AP Biology Heredity Unit 5 notes
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
Genetics: the study of heredity and heredity variation
Heredity: the transmission of traits from one generation to the next, from parents to offspring.
Genes: segments of DNA that code for the basic unit of heredity. These are the instructions for making proteins that carry out various function in the body.
Inheritance: offspring acquire genes from their parents by inheriting chromosomes. Each gamete (sperm or egg carries a unique combination of genes, ensuring genetic diversity.
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
mitosis:
produce cells with same information
identical daughter cells
exact copies (clones)
same amount of DNA
same number of chromosomes
same genetic information
Asexual reproduction:
single-celled eukaryotes
yeast (fungi)
protists
paramecium
amoeba
simple multicellular eukaryotes
hydra
disadvantages? no natural variation
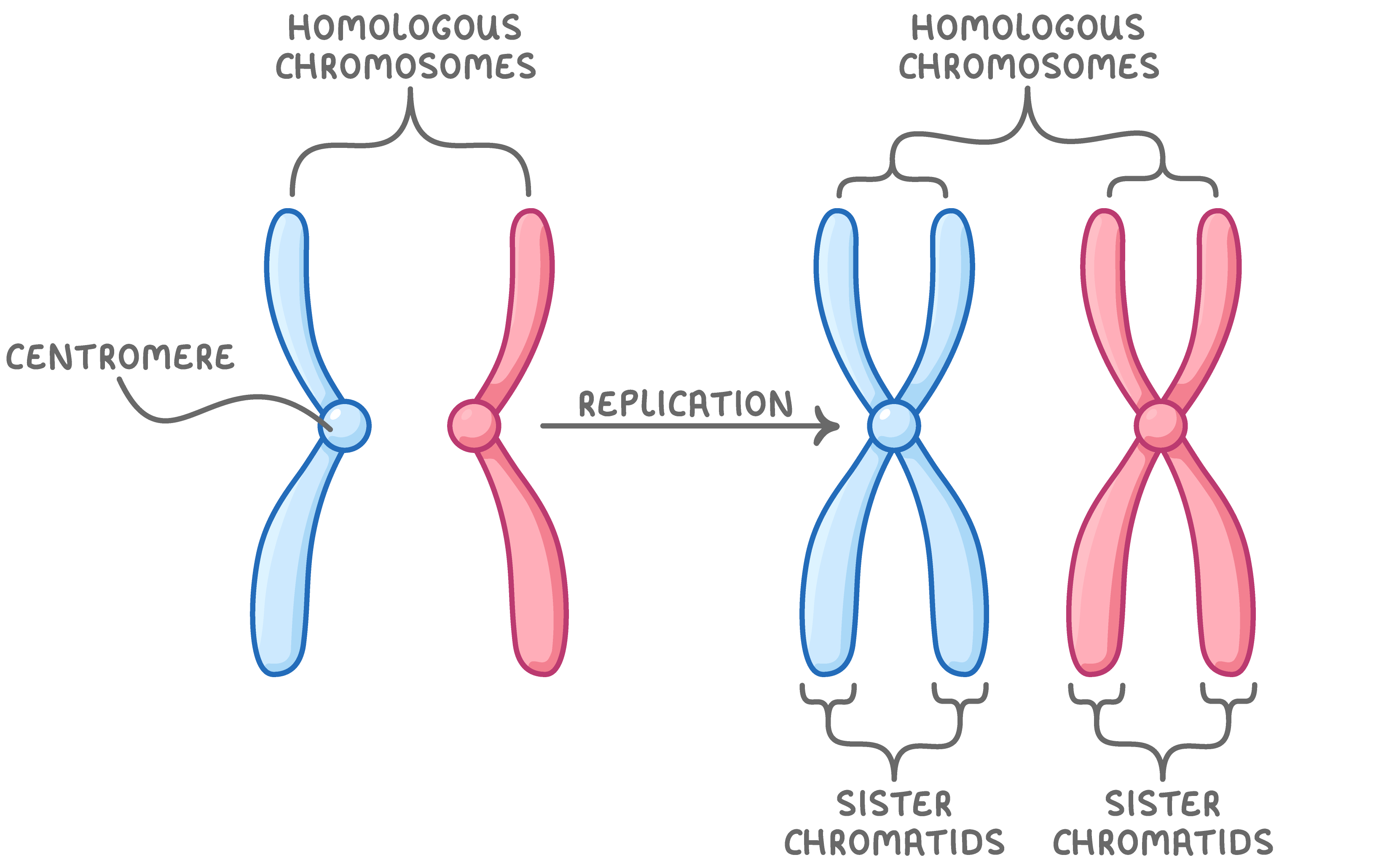
Homologous Chromosomes:
paired chromosomes (one from each parent) that are similar in size, shape, and genetic content. the carry the same genes, although the specific versions (alleles) of these genes may differ
both chromosomes of a pair carry “matching” genes
control same inherited characters
homologous = same information
genetic variation: during meiosis homologous chromosomes can exchange segments through the process called crossing over, leading to genetic recombination. This results in four unique gametes, each with different combination of alleles, increasing genetic diversity in offspring
how do we make sperm and eggs?
must reduce 46 chromosomes → 23
