Microtubules
Microtubules are long, hollow cylinders made of the protein tubulin
Roles of Microtubules in Cells
organelle positioning
vesicle trafficking
mitotic spindle formation pulling apart chromosomes
form stable structures in cilia and flagella
movement of cilia and flagella depends on microtubules
Subunits
tubulin: dimeric protein composed of 2 globular proteins held together by non-covalent bonds
alpha-tubulin
beta-tubulin
each subunit binds GTP
GTP bound to alpha-tubulin CANNOT be hydrolyzed
GTP bounds to beta-tubulin can be hydrolyzed to GDP
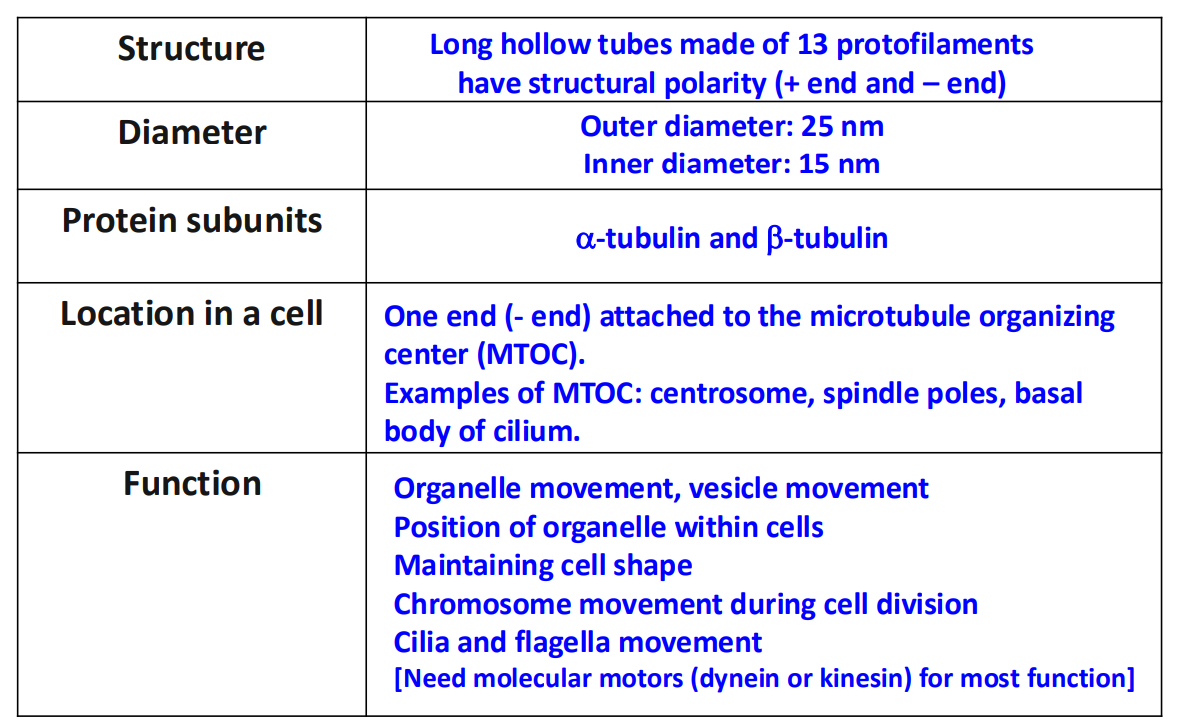
Structure
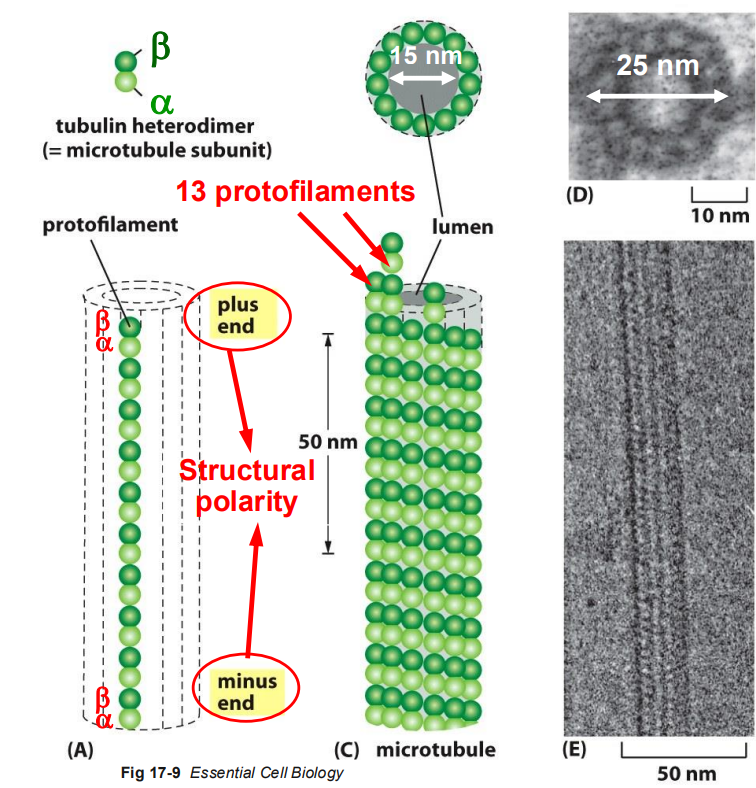
hollow tubes composed of tubulin dimers (alpha and beta-tubulin stack together forming the wall of the MT)
hollow tubes made of 13 parallel protofilaments
inner diameter = 15nm
outer diameter = 25 nm
