Ch 4 -The Nursing Process- Pharm
Overview of the Nursing Process
Key Terms
Analysis: Using data to determine client need or nursing diagnosis.
Assessment: Collection of subjective and objective data.
Evaluation: Decision-making process determining the effectiveness of nursing actions or interventions.
Expected Outcome: Expected behavior and physical and mental state of the client after a therapeutic intervention.
Implementation: Carrying out of a plan of action.
Independent Nursing Actions: Actions that do not require a physician’s orders.
Initial Assessment: Gathering of baseline data.
Nursing Diagnosis: Description of a client problem.
Nursing Process: Framework for nursing action, consisting of a series of problem-solving steps, which helps members of the health care team provide effective and consistent client care.
Objective Data: Information obtained through a physical assessment or physical examination, laboratory tests, or scans.
Ongoing Assessment: Continuing assessment activities that proceed from the initial nursing assessment.
Planning: Design of steps to carry out nursing actions.
Subjective Data: Information supplied by the client or family.
Definition: The nursing process is a systematic, patient-centered, and goal-oriented framework that guides nurses in clinical reasoning and problem-solving to provide effective client care. It acts as a roadmap for delivering professional nursing care and ensures that interventions are based on scientific evidence and specific client needs.
Orderly Plan: It involves a specific cycle that includes:
Gathering comprehensive data.
Identifying nursing-specific problems (not medical diagnoses).
Developing measurable outcomes.
Implementing a targeted plan of action.
Evaluating the results and revising the plan as necessary.
Learning Objectives
List the five phases of the nursing process.
Discuss assessment, analysis, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation as they apply to the administration of drugs.
Differentiate between objective and subjective data.
Identify common nursing diagnoses used in the administration of drugs and nursing interventions related to each diagnosis.
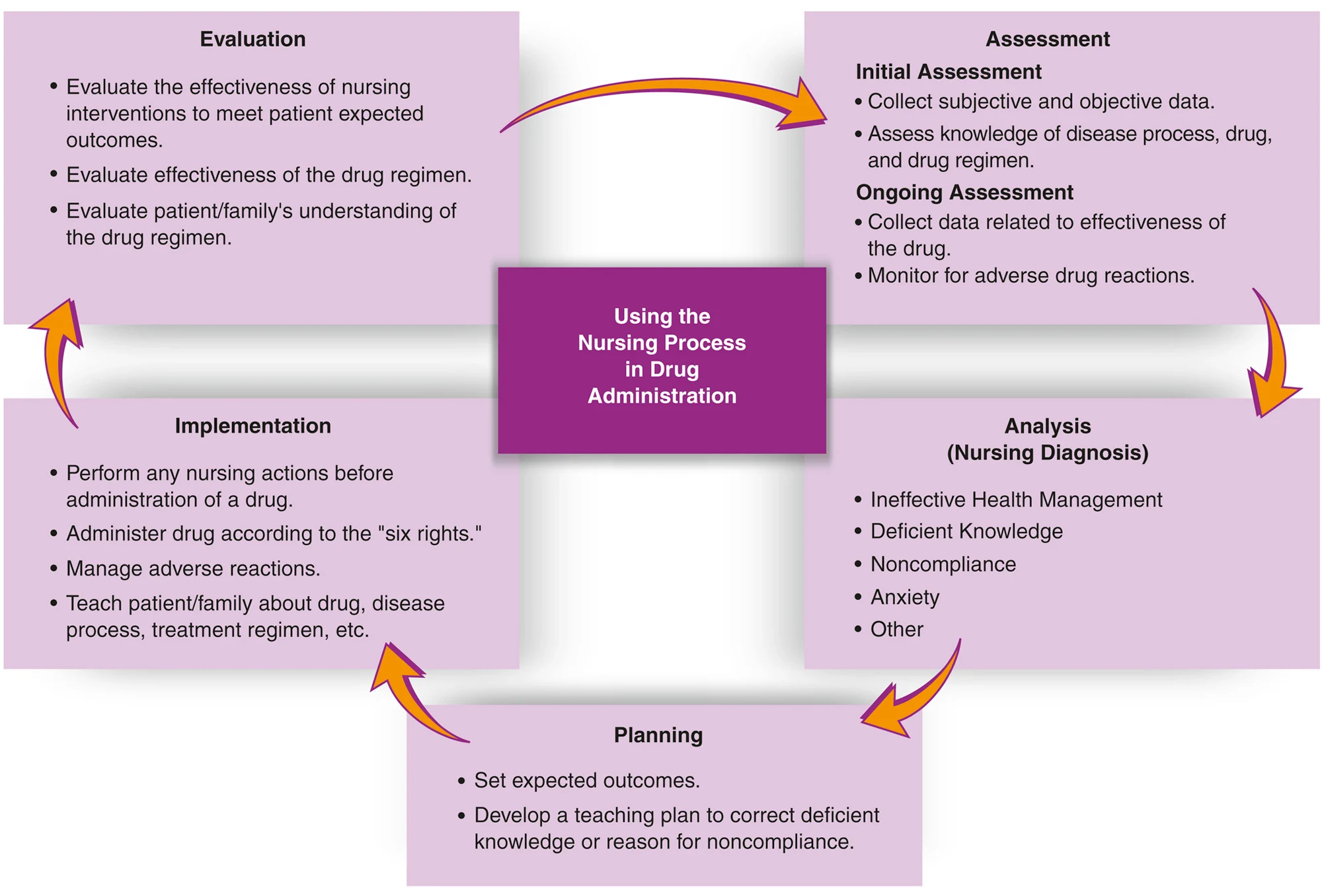
The Five Phases of the Nursing Process
Assessment
Nursing Diagnosis
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
Phase 1: Assessment
Purpose: To establish a comprehensive database about the client’s health status, including physiological, psychological, socio-cultural, and spiritual data.
Sources of Data:
Primary Source: The client (usually the most reliable).
Secondary Source: Family members, medical records, or other healthcare professionals.
Types of Data:
Objective Data (Signs):
Observations or measurements made by the nurse using the senses (sight, hearing, touch, smell).
Examples: Vital signs (BP=120/80), lab results, wound appearance, lung sounds.
Subjective Data (Symptoms):
Information stated by the client that cannot be measured directly by the nurse.
Examples: "I feel nauseous," "My pain level is a 7/10," or feelings of anxiety.