must reduce the number of chromosomes by half
Meiosis: production of gametes
alternating stages
chromosome number must be reduced
diploid → haploid
2n → n
humans: 46 → 23
meiosis reduces chromosome number
makes gametes
fertilization restores chromosome number
haploid → diploid
n → 2n
Meiosis
specialized type of cell division that results in four genetically unique haploid cells, crucial for sexual reproduction. It ensure genetic diversity and reduces the chromosome number by half, which is essential for forming gametes (sperm and eggs in animals, pollen and ovules in plants)
reduction division
special cell division for sexual reproduction
reduce 2n → 1n
diploid → haploid
“two” → “half”
makes gametes
sperm, eggs
Preparing for meiosis
1st step of meiosis
duplication of DNA
why bother?
meiosis evolved after mitosis
convenient to use. “machinery” of mitosis
DNA replicated in S phase of interphase of meiosis (just like in mitosis)
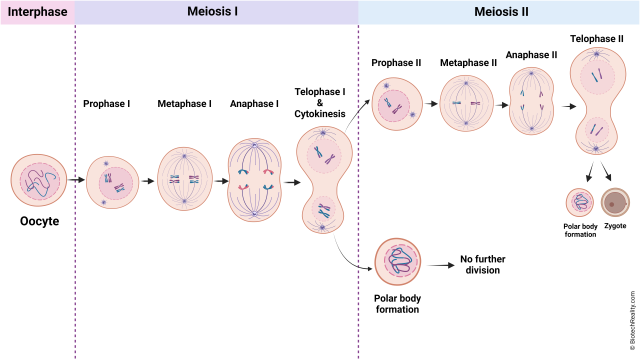
Steps of meiosis
meiosis 1
interphase (preparation: the cell undergoes G1, S / where DNA replication occurs, and G2 phases. chromosomes are in the chromatin form)
prophase 1 (synapse: homologous chromosomes pair up to form tetrads / four sister chromatids) (crossing over: occurs at the chiasmata, where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, increasing genetic diversity)
metaphase 1 (independent orientation: tetrads line up randomly align the metaphase plate. the arrangement is random, which contributes to genetic variation)
anaphase 1 (homologous chromosome separation: homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles. sister chromatids remain attached.)
