Respiratory, Nervous, Urinary, Itegumentary systems, eye and ear
Respiratory System
Responsible for gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out).
Plays a crucial role in vocalization and olfactory senses.
Key Components
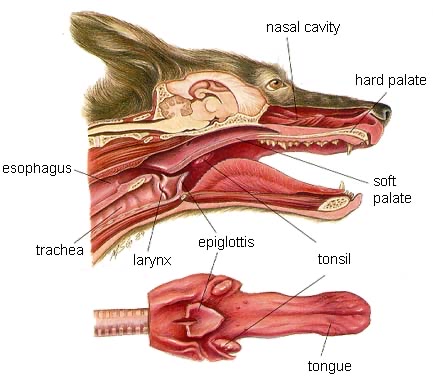
Nose: Filters and warms incoming air.
Pharynx: Common area in the back of the throat, passage for air and food.
Larynx: Provides passage for air to the trachea and prevents food/water entry.
Trachea: Connects the larynx to the bronchi; contains cartilage to maintain shape and prevent collapse.
How cats purr and dogs smell.
Cats: Produce sounds like purring through the larynx which regulates airflow.
Dogs: Utilize the respiratory system for olfactory sensing; linked to their ability to smell.
Importance of Panting
Purpose: Regulates body temperature and helps with:
Water elimination
pH balance (acid/base control)
Temperature regulation
Nervous System
Coordinates body functions and responses to internal/external stimuli.
Neuron Diagram
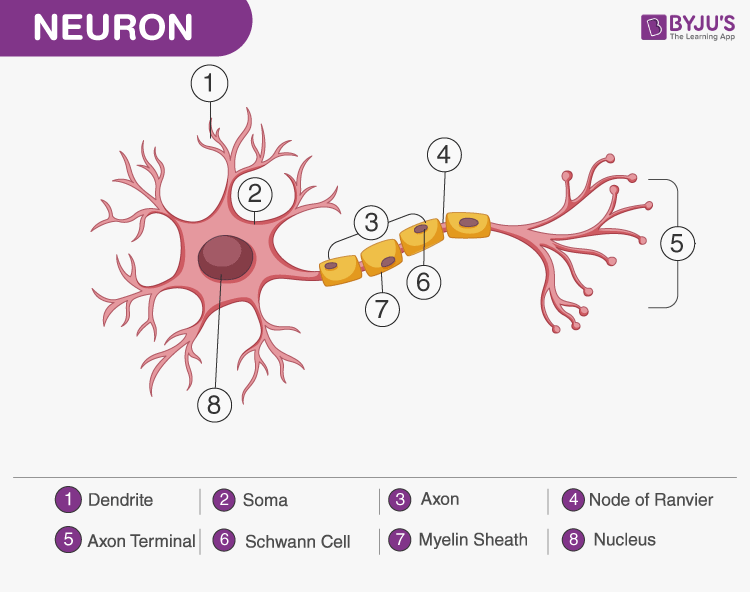
Dendrite
Soma (cell body)
Axon
Node of Ranvier
Axon Terminal
Schwann Cell
Myelin Sheath
Nucleus
Central and Peripheral Nervous System
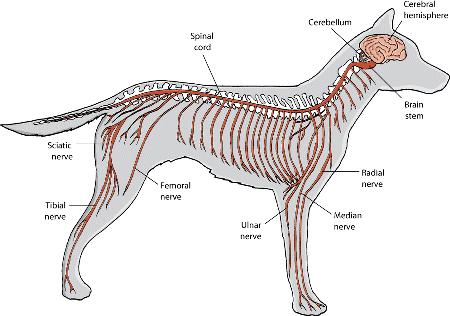
Autonomic Nervous System: Operates involuntarily.
Sympathetic System: Involved in "fight or flight" responses (e.g., reacting to a loud noise).
Parasympathetic System: Promotes relaxation (e.g., a sleeping pet).
