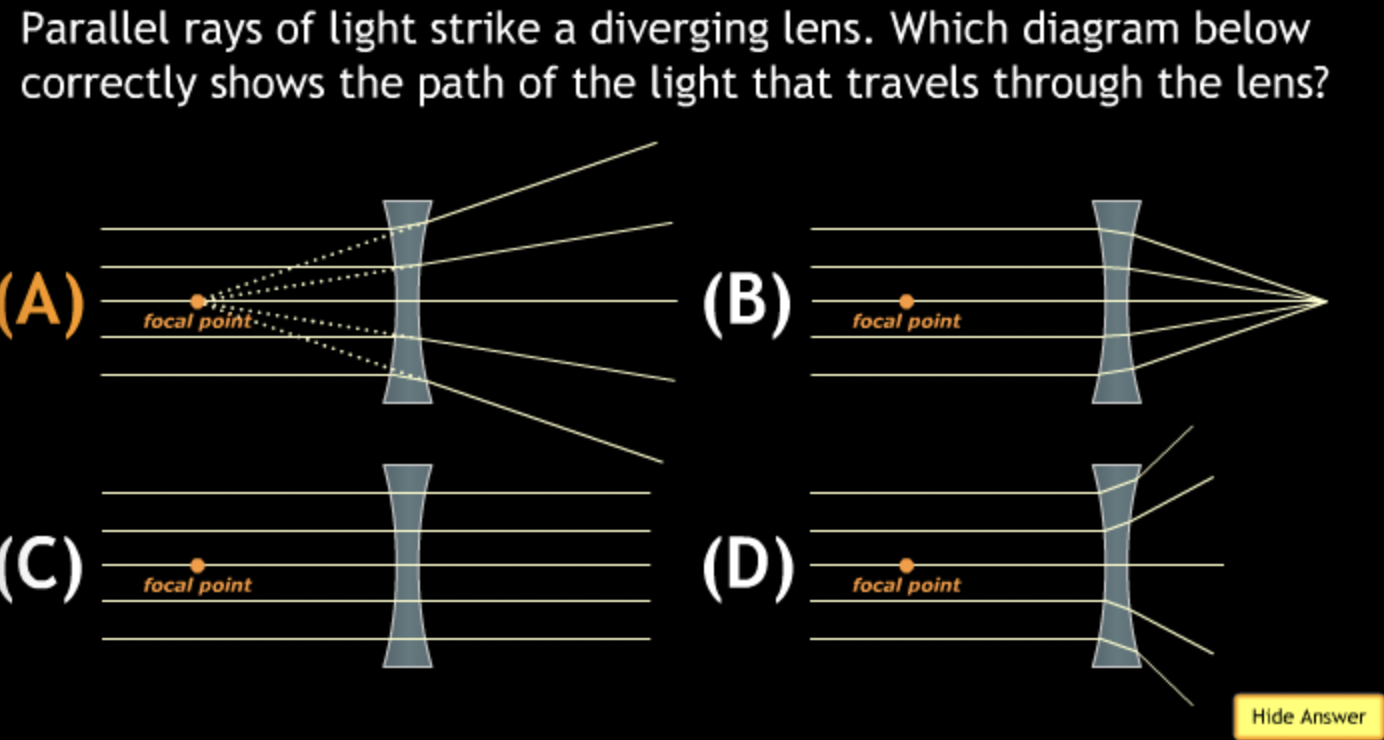
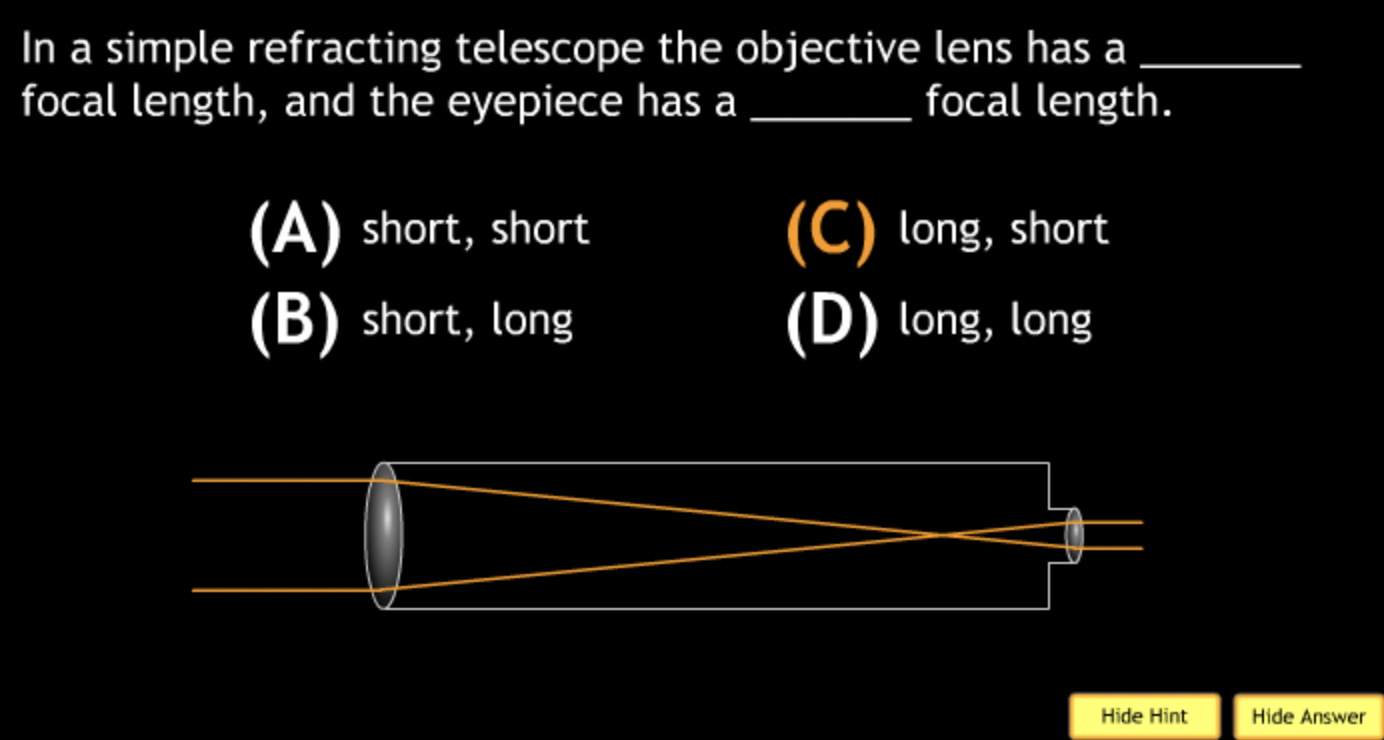