have structural polarity - the two ends of the polymer are different from each other - which is crucial for MT assembly and function
beta-tubulin end: + end
alpha-tubulin end: - end
tubulin dimers can be ADDED and REMOVED at both ends BUT at different rates
Minus End (Alpha-Tubulin)
Plus end (Beta-Tubulin)
Characteristics
Does not readilt bind to beta-tubulin in an incoming dimer (not the right conformation)
Addition of subunits causes a conformational change in beta-tubulin that increases binding for more subunits (binds alpha-tubulin of an incoming dimer)
Growth Rate
slow growing end
fast growing end
Microtubule Assembly
In Vivo
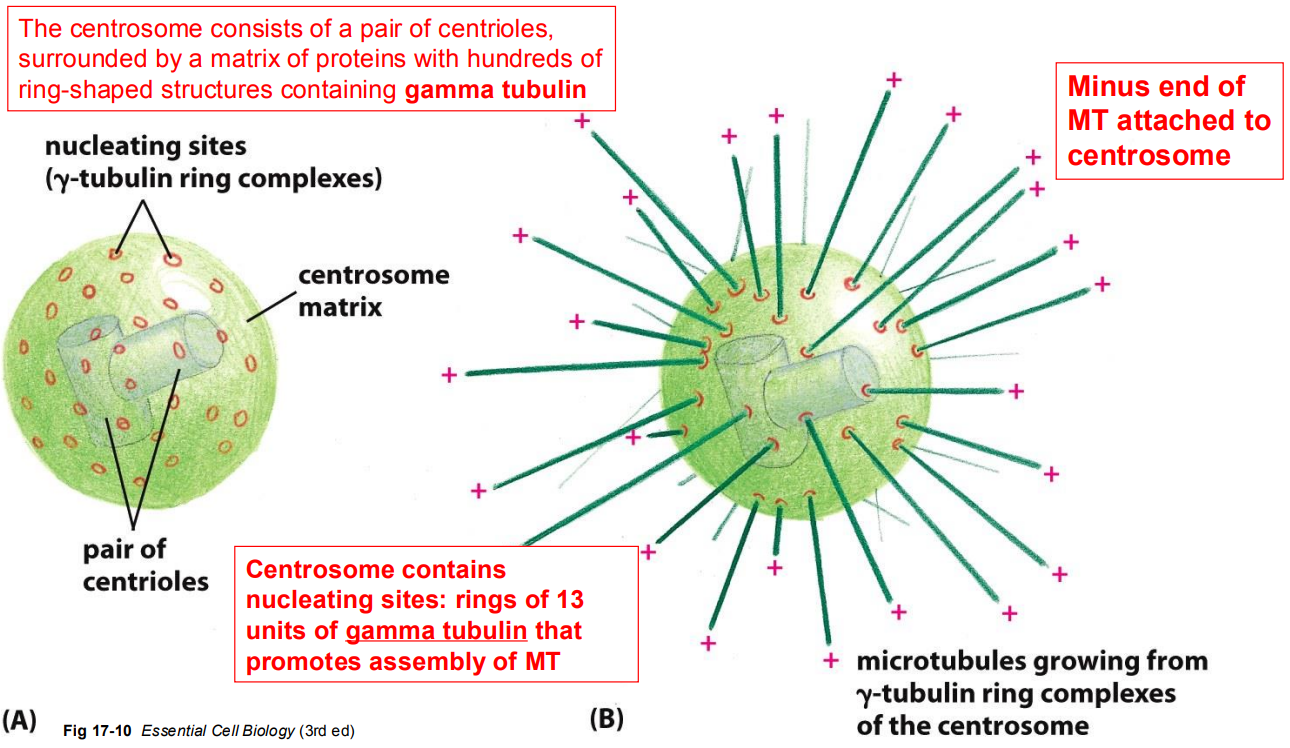
A. In Vivo (inside the cell): microtubule organizing centres (MTOCs) in cells provide the right conditions for rapid nucleation of microtubules
