
IB Geography Unit 6
6.1.1 Threats to Individuals and Businesses
6.1.1.1 Hacking, ID Theft
Stealing intellectual property
Taking control of online bank accounts
Viruses
Disrupting computer controlled services
Different types of Methods:
Phishing - Internet Danger
Occurs when visiting sites or reading emails.
typically a link that will pretend to be someone else and request credentials, e.g. bank details, Nigerian uncle, fake blackmail.
Trojans - Computer Danger
Occurs when using infected sites, outdated software, links and attachments
Intercepts data that you input, they will typically copy your information and quickly use to steal data.
can be performed by collecting data when it’s entered, using web injection, and/or bypassing two-factor authentication
Interception - Connection Dangers
Occurs when using unprotected internet connections or Wi-Fi hotspots
can be used to directly change visible data on a device, URL/IP remapping, causing trusted links to send you somewhere else.
All data can be intercepted and stolen
Case Study:
Bangladesh Bank Heist - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bangladesh_Bank_robbery
False instructions were sent to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, to send US$1 billion to the Bangladesh bank, performed over 35 transactions. $81 million were successfully sent to the hackers account in the Philippines before New York realised, only retrieving $18 million since.
6.1.1.1 (2) Implications of Surveillance for Personal Freedoms
To what extent should a society accept government surveillance of its citizens personal data
UN surveillance guidelines:
Any government surveillance should be properly regulated by legal frameworks, and must fall under a specific aim
Any form of illegal surveillance should be criminalised
Anonymity online should a personal right
Measures must be taken to avoid commercialisation of trade in surveillance technology
Case Study:
Surveillance in China
Characteristics of surveillance
1 camera per 3 people
30x more cameras than US
initially started to suppress protests
Aim of surveillance
Have a record of public crime
help people who have lost items
Impact
a) Positives
People feel more safe
Decrease in crime rates
Facial recognition can be applied globally
b) Negatives
Suppression of masses to maintain power
6.1.1.2 Economic, Political and Environmental Risks to the Supply Chain
Environmental Risks:
Natural disasters
Extreme weather
Pandemic
Geopolitical Risks:
Political instability
Trade restrictions
Terrorism
Corruption
Theft and illicit trade
Piracy
Economic:
Demand shocks
Price volatility
Border delays
Currency fluctuations
Energy Shortages
Case Studies:
Environmental - Japan Earthquakes
The 2011 earthquake and tsunami that affected the Fukushima plant, also caused damage to several trade and production infrastructures, causing problems to arise in supply chains, as they could not handle good/services throughout the country
Geopolitical - Boko Haram and Somalia Pirates
in Somalia there is a large quantity of trade pirates due to the close proximity to the Bab al-Mandab Strait, which is a major choke point for trade ships. causing issues in supply chains for other countries
Boko Haram is a terrorism group located in Nigeria and cause fear of travelling through the country, therefore limiting the supply chains that run throughout Nigeria
Economic - Argentina hyperinflation
Argentina is facing a case of hyperinflation, with annual inflation rates reaching over 100%. With their weakening currency imports and exports decrease, causing supply chain issues as they no longer have access to good that they can’t produce at large scales.
6.1.2 New and emerging threats to political and economic sovereignty of states
6.1.2.1 Profit Repatriation and Tax Avoidance by TNC’s
Repatriation:
the act or process of restoring or returning someone or something to the country of origin, allegiance, or citizenship
Case Study:
Glencore - Zambia Copper Mines
Situation:
Nearly all copper mines in Zambia are owned by TNC’s
in the last 10 years US$29bn worth of copper has been extracted from Zambia while paying minimal tax
Copper accounted for 2.3% of Zambia’s GDP but makes up 70% of their exports
Transfer Pricing:
involves TNC’s selling products internally between subsidiaries, therefore avoiding high tax rates in the original country (Zambia) by selling in low tax countries like Switzerland
Glencore owns the Mopani copper mines, who sells to glencore at a loss, therefore artificially reducing the price. Then they sell it from Switzerland at full market price, with low tax rates.
