UGA GEOG1111 Chapter 9
Geologic Time and Change
Endogenic systems involve internal processes – Tectonics, Earthquakes, Volcanoes.
Flows of heat and material are deep below the surface, with radioactive decay being the main energy source.
Exogenic systems involve external processes – Weathering, Erosion, Rivers, Oceans, Glaciers.
Powered by solar energy & gravity
Absolute vs. Relative timescale:
Relative – Sediment at the top is younger than the sediment at the bottom (Stratigraphy)
Absolute – uses radioactive decay of isotopes to find the exact age
Uniformitarianism – physical processes operating today operated in the past
Catastrophism – Compressed timescale for Earth’s existence
Punctuated Equilibrium – Periods of stability interrupted by dramatic changes
 We are in the Cenozoic and Quaternary.
We are in the Cenozoic and Quaternary. 
Core:
Inner Core – solid iron
Outer Core – Molten Iron
Mantle:
Guttenberg discontinuity – Line in between Mantle and core
80% of Earth’s surface
Lithosphere: Rocky, rigid layer made up of crust and upper mantle
Asthenosphere: is a plastic layer below the crust; drives plate tectonics
Minerals are a natural compound having a specific chemical formula and crystalline structure.
Rocks are a bunch of minerals cemented together.
Igneous (was molten)
Sedimentary (from sediment)
Metamorphic (changed by heat/pressure)
Silicates: common mineral family (quartz, feldspar, gemstones)
Oxides: Oxygen + other metal (iron oxide, calcium oxide)
Carbonate: Carbon + Oxygen + Metals (Calcite: CaCO3)
Igneous: forms from magma found below the earth’s surface.
Intrusive – forms within the earth’s crust. Cools slowly. (granite)
Extrusive – molten material above the earth’s surface. Cools quickly. (lava/basalt)
Sedimentary: Rocks formed from sediment
Existing rock -> weathering; erosion; deposited and buried
Fragments of other rocks -> transport by water
Sandstone (sand), Shale (mudstone), Limestone (CaCO3), Coal (plants)
Metamorphic: Rocks put under intense heat and/or pressure, altering the chemical composition
Regional metamorphism – sediment collecting in broad depression
Contact metamorphism – heating due to rising magma
Foliated = wavy striations, non-foliated = homogenous
Shale (clay) -> Slate, Granite -> Gneiss; Basalt -> Schist; Limestone -> Marble; Sandstone -> Quartzite.
Hydrologic cycle – erosion, transportation, deposition
Rock cycle – 3 basic rock types
Tectonic cycle – moves material between the surface and mantle
Continental crusts light, ocean floor dense
Shapes of continents, geology, fossils suggest close past proximity
Geodetic measurements in Greenland indicated movement
sea floor spreading: undersea mountain ranges
mid-ocean ridges: upwelling magma: crust fractures, spreads and cools
magnetic reversals – particles align themselves with prevailing magnetic field
youngest crust: spreading center; oldest oceanic crust at subduction zones (208 mya)
 Relief – Vertical elevation differences in the landscape | Topography – Describes earths surface
Relief – Vertical elevation differences in the landscape | Topography – Describes earths surface
Crustal orders of Relief:
1st order: Huge continental platforms/ocean basins
2nd order: Mountain masses, plains, lowlands
3rd order: Individual mountains, valleys and cliffs.
Hypsometry – distribution of Earth’s surface and elevation in relation to sea level
Earth’s Topographic Regions: Plains (ie: Great Plains), High Tablelands (ie: Colorado Plateau), Hills/Low Tablelands (ie: Appalachians), Mountains (ie: Sierra Nevada), Widely Spaced Mountains (ie: Great Basin Mountains), & Depressions (ie: Snake River)
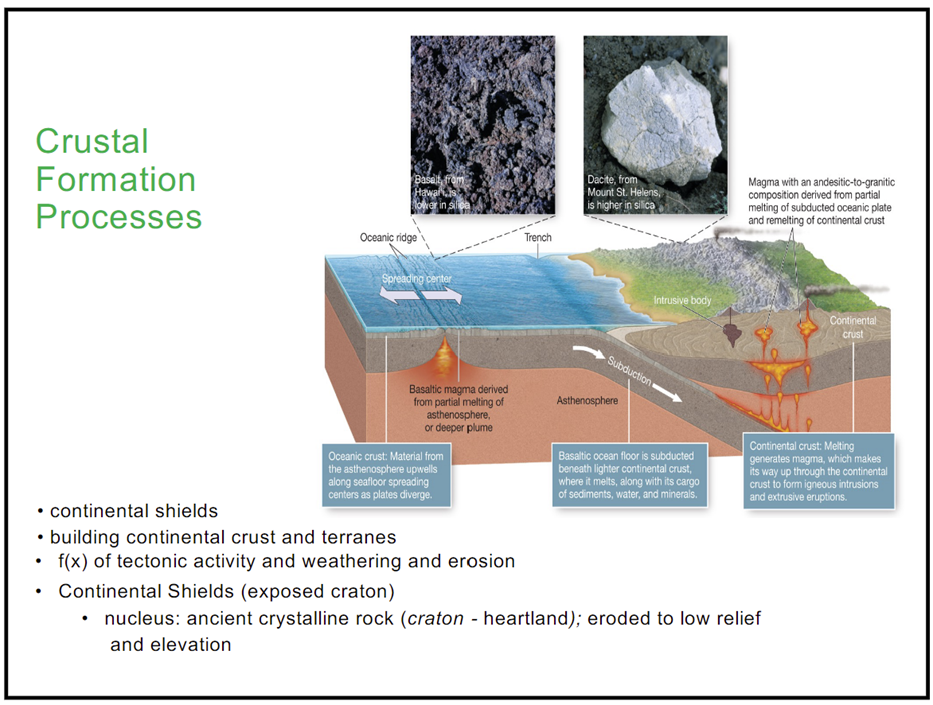
Crustal Formation:
Residual Mountains and stable continental cratons, formed from inactive remnants of ancient tectonic activity
Tectonic Mountains and landforms, produced by folding, faulting, and crustal movements
Volcanic features, formed by surface accumulation of molten rock from eruptions of subsurface materials
 Rocks are subjected to stress due to tectonic forces, gravity, and pressure from overlying rocks.
Rocks are subjected to stress due to tectonic forces, gravity, and pressure from overlying rocks.
Three types of stress: Tension, compression, and shear
Strain is how rocks respond to stress à expressed in rocks folding or faulting

Anticline – ridge of a fold, slope downward away from axis
Syncline – trough of a fold, slope downward towards the axis (trough)
Thrust fault – overturned folds
Warping – greater in extent; ie: isostatic rebound (Canada)
Faulting: when the stress is so great, the crust breaks
Normal Fault – Pulling rocks apart (tension fault)
Reverse Fault – Compression pushing against rocks (thrust fault), one part of crust overruns the other
Strike-Slip Fault – Stress applied is in a shearing direction and you get a break.