NURS-1001: Week 13: Clinical judgment- knowing, being & doing
- Think like a nurse
- Nursing process
- Development as a nurse
- Think like a nurse (our thoughts)
- Multitasking (interesting…)
- Objective assessments
- Using tuition and past experiences to better care for our patients and ourselves
- Think like a nurse:
- Clinical reasoning:
- “The cognitive process of thinking about patient issues, making inferences, and deciding on the actions to be implemented in a particular situation” (Potter & Perry, 2021).
- Application of knowledge and experiences
- Critical thinking apply to patient
- Available information that you have to make a decision
- Critical thinking:
- “A complex phenomenon that can be defined as a process and as a set of skills; an active, organized, cognitive process used to carefully examine one’s thinking and the thinking of others” (Potter & Perry, 2021).
- More broad than clinical reasoning
- Using knowledge from inside and outside of the clinical setting
- Individualistic considerations to a patient
- Social determinants of health
- Knowing when to investigate further, what information is misleading, when to recognize when more knowledge is needed.
- Knowing what questions to ask and how to ask them.
- Clinical decision-making:
- “The use of critical thinking skills throughout the nursing process to obtain relevant information about the patient and to plan and provide effective care and measure the outcomes of the care provided” (Potter & Perry, 2021).
- Demonstrated through actions and behaviours.
- Clinical decision-making process:
- Based on interpretation and reflection of patient situation
- Unique to the individual
- Requires clinical reasoning and critical thinking
- Precipitated by reflection
- Must be able to fully assess the situation
- Pathophysiology, diagnosis, physical, social and emotional factors, coping resources
- Complex
- Recognize biases…
- Clinical reasoning, reflections, nursing process
- Understand patients perspective
- Involve patient in decision making
- Always follow up with reflection and patient outcomes.
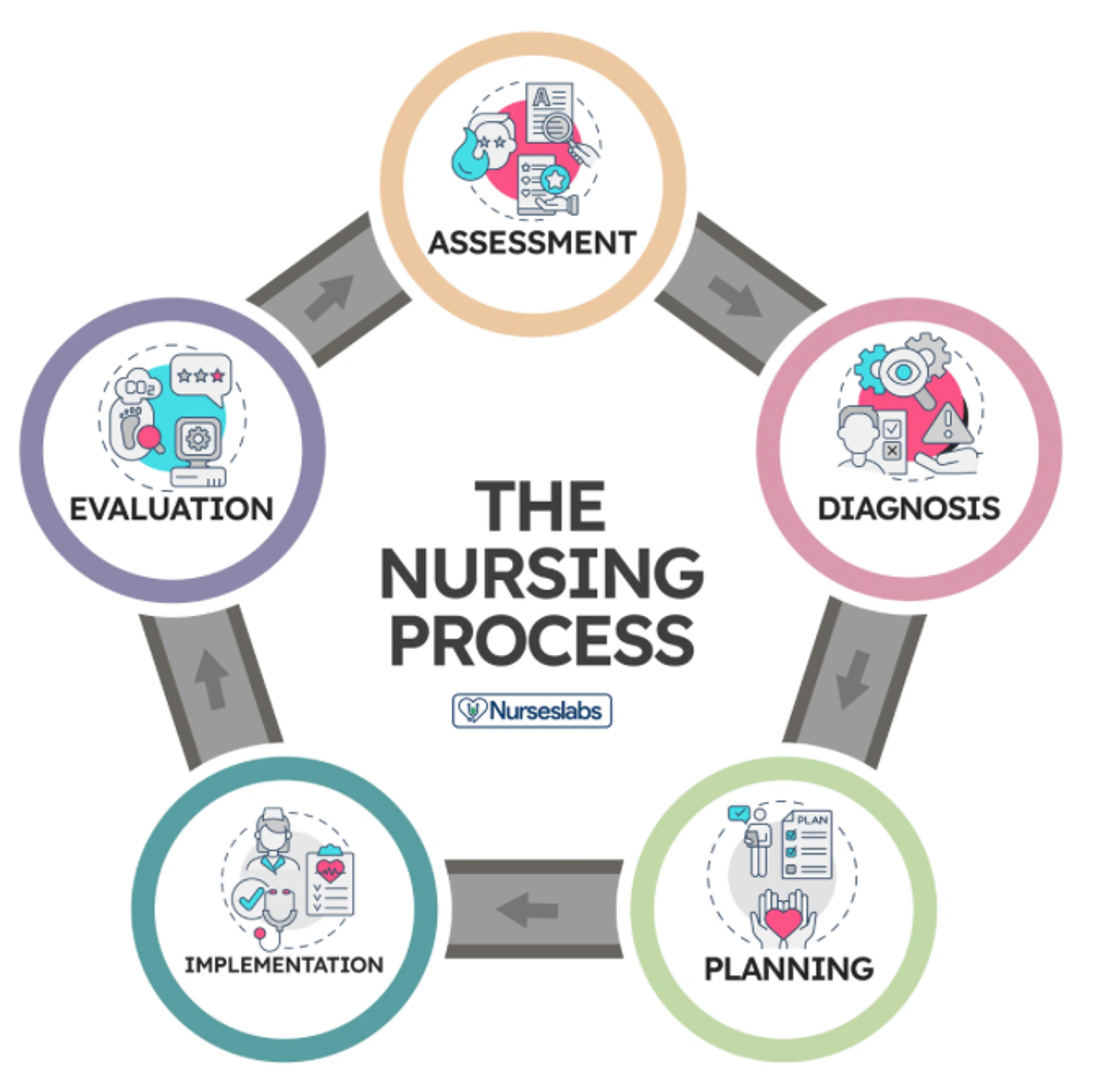
- Assessment
- Different interventions to meet those goals
- Diagnose:
- Planing:
- Care plan strategy to maintain health goals
- Implement:
- Health teaching, connecting with other providers
- Evaluation
- What was pateint response to those evaluations
- How did they respond
- Nursing assessment:
- Collection of patient data to inform diagnosis and interventions
- Collected from:
- Primary sources
- Patient
- Primary data from asking patient
- Secondary sources
- Care givers
- Other HCPs
- Lab results
- Past medical history…
- Tertiary sources
- Textbooks
- Relevant literature
- Best practice resources
- Diagnostic manual
- Cues and inferences
- Cues = the patient's expressions
- Important information
- Picks up on people's thoughts and expressions
- Information that the nurse obtains with their senses
