Lecture 7: Agriculture
Land Usage (Jamaica)
Jamaica’s total land area → 10,830 km2
1997
- Agriculture including pastures 46%
- Forest 24%
- Human Settlement 4%
- Mining and Wetlands 6%
- Shrubs and woodland 20%
NOW
- Agriculture Lands 41% (Land crops 20% and land in pastures 21%)
- Forests 40% (Undisturbed 19%)
Agriculture
Agriculture is the growing of crops & the tending of livestock for subsistence, sale, or exchange.
Types of Agriculture
- Subsistence Agriculture → The production of food to feed oneself and one’s family.
- Industrialized Agriculture → Large scale production of crops and livestock for sale. Emphasizes high yields. Relies on the large input of energy to run machinery, irrigate crops and produce fertilizers and pesticides.
- Sustainable Agriculture → The growing of crops and livestock in an environmentally friendly way.
Features of Subsistence / Low Input Agriculture
- Human Labor
- Slash and Burn
- Shifting Cultivation
- Fallow Periods
- Animal Manure
- Mixed Cropping
Negative Effects of Subsistence / Low Input Agriculture
- Food insecurity
- Slash and Burn Cultivation leads to:
- Deforestation and vegetation loss
- Shifting Cultivation as plots are abandoned after 2-5 years due to loss of soil fertility.
- Increased fire hazards and global warming.
Green Revolution → Transformation in agricultural practices between 1940’s and 1960’s. The objective was to eradicate famine and increase food production. Shift from subsistence to industrialized agriculture.
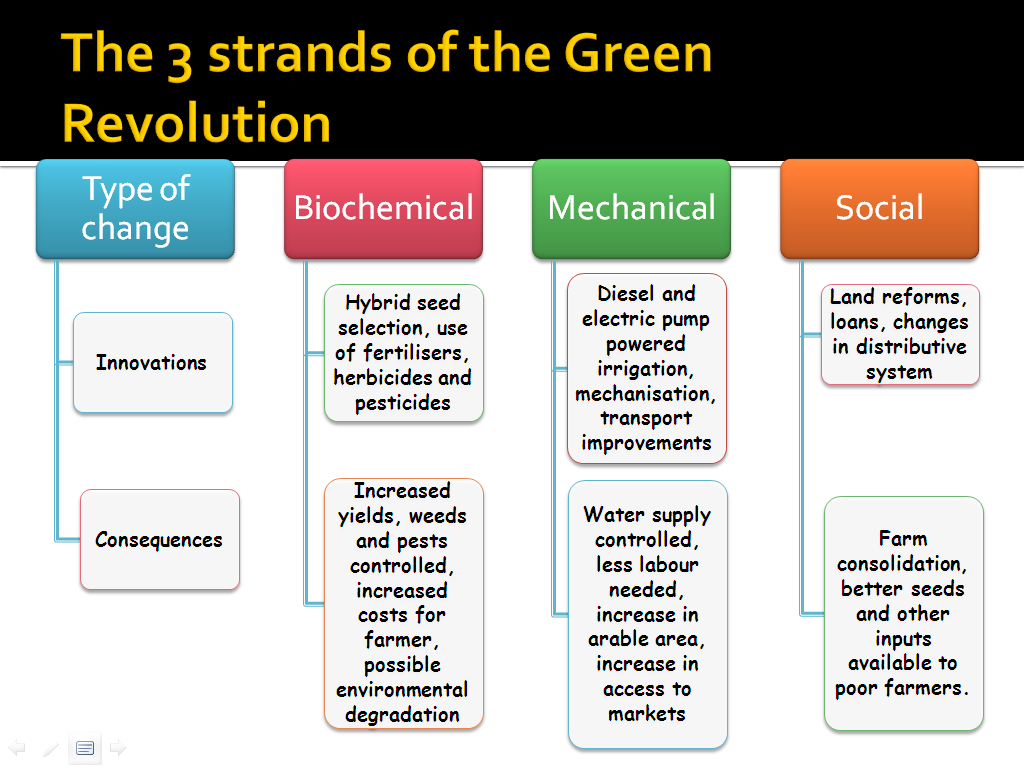
Features of Industrialized / High Input Agriculture
- Mechanization (fossil fuel use)
- Conventional Tillage
- Monocropping
- Genetic Engineering
- Synthetic Pesticides
- Synthetic Fertilizers
- Irrigation
Mechanization and its Negative Effects
- Causes land degradation through soil compaction by heavy machinery
- Increases soil erosion
- Causes decline in soil fertility
- Erosion damage causes decreased water quality
Conventional Tillage and Its Negative Effects
In conventional tillage the soil is extensively broken up. This:
- Disrupts the soil structure
- Increases soil erosion
- Causes decline in soil fertility
- Erosion damage causes decreased water quality
Monocropping and Its Negative Effects
- Also called monoculture
- Cultivation of a single crop, usually on a large area of land
- Simplifies ecosystems reducing biodiversity
- Encourages the build up of pests thus increasing the use of pesticides
- Depletes the soil of nutrients
Pesticides
Definition → Any chemical designed to kill or inhibit the growth of an organism that people consider undesirable.
Types of Pesticides
- Synthetic or inorganic pesticides are man-made
- Organic pesticides are based on natural plant compounds such as neem.