telophase 1 & cytokinesis 1 (formation of two haploid cells: each cell now has a haploid set of chromosomes, but each chromosome still consists of two sister chromatids)
1st division of meiosis separates homologous pairs ( 2n → 1n ) “reduction division”
meiosis 2
prophase 2 (spindle formation: the spindle apparatus forms in each haploid cell, and chromosomes condense)
metaphase 2 (chromosome alignment: chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate similar to mitosis, but with half the chromosome number)
anaphase 2 (sister chromatid separation: sister chromatids are separated and move towards opposite poles of the cell)
telophase 2 & cytokinesis (formation of four haploid cells: nuclei reappear around each set of chromosomes, and the cells divide, resulting in four genetically unique haploid cells)
2nd division of meiosis separates sister chromatids (1n → 1n) “just like mitosis”
key takeaways:
haploid cells: meiosis produces four haploid cells from a single diploid parent cell, each with half the number of chromosomes (e.g 23 in humans)
genetic diversity:
crossing over: occurs in prophase 1, creating genetic diversity
independent assortment: during metaphase 1, chromosomes are distributed randomly, contributing to genetic diversity
random fertilization: the combination of gametes during fertilization adds to genetic variability.
nondisjunction: if chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate properly during meiosis, it results in gametes with abnormal chromosome numbers, which lead to genetic disorders
Meiosis 1
1st division of meiosis
separates homologous pairs
Trading pieces of DNA
crossing over
during prophase 1, sister chromatids intertwine
homologous pairs swap pieces of chromosome
DNA breaks & re-attaches
Crossing over
3 steps
cross over
breakage of DNA
re-fusing of DNA
new combination of traits
Meiosis 2
2nd division of meiosis
separates sister chromatids
mitosis vs meiosis
Mitosis | Meiosis |
1 division | 2 divisions |
daughter cells genetically identical to parent cell | daughter cells genetically different from parent |
2n → 2n | 2n → 1n |
produces cells for growth and repair | produces gametes |
no crossing over | crossing over |
low genetic variation (offspring are clones of parent) | high genetic variation (offspring have unique genetic combinations) |
The value of sexual reproduction
sexual reproduction introduces genetic variation
genetic recombination
independent assortment of chromosomes
random alignment of homologous chromosomes in Metaphase 1
crossing over
mixing of alleles across homologous chromosomes
random fertilization
which sperm fertilizes which egg?
dividing evolution
providing variation for natural selection
Variation for genetic recombination
independent assortment for chromosomes
meiosis introduces genetic variation
gametes of offspring do not have same combination of genes as gametes from parents
random assortment in humans produces 8,388,608 different combination in gametes
Variation from crossing over
crossing over creates completely new combination of traits on each chromosome
creates an infinite variety in gametes
Variation from random fertilization
sperm + egg = ?
any 2 parents will produce a zygote with over 70 trillion possible diploid combination
Sexual reproduction creates variability
sexual reproduction allows us to maintain both genetic similarity and differences
Sperm production
spermatogenesis
continuous & prolific process
each ejaculation = 100-600 million sperm
Egg Production
Oogenesis
eggs in ovaries halted before Anaphase 1
Meiosis 1 completed during maturation
Meiosis 2 completed after fertilization
1 egg + 2 polar bodies
Differences across kingdoms
not all organisms use haploid & diploid stages in same way
which on is dominant (2n or n) differs
but still alternate between haploid & diploid
must for sexual reproduction
Mendelian Genetics
Common Ancestry
DNA and RNA carry genetic information
The genetic code is shared by all living systems
Gregor Mendel studied inheritance and created two laws that can be applied to the study of genetics
Gregor Mendel
Mendel was an Austrian monk who experimented on pea plants and discovered the basic principles of heredity.
why pea plants?
many varieties
controlled mating
relatively short generation time
Pea Plant Traits
Mendel only tracked characteristics that came in two distinct forms:
examples:
color (purple or white)
seed shape (round or wrinkled)
to help control his experiments, he used true breeding plants
true breeding: organisms that produce offspring of the same variety over many generations of self-pollination.
example: true-breeding purple pea plants will only produce purple offspring with self-pollination.
