The product
Gift wrap
Wrapping increase quality of product
However, expectation disconfirmation. Badly wrapped present lower expectation, so the present may exceed the low expectation => good
Acquaintance should wrap gift neatly, cause it reflect the importance of relationship
Shelf positioning and attention
Product in horizontal center receive more visual attention => more likely to get pick
Central fixation bias: Tendency to look at central products
Gaze cascade: Increase eye visual on the product we will buy
Central gaze cascade effect: Increase attention for horizontal central product prior to purchase
Atalay
Prove effect of central fixation bias
on choice likelihood
67 PPT look and chose product on computer with eye tracker
Product in middle are looked at more and choose more
Measured eye movement with eye-tracker => objective and reliable data
Too deterministic, buying a product depends on other factors (money)
Key study: Food package design and taste perception. Becket et al
Customer choose new product based on packaging, or when they have to make quick decision
Cross-modal correspondence: Great intensity in one sensory will affect the other senses (Taste perception influenced by food look, 7UP is sweeter with green bottle)
Bright color make food flavor more intense
Shape affects perception, sharp edges means strength, round edges mean friendliness
Processing fluency and congruence: We like things that are easy to understand. 2 aspect of design should fit in well to increase liking. => How well 2 aspect of packaging go together. Bold color (strength) and round edges (relaxing) confuse customer, make it harder to understand product
Aim
See if color and shape of yogurt packaging affect taste
Hypothesis:
Yogurt in sharp edges container + bold color will have stronger flavor
Attitudes towards yogurt will be better if shape+color go well together
Customer with more design sensitive will be affected more
Method
Field experiment, told this is taste test for new yogurt
Large German supermarket
Sample
Opportunity, approached and asked if they can take part in study
151 German, mostly male
Procedure
Pre-test: There were many container design and color combination, ppt chose the 2 pairs that differ from each other the most
PPT watched 20 second movie of one of 4 variants spinning 360 degree (square/circle with bold or light color)
Taste lemon yogurt
Completed computer questions (all scale 1-7)
About the product: taste intensity, and estimated selling price
Design sensitivity: “packaging is important to me”
Manipulation check: test to see if design has effect on ppt, “This product looks potent to me”
Results
Angular packaging perceived more potent, only design sensitive ppt see high color saturation as potent
Only shape design affect taste intensity for design sensitive ppt
Sharp design rated more positively and suggested a higher selling price (cause sharp = more impressive = more expensive). Surprisingly, same for low color (cause high saturation seem as cheap)
Conclusion
Angular product more intense taste but only for who pays attention to packaging
Color saturation doesn’t contribute to taste intensity, too bright color seems cheap and taste worse
Pretest to select packaging variants so potent rating is different, to measure IV change to potent ratings
Good reductionist: Break color into small details like saturation, study them individually => more detailed than just different colors
Color saturation was not noticeable, can’t measure its effect
Only measure sour, lack sweet or salty.
Only Germans
Deception: False aim of study + sensitivity questionnaire was to measure lifestyle. But reduce demand characteristics
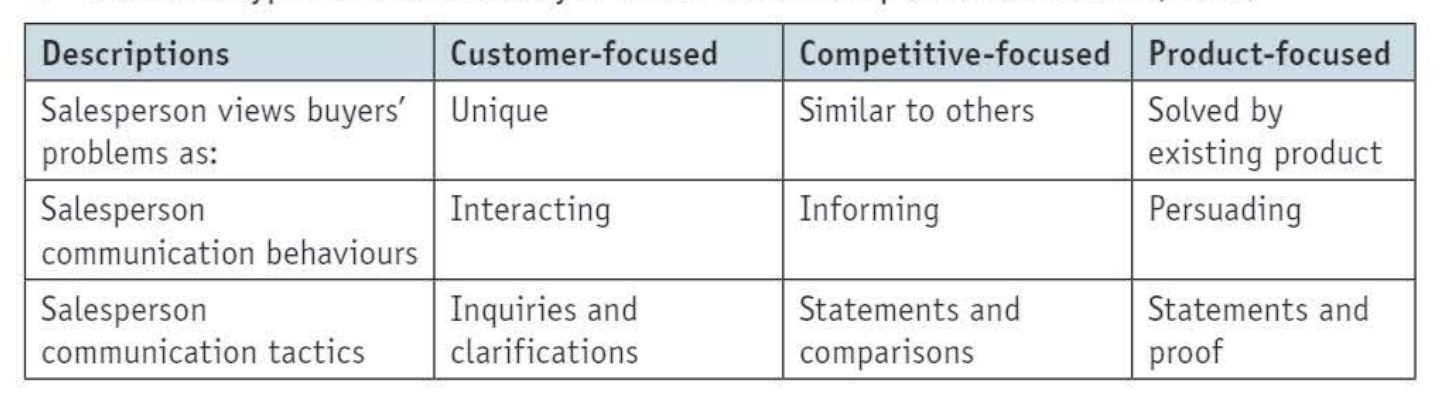
3 Sales techniques (DelVecchio)
Customer-focused
View each buyer has unique problem
Sales person active engage to solve the problem ⇒ ask questions like consultant to understand needs
Corporation increase sales and avoid conflict
Competitor-focused
Less collaboration to find solutions to individual customers, but convince how you are similar to other customer groups and why their product is better than other options
See buyer's problem as similar to other buyers
