3. menstrual cycle (1)
GnRH pulse center
●
is stimulated by: leptin, activin, high level -.of estrogens at ovulation
Is inhibited by : inhibin, CRH, TRH,
.prolactin, estrogen, progestin, androgens
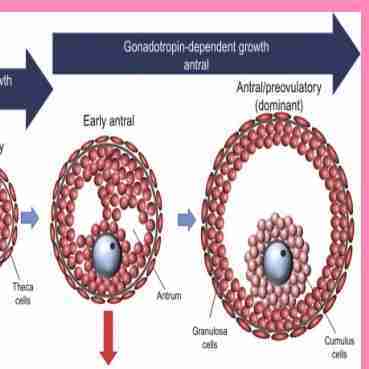
(primary oocyte surrounded by .several layers of cuboidal granulosa cells) 12 week of G.The main role of LH is its action on theca cells to synthesis androgen that are converted to estrogens in .
The follicular phase begins with the onset of .menses until the preovulatory surge of LH The luteal phase begin with the pre-ovulatory LH ●.surge and end with the first day of menses
If no fertilisation then the declining CL function ● (10-12 days after ovulation)with ↓E. & P
levels→ apoptosis of endometrium & release ofPG & lysosomal enzymes fromcells→vasoconstriction →ischemia & breakdown of blood vessels & cells followed by vasodilation with escape of cells & proteolytic enzymes into the stroma→endometrial sloughing at thejunction of superficial & basal layer →menstrual bleeding
75% of menstrual blood is arterial & 25% is .venous
Day 14 of mc the maximum effect of the estrogen ●
will lead to the secretion of a thin watery-like mucus from the cervical glands this will facilitate .the penetration of the cervical canal by the sperms
more than 10 cm length between the two .slides (+ve test: spinnbarkeit phenomena or test)
High estrogen states stimulate the maturation an
proliferation of vaginal epithelial cells and the .accumulation of glycogen
Presence of progesterone will lead to formation of
navicular cells (large cell with folded margin)
progesterone causes alveolar proliferation but no .secretory changes