Generations
P generation: true-breeding parental generation
F1 generation: (first filial) hybrid offspring of P generation (only displays one of the parents traits)
F2 generation: (second Filial) offspring of the F generation (both parents traits displayed. 3:1 observed ratio dominant to recessive.

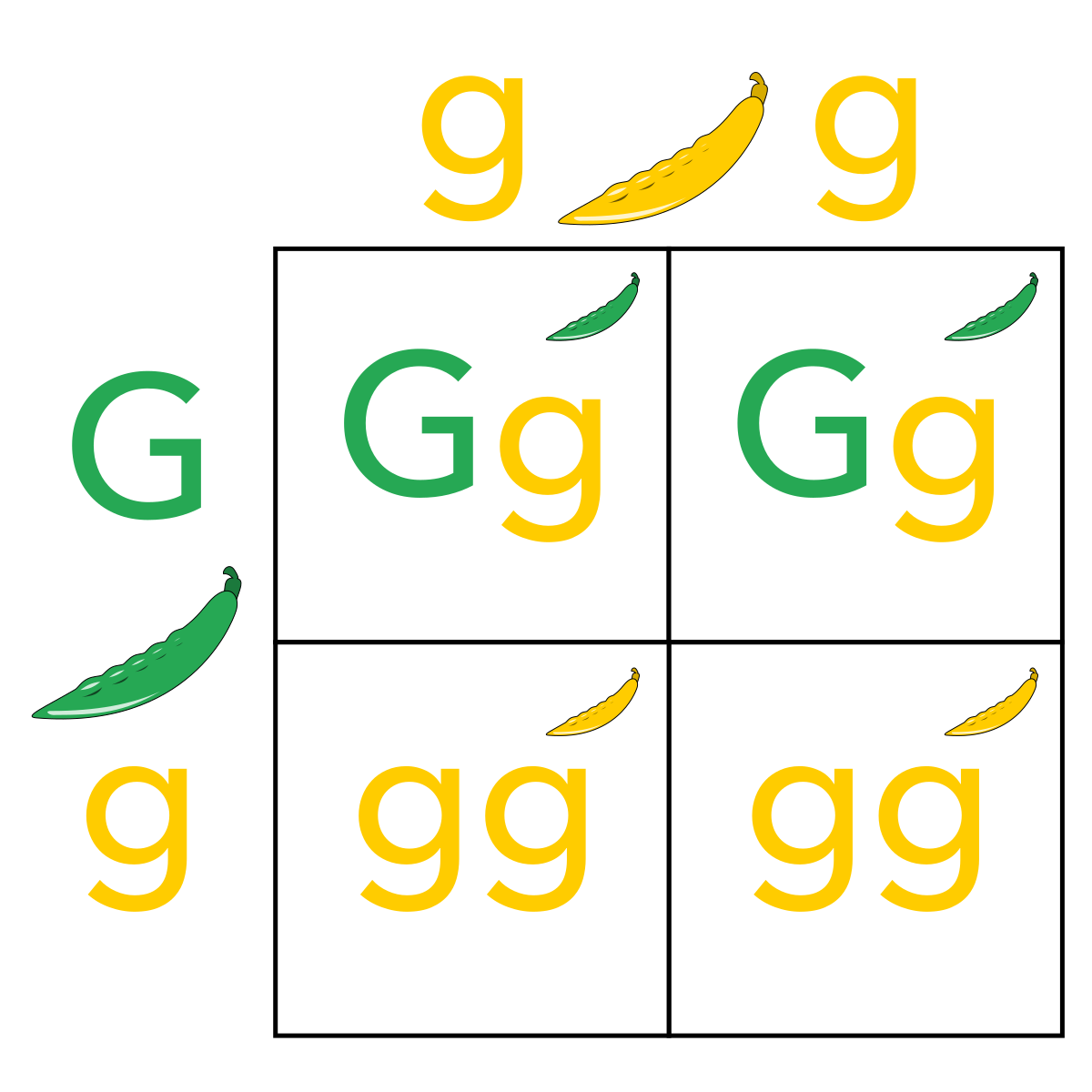
Punnett Squares
diagrams used to predict the allele combinations of offspring from a cross with known genetic compositions
capital letter denote dominant traits
lower case letters denote recessive traits
Genetics Vocabulary
Homozygous: an organism that has a pair of identical alleles for a character
example:
homozygous dominant: AA
homozygous recessive: aa
Heterozygous: an organism has two different alleles for a gene
example:
Aa
Genotype: the genetic makeup (alleles) for an organism
Phenotype: an organisms appearance, which is determined by the genotype
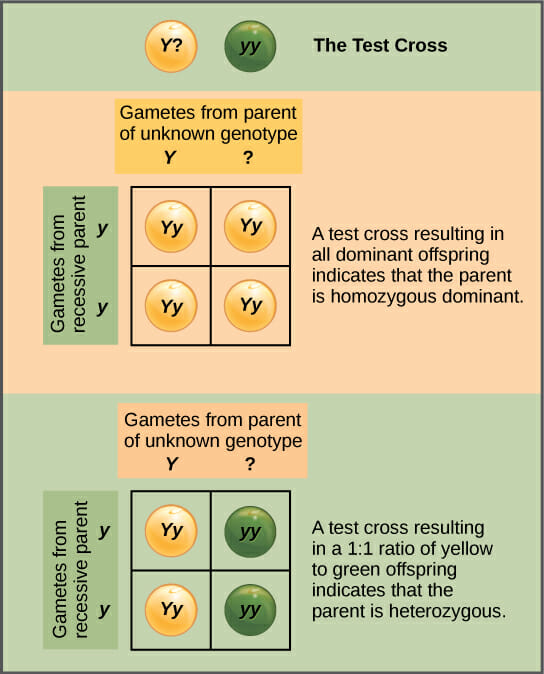
Testcross
helps to determine if the dominant trait is homozygous dominant or heterozygous
Principles of Heredity
Mendel’s experiments allowed him to develop two fundamental principles of heredity:
The law of segregation
The law of independent assortment
Discoveries
Mendel noticed that the cross between purple and white true breeding pea plants produced only purple F1 offspring
Did the white characteristic disappear?
No, because the white pea flower characteristic came back in the F2 generation
