12. Concepts and Intelligence
Concepts
Mental representations or general ideas that can be used to group together thing that have things in common - level of similarity between them.
2 groups of fundamental concepts
Who/what?
Where? When? why? how?
Doll sharing example - Childs perception of the doll different than the adults concept of how they view it
Categories in infancy
→ Early concept categories
Perceptual categorization
Things that appear to be the same
→ Infants are able to categorize dogs and cats
Are able to distinguish them based off of appearance (8-9 months)
Starts at 6 months
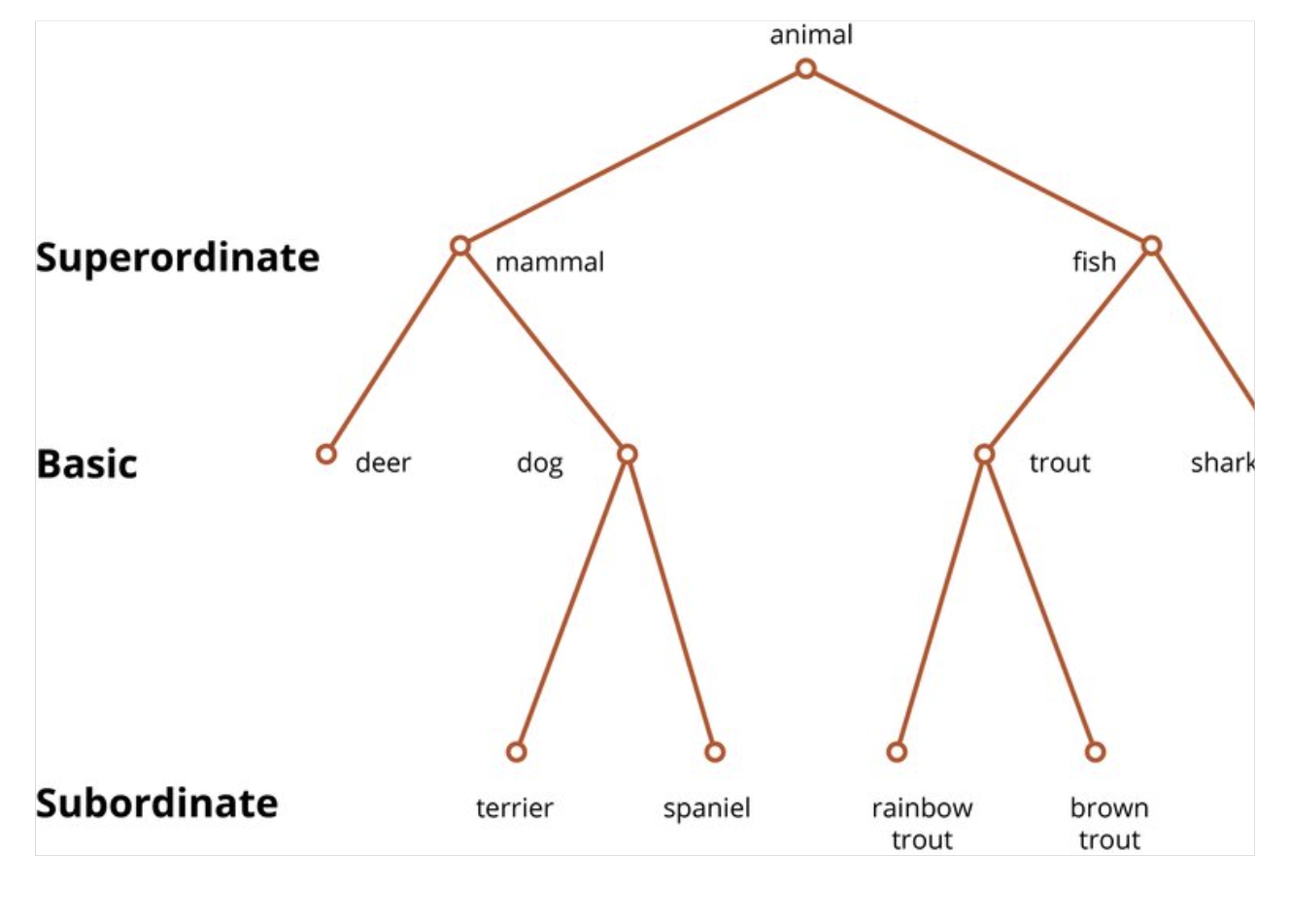
Categories beyond infancy
Breaking them beyond into other categories
Superordinate
Top level
Animals
Subordinate level
Low level
Basic level
Mid level
Children get these categories mixed up
Dogs → associated to other things that look the same
Causal Understanding
Causal understanding and concepts are related
“Wug” , “Gillie”
Both very visually different from one another with characteristics
What are things that would help people categorize these things?