Glencore:
Largest commodities trader in the world
Annual revenue (US$180bn) is 8x larger than Zambia’s GDP (US$20bn)
Able to buy out governments with bribing
6.1.2.2 Disruptive Technological Innovations
Disruptive Technology
Disruptive technologies is an innovation that significantly alters the way that consumers, industries, or businesses operate
e.g. Tv’s, GPS, cars, planes, etc
6.1.3 Renewed nationalism & tribalism
6.1.3.1 Globalisation and Tribalisation
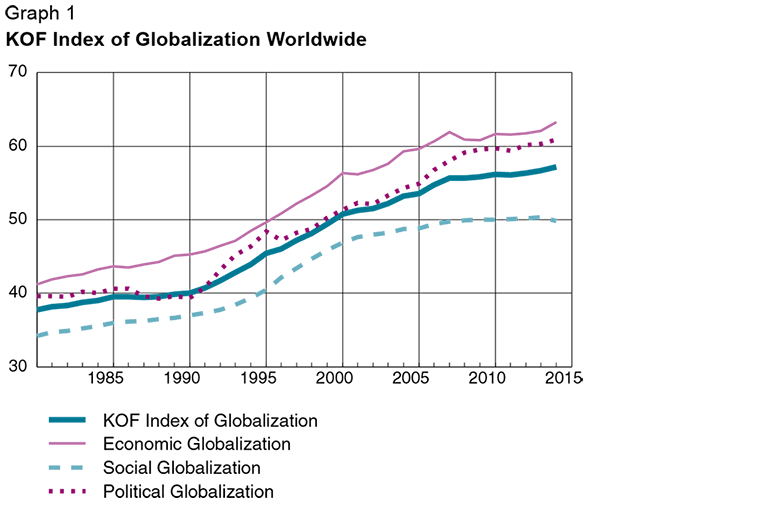
Globalisation: 🔗 4.1 KOF
The process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide
e.g. McDonald’s, Ikea, Coca-Cola
The rate of globalisation is slowing down, as visible in Graph 1
Tribalisation/Nationalism:
Promoting the interests of a particular nation, with the aim of gaining sovereignty and renewing identity
Currently seeing a rise in HIC’s like most of the EU and America
Often related with religion, e.g. Boko Haram
Case Study:
Boko Haram - western education is a sin (Tribalisation/Nationalism)
Based in north east Nigeria
Main belief being, remove all western culture and ideology from the country
main religion belief is Islamic
Brexit (Tribalisation/Nationalism)
UK withdrawing from the EU., voted for by UK citizens in a referendum
Brexit happened because the UK population believed decisions about the UK should be made by the UK
the overall desire was to reinstate their sovereignty
U.S. States - Donald Trump (Tribalisation/Nationalism)
‘Make America Great Again’
US - Mexico border, Anti immigration
6.2.1 Transboundary Pollution (TBP)
6.2.1.1 TBP and it’s consequences
Transboundary Pollution: 🔗 2.1.3, 4.2.1, 5.1.1
Emissions that are produced, and travel across land without recognition of borders.
Acid deposition:
rainfall that has a pH of less than 5.5 as a result of sulphur dioxide and nitrous oxides dissolving in water vapour held in the atmosphere.
typically caused by sulphur dioxide pollution from coal-fired power stations and nitrous oxides from petrol powered vehicles
Dry Deposition - when particulate matter falls close to the source (generally not transboundary)
Wet Deposition - when the pollution is carried by wind away from the source and to another location, this is a large problem for smaller countries like in the EU
Strategies to Reduce Impacts:
Gothenburg Protocol - 1983
signed by all EU countries, Russia, America, and Canada
called for the reduction of acidification, eutrophication by setting emissions ceilings for sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds and ammonia
Case Study:
Global action following the Chernobyl accident
After the explosion polluting particles Caesium-137 were discovered in extremely high levels 2 weeks after the explosion in Austria, Slovenia, Norway, Sweden and Finland.