Dominant vs Recessive
Mendel hypothesized that the purple must be a dominant trait to the white flower, which is a recessive trait
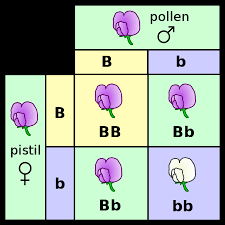
Mendel performed the same crosses for each of the seven characteristics of pea plants and found the same results
he found that the F2 generation was always a 3:1 ratio
Mendel’s Model
to explain the 3:1 ratio he observed in the F2 generation, Mendel created a model with four concepts:
Alternative versions of genes (alleles) account for variations in inherited characteristics
For each character, an organism inherits two copies (two alleles) of a gene, one from each parent
If two alleles at a locus differ, then the dominant allele determines the appearance and the recessive alleles has no noticeable effect
Law of segregation: the two alleles for the same trait separate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes
Alleles: A closer look
Alleles: Different versions of the same gene.
somatic cells are diploid
they contain two copies of each chromosome
Alleles: alternative versions of a gene
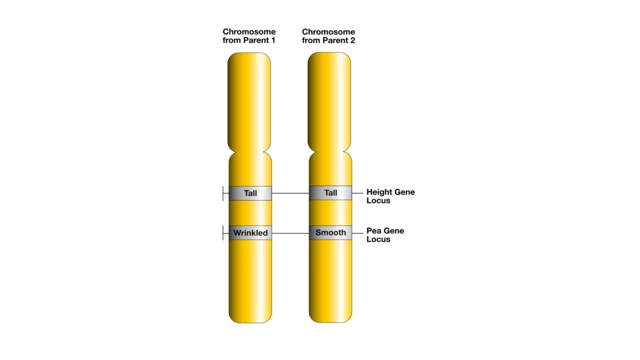
The Law of Segregation:
definition: during meiosis, only one allele for a trait is passed on to each gamete. this means that the two alleles for a gene separate so that each gamete receives only one allele.
implication: each parent contributes one allele for each trait to their offspring.