Types of Assessments:
Initial (Baseline) Assessment: During admission
Conducted when the client is first seen for care.
Provides a thorough baseline of data for future comparisons.
Ongoing Assessment:
Conducted during each client encounter to allow for comparison with baseline data.
Relevance to Drug Administration:
Before giving medication, a nurse must assess for contraindications or baseline values (e.g., check apical pulse before Digoxin). After administration, the nurse assesses for therapeutic effects and adverse reactions.
Important Assessment Metrics:
Objective Data: Blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, temperature, weight, appearance, lung auscultation.
Subjective Data: Client statements regarding pain relief or symptom changes post-drug administration.
Phase 2: Nursing Diagnosis
Definition: A clinical judgment method used to identify client problems that can be addressed through nursing actions based on assessment data (both subjective and objective).
Analysis: This is the bridge between assessment and diagnosis. It involves clustering data, identifying patterns, and determining the client's needs.
Definition of Nursing Diagnosis: A clinical judgment about individual, family, or community responses to actual or potential health problems. This differs from a medical diagnosis, which focuses on the disease process; the nursing diagnosis focuses on the human response.
NANDA-I Taxonomy: North American Nursing Diagnosis Association-International provides a standardized list of nursing diagnoses to ensure consistency among practitioners.
The Three-Part Statement (PES):
Problem (P): The NANDA-I label (e.g., Ineffective Airway Clearance).
Etiology (E): The cause or "related to" (R/T) factor (e.g., R/T retained secretions).
Signs/Symptoms (S): The "as evidenced by" (AEB) defining characteristics (e.g., AEB crackles in lungs and productive cough).
Common Nursing Diagnoses Related to Drug Administration:
Dehydration
Health Seeking Behavior
Ineffective Health Management (difficulty adhering to drug schedules)
Deficient Knowledge (regarding medication effects/side effects).
Anxiety
Noncompliance: The client chooses not to follow the prescribed therapy.
Risk for Injury: Related to drug side effects like dizziness (orthostatic hypotension).
Phase 3: Planning
Development of Expected Outcomes:
SMART Goals: Outcomes must be Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, and Time-bound.
Goal Statement: Broad expectations indicating a solution to a client's problems.
Example Goal: The client will effectively manage their drug regimen.
Example Expected Outcome: The client will take prescribed medication(s) as directed upon discharge from the care facility.
Interventions:
Appropriate nursing interventions are selected based on expected outcomes to create a detailed client care plan, defining steps necessary for achieving those outcomes.
Phase 4: Implementation
Definition: The actual execution of the care plan regarding drug administration.