Responses Examples
Sympathetic Examples:
Cat chased by a dog
Horse spooked by a noise
Aggressive response to stimuli
Parasympathetic Examples:
Dog chewing a bone
Cat purring when petted
Urinary System
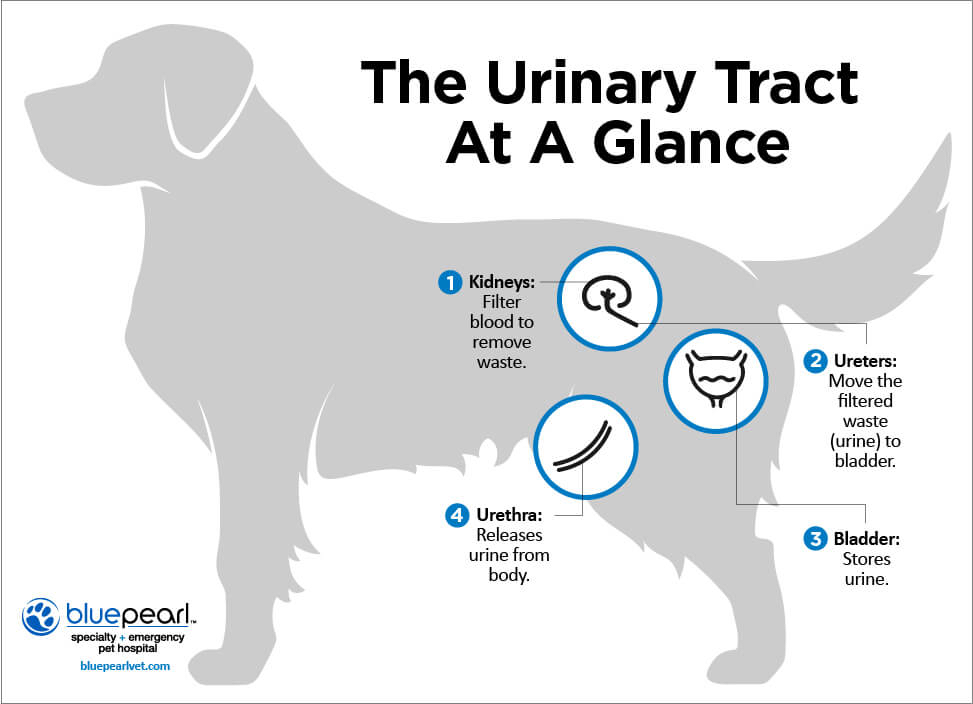
Main function is waste removal and filtration from the blood.
Proper functioning is vital; issues can arise from diseases, age, or toxins.
Nephron Function
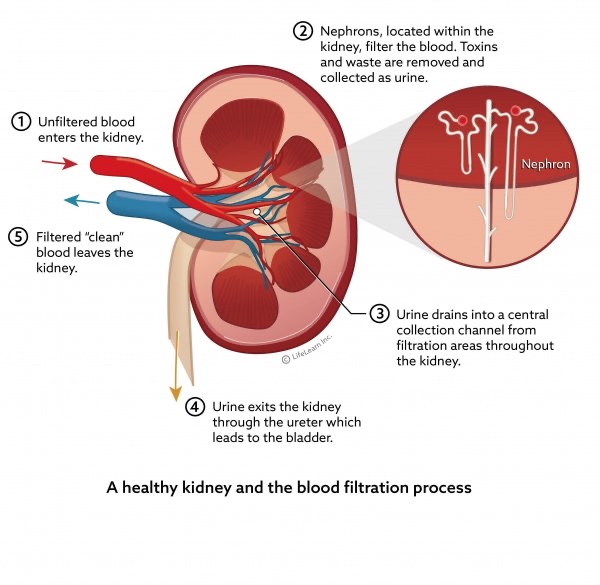
Blood Filtration: Toxins are removed by nephrons in the kidneys.
Collection: Urine collects in a central channel after filtration.
Excretion: Urine exits the kidney via the ureter to the bladder.
Integumentary System
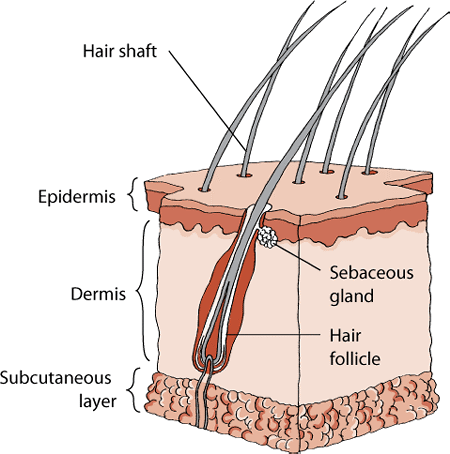
The skin is the largest organ and comprises two layers:
Epidermis: The outer layer responsible for skin pigment.
Dermis: The inner layer containing hair follicles, glands, nerve endings, and blood vessels.
