Cells and Batteries
Cells
cells use chemical reactions to produce electricity
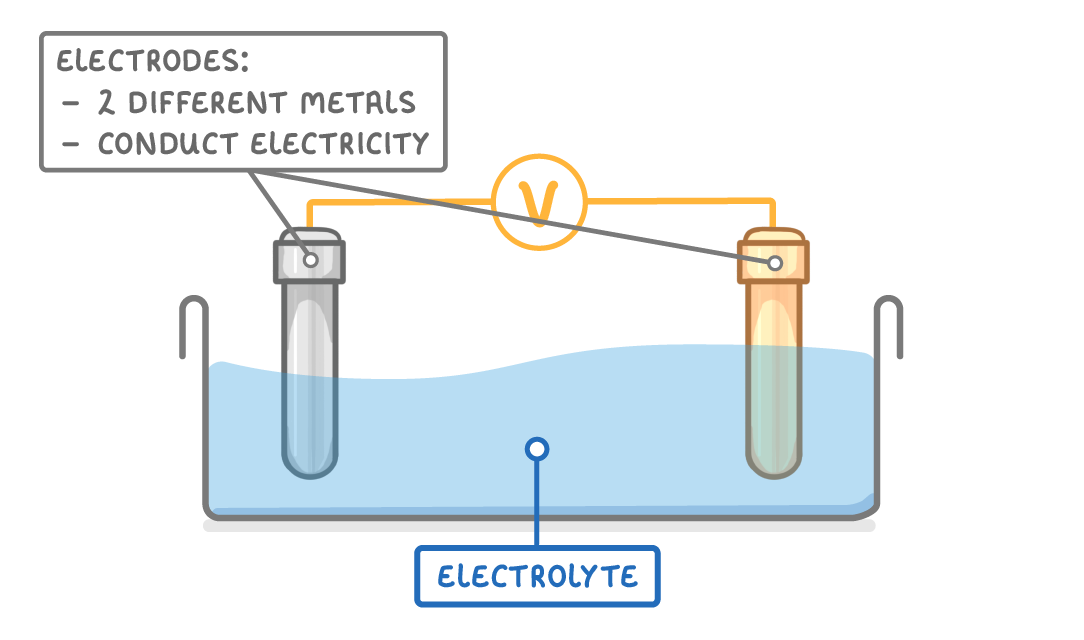
Factors that affect voltage cell
The metals used for the two electrodes (the greater the difference in reactivity of the two metals, the greater the voltage will be).
The type/concentration of the electrolyte used.
The conditions (e.g., temperature)
Cells and batteries - rechargeable/non-rechargeable
Rechargeable cells/batteries - are rechargeable because chemical reactions can be reversed when an external electrical current is applied (charger).
Examples - mobile, laptop.
Non-rechargeable cells/batteries - are not rechargeable because chemical reactions producing electricity stop when a reactant is used up.
Examples - smoke alarms, TV remotes, alkaline batteries.
Batteries
Batteries use chemical reactions to produce electricity, but consist of two or more cells connected together in series to provide a greater voltage.
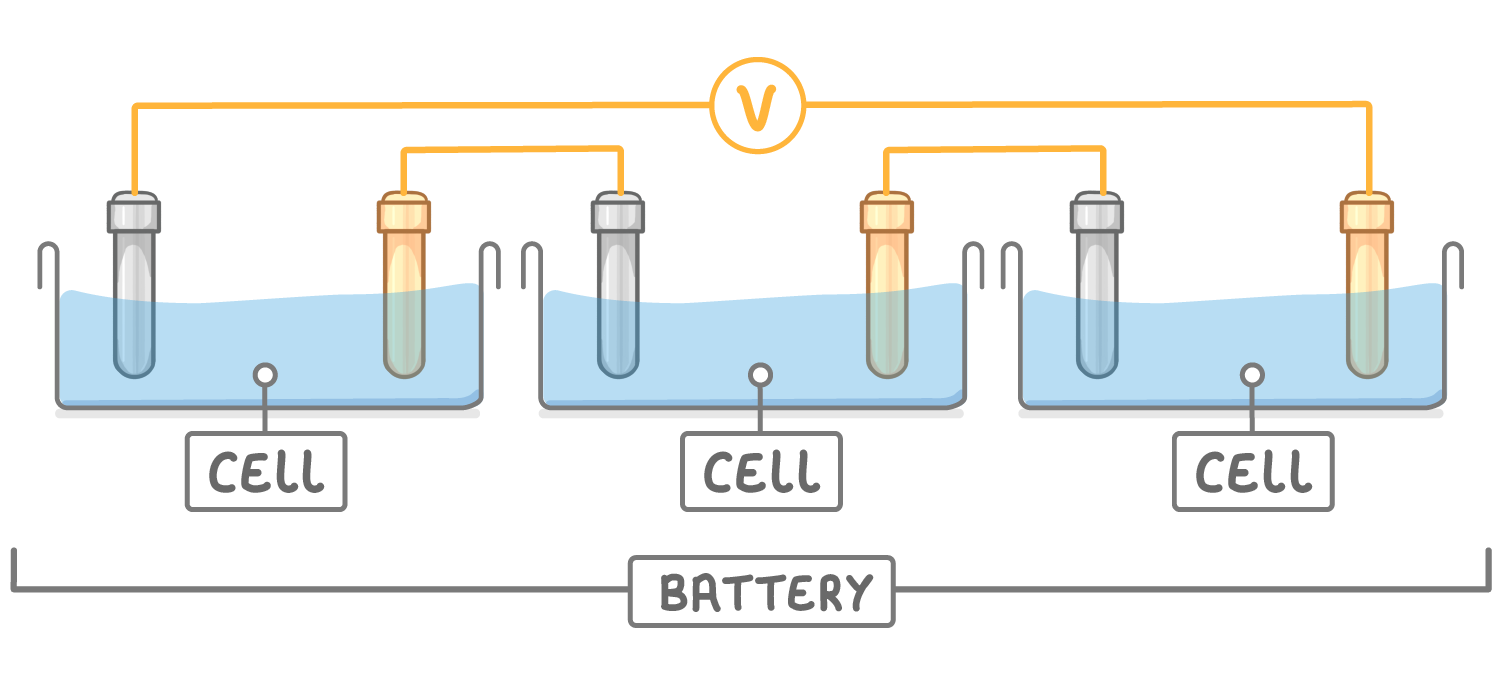
|