the World Association of Nuclear Operators (WANO) was formed, with the main goal - to maximise the safety and reliability of nuclear power plants worldwide
6.2.2 Environmental Impacts of Global Flows
6.2.2.1 Localised Pollution, and Impacts Along Shipping Lanes
Choke Points:
shipping routes where there is a high density of ships, e.g. Suez canal, Panama canal, Baltic sea, East asia, etc
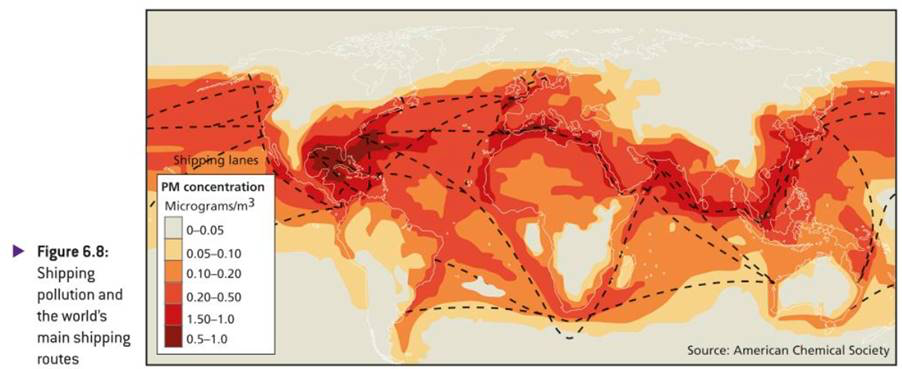
Other Environment impacts of Shipping
Deliberate and accidental oil and chemical discharges
Waste dumping
Air pollution
Damage to sea floor from the anchor
Noise pollution for sea life
Pest organisms that become invasive through ballast water (pacific sea star from japan, moving to port Phillip bay)
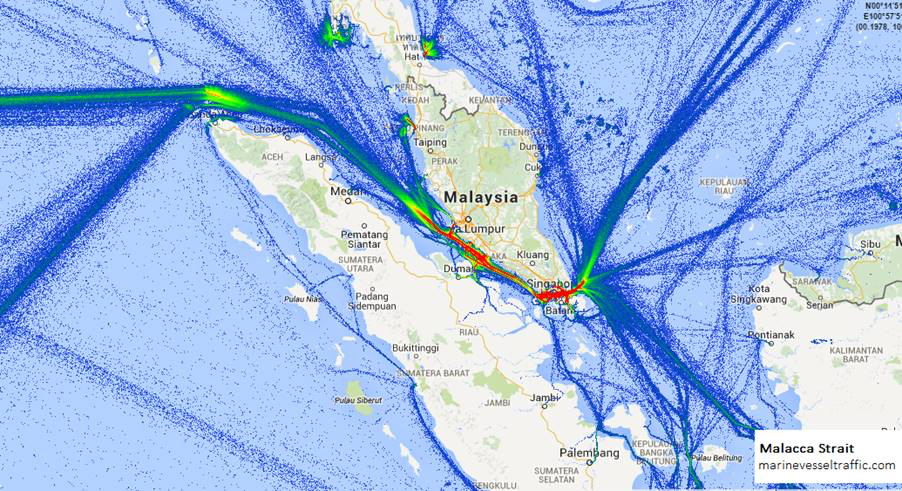
Case Study:
Singapore Oil Spills
Singapore has the 2nd busiest port in the world - as well 4 of the busiest ports are also located in Asia
Due to high traffic and the narrowness of the channel, there has been 11 major oil spills
6.2.2.2 Carbon Footprints of Different Flows
Flow of Goods
Food Miles:
total pollution created when transporting the food you purchase
Meat production:
one of the highest producers of pollution due to the production of the product
→ increasing global middle class