During gamete formation, the two alleles for each gene segregate (separate) from each other.
This means that each gamete receives only one allele for each gene.
Key concepts:
Alleles: Different versions of the same gene.
Homologous Chromosomes: Pairs of chromosomes, one from each parent, that carry genes for the same traits.
Meiosis: The process of cell division that produces gametes (sperm and egg cells).
Significance:
Explains how genetic variation is maintained in populations.
Provides a foundation for understanding the inheritance of traits.
Visual Representation: Often depicted using Punnett squares to predict the possible offspring genotypes and phenotypes from a cross between two individuals.
Monohybrid Crosses
the law of segregation was determined by doing crosses between true-breeding plants which produced F1 hybrids, known as monohybrids
examples: BB x bb produce F1 that are all Bb
Monohybrid Crosses: a cross between the F1 hybrids
BB x Bb

The law of Independent Assortment
definition: alleles for separate traits are passed on independently of each other, provided the genes are not linked on the same chromosome.
implication: the inheritance of one trait generally does not affect the inheritance of another trait.
Mendel’s second principle is the law of independent assortment: genes for one trait are not inherited with genes of another trait
instead of following one trait in his crosses, this time Mendel followed Two traits (i.e. pea pod color and pea pod shape)
This law only applies to: genes that are located on different chromosomes (not homologous) OR genes that are very far apart on the same chromosome
Dihybrid Crosses
the law of independent assortment was determined by doing crosses between plants that were true breeding for two traits, which produces F1 hybrids known as dihybrids
example: YYRR x yyrr
all F1 dihydrides would be YyRr
Dihybrid cross: a cross between F1 dihybrids
YyRr x YyRr
How to solve Genetics Problems
Write down the symbols for the alleles (sometimes they are given to you)
Write down the genotypes given
a. if phenotypes are given, then write down the possible genotypes
determine what the problem is asking, and write out the cross as: [genotype] x [genotype]
set up the Punnett square
Law of Probability
the law of segregation and independent assortment reflect rules of probability.
The multiplication rule: the probability that two or more independent events will occur together in some specific combination
example: if you flip a coin twice, what is the probability that it will land heads up both times?
½ x ½ = ¼
example: what is the probability of having 3 girls in a row?
½ x ½ x ½ = 1/8
The addition rule: the probability that two or more mutually exclusive events will occur
example: what is the chance of rolling a dice and it lands on a 1 or 6?
1/6 + 1/6 = 1/3
Pedigrees
many human traits follow Mendelian patterns of genetics
Pedigrees: family trees that give a visual of inheritance patterns of particular traits.
Reading Pedigrees
circles: represent females
squares: represent males
filled in symbols: indicate individuals who express the trait being studied
autosomal traits: equally likely to affect males and females
sex-linked traits: more likely to affect one sex over the other, often found on the X chromosomes. males (XY) are more likely to express X-linked recessive traits because they only have one X chromosome.
Sex linked recessive: rarely affect females (XX) because they only need two copies of the recessive allele to express the trait, whereas males need only one.
if a trait is dominant, one parent must have the trait
0 dominant traits do not skip a generation
if a trait is X-linked, then males are more commonly affected than males.