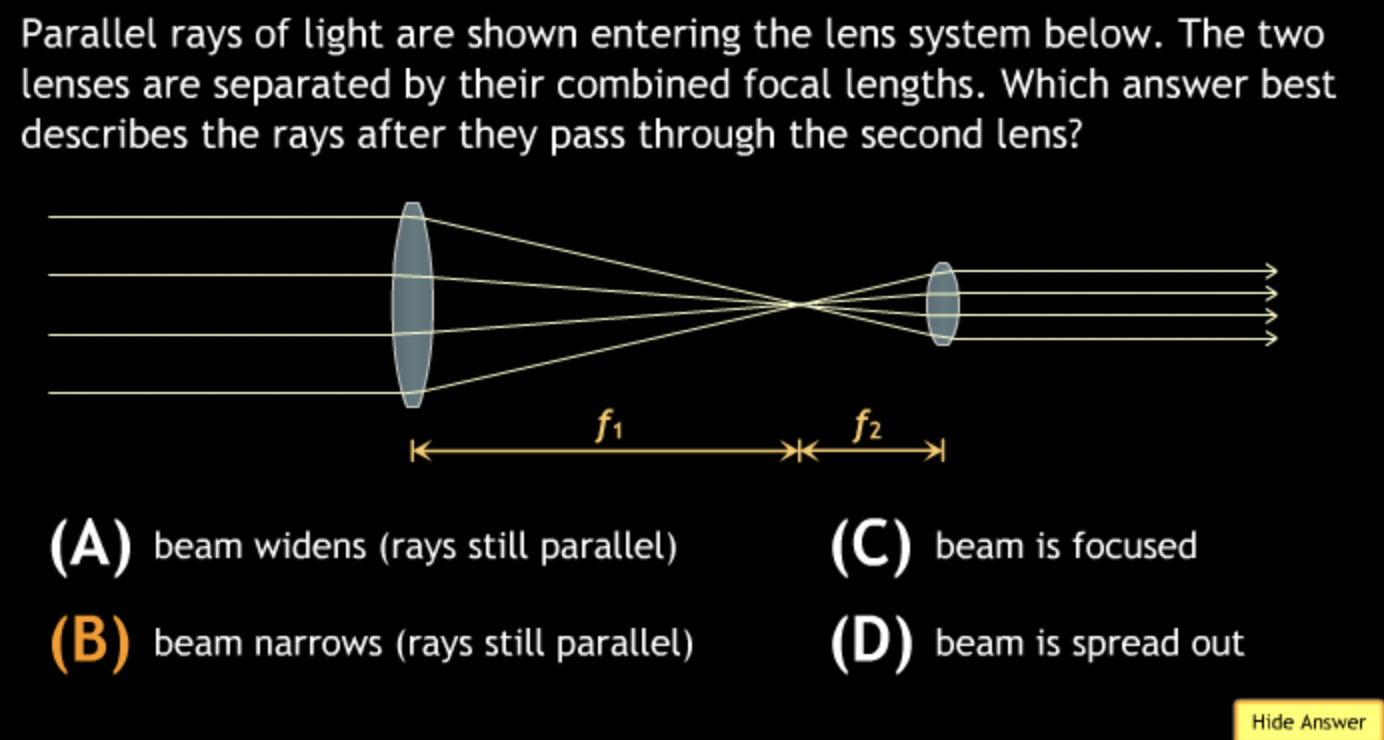




field of view will? → increase

field of view will? ^> decrease