microtubules grow from gamma tubulin rings of the centrosome
structure of centrosome
pairs of centrioles - in the middle
centrosome matrix
a-ring-shaped gammtubulin - floats in matrix
Minus end of MT is attached to the centrosome
microtubules originate from Microtubule Organizing Centers (MTOC) - minus end of MT attached to a MTOC
interphase cells
ciliated cell
dividing cell
In Vitro
B. In Vitro (monomers in a tube) - initiating cytoskeletal polymerization (nucleation) to build microtubule or actin polymers is a slow process in vitro
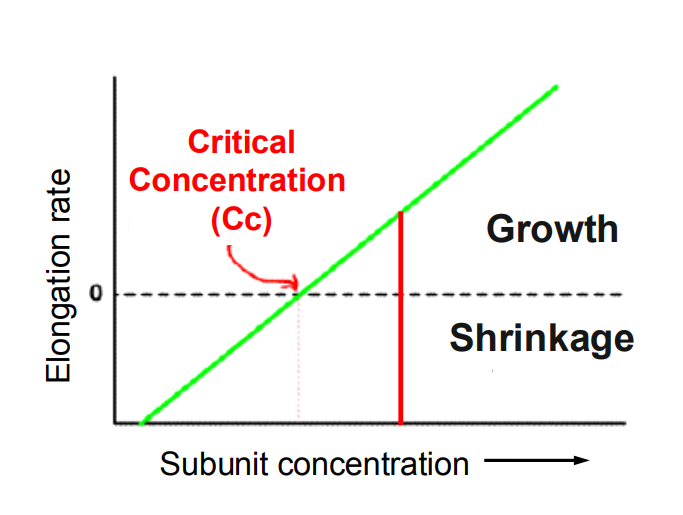
Critical Concentration: the [ ] at which the length of the filament is stable
CC = rate of subunit addition = the rate of subunit loss
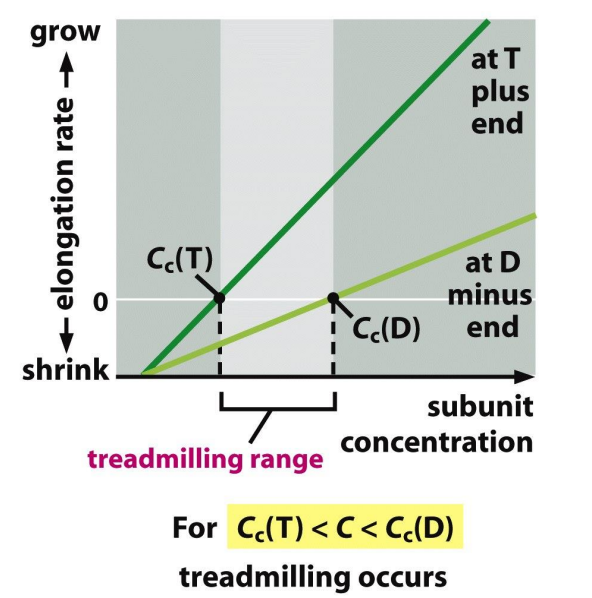
Critical [ ] at 2 ends of a microtubule is diff
Cc (minus end) > Cc (plus end)
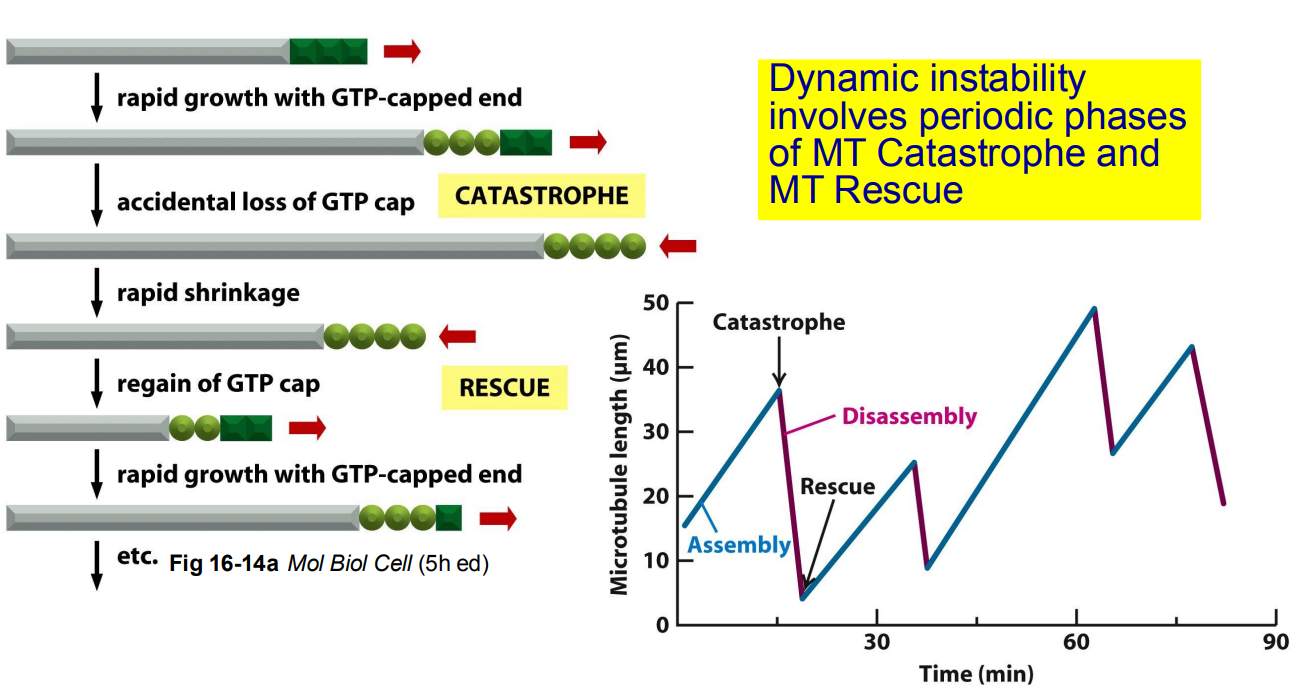