The Eye
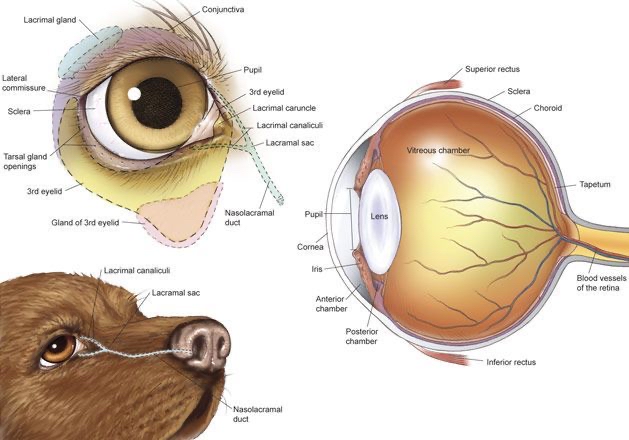
Retina: Connects to the optic nerve, processes visual information.
Cornea: The outermost front part of the eye, plays a role in light refraction.
Tapetum: Reflective layer allowing better vision in low light.
Visual Perception in Animals
Rods: Highly sensitive to light; present in most domestic animals; allow limited color perception.
Cones: Responsible for color vision, require more light than rods.
The Ear
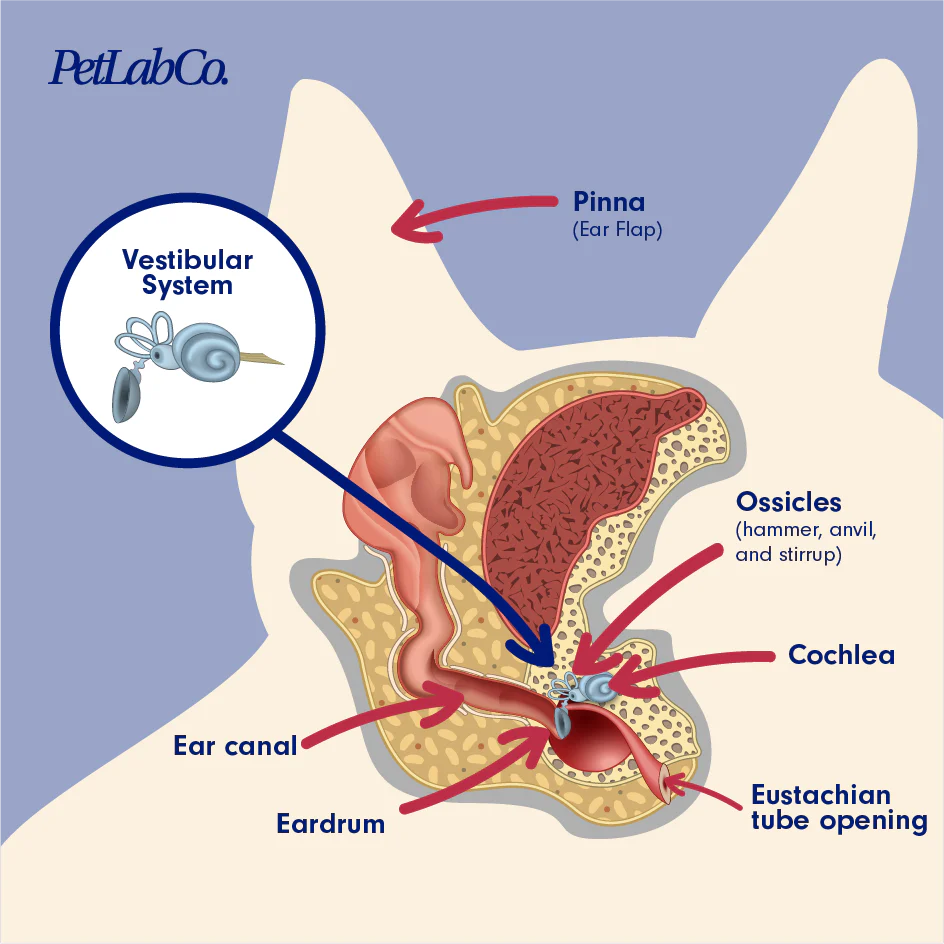
Essential for hearing and balance; animals hear different frequencies compared to humans.
Vestibular Sense
Located in the inner ear, it helps maintain balance:
Comprises fluid-filled canals that send nerve impulses to the brain.
Disturbance can lead to balance issues, often due to infections.
References
Sirois, M. (2021). Elsevier's Veterinary Assisting Textbook (3rd ed.). Elsevier.