The Six Rights of Medication Administration:
Right Patient: Identify using two identifiers (name and DOB).
Right Drug: Check the label against the MAR three times.
Right Dose: Verify calculations and appropriateness for the client.
Right Route: Ensure the medication is given as prescribed (e.g., PO, IV, IM).
Right Time: Administer within the facility's approved time window.
Right Documentation: Record immediately after administration.
Process:
Review all relevant assessment data before drug administration.
Decision-making in drug administration depends on data analysis:
Example 1: If a client’s baseline blood pressure is 188/110, and the ongoing reading is 182/110, the drug may be administered.
Example 2: If the pre-administration blood pressure drops to 98/70, the nurse might withhold the drug and inform the provider.
Phase 5: Evaluation
Purpose: To assess the effectiveness of nursing interventions in meeting expected outcomes.
Evaluation Activities Include:
Determining understanding of the drug regimen by the client or family.
Monitoring the client's response to therapy, typically through:
Frequent blood pressure checks, inquiry about pain relief, or monitoring pulse rates.
Observing for adverse drug reactions (ADRs).
Outcome of Evaluation:
Met: The intervention was successful; the goal can be discontinued.
Not Met: The nurse must restart the cycle: re-assess the client, revise the diagnosis, or change the intervention strategies.
Example of Nursing Interventions Based on Expected Outcomes
Goal: Maintain baseline blood pressure.
Expected Outcome: Client experiences no further elevation in blood pressure.
Nursing Interventions:
Administer medications as prescribed.
Monitor blood pressure hourly.
Mitigate environmental stressors.
Evaluation Criteria: Blood pressure remains at or below baseline levels.
Integration of the Five Phases in Drug Administration
Assessment:
Initial collection of subjective and objective data.
Assess client’s knowledge of the disease, drugs, and drug regimens.
Ongoing Assessment:
Continuous data collection related to drug effectiveness and monitoring adverse reactions.
Analysis (Nursing Diagnosis):
Common diagnoses include:
Ineffective Health Management
Deficient Knowledge
Noncompliance
Anxiety
Additional considerations as necessary.
Planning:
Establish expected outcomes and develop educational plans to address gaps in knowledge or compliance issues.
Implementation:
Execute nursing actions before administering medications, ensuring adherence to the "six rights" of medication administration (right patient, right drug, right dose, right route, right time, right documentation).
Evaluation:
Regularly assess the effectiveness of interventions against expected outcomes and adjust care plans as necessary.
Chapter Review: Prepare for the NCLEX-PN
RECALL THE FACTS
When the nurse enters subjective data in the client’s record, this information is obtained from:
A. the primary health care provider
B. other members of the health care team
C. the client or family
D. laboratory and x-ray reports
What is the name of one of the organizations that approves and standardizes nursing diagnoses?
A. ANA
NLN
NCSBN
NANDA-I
A client states that they do not understand why a specific medication has to be taken. The most accurate nursing diagnosis for this client would be:
Altered Health Management
Anxiety
Deficient Knowledge
Which of the following would be an appropriate expected outcome related to drug administration?
The client will verbalize three ways to use crutches.
The client will take an antibiotic pill daily.
The client will understand the use of blood pressure medications.
The client will demonstrate ways to prevent having to use insulin.
Which of the following is an independent nursing action?
Administering insulin
Withholding a drug according to physician standing orders
Client teaching about drug therapy
Asking respiratory care to come do an inhalation treatment
During the evaluation phase of the nursing process, the nurse:
makes decisions regarding the effectiveness of nursing interventions based on the outcome
ensures nursing procedures have been performed correctly
makes notations regarding the client’s response to medical treatment
makes a list of all adverse reactions the client may experience while taking the drug
ANALYZE THE FACTS
Which of the following is an example of objective client data?
Adult child states, “Mom’s BP is always 150/90."
“My pain is about 7/10 right now.”
“I think the doctor said my blood sugar was 105."
The nurse’s aide reports a BP132/78.
The nurse makes a note in the chart that the client’s pain has lessened following a 14-day course of antibiotics. This is an example of which phase of the nursing process?
Assessment
Analysis
Implementation
Evaluation
ALTERNATE-FORMAT QUESTIONS
Arrange the following steps of the nursing process correctly:
Assessment
Analysis (Nursing Diagnosis)
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
The nurse greets the new clinic client, saying, “Tell me about the pain you are having.” This is an example of gathering data. Describe the type of data. (Select all that apply.)
[x] Baseline assessment
[ ] Objective data
[ ] Ongoing assessment
[x] Subjective data