dynamic instability: rapid cycles of growth and shrinkage of microtubules
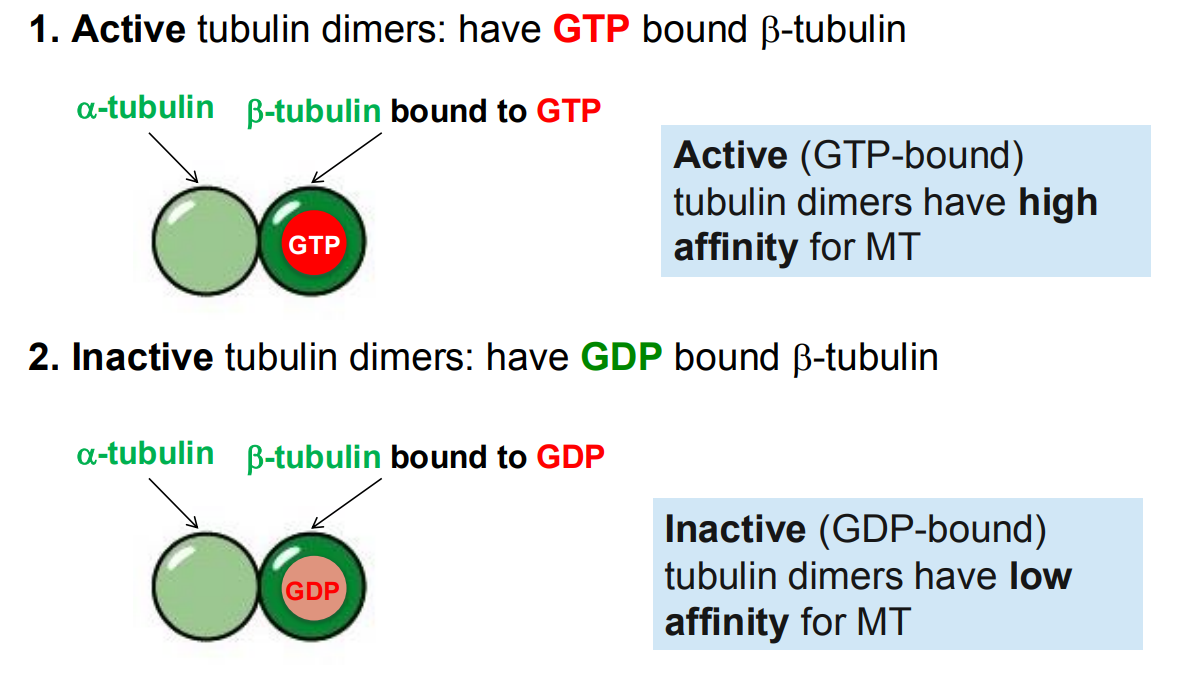
Active
Inactive
structure
tubulin dimers that have GTP bound beta-tubulin
tubulin dimers that have GDP bound beta
affinity for MT
high affinity
low affinity
GTP tubulin dimers convert to GDP tubulin dimers. The end of a microtubule could be
GTP-bound end: high affinity for GTP-bound tubulin → MT grows
GDP-bound end: low affinity for tubulin → MT disassembles
GTP Cap: a region at the end of a polymerizing microtubule where GTP hydrolysis has not yet occurred
growing MT have a GTP at + end
GTP hydrolysis controls the dynamics of microtubule polymerization
Microtubule growth (formation of GTP cap)
Microtubule shrinks
rate of GTP hydrolysis
addition of tubulin > faster than GTP hydrolysis
GTP hydrolysis > addition of tubulin
