7.1: Statistics and Parameters
Statistics and Parameters
- Statistic: a number that describes some characteristic of the sample
- Relevant symbols
- Mean: x̄
- Proportion: p̂
- Standard deviation: S
- Parameter: a number that describes some characteristic of the population
- Relevant symbols
- Mean: μ
- Proportion: p
- Standard deviation: σ
- Samples are taken to try to estimate the population (μ or p)
- Ultimate goal: Estimate parameters based on statistics
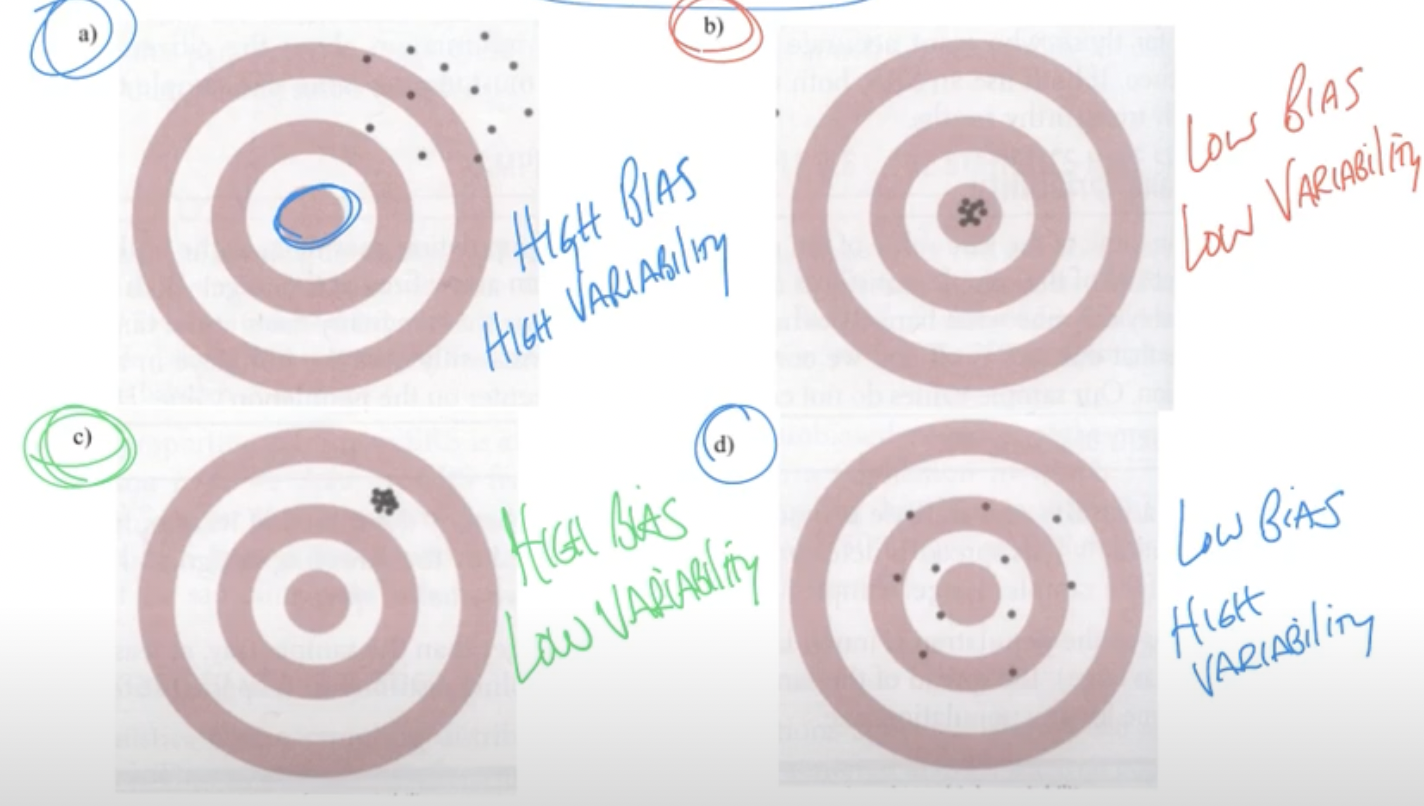
Distribution, Variability, and Bias
- Sampling distribution: the distribution of values taken by the statistic in all possible samples of the same size from the same population
- Eg. sample mean, proportion
- Sampling variability: how much results vary between samples
- Every time a sample is taken, the results will vary
- Measured using the spread of the random sample
- Based primarily on the size of the random sample
- As a general rule of thumb,
- Larger sample: less variability
- Smaller sample: more variability
- The spread does not depend on the size of the population, as long as it is at least 10x larger than the sample