Dominant: affected individuals appear in every generation
Recessive: trait skips generations
Non-Mendelian Genetics
many traits do not follow the ratios predicted by Mendel’s laws. why?
varying degrees of dominance
many traits are produced through multiple genes acting together
some traits are determined by genes on the sex chromosomes
some genes are adjacent or close to one another on the same chromosome and will segregate as a unit
some traits are the result of non-nuclear inheritance (ie chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA)
Degrees of Dominance
Alleles can show varying degrees of dominance
in Mendel’s experiments, he worked with traits that showed complete dominance
homozygous dominant and heterozygous individuals are phenotypically the same
incomplete dominance: neither allele is fully dominant
F1 generation has a phenotype that is a mix of those of the parental generation
example: red flowers crossed with white flowers will produce pink offspring
codominance: two alleles that affect phenotype are both expressed
example: human blood group
type AB blood: A and B are both expressed
Multiple Alleles: genes that exist in forms with more than two alleles
example: human blood group
Alleles: I ^A , I ^B , i
Pleiotropy: a single gene influences multiple phenotypic traits
example: in pea plants, the gene that controls flower color also affects seed coat color
Multiple Genes
in many cases, two or more genes are responsible in determining phenotypes.
Epistasis: the phenotypic expression of a gene at one locus affects a gene at another locus
example: coat color in labs and some mice
One gene codes for pigment and a second gene determines whether or not that pigment will be deposited in the hair

Polygenic inheritance: the effect of two or more genes acting on a single phenotype
example: height, human skin color
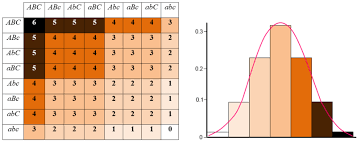
Sex Chromosomes
Sex linked Genes: Thomas Hunt Morgan experimented with fruit flies and determined that specific genes can be carried on sex chromosomes
sex linked gene: a gene located on either the X or the Y chromosome
Y-linked genes: genes specifically found on the Y chromosome
very few Y linked genes, so very few disorders
X-linked genes: genes found on the X chromosome
Inheritance of X-linked Genes:
fathers can pass X-linked alleles to all of their daughters, but none to their sons
mothers can pass X-linked alleles to both daughters and sons
If an X-linked trait is due to a recessive allele:
females will only express trait if they are homozygous
because males only have one X chromosome, they will express the trait if they inherit it from their mother
they are called hemizygous (since the term heterozygous does not apply)
due to this, males are much more likely to have an X-linked disorder
X - linked Disorders
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
progressive weakening of muscles
Hemophilia
inability to properly clot blood
Color Blindness
inability to correctly see colors
X - inactivation:
females inherit two X chromosomes, which is double than males!
during the development, most of the X chromosome in each cell becomes inactive
the inactive X in each cell of a female condenses into a Barr body
helps to regulate gene dosage in females
Linked Genes
Genetic Recombination:
Genetic recombination: production of offspring with a new combination of genes from parents
Parental types: offspring with the parental phenotype
Recombinants: offspring with phenotypes that are different from the parents
Mendel also observed recombinants during his crosses
example: green wrinkled plant crossed with a yellow-round plant
yyrr x YyRr
50% recombination, however, indicates that genes are unlinked, or on different chromosomes
Linked genes: genes located near each other on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together
meiosis and random fertilization generate genetic variation in offspring due to:
independent assortment of chromosomes
crossing over in meiosis I
any sperm can fertilize any egg
linked genes: crossing over
linked genes show parental phenotypes in offspring at higher than 50%
during crossing over chromosomes from one paternal chromatid and one maternal chromatid exchange corresponding segments
crossing over helps to explain why some linked genes become separated during meiosis
the further apart two genes are on the same chromosome, the higher the probability that a crossing over event will occur between them and the higher the recombination frequency
mapping distance:
experiments performed by Sturtevant, allowed scientists to map genes and their locations on chromosomes
linkage map: genetic map that is based on recombination frequencies
the distance between genes are map units
one map unit is equivalent to a 1% recombination frequency
express the relative distances along chromosomes
50% recombination means that the genes are far apart on the same chromosome or on two different chromosomes
Non-Nuclear DNA
some traits are located on DNA found in the mitochondria or chloroplasts
both chloroplasts and mitochondria are randomly assorted to gametes and daughter cells
in animals, mitochondria are transmitted by the egg, NOT the sperm
in plants, mitochondria and chloroplasts are transmitted in the ovule, NOT the pollen
therefore, both mitochondria and chloroplasts determined traits are maternally inherited
Statistical Analysis: Chi Square
Chi-square: a form of statistical analysis used to compare the actual results (observed) with the expected results
help to:
determine whether the data obtained experimentally provides a “good fit” to the expected date
determine if any deviations from the expected results are due to random chance alone or to other circumstances (ie data collection error)
designed to analyze categorical data
Chi square (X ^ 2)
use the equation to test the “null” hypothesis
the prediction that data from the experiment will match the expected results
formula:
∑ = sum
how to solve chi square:
1. State Your Hypotheses
Null Hypothesis (H₀): This usually states there is no significant difference between observed and expected data. Any differences are due to chance.
Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): This states there is a significant difference between observed and expected data./
2. Set Up a Table
Create a table to organize your data:
category (results) | observed (O) | expected (E) | (O-E) | (O-E)² | (O-E)² / E |
3. Calculate Expected Values
Equal Probability: If you expect an equal distribution among categories, divide the total number of observations by the number of categories.
Based on Ratios: If you have a specific ratio (e.g., from a Punnett square), apply that ratio to the total number of observations.
4. Fill in the Table
Observed (O): Record the actual counts from your experiment or data.
Expected (E): Record the expected counts you calculated.
(O - E): Subtract the expected value from the observed value for each category.
(O - E)²: Square the difference you just calculated.
(O - E)² / E: Divide the squared difference by the expected value for each category.
5. Calculate the Chi-Square Value (x²)
Sum the values in the last column of your table: x² = Σ [(O - E)² / E]
6. Determine Degrees of Freedom (df)
Subtract 1 from the number of categories: df = (number of categories) - 1
7. Find the Critical Value
Use a chi-square distribution table. These are usually provided in AP Biology resources or exams.
Locate the critical value that corresponds to your degrees of freedom and the significance level (usually 0.05 in AP Biology).
8. Compare Your Chi-Square Value to the Critical Value
If your x² value is greater than the critical value: Reject the null hypothesis. The difference between observed and expected data is statistically significant.
If your x² value is less than or equal to the critical value: Fail to reject the null hypothesis. The difference between observed and expected data is likely due to chance.
9. Conclusion
State whether you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Explain what this means in the context of your experiment or data.
If you reject the null hypothesis, you might suggest possible reasons for the significant difference.
Important Notes:
The chi-square test is used to analyze categorical data (counts or frequencies).
The expected values should generally be greater than 5 for each category to ensure the validity of the test.
AP Biology questions often require you to not only calculate the chi-square value but also interpret the results in the context of the problem.
Environmental Effects on Phenotype
environmental factors:
various environmental factors can influence gene expression and lead to phenotypic plasticity
individuals with the same genotype exhibit different phenotypes in different environments
examples:
temperature can change coat color in rabbits and Siamese cats
soil pH can affect flower color
UV exposure can increase melanin production in the skin
Chromosomal Inheritance and Disorders
genetic disorders
some genetic disorders can be linked to affected or mutated alleles or chromosomal changes
mutated alleles
Tay-sachs disease
autosomal recessive disease
mutated HEX gene
body fails to produce an enzyme that breaks down a particular lipid
affects central nervous system and results in blindness
sickle cell anemia
autosomal recessive disease
mutated HBB gene
sickled cells contain abnormal hemoglobin molecules
chromosomal changes
nondisjunction: chromosomes fail to separate properly in meiosis I or meiosis II
karyotyping can detect nondisjunction
example: down syndrome
three copies of chromosome 21