Stories → Children setting up narratives
Wugs → have spikes and are ready to fight
Gillies → Can fly away
Theory of mind
→ Innate thinking that other people think like we do
False-belief problems
Ages 3-6 → Always changing
Theory of mind module (ToMM)
Theoretical brain mechanisms devoted to understanding other human beings
Sally-Anne task
Both have different objects
Sally puts ball in basket and walks away
Anne takes the ball and puts it in her box
Question is:
Where is sally going to look for the ball?
In order to pass the test they have to understand the different perspectives of the 2
3 yr olds
Children dont have an understanding of what they used to think
Candy vs pencils in a candy box example
ASD → Disorder of understanding how other people behave
Intelligence
What is it?
Lots of definitions of intelligence
→ Piaget
How do we learn and understand the world around us?
Adaptive thinking/behaviours/actions
ALSO…
Problem solving
High social competence
verbal ability
Psychometric approach to Intelligence
Theoretical perspective that sees intelligence as trait based behaviours
Set of traits that convert to one set of behaviours and has variance across individuals
One specific assumption in this approach:
Assumes that some people perform better than others, even as a set of traits
Singular intelligence vs distinct abilities?
Different theorists have different povs on this issue
Notion of intelligence was tied to white supremacy during victorian times
Whites superior to everyone else in intelligence
Binet and Simons Intelligence test
To determine whether or not children that are in regular schools need more attention than others
Government request: Which kids belong in this classroom, and which ones dont
They also came up with:
→ Mental age (MA)
Age graded questions that you can complete successfully
Chronological age vs actual age
Advanced or behind - The norm of intelligence and comprehension by age
how we test intelligence?
IQ score
Batteries of test
Why bother?
Can predict other factors
Academic performance
Job success - wealth
assess our general adjustment and health
→ test taking is a Eurocentric approach to performance
Testing can be more fatiguing and that can make you do worse on them
Is it fair- other cultures use different sets of practice
Assessing infant intelligence
Bayley scales of intelligence (1-42 months, 3 ½ years pf age)
Motor scale
Motor milestones
Throw a ball, hold utensils, crawling
Mental scale
Categorizing objects, hidden toys/objects
Infant behavioural record
Caregiver report
rating scale on general behaviour
Outgoing/not outgoing, goal directed behaviour
DQ (Developmental Quotient) - summary of these 3 sub scales
→ relationship to IQ?
Early predictor of IQ?
How stable is IQ?
If DQ and IQ are related we should see a perfect correlation
More of a negative correlation - so no correlation
Child IQ 7-8 more predictive
Is IQ from nature based factors?
Intelligent parents = you’re probably going to inherit it as well
IQ scores are going to be similar when genetically similar
Environment matters
Contribution to IQ scores
Attentional processes, Memory
Experience changes IQ scores
Enrichment programs
Became federally funded by government to enhance academic performance
Delayed children regained skills
Found responsive caregiving and opportunities increased IQ assessments
Intervention in normal vs deprived environments
Schooling
Better opportunities - adds to higher iQ
More schooling = IQ gain
Experience based facilitation effect
taught to the test
IQ is supposed to be trait based that stays stable- its foundational
Flynn effect
rising trend to increasing IQ scores across generations of people
Reason to reforming IQ test
Practice test
Practice Test: Cognitive Development and Intelligence
Section 1: Categorization and Causal Understanding
What are the three basic levels of categorization?
a) Basic level, Mid level, High level
b) Basic level, Mid level, Advanced level
c) Basic level, Mid level, Superordinate level
d) Basic level, Abstract level, Concrete levelHow do children often categorize dogs?
a) Based on their behavior
b) Based on their association with other similar-looking things
c) Based on their intelligence
d) Based on their sizeHow do stories help children with categorization?
a) They allow children to memorize concepts better
b) They help children set up narratives that aid in organizing concepts
c) They make learning fun
d) They simplify learning by reducing complexityWhat are the main characteristics of Wugs and Gillies?
a) Wugs can fly, and Gillies are ready to fight
b) Wugs have spikes and are ready to fight, while Gillies can fly away
c) Wugs are fast, and Gillies are strong
d) Wugs are social, and Gillies are independent
Section 2: Theory of Mind
5. What is Theory of Mind?
a) The understanding that all people think exactly the same way
b) The innate ability to understand that others have different thoughts and perspectives
c) The belief that thinking is universal
d) The idea that thoughts are only shaped by experience
At what age do children typically struggle with false-belief problems?