→ ∴ increased consumption of meats as number of HIC’s increase
→ Nutrition transition - change of diet
Flow of People
Migration:
The movement of people from LIC’s to HIC’s is a major contributor to global emissions, with the rate of migrations being at an all time high
Between 2008 and 2033 will add 7 million people to the UK, which will add around 500 million tonnes of CO2 by 2033
Tourism:
Increased globalisation, leads to increased tourism
Tourism hotspots like Europe lead to higher localised pollution
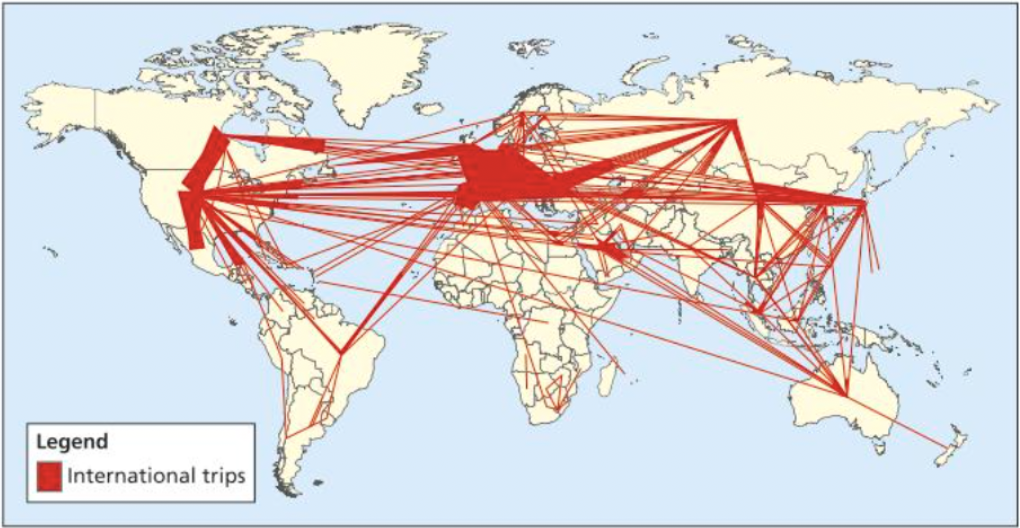
6.2.3 Environmental issues from global shift of industry
6.2.3.1 Polluting Manufacturing Industries
Global Shift:
The gradual movement of manufacturing from HIC’s to newly industrialised countries (NIC’s)
Global shifts started as the rise of globalisation begun
the main goal of moving manufacturing is to decrease costs with use of either lower tax rate laws, cheaper labour, less trade barriers, and potential FDI
Environmental Impact:
typically there are lower environmental regulations and restrictions in emerging economies
Lack of infrastructure that is sustainable
desire for profit is being placed over desire for sustainability
Case Study:
Industry Shift From USA to Mexico - Environmental Impacts