- Inference = how the nurse interprets the cue
- Intuition and past experiences to help pick up cues
- Data:
- Objective
- Inspection, observed behavior, measurements
- Observations of a patient's health status
- Subjective
- Patient gives verbal description of health concerns
- Only by patient and their experience
- Feelings, symptoms…
- Compare all this data for normal or abnormal results
- Critical thinking
- Ask what they think they need and ask them in the right way
- Document clearly
- Use Critical thinking

^highlights. Shows how we synthesize all domains of knowledge and assess. Critical thinking that informs the rest of our nursing process.
- Data collection:
- Key identifiers
- Source of data
- From the patient
- Interpreter
- Caregiver
- Reason for the assessment
- Hospital, clinic?
- What are their perceived health challenges and why are we assessing them?
- Presenting problem
- Developmental variables
- Relationship status, children, occupation, educational experiences, housing, safety measures (helmet, seat belt)
- Psychological variables
- Support system
- Perception of their health
- Spiritual variables
- Rituals
- Believes (no pharmaceuticals)
- Sociocultural variables
- Cultural considerations
- Power of attorney?
- Language barriers
- Physiological variables
- History of illness
- When it began
- Have the experiences
- Other injuries?
- Past hospitalizations?
- Family health history?
- Medications
- Systems assessment
- Physical assessment
- Vital signs
- All this data forms diagnosis of assessment
- Documentation:
- Record all findings clearly and concisely
- Allow for data base
- Identify health trends for this patient over time
- Double-check for accuracy when inputting data
- Verify with patient
- Abnormal finding? → Go back and recheck it.
- Use as baseline
- Data analysis:
- Critical thinking – discover relationships and patterns
- Patterns, how many times have they accessed healthcare for the same health concern.
- Interpret findings to monitor for abnormal results
- Areas for further investigation
- Validate findings
- Simplified with assessment form or mind map
- Visual representation that helps identify connections
- Assist critical thinking
- Assessment forms (help prompt assessment)
- Categorize information put into EMR
- Has all info you wanna collect
- Alert you when something is abnormal
- Not bring in the computer in patient room, not therapeutic
- Interdisciplinary considerations:
- Collaboration
- Pre-assessment
- Info is reviewed by a therapist or psychiatrist
- Based on the information they can monitor the patient
- Continued monitoring
- Workflow
- Activity: Case Study
- A patient presents to the ER where you are working, the patient describes a rapid heart rate, excessive sweating and shortness of breath. They state the symptoms began an hour ago, when they found out some incredibly shocking news from their partner.
- Based on this information, what information or measurements will you gather first?