a) 1-3 years old
b) 3-6 years old
c) 6-9 years old
d) 9-12 years oldIn the Sally-Anne task, where will Sally look for the ball?
a) In Anne’s box
b) In the basket where she originally placed it
c) On the floor
d) In Anne’s handsHow does ASD relate to Theory of Mind? a) ASD is a disorder that affects understanding of other people’s behaviors
b) ASD has no connection to Theory of Mind
c) ASD improves the ability to predict others' thoughts
d) ASD only affects problem-solving skills
Section 3: Intelligence and Testing
9. Which psychologist is associated with theories of intelligence and how we understand the world?
a) Binet
b) Piaget
c) Simon
d) Vygotsky
What are key factors in intelligence according to the psychometric approach?
a) Problem-solving, high social competence, and verbal ability
b) Memorization, motor skills, and strength
c) Physical speed, size, and verbal ability
d) Abstract reasoning, creativity, and humorWhat was the original purpose of Binet and Simon’s intelligence test?
a) To rank students based on intelligence
b) To determine if children needed additional academic attention
c) To measure intelligence across different cultures
d) To evaluate job performanceWhat does the term ‘Mental Age (MA)’ refer to?
a) The actual age of a child
b) The age at which a child successfully completes age-graded tasks
c) The cognitive age of an adult
d) The physical age of a childWhat is the Flynn Effect?
a) A decline in intelligence over time
b) A trend showing increasing IQ scores across generations
c) The genetic basis of intelligence
d) A method for identifying intelligence through behavior
Section 4: IQ and Environmental Factors 14. How does environment contribute to IQ scores?
a) It does not contribute at all
b) It only affects IQ during early childhood
c) It plays a role in attentional processes, memory, and experience
d) It is entirely genetic
What is a key finding about the relationship between Developmental Quotient (DQ) and IQ?
a) They are perfectly correlated
b) There is no strong correlation between the two
c) A high DQ guarantees a high IQ
d) IQ is entirely based on DQWhat are Bayley Scales of Intelligence used for?
a) To measure adult intelligence
b) To assess intelligence in infants and toddlers
c) To evaluate intelligence in teenagers
d) To predict job successHow does schooling impact IQ scores?
a) More schooling is associated with an increase in IQ
b) Schooling has no effect on IQ
c) Schooling lowers IQ
d) IQ is entirely genetic and unaffected by schooling
Short Answer Questions:
18. Describe how intelligence is tested and why it is measured.
Explain the impact of enrichment programs on IQ development.
What is the criticism of IQ testing from a cultural perspective?
End of Test
Answer Key:
Section 1: Categorization and Causal Understanding
c) Basic level, Mid level, Superordinate level
b) Based on their association with other similar-looking things
b) They help children set up narratives that aid in organizing concepts
a) Wugs can fly, and Gillies are ready to fight
Section 2: Theory of Mind
5. b) The innate ability to understand that others have different thoughts and perspectives
6. b) 3-6 years old
7. b) In the basket where she originally placed it
8. a) ASD is a disorder that affects understanding of other people’s behaviors
Section 3: Intelligence and Testing
9. b) Piaget
10. a) Problem-solving, high social competence, and verbal ability
11. b) To determine if children needed additional academic attention
12. b) The age at which a child successfully completes age-graded tasks
13. b) A trend showing increasing IQ scores across generations
Section 4: IQ and Environmental Factors
14. c) It plays a role in attentional processes, memory, and experience
15. b) There is no strong correlation between the two
16. b) To assess intelligence in infants and toddlers
17. a) More schooling is associated with an increase in IQ
Short Answer Questions (Sample Responses):
18. Intelligence is tested using standardized measures such as IQ tests, which assess cognitive abilities, problem-solving, and verbal skills. It is measured to evaluate cognitive development, identify learning needs, and predict academic and job performance.
Enrichment programs provide stimulating environments that enhance cognitive development. They have been shown to improve IQ scores by exposing children to complex problem-solving, language development, and social interactions.
IQ testing has been criticized for cultural bias, as many tests favor individuals from specific linguistic and socioeconomic backgrounds. Some argue that IQ tests do not accurately measure intelligence across diverse populations due to differences in education, upbringing, and test familiarity.
Let me know if you need any modifications! 😊