1 item = 1.4kg of CO2
Heavy metals are being produced without adequate processing methods
Illegal dumping
6.2.3.2 Environmental issues from global agribusiness
Agro-Industrialisation:
large-scale, intensive, high-input, high-output, commercialised, technologically advanced forms of farming food and fibre
Western farming practices
Positives and Negatives of Agro-Industrialisation:
Positives Negatives | ||
Socio-economic | - Increased production/higher yields - More high skill jobs, better efficiency, benefits consumers - Avoided Malthusian check | - Fewer low skill jobs - Small scale farmers struggle against larger farms - unfair competition |
Environmental | - conservation methods are being introduced, reducing harmful chemical use, etc. | - GHG emissions - 10% of the UK’s GHG comes from Ag - Water pollution - Salinisation - Loss of Biodiversity - Land erosion/degradation |
Past 50 Years: Positive Impact
Wheat yields have increased from 2.6 to 8 tonnes/hectare
Barley yields have increased from 2.6 to 5 tonnes/hectare
Dairy production has increased from 4,000 L/yr to 5,800 L/yr
Environmental Impacts: Negative Impact
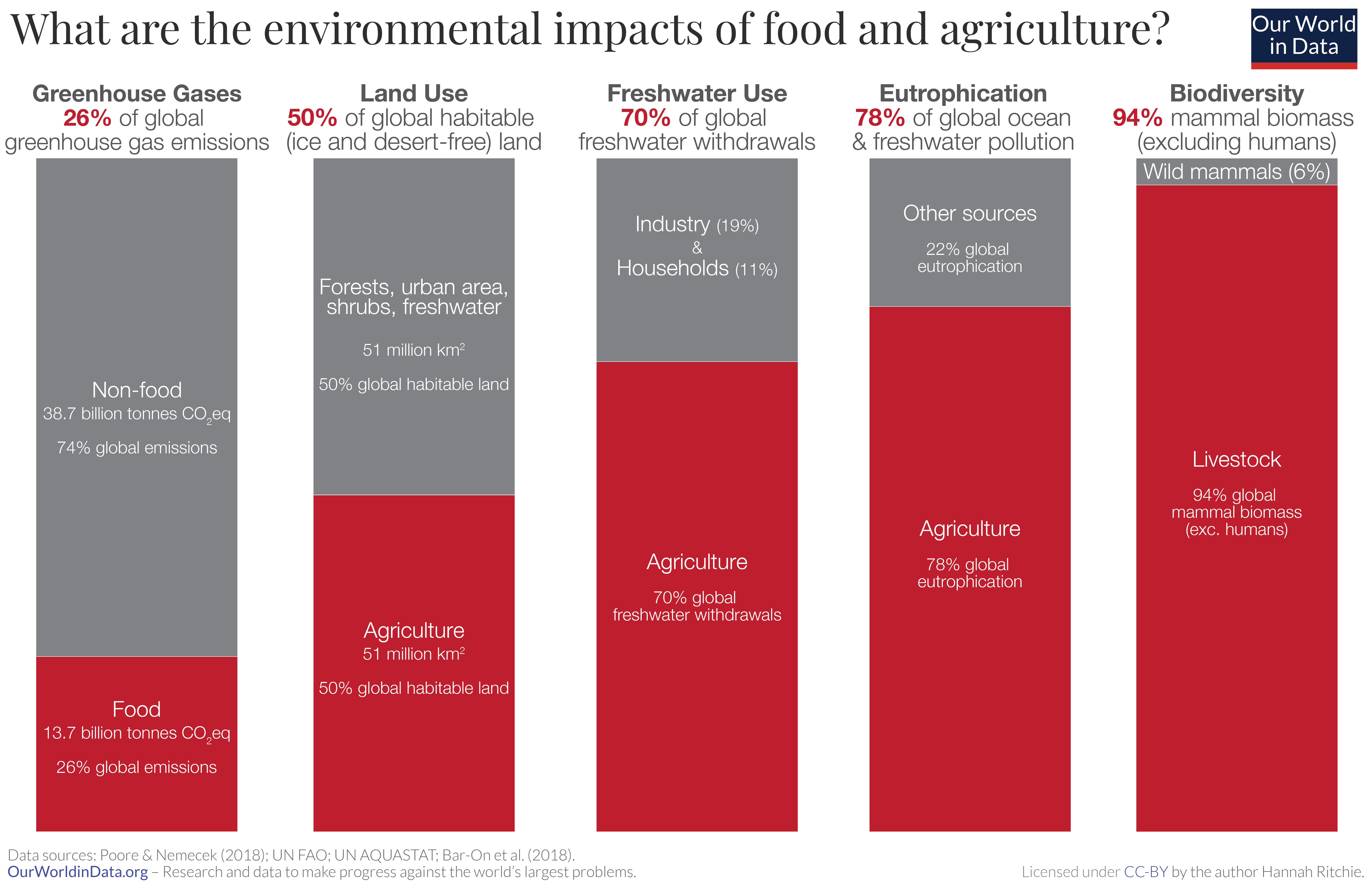
Food production accounts for 26% of all global GHG emissions with livestock making up 31% of that.