Benefits of pesticides
- Reduced pest and disease levels results in
- Increased production
- Improved food quality
Negative Effects of Synthetic Pesticides
- Genetic Resistance → Fast-breeding insect species undergo natural selection and develop genetic resistance to chemical pesticides.
- Mobile → When applied pesticides may move through the soil, water or air.
- Health Impacts → Pesticides have been linked to cancers and low sperm count
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Reduction in nutrient recycling soil organisms
- Loss of plant genetic diversity
- Endangerment & extinction of wildlife
- Persistent → pesticides adhere to sediment and become bioaccumulated and biomagnified
Negative Effects of Synthetic Pesticides Use
- Bioaccumulation → Increase in concentration of contaminants in the tissue of organisms
- Biomagnification → Increase in concentration of contaminants up the food chain
Fertilizers
Definition → Substances that add plant nutrients to soil and improves its ability to grow crops.
Types of Fertilizers
- Commercial Inorganic Fertilizer → Commercially prepared mixtures of plant nutrients
- Organic Fertilizer
N. B. Conventional agriculture relies on synthetic inorganic fertilizers
Negative Effects of Synthetic Fertilizer Use
- Supply only 2 or 3 of the 20+ nutrients needed by plants
- Leads to soil compaction
- Water pollution
- Increases nitrates and phosphates in waterbodies, drinking water, food and air
- Leads to eutrophication in the aquatic environment.
Genetic Engineering
Definition → Transfer of genetic material from one organism to another.
Benefits:
- Improve the appearance and taste of agricultural produce.
- Increase shelf life of fruits and vegetables.
- Provides genetic resistance to pest and diseases which reduces the need for application of pesticide to crops or livestock.
Negative Effects
- Genetically altered organisms might mutate and cause unforeseen effects
- Natural population balances in an ecosystem may be disturbed
- Health impacts such as allergic reactions to introduced genes in foods
Lack of GMO labeling prevents consumers from making a choice not to use GMO’s.
Irrigation
Definition → The application of water to crops.
Types of Irrigation
- Natural/Rainfall
- Flood irrigation
- Overhead/sprinkler
- Drip irrigation - most efficient water use (90%)
Flood Irrigation
Flood irrigation is wasteful of water and causes land degradation because of:
- Soil erosion
- Salinization (build up of salts in the soil)
- Waterlogging.
Land Degradation
Definition → Deterioration in the quality of land, its topsoil, vegetation, and or water resources. Usually associated with industrial agriculture and may lead to desertification.