structure of growing MT
straight
curved protofilaments at the end; looks like protofilaments are peeling
treadmilling: the polymer grows at the plus end and shrinks at the minus end
involves periodic phases of MT catastrophe and MT rescue
Provide examples of how proteins can interact with microtubules or tubulin to influence their structure, which, in turn, will influence function
Learning Objective 6
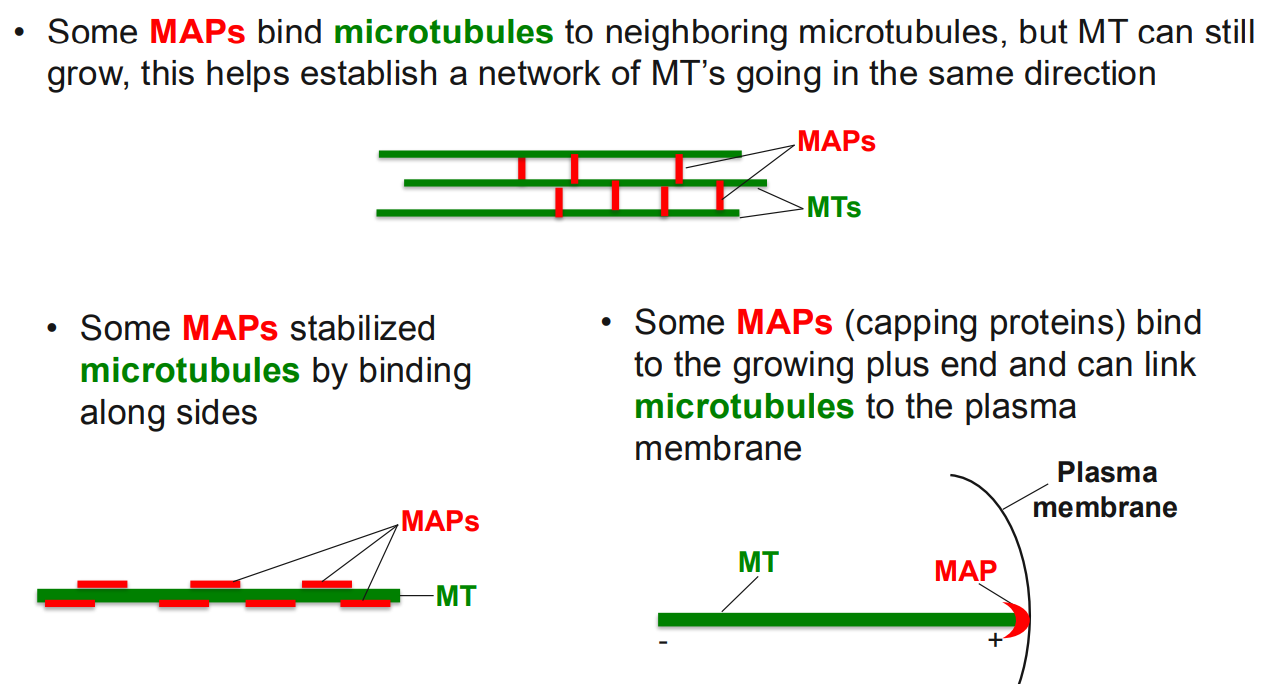
MAPS (capping protein) at the plasma membrane helps to influence cell shape and to form polarize cells
function
some MAPS bind microtubules to neighboring microtubules, but MT can still grow → helps establish a network of MT’s going in the same direction
MAPS stabilize microtubules by binding along sides
MAPs bind to the growing plus end and can link microtubules to the plasma membrane