Eutrophication:
Occurs when runoff from farms using high nutrience fertiliser flows into water systems causing blue algae to grow causing a hypoxic aquatic environment, this deoxygenates the water further increasing the hostility.
Agriculture accounts to 78% of all cases of eutrophication around the world.
6.3.1 Civil society response to environmental and social risks of global interactions
6.3.1.1 Greenpeace
Background:
Founded in 1971
Based in the Netherlands
Operates in more than 55 countries
they are a global campaigning network
Campaigns:
Asian Pulp Paper (APP) & Mattel
6.3.2 Strategies to build resilience
6.3.2 (2) Crowdsourcing
6.3.3 New tech, cyber-tech and e-passports
6.1.1 Threats to Individuals and Businesses
6.1.1.1 Hacking, ID Theft
Stealing intellectual property
Taking control of online bank accounts
Viruses
Disrupting computer controlled services
Different types of Methods:
Phishing - Internet Danger
Occurs when visiting sites or reading emails.
typically a link that will pretend to be someone else and request credentials, e.g. bank details, Nigerian uncle, fake blackmail.
Trojans - Computer Danger
Occurs when using infected sites, outdated software, links and attachments
Intercepts data that you input, they will typically copy your information and quickly use to steal data.
can be performed by collecting data when it’s entered, using web injection, and/or bypassing two-factor authentication
Interception - Connection Dangers
Occurs when using unprotected internet connections or Wi-Fi hotspots
can be used to directly change visible data on a device, URL/IP remapping, causing trusted links to send you somewhere else.
All data can be intercepted and stolen
Case Study:
Bangladesh Bank Heist - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bangladesh_Bank_robbery
False instructions were sent to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, to send US$1 billion to the Bangladesh bank, performed over 35 transactions. $81 million were successfully sent to the hackers account in the Philippines before New York realised, only retrieving $18 million since.
6.1.1.1 (2) Implications of Surveillance for Personal Freedoms
To what extent should a society accept government surveillance of its citizens personal data
UN surveillance guidelines:
Any government surveillance should be properly regulated by legal frameworks, and must fall under a specific aim
Any form of illegal surveillance should be criminalised
Anonymity online should a personal right
Measures must be taken to avoid commercialisation of trade in surveillance technology
Case Study:
Surveillance in China
Characteristics of surveillance
1 camera per 3 people
30x more cameras than US
initially started to suppress protests
Aim of surveillance
Have a record of public crime
help people who have lost items
Impact
a) Positives
People feel more safe
Decrease in crime rates
Facial recognition can be applied globally
b) Negatives
Suppression of masses to maintain power
6.1.1.2 Economic, Political and Environmental Risks to the Supply Chain
Environmental Risks:
Natural disasters
Extreme weather
Pandemic
Geopolitical Risks:
Political instability
Trade restrictions
Terrorism
Corruption
Theft and illicit trade
Piracy
Economic:
Demand shocks
Price volatility
Border delays
Currency fluctuations
Energy Shortages
Case Studies:
Environmental - Japan Earthquakes
The 2011 earthquake and tsunami that affected the Fukushima plant, also caused damage to several trade and production infrastructures, causing problems to arise in supply chains, as they could not handle good/services throughout the country
Geopolitical - Boko Haram and Somalia Pirates
in Somalia there is a large quantity of trade pirates due to the close proximity to the Bab al-Mandab Strait, which is a major choke point for trade ships. causing issues in supply chains for other countries
Boko Haram is a terrorism group located in Nigeria and cause fear of travelling through the country, therefore limiting the supply chains that run throughout Nigeria
Economic - Argentina hyperinflation
Argentina is facing a case of hyperinflation, with annual inflation rates reaching over 100%. With their weakening currency imports and exports decrease, causing supply chain issues as they no longer have access to good that they can’t produce at large scales.
