U2 M8 Price Ceiling
The Rationing Function of Prices
rationing: dividing something out
ex. you don’t have an infinite amount of money, u need to ration ur money to buy a lambo
If we didn’t have scarcity, no need for rationing
Once scarcity arises, there has to be a way to ration available resources, goods, or services
Price system is 1 form of rationing
Methods or non-price rationing
queues, random assignments, coupons
ex. Mr. Mordkoff gives only half of his class a certain assignment at a time
colleges: money has to be rationed (can’t afford it), acceptance method(some will get out some won’t → that’s a non-price form of rationing)
Price Controls
legal restrictions on how high or low a market price can go
Price Ceilings and Price Floors
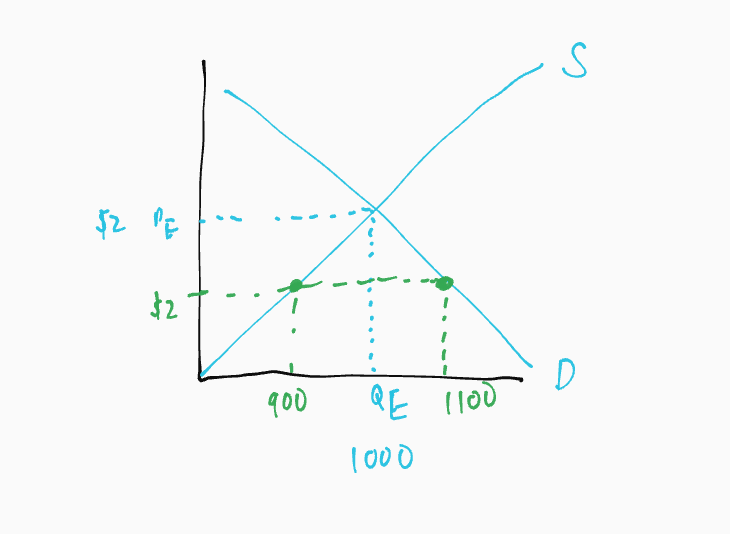
Price Ceiling
a policy that puts a maximum price on an item. This hinders the rationing function of prices.
If set below the market clearing level, a prolonged shortage will result.
If the price ceiling is above the equilibrium price, nothing will change (in the short run) because equilibrium is the best price
Why Price Ceilings?
To protect lower income citizens from not being able to purchase or obtain certain goods or services (I.e. rent control)
To necessities, to protect consumers from exorbitant, unethical, high prices, that could be set by producers (ie - electricity, water, etc.)
Effects of Price Ceiling
Shortages
Inefficient allocation to consumers:
if you were willing to pay at equilibrium before the price ceiling, now you might not be able to buy your gasoline because of the shortage
Wasted Resources
waste time looking over for a good because of the shortage
Inefficiently low quality:
no incentive to try hard because they can’t get a higher profit margin (they’ll skimp out on other things)
Black Markets
selling goods illegally