Group customers together
"Salesperson tell you your neighbors have all buy a product, you think they are the same like you so you trust the product"
Promote Unique Selling Point / FAB model
Product focused
Convince buyer they need the product
Convince how product fit their life
Focus on product features and advantages
Salesperson need to be seen knowledgeable in order to gain respect
If ask too many questions, or compare product with competitor too much, then not respected
Ignore customer preferences and needs
Focus on buyer response rather than salesperson, salesperson might overestimate their ability
Most ppt were old experienced male 10+ years experience in B2B, not generalizable for young women
Lack culture differences: Japanese has high intolerance of uncertainty, want to know everything before buying, so product focused is better for them
Interpersonal influence techniques
Disrupt-then-reframe
Seller make disrupting message to increase ambiguity. We are ambiguity averse, we want answer to confusing statements. High “NFCC” people seek for answer more, after NFCC is satisfied, we are more relaxed and easier to persuade.
E.g: Instead of “That’s 3 euro”, say “membership is 300 cents, that’s 3 euro.”
Mini study: Kardes
See if DTR determined by NFCC
Researcher act as student council member, ask for 3 Euros membership with disrupting message: 300 cents, that’s 3 euros.
Do questionnaires to measure NFCC
High NFCC and DTR group buy more membership
Real world setting
If student is in a hurry, their NFCC is low cause they don’t care
Foot in door: Offer small request, then bigger request (consistency)
Door in face: Offer expensive request, then offer cheaper one (anchor bias).
Cialdini’s 6 ways to close a sale (L SCARS)
Reciprocation: Salesperson give gift for customer so they feel entitled to buy
(e.g: waiter are tipped higher when give guest candy)
Scarcity
Liking: Salesperson should build relationship before sell something (find common interest, compliment)
Authority: Salesperson should be dominant. (Dress professional, charisma, good reputation)
Social proof: We look at others action to know what to do, salesperson should convince customer that other customers are using that product. Especially if it’s their first time buying it.
-Proof that social (others) are doing something-
Consistency: People stay consistent to something they commit
Use foot in door, one small request and customer will follow up to bigger ones
Buying the product
EKB model
Information processing steps. 5 stages:
Identifying needs
Search for info
Consider different alternative
Purchase decision
Outcome (the customer satisfaction with the purchase after some time)
Input of product (price,…)
Consider internal factor (belief, past experience with product) and external factor (friends and family, culture)
Recall competitor products for comparison
Customer must pay attention to information or it will get lost
Holistic: Consider interaction from multiple factors, suggest customer is unique
Only consider product we buy cause we need them. What about impulse purchase?
Choosing a store
Mini study: Sinha
247 rich Indian shoppers in one city as they left a store do survey and interview why they choose that store
Convenience
Service, ambience
Wide range of product
Male prefer convenience and “go and grab” style more, female prefer wide range of product more
Idiographic: Both questionnaire and open interview, categorize interview answer in groups
Post-purchase cognitive dissonance
Conflict between belief and behavior
Higher effort to search for right product, more likely to experience dissonance
Spontaneous purchase also cause dissonance, customer realize why they buy product without consideration
Customer should change their way of thinking to reduce dissonance : adaptive preference formation
Read positive reviews online => social proof that this product is good
Mini study: Nordvall
100 Swedish do virtual shopping trip online
Given pairs of organic and non-organic product, choose one
Dissonance do occur even for low-involvement product, ppt feel bad for rejecting a product
Not realistic, customers wouldn’t be asked to rate items