What is FinTech - LinkedIn Learning
FinTech is emerging and rapidly growing areas like blockchain, robot-advising, AI, online lending and crowdfunding. These can disrupt traditional finance and this leads to increased focus on it.
FinTech impacts investment advisory services, trading stocks, blockchain (trade settlements, online marketplace lending, capital/business formation
Regulation within FinTech is limited right now as it is built for the old system, were technology is not so much involved. This leads to issues for investor protection, SEC rules built for the old era.
As of 2019, it has not lead to an impact but it will in the future (now)
Algorithmic/Computer-driven Trading
Makes of over 90% of trades on the stock market
Human being a stock picker is old and the role for humans is now in designing algorithms to make these algorithmic trades
Algorithmic trading can be either market making (attempt to capitalize on the bid-ask spread, high-frequency traders) or data mining (based on patterns and data, looking at stock prices and other data points and capitalizing on them)
Blockchain
21st century version of a ledger book.
A blockchain is a distributed secure logfile that is protected by a super-secure username and password and it contains a complete record of every transition on the blockchain
First popularized as a behind the scenes tool for bitcoin
Blockchain underlies in every digital currency. Blockchain can speed up assets transfer
Blockchain Mechanics
Similar to Wikipedia. People can write entries into a record of information, and a community of users can control how the record of information is amended and updated. Blockchain automated this process to make it faster and simpler
What is Bitcoin?
The first successful peer-to-peer digital currency
Bitcoin comes with a build-in ledger, the blockchain, which records all of the transactions that occur. This is a public ledger of transactions
Built-in auditors/accountants called ‘miner's. Mining is to make sure the system is working and no counterfeit is occurring
Three Parts of Bitcoin
Private key cryptography
A distributed network with a shared ledger
Auditing of transactions (mining)
Features of Bitcoin
Deflationary, as the number of users grows the number of bitcoin grows at a slower pace
Divisible to 8 decimal places
Minimal transaction fees
The fees get paid out to the miners, voluntary fees but you pay to ensure your transaction gets reviewed
Consensus driven - no central authority
Counterfeit resilient
Cognitive Tasks Performed by AI
Natural language processing, knowledge representation, automated reasoning computer vison and machine learning
AI advantages
Efficiency, fast, good at solving new problems, good at dealing with information overload and organizing/processing it into knowledge
AI disadvantages
Costly upfront, slow software development, in 2019 few practical products
AI Impact of Industry
Chatbots that are AI-powered
Intelligent personal investment products
CFA exam has added a AI section
Companies are spending heavily on AI
What is AI?
AI is a branch of computer science focused on the automation of intelligent behavior
Intelligence is flexible responses rather then mechanical behavior. Having the ability to adapt to ambiguous or contradictory messages
It has to be able to assess relative importance of different elements of a situation (for example, quality vs. price)
Find similarities between situations despite difference’s which may separate them (find two dogs in two different pictures)
Ai should be able to draw distinctions between situations despite similarities
What is Robo-Advising?
The use of automation and digital techniques to build and manage portfolios of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and other investments
Current capabilities are basic, uses surveys to allocate assets
The portfolio gets monitored, rebalanced and reported on
Robo-Marketing
Fills a void are millennials, a low-cost way to invest in the markets
Robo-Advising in the works
Creates a survey with a survey to create a portfolio
Age, risk-tolerance, international stocks, national stocks, research/knowledge on topic, bonds, small cap vs large stocks, how much to invest and savings to invest in the future
Creates a variety of ETFs that are recommended to invest in
The parameters that are required by robo-advising needs to set-up by humans and then the robo-advisier can use it to make recommendations
AI can be used to watch the market change and then make adjustments to the robo-advising recommendations
This allows for automated portfolio rebalancing, reinvesting and watching of the stock market to have the best investments
Online investing and lending company’s are a great example of FinTech as they use online money that other people have invested to put into other loans. Everything has tons of data as its mostly automated and focus on transparency
The rise of online lending and crowdfunded-based lending
Using AI within excel called Ideas
Cryptocurrency
Act as a medium of exchange
No centered agency/government baking
No physical form, in digital wallets
Nealy impossible to duplicate
Created and stored using blockchain
Transactions and transfers are anonymous
Finite supply, for example Bitcoin will only create 21 billion max and each year it will release few and fewer
Cryptocurrency Investing
Crypto ETFs may be coming in the future (looks like there is now)
Limited investing offers
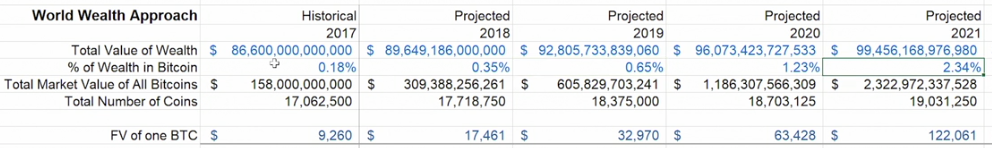
The worth of cryptocurrency can be grey and not have an exact method of determining it. Exchange rate is difficult.
Valuing crypto can be done a few ways, based on financial models that can vary based on different approach’s
Very risky trades
Using a crypto website allows for trade, for example, bitcoin but this if not a trader this can be difficult as we don’t have all day to watch the market. This leads to turning to algorithmic trading
A computer program can do the trading for you though AI automation and use a financial model that is we are confident in
Blockchain in a Nutshell
Shared ledger + consensus to help with auditing + cryptography + shared contract
Has shifted to smart contracts (smart legal contracts for example)