English 8 June Exam
Section 1: Subject verb agreement
Subject verb agreement is a tool to make sure that our verb agrees with the subject
I jump
She jumps
The verb must agree with the tense of the subject.
Present tense: He, she, it waits. I wait. They wait
Past tense: He, she, it waited. I waited. They waited
Future: He, she, it will wait. I will wait. They will wait.
Present perfect: He, she, it has waited. I have waited. They have waited.
Past perfect: He, she, it had waited. I had waited. They had waited.
Future perfect: I will have waited. She will have waited. They will have waited.
Section 2: Poetry
Figures of Speech: Usually, the figures of speech impact the meaning of the phrase.
Simile: A simile is a direct comparison. It usually contains the words like or as. It is a comparison of 2 unlike things.
Ex. My love is like a red, red rose.
Metaphor: A metaphor is a statement that a thing is something else; it is not merely like it.
Ex. My love is a red, red rose.
The isolated cabin was an oven,
Personification: Personification is a figure of speech in which inanimate objects or abstract ideas are given human characteristics. It is a kind of metaphor.
Ex. The moon winked from above.
The waves bow before the shore.
Apostrophe: An apostrophe is an address to the inanimate as if human, the dead as if alive, and the absent as if present.
Ex. Roll on, though deep and dark blue Ocean, roll!
Hyperbole: Hyperbole is deliberate exaggeration for effect. It is common in everyday speech.
Ex. This exam is going to kill me.
I cried a river for you.
Irony: Irony is saying the opposite of what one means in such a way that the meaning is nevertheless, obvious.
Ex. You’ve been sulking all evening —that’s a fine way for a young man to behave!
Poetic devices: Impacts the sound of the phrase.
Alliteration: Alliteration consists of a succession of similar consonant sounds.
Ex. See a teakettle spout steaming.
Onomatopoeia: Onomatopoeia is the use of words to imitate the sounds they describe.
Ex. Water plops into the pond
Splish-splash downhill.
Assonance: assonance consists in using the same vowel sound in conjunction with different consonants.
Ex. Oh, no man knows.
Rhyme: Rhyme is a repetition of vowel and consonant sounds at the end of words.
brown, town, clown, crown, renown.
Section 3: Expository writing
The purpose of expository writing is to present a main idea and then develop or expand the idea.
Topic sentence: The main idea. (The reader should know what the topic is right from the start.)
Supporting sentences
develop main idea in the TS by using specific example details that tell how or why; give concrete examples when possible.
Usually reasons are organized in order of importance, starting with less important reasons and ending with the most important.
Transitional Terms: these terms and expressions are important, but do not overuse them.
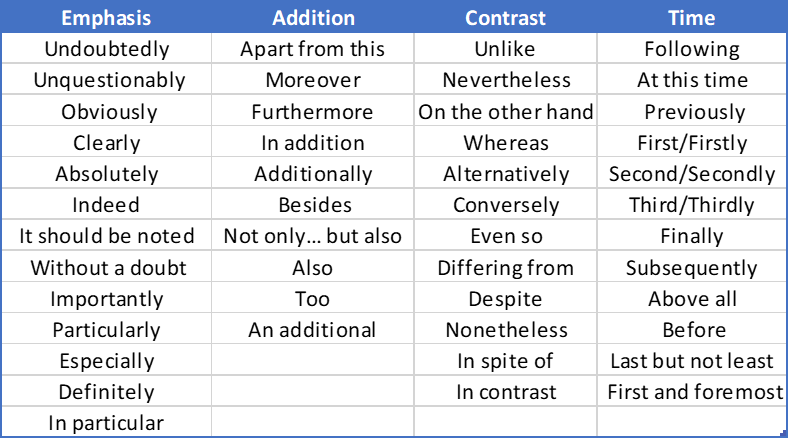
Choose a cross-section of information
Variety in sentence length; variety in punctuation.
Bring personality to paragraph
Try a question mark or an exclamation mark!
PUNCH FACTOR!!!