- Take vitals
- Heart rate elevated:
- Respiratory rate elevated
- Def anxious
- Physical assessment:
- Chest
- Heart Rate
- Thorough interview
- Nursing diagnosis:
- “Clinical judgement about an individual, family, or community responses to actual and potential health problems or life processes that is within the domain of nursing (NADA International, 2021).
- Determine nursing diagnosis based on assessment data
- Requires clinical reasoning and critical thinking
- Based on responses to a health problem, rather than disease
- Different than medical diagnosis
- Med diagnosis:
- Disease condition made by the MD
- Nursing diagnosis
- Patient response on their
- Physiological, physical response
- Based on interventions by nurse
- Can be collaborative – nurse monitors for changes
- Monitor the patient, detect onset of changes, and protect them from complications
- Interventions can be collaborative
- Purpose of nursing diagnosis:
- Provides a definition, giving all HCP understanding of patient needs
- Teaching skill for students
- Enables nurses to communicate their actions
- Among other nurses, HCP, or public
- All work on common goals
- Distinguishes nurses role from others
- What interventions to be requires
- Help focus on the scope of nursing practice
- Fosters the development of nursing knowledge
- Were the goals met or not
- Apply to the future. Do I need to change my approach?
- Development of a nursing diagnosis:
- Assess defining characteristics
- Patterns of data and assessment findings
- Use clinical criteria
- S&Ss, risk factors
- Which signs and symptoms are abnormal or normal
- Compare patient factors with accepted norms
- Lab & diagnostic tests, values, professional standards, anatomy/physiology
- Assess patient's needs and goals
- Allows diagnosis to be individuals and specifically tailored for the individual
- Done in collaboration with patient
- Components of nursing diagnosis:
- Diagnostic label
- Name of the health problem
- Descriptors
- Compromised, decreased, deficient, delayed, imbalanced, impaired
- Related factors
- Etiology from assessment data
- Labels probable cause of health problems
- Related to..
- Requires critical thinking and individualization
- Examp: Related to weakness, related to poor skin integrity
- Do not include medical diagnosis
- Behaviours or conditions nurses are able to treat
- Defining characteristics
- Description of what you are seeing
- “Manifested by… evidenced by…”
- Types of nursing diagnoses:
- Actual Nursing Diagnosis
- Acute pain related to decreased myocardial flow as evidenced by grimacing, expression of pain and guarding behaviour
- Risk Nursing Diagnosis
- At risk for infection related to surgical incision over the right hip interrupting the skin integrity.
- Health Promotion Nursing Diagnosis
- Readiness for enhanced breastfeeding as manifested by expressed desire.
- Wellness Nursing Diagnosis (positive goals to improve on)
- Readiness for enhanced management of physical activity.
>Red = nursing diagnosis
>Yellow = related factors
>Green = definition characteristics
- Source of errors:
- Errors in data collection
- Skill at assessment
- Check data and assess for inaccuracies
- Collect data in an organized way
- Stereotyping
- Dont assume a specific finding is based on gender or ethnicity
- Errors in data interpretation
- Cues
- Cultural influences or developmental stages
- Errors in diagnostic statement
- Incorrect wording
- Not specific
- Presence of another possible diagnosis
- Planning:
- After diagnosis, develop plan for care
- Patient centered goals, outline expectations and determine interventions
- Prioritization of needs/interventions
- High
- Done first
- Breathing circulation
- Intermediate
- Non life threatening
- Pain management
- Low
- After other priorities are met
- Long term health goals
- Health education or health promotion
- Patient may have multiple needs, need to look at what needs to be cared for first
- Collaborative with patient, family, interdisciplinary team, literature
- Adjust plan based on met/unmet needs
- Goal setting:
- Reflect patients health and wellness
- Focus on one behaviour response
- Solution of nursing diagnosis
- Develop goals with patient as mutual collaborator
- Goal
- Short term
- Within a few hours to a week
- Measurement, time frame
- Long term
- Days to a few months
- Towards discharge
- Know how to use meds before discharge
- Clear plan to be successful
- Expected outcomes
- Used interchangeably with goals
- Goals are solution of diagnosis
- Measurable, time, realistic… Basically smart goals.
- Patient care plan:
- Written plan
- Assessment
- Nursing diagnosis
- Goals
- Interventions
- Evaluation
- Identification of clinical needs
- Organized information for sharing
- Communication is easily exchanged between nurses
- Used between nurse shift change
- Institutional care plan
- Kardex
- Legal medical record.
