ACCT501_Chapter_4_Flashcards
Chapter 4: Revenue Recognition and the Statement of Income
Learning Objectives
LO1: Explain the nature of revenue and its significance.
LO2: Identify and explain the contract-based approach to revenue recognition.
LO3: Discuss how revenue recognition is influenced by returns, warranties, consignment, and third-party sales.
LO4: Differentiate between single-step and multi-step statements of income.
LO5: Distinguish between comprehensive income and net income.
LO6: Explain expense presentation by function vs. nature.
LO7: Calculate and interpret basic earnings per share (EPS).
Understanding Revenues
Definition: Revenues are inflows of economic benefits resulting from a company's ordinary operating activities, specifically through cash and accounts receivable.
Sources of Revenue:
Sales of goods
Provision of services
Earnings Assessment:
Quantity: Measured by revenue growth.
Quality: Evaluated by the source of growth.
Revenue Recognition Overview
Challenge: Determining the timing of revenue recognition can be complex.
Approaches:
IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards): Contract-based approach (asset-liability approach).
ASPE (Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises): Earnings-based approach.
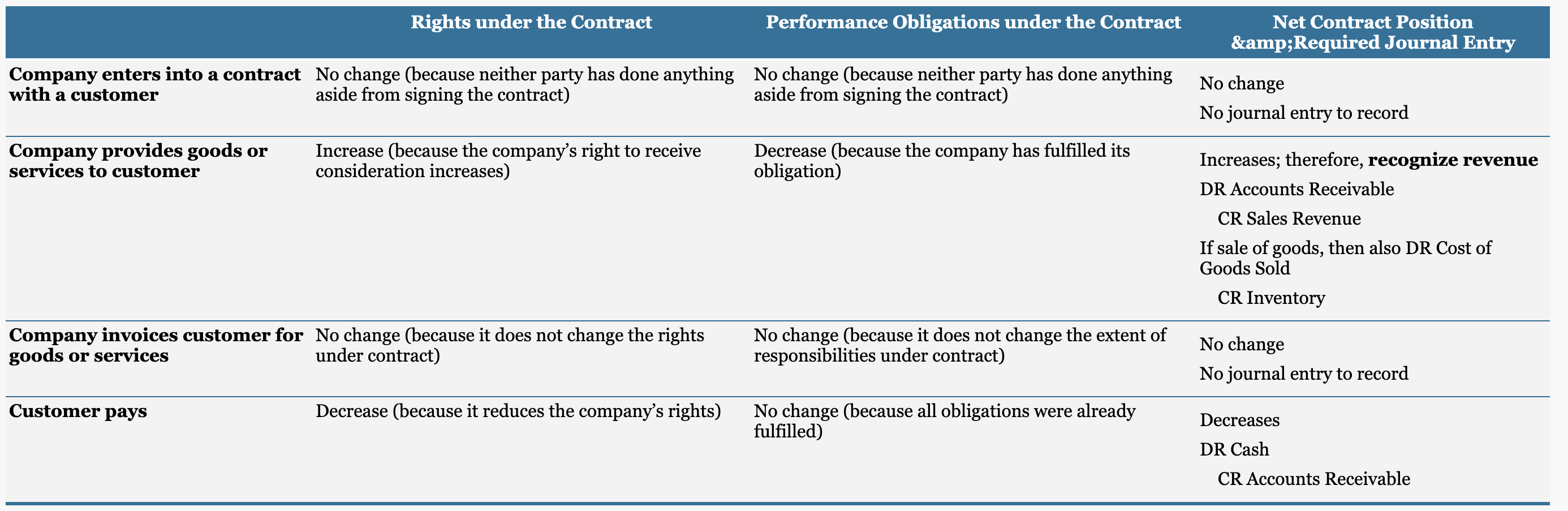
Revenue Recognition: Contract-based Approach
Revenue is recognized when a company’s net position in a contract increases, indicated by:
Increase in rights under the contract.
Decrease in performance obligations.
Performance Obligations: These must be fulfilled to recognize revenue.
Revenue Recognition: Five-Step Model
Identify the contract: Understand the terms and conditions.
Identify performance obligations: Define what needs to be delivered to fulfill the contract.
Determine transaction price: Establish the price the company expects to receive.
Allocate the transaction price: Assign the price to performance obligations based on their standalone selling prices.
Recognize revenue: Revenue is recognized when performance obligations are satisfied, either at a point in time or over time.
Revenue Recognition Issues
Right of Returns: Companies must estimate expected product returns.
Warranties:
Assurance warranties: Not considered separate performance obligations.
Service warranties: A portion of the transaction price must be allocated to these.
Consignment Sales: Revenue is recognized only when goods are sold.
Third-Party Sales: Companies acting as agents recognize only their commission.
Statement of Income Types
Single-Step Income Statement: Simplifies income calculation without separating operational results.
Multi-Step Income Statement: Provides detailed information, separating operational revenues from non-operational revenues and expenses.
Hybrid Forms: Companies may use elements from both formats in their statements.
Comprehensive Income
Definition: Comprehensive income is the total change in shareholders' equity from non-owner sources, which includes:
Gains/losses from revaluation to fair value.
Gains/losses from foreign exchange rate changes.
Formula: Comprehensive Income = Net Income + Other Comprehensive Income.
Expense Presentation
Function: Groups expenses according to their functional area (e.g., cost of sales, administrative expenses).
Nature: Lists expenses based on type (e.g., wages, depreciation).
Financial Statement Analysis - Earnings per Share (EPS)
EPS Definition: Represents net income attributable to common shares, calculated after deducting preferred share dividends.
Significance: Used to assess company performance and is frequently cited in financial analysis.
Calculation: Basic EPS can be calculated when there is no change in common share numbers or when changes occur.
(EPS = [Net income - preferred dividends]/ weighted avg of common shares outstanding)
Example Calculation: Montgomery Ltd. reported net income of $625,000 with preferred dividends of $30,000, resulting in 250,000 common shares outstanding.