Molecular Motors
Explain how motor proteins work and how their movement relates to the polarity of the microtubule
Molecular motors are proteins
function
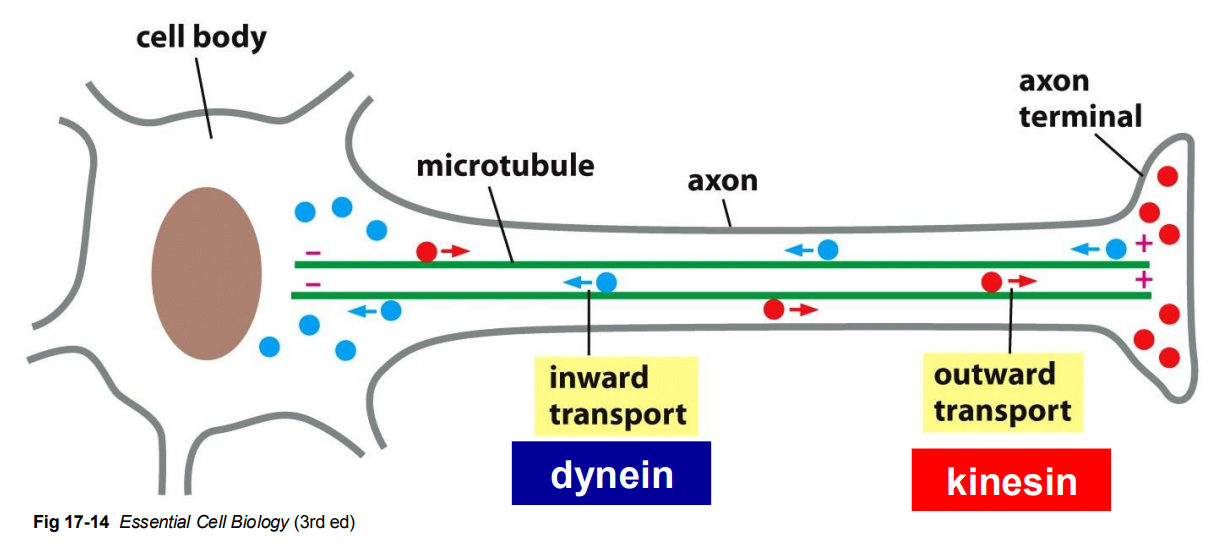
microtubules and their motor proteins help to position organelles within the cell
use ATP hydrolysis to produce force and movement along cytoplasmic polymers (microtubules or actin)
molecular motors bind ATP in the motor domains (heads)
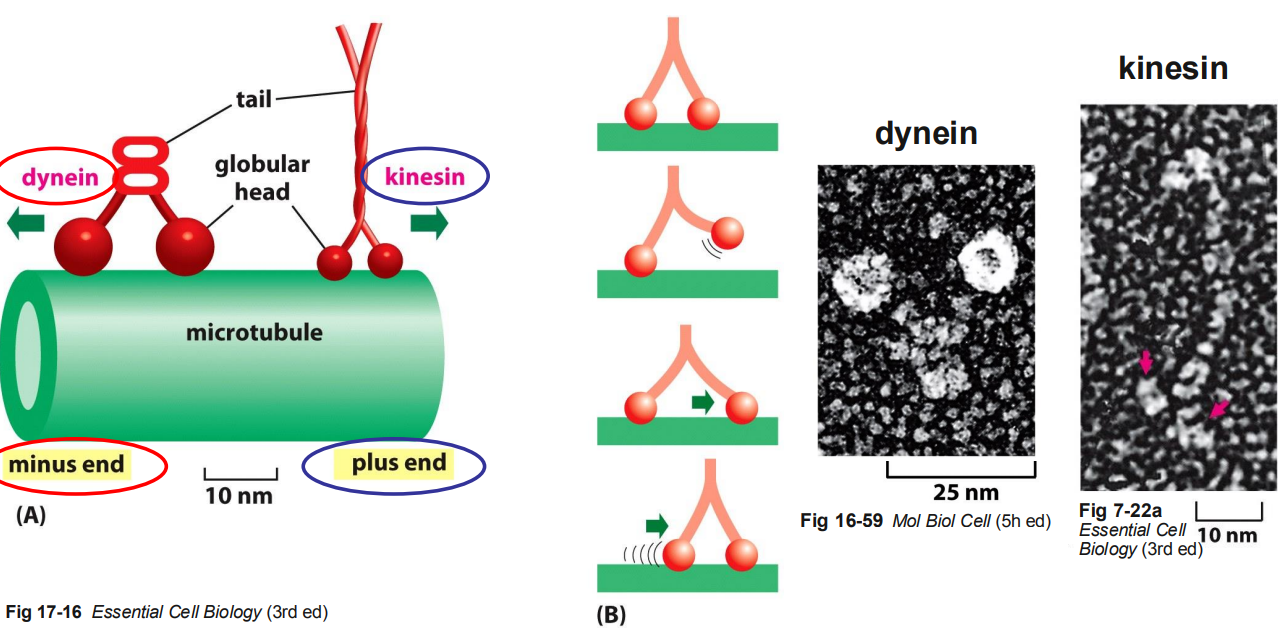
2 types of microtubule motor proteins - both move along microtubule using their globular heads
head region - associate with their filament tracks (microtubule and actin filaments)
tail region - bind to cargo
DyNEIN
KineSIn
Moves towards which end of a microtubule
moves towards minus end = nein = no
always move towards the centrosome or other MTOC
moves towards plus end = si = yes
always moves away from the centrosome and towards the periphery of cell