Caused by:
- Overgrazing (animals feed too long or their numbers exceed the carrying capacity of rangeland)
- Flood irrigation
- Deforestation
- Conventional ploughing.
Desertification → Process whereby productive crop or range land turns into unproductive desert.
- Associated with industrial agriculture as well as rural poverty.
- The livelihoods of nearly one billion people in some 100 countries are threatened by desertification.
- About 25 per cent of the Earth's land, or 3.6 billion hectares, is desertified.
Sustainable Agriculture
- Crops grown in harmony with the environment
- Health of humans and livestock important
- Environment important
- Social justice important
Examples: Organic agriculture and Permaculture
Features of Sustainable Agriculture
- Companion cropping/mixed farming
- Soil conservation (preventing soil erosion)
- Alternatives to synthetic fertilizers (addition of organic matter)
- Use of alternatives to the use of synthetic pesticides
Mixed Cropping and Its Benefits
- Includes companion cropping and intercropping.
- Cultivation of more than one crop.
- Reduces the build up of pests thus reducing the use of pesticides
- Including legumes in the system adds nitrogen to the soil.
Soil Conservation Methods
- Methods used to:
- reduce soil erosion
- prevent depletion of soil nutrients
- restore nutrients
- Most methods involve keeping the soil covered with vegetation
Major Methods Include:
- Conservation tillage
- Contour farming
- Terracing
- Alley cropping
- Windbreaks/ Shelterbelts
- Maintaining & restoring soil fertility
Conservation Tillage → Crop cultivation with little or no soil disturbance
- Minimum Tillage
- No-till Farming
Contour Farming → Rows planted along the contour of the land. Used mainly on gently sloping land.
Terracing → Level areas created across the contour. Used on steeper slopes.
Alley Cropping → Planting crops with rows of trees on each side or amongst trees of the forest.
Windbreaks/Shelterbelts → Row of trees planted to block wind flow.
Organic Fertilizer
Organic materials, such as animal manure, applied as a source of plant nutrients. They improve soil structure, helps to retain soil moisture and stimulate beneficial bacteria and fungi.
Three Basic Types of Organic Fertilizer
- Animal Manure
- Green Manure
- Compost
Animal Manure → Dung and urine of farm animals.
Green Manure → Freshly-cut or still-growing vegetation that is ploughed into the soil.
Compost → Partially decomposed organic plant and animal matter
- Made up of animal manure, topsoil, kitchen scraps
- Rich, natural fertilizer
Alternatives to Pesticides
Agricultural Methods:
- Tillage of land → to expose pests
- Proper timing of planting, fertilizing and irrigating
- Crop rotation
- Plant rows of hedges or trees (habitat for natural predators to pest)
Genetic Control
- Breed crops and animals resistant to pests
- Sterilize members of the pest population
Natural Enemies (Biological Control) → Predators, parasites & pathogens can be encouraged or imported to regulate pest populations.
Consideration → care should be taken to avoid biotic pollution.
Pheromones → Chemical sex attractant that may be used in traps.
Hormones → Chemical sex attractant that may be used in traps.
Quarantine → Restriction of the importation of exotic plant and animal material that might harbor pests.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Combines use of biological, cultural and chemical control
- Non-chemical controls used as far as possible; pesticides used sparingly when other methods fail
Sustainable Livestock Production
- Free Range → Livestock allowed to forage outdoors
- Integrating crop and livestock production to create closed system
- Natural remedies replace antibiotics
- Hormones avoided
Legislations
- Town and Country Planning Act 1958 → Primary law governing land use in Jamaica
- The Watersheds Protection Act, 1963 → Law governing watersheds in Jamaica
- The Forest Act 1996 → Law for the management and reservation of forests
- Country Fires Act 1955 → Aims to prevent the lighting of arbitrary fires in rural area
- The Pesticides Act 1987 → Regulates the manufacture, importation use and sale of pesticides.