6.1.2 New and emerging threats to political and economic sovereignty of states
6.1.2.1 Profit Repatriation and Tax Avoidance by TNC’s
Repatriation:
the act or process of restoring or returning someone or something to the country of origin, allegiance, or citizenship
Case Study:
Glencore - Zambia Copper Mines
Situation:
Nearly all copper mines in Zambia are owned by TNC’s
in the last 10 years US$29bn worth of copper has been extracted from Zambia while paying minimal tax
Copper accounted for 2.3% of Zambia’s GDP but makes up 70% of their exports
Transfer Pricing:
involves TNC’s selling products internally between subsidiaries, therefore avoiding high tax rates in the original country (Zambia) by selling in low tax countries like Switzerland
Glencore owns the Mopani copper mines, who sells to glencore at a loss, therefore artificially reducing the price. Then they sell it from Switzerland at full market price, with low tax rates.
Glencore:
Largest commodities trader in the world
Annual revenue (US$180bn) is 8x larger than Zambia’s GDP (US$20bn)
Able to buy out governments with bribing
6.1.2.2 Disruptive Technological Innovations
Disruptive Technology
Disruptive technologies is an innovation that significantly alters the way that consumers, industries, or businesses operate
e.g. Tv’s, GPS, cars, planes, etc
6.1.3 Renewed nationalism & tribalism
6.1.3.1 Globalisation and Tribalisation
Globalisation: 🔗 4.1 KOF
The process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide
e.g. McDonald’s, Ikea, Coca-Cola
The rate of globalisation is slowing down, as visible in Graph 1

Tribalisation/Nationalism:
Promoting the interests of a particular nation, with the aim of gaining sovereignty and renewing identity
Currently seeing a rise in HIC’s like most of the EU and America
Often related with religion, e.g. Boko Haram
Case Study:
Boko Haram - western education is a sin (Tribalisation/Nationalism)
Based in north east Nigeria
Main belief being, remove all western culture and ideology from the country
main religion belief is Islamic
Brexit (Tribalisation/Nationalism)
UK withdrawing from the EU., voted for by UK citizens in a referendum
Brexit happened because the UK population believed decisions about the UK should be made by the UK
the overall desire was to reinstate their sovereignty
U.S. States - Donald Trump (Tribalisation/Nationalism)
‘Make America Great Again’
US - Mexico border, Anti immigration
6.2.1 Transboundary Pollution (TBP)
6.2.1.1 TBP and it’s consequences
Transboundary Pollution: 🔗 2.1.3, 4.2.1, 5.1.1
Emissions that are produced, and travel across land without recognition of borders.
Acid deposition:
rainfall that has a pH of less than 5.5 as a result of sulphur dioxide and nitrous oxides dissolving in water vapour held in the atmosphere.
typically caused by sulphur dioxide pollution from coal-fired power stations and nitrous oxides from petrol powered vehicles
Dry Deposition - when particulate matter falls close to the source (generally not transboundary)
Wet Deposition - when the pollution is carried by wind away from the source and to another location, this is a large problem for smaller countries like in the EU
Strategies to Reduce Impacts:
Gothenburg Protocol - 1983
signed by all EU countries, Russia, America, and Canada
called for the reduction of acidification, eutrophication by setting emissions ceilings for sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds and ammonia
Case Study:
Global action following the Chernobyl accident
After the explosion polluting particles Caesium-137 were discovered in extremely high levels 2 weeks after the explosion in Austria, Slovenia, Norway, Sweden and Finland.
