Topic 1 - neutralisation
Definition of neutralisation - the reaction of an acid and an alkali forming salt and water
| Acid | Salt formed |
|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid | Chloride |
| Sulfuric acid | Sulfate |
| Nitric acid | Nitrate |
| Bases | Alkalis |
|---|---|
| Sodium hydroxide | Sodium hydroxide |
| Calcium oxide | Potassium hydroxide |
| Potassium hydroxide | |
| Lithium oxide | |
| Copper oxide |
Alkali - a soluble base typically metal hydroxides
Base - metal oxides or metal hydroxides
Acid + metal = salt + hydrogen
Acid + alkali = salt + water
Acid + base = salt + water
Acid + metal carbonate = salt + water + carbon dioxide
| Indicator | Colour in hydrochloric acid | Colour in water | Colour in sodium hydroxide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red litmus | Same | Same | Blue |
| Blue litmus | Red | Same | Same |
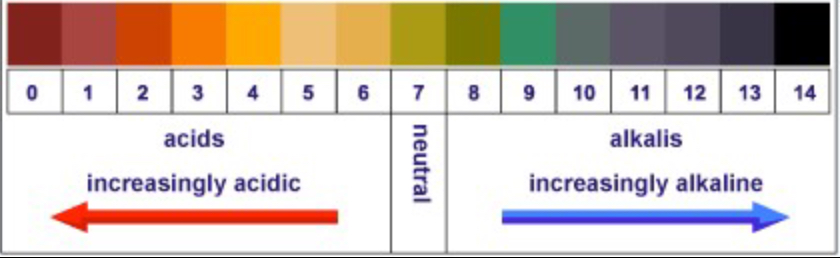
| Universal indicator solution | Red | Green | Purple |
| Methyl orange | Red | Orange | Orange |
| Screened methyl orange | Dark red | Green | Green |
| Phenolphthalein | Colourless | Colourless | Dark pink |
Indicator - a chemical that gives a colour change in acidic, alkaline and neutral soloutions.