- Biased statistic: a statistic which consistently overestimates or underestimates the parameter (mean or proportion)
- Unbiased statistic: a statistic in which the distribution of samples is centered around the true population’s parameter
Bias vs. variance
Means and Proportions
Proportion problems generally involve categorical variables
Binomial distributions will become approximately normal distributions if np≥10 and n(1-p)≥10
- n = sample size
- p = population proportion
- p̂ = sample proportion
- Normal distribution means the use of z-scores as a standard measure
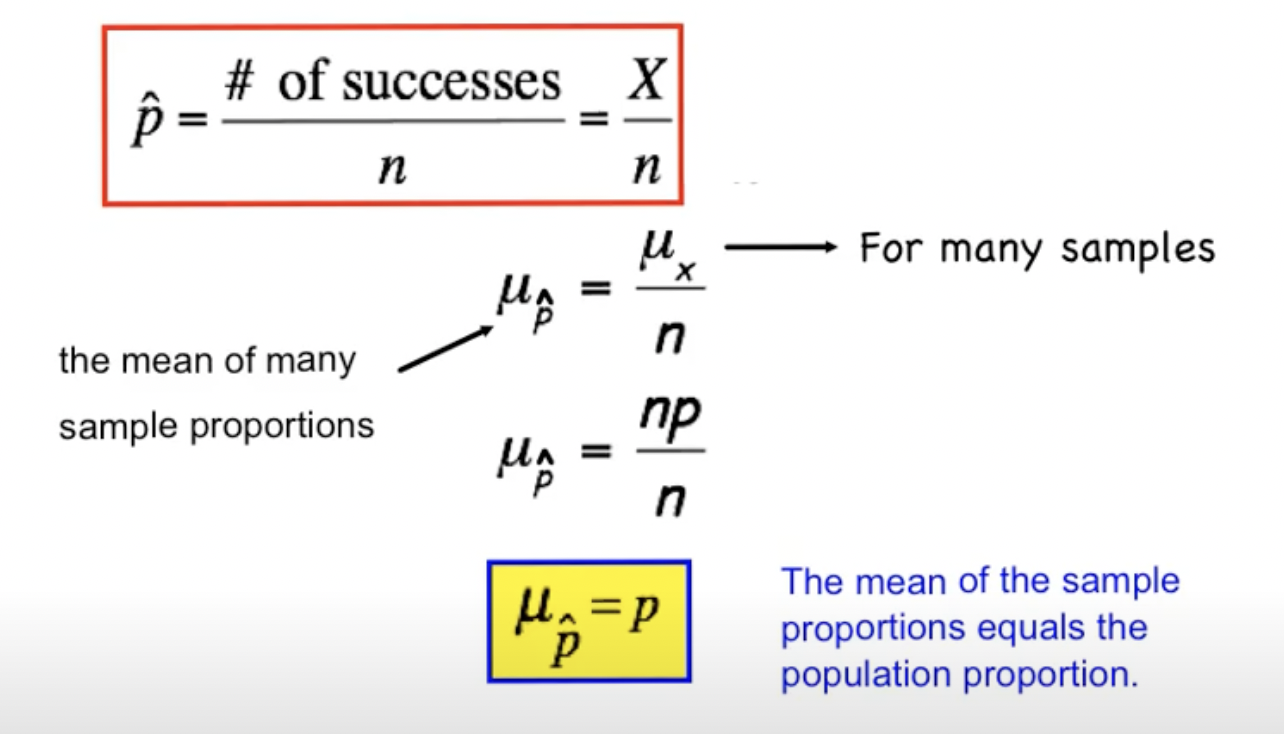
Statistics are unbiased if they are equal to the true parameters, so p̂ is an unbiased estimator of p
Verifying Conditions
- If an SRS is taken of size n from a large population with proportion p,
- Some conditions must be stated and checked
- Is the population more than 10x larger than the sample size?
- The 10% condition verifies that the standard deviation formula may be used
- Is np ≥ 10 and is n(1-p) ≥ 10?
- This verifies that a normal approximation may be used
- If these conditions are met, the mean of the sample proportions will equal the true population proportion