the World Association of Nuclear Operators (WANO) was formed, with the main goal - to maximise the safety and reliability of nuclear power plants worldwide
6.2.2 Environmental Impacts of Global Flows
6.2.2.1 Localised Pollution, and Impacts Along Shipping Lanes
Choke Points:
shipping routes where there is a high density of ships, e.g. Suez canal, Panama canal, Baltic sea, East asia, etc

Other Environment impacts of Shipping
Deliberate and accidental oil and chemical discharges
Waste dumping
Air pollution
Damage to sea floor from the anchor
Noise pollution for sea life
Pest organisms that become invasive through ballast water (pacific sea star from japan, moving to port Phillip bay)
Case Study:
Singapore Oil Spills
Singapore has the 2nd busiest port in the world - as well 4 of the busiest ports are also located in Asia
Due to high traffic and the narrowness of the channel, there has been 11 major oil spills

6.2.2.2 Carbon Footprints of Different Flows
Flow of Goods
Food Miles:
total pollution created when transporting the food you purchase
Meat production:
one of the highest producers of pollution due to the production of the product
→ increasing global middle class
→ ∴ increased consumption of meats as number of HIC’s increase
→ Nutrition transition - change of diet

Flow of People
Migration:
The movement of people from LIC’s to HIC’s is a major contributor to global emissions, with the rate of migrations being at an all time high
Between 2008 and 2033 will add 7 million people to the UK, which will add around 500 million tonnes of CO2 by 2033
Tourism:
Increased globalisation, leads to increased tourism
Tourism hotspots like Europe lead to higher localised pollution

6.2.3 Environmental issues from global shift of industry
6.2.3.1 Polluting Manufacturing Industries
Global Shift:
The gradual movement of manufacturing from HIC’s to newly industrialised countries (NIC’s)
Global shifts started as the rise of globalisation begun
the main goal of moving manufacturing is to decrease costs with use of either lower tax rate laws, cheaper labour, less trade barriers, and potential FDI
Environmental Impact:
typically there are lower environmental regulations and restrictions in emerging economies
Lack of infrastructure that is sustainable
desire for profit is being placed over desire for sustainability
Case Study:
Industry Shift From USA to Mexico - Environmental Impacts
1 item = 1.4kg of CO2
Heavy metals are being produced without adequate processing methods
Illegal dumping
6.2.3.2 Environmental issues from global agribusiness
Agro-Industrialisation:
large-scale, intensive, high-input, high-output, commercialised, technologically advanced forms of farming food and fibre
Western farming practices
Positives and Negatives of Agro-Industrialisation:
Positives Negatives | ||
Socio-economic | - Increased production/higher yields - More high skill jobs, better efficiency, benefits consumers - Avoided Malthusian check | - Fewer low skill jobs - Small scale farmers struggle against larger farms - unfair competition |
Environmental | - conservation methods are being introduced, reducing harmful chemical use, etc. | - GHG emissions - 10% of the UK’s GHG comes from Ag - Water pollution - Salinisation - Loss of Biodiversity - Land erosion/degradation |
Past 50 Years: Positive Impact
Wheat yields have increased from 2.6 to 8 tonnes/hectare
Barley yields have increased from 2.6 to 5 tonnes/hectare
Dairy production has increased from 4,000 L/yr to 5,800 L/yr
Environmental Impacts: Negative Impact

Food production accounts for 26% of all global GHG emissions with livestock making up 31% of that.
Eutrophication:
Occurs when runoff from farms using high nutrience fertiliser flows into water systems causing blue algae to grow causing a hypoxic aquatic environment, this deoxygenates the water further increasing the hostility.
Agriculture accounts to 78% of all cases of eutrophication around the world.
6.3.1 Civil society response to environmental and social risks of global interactions
6.3.1.1 Greenpeace
Background:
Founded in 1971
Based in the Netherlands
Operates in more than 55 countries
they are a global campaigning network
Campaigns:
Asian Pulp Paper (APP) & Mattel
6.3.2 Strategies to build resilience
6.3.2 (2) Crowdsourcing
6.3.3 New tech, cyber-tech and e-passports