Characteristics:
TS > S1 > CD > S2 > CD > S3 > CD > CS
Brings personality of writer
Variety in punctuation
Use general word knowledge to support (maybe a statistic or well-known fact)
Perhaps a famous quote that relates to topic
How about song lyrics to relate
Try to keep third-person (can include some yous & Is.)
Aim for present/present-perfect tense
PUNCH FACTOR
Section 4: Shakespeare
Shakespeare was born in 1564, approximately April 23, the third child of John and Mary Shakespeare. He died, also on April 23, at 52.
He was a famous actor, poet, and playwright.
He grew up during the time of Elizabethan England.
Fell in love at 18, married Anne Hathaway, and had several children.
He wrote 37 plays and 154 sonnets.
he never published his plays.
His fellow actors posthumously recorded his work as a dedication to their fellow actor in 1623, publishing 36 of Shakespeare’s plays.
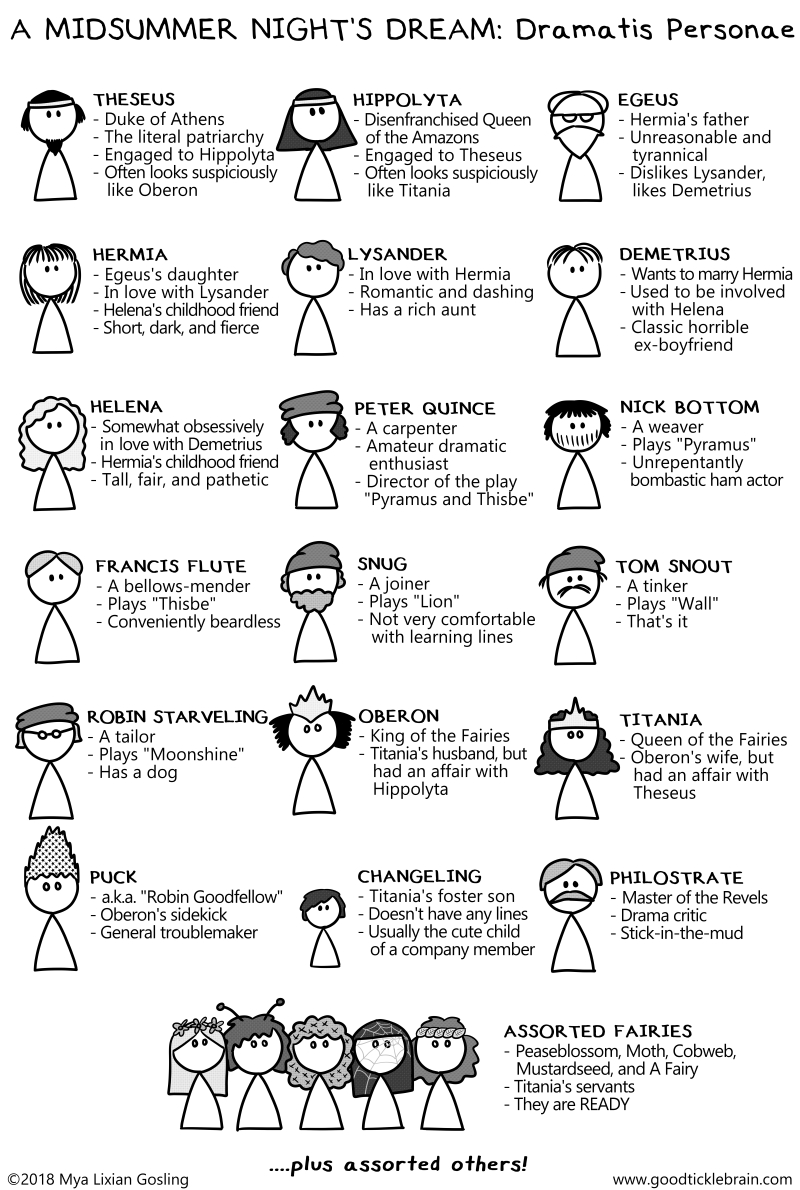
Characters in Midsummer Night’s Dream:
Three paragraph Literary analysis:
(TS-S1-S2-S3-CS)-(S1-CD-E-S2-CD-E-S3-CD-E-CS)-(TS