- Reference of patient needs
- Focuses on interventions
- Allergies, diagnosis tests, specialists appointments, and potential discharge date.
- EMR care plan
- Update kardex and care plan as needed
- Update without info being smudged, easy to update
- Improves patient satisfaction
- Dynamic and can be updated
- Components of a patient care plan:
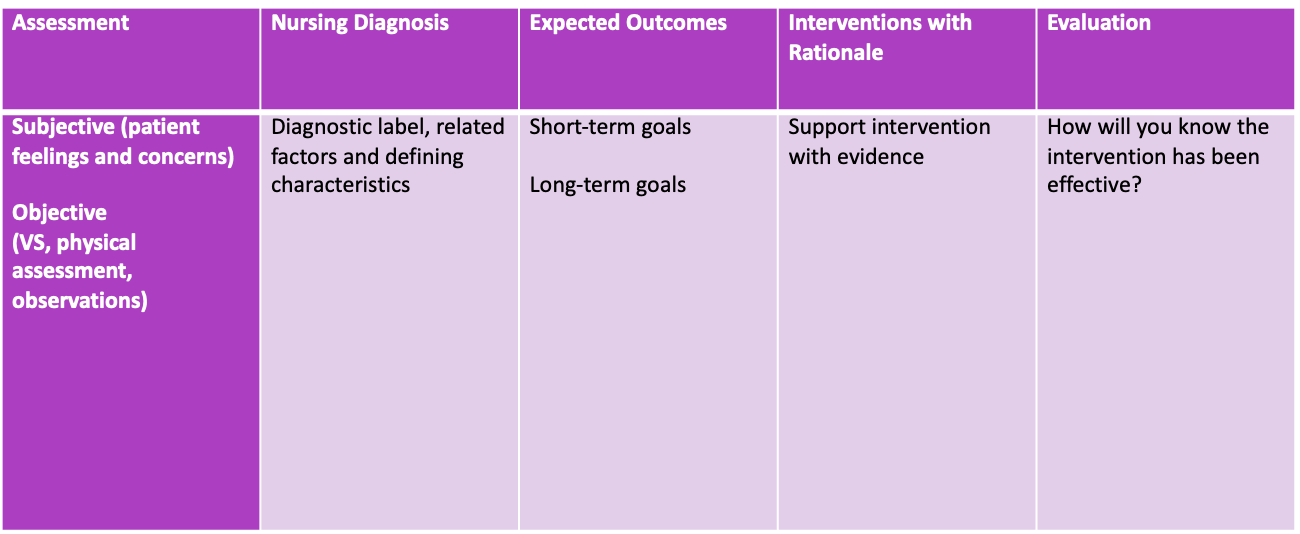
>at least two interventions per goal and supported by literature, use a rationale.
- How can I know everything?
- Need to know where to access certain information
- Continue to gain experience and skill
- Graduating as a novice nurse
- Someone with no previous work experience
- Become a competent = intent nurse after 2 or 3 years of practice
- Greater ability to think critically
- After 5 years
- Analytical abilities
- Pass on knowledge
- How does it all come together?
- Critical thinking
- Critical reasoning
- Decision making
- Evidence based practice
- Our own art or nursing
- Nursing journey:
- Hills with ups and downs
- Who we are as a nurse and where we are going!
- She liked the image as it reflects a nursing journey!!! 🙂
- Summary:
- Highlight important qualities of nurse decision making, critical thinking, and clinical reasoning
Application of nursing process with emphasis on assessment and diagnosis
Create care plans with interventions and patient goals
This concludes NURS 1001 – Nursing as a Profession
- FINAL EXAM:
- December 14 @ 3 PM
- Bring student card, pencil, eraser, and PEN
- Multiple choice questions, short answer, essay style
- SCAN TRON IS PENCIL
- WRITING ANSWERS ARE PENNNN
- 35% of final grade
- FINAL EXAM:
- Content from Potter & Perry and lectures
- CNO documents
- As nurses must know what the documents contain – relevant to practice
- Code of Conduct
- Scope of Practice
- Competency for Entry Level RN
- 50 MC
- 6 short answer (30 marks) - number to choose from
- Main concepts discussed in lecture and readings
- 2 long answer (20 marks)
- One to answer from WEEK 13 - clinical judgement.
- Short answer- understand main concepts discussed in lecture/readings
- Long answer- apply examples from readings, lectures and seminars as evidence- topics will be from course content
- Cumulative with heavier emphasis on weeks 7-12
- Content from Potter & Perry and lectures
POTTER AND PERRY - HEAVY EMPHASIS






