Toxicology Exam 3
The name of the plant from which cocaine is extracted.
Erythroxylon Coca
The classification of amphetamines under the Controlled Substances Act (Public law 91-513) of 1970.
Class 2
Which are the forms of cocaine.
Hydrochloride Salt (purity >50%)
Crack
What form of cocaine, crack is and how it is prepared.
Crack is a freebase form of cocaine
Crackling sound when smoked
Prepared by adding baking soda to aqueous cocaine HCl and heating it to remove water. After heating, the mixture is cooled and filtered. The freebase cocaine precipitates into small pellets that can be smoked in a crack pipe.
The complete metabolic pathway of cocaine to benzoylecgonine, ecgonine methyl ester and cocaethylene (with structures).
Cocaine →
Ecgonine methyl ester → ecgonine
→ Norcocaine (P450)
→ Benzoylecgonine → ecgonine
→ Ethylcocaine/cocaethylene → ecgonine
The receptors through which cocaine mediate its activity.
Norepinephrine and Dopamine
The effects of cocaine mediated by dopamine.
Euphoria, psychic energy, heightened sexual excitement, self confidence, paranoia, hallucinations, dysphoria
The effects of cocaine mediated by norepinephrine.
Mydriasis, vasoconstriction, hypertension, tachycardia, tachypnea
The pharmacodynamic mechanism of action of cocaine on dopaminergic nerve terminal.
Prevents the reuptake of dopamine into the presynaptic dopaminergic neuron by binding to receptors on the dopamine transporter located on the dopaminergic nerve terminal.
Mediated by NaCl, dependent on active transport
Inhibited when coke binds to sodium binding site and alters chloride binding site
Which compounds are used as cutting agents in cocaine.
The differences on the bioavailability of cocaine after per os, intravenous and intranasal administration.
After IV and SM: peak concentration is immediate. First order elimination with a half like of 60 min
After IN and PO: peak concentration 30-60 minutes after, half-like is 4-5 hours
Which is the unique metabolite of cocaine which is formed only after simultaneous use of alcohol.
The unique metabolite of cocaine which is produced only after consumption of ethanol is:
Amphetamines
Which chemical class do the amphetamines represent?
Sympathomimetic drugs
The structures of amphetamine, methamphetamine, methylene-dioxy-amphetamine, methylene-dioxy-methamphetamine, and methylene-dioxy-ethylamphetamine.
Methamphetamine:
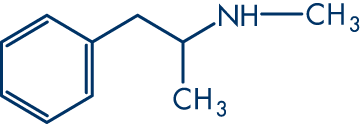
methylene-dioxy-amphetamine:
methylene-dioxy-methamphetamine:
methylene-dioxy-ethylamphetamine:
The classification of amphetamines under the Controlled Substances Act (Public law 91-513) of 1970.
Schedule II
The receptors through which amphetamines mediate its activity.
Dopaminergic and adrenergic receptors
At least one synthetic route of methamphetamine.
Phenyl-2-Propanone (P2P) + methylamine + aluminum foil + HgCl2 + C2H5OH → d-methamphetamine
Which amphetamine can be used for therapeutic purposes and for which treatments.
Dextroamphetamine: narcolepsy and ADHD
The effects of amphetamine and methamphetamine.
Hyperstimulation, peripheral vasoconstriction, tachycardia, pupillary dilation, euphoria, intensification of feelings, convulsions, hyperthermia, behavioral changes.
The street names of methamphetamine.
MA HCl, speed, crank, go, crystal, meth, ice
Which adulterants are added to amphetamines formulations. What is the role of each adulterant?
Sugars: add volume
Caffeine, phenylpropanolamine, ephedrine, pseudoephedrine: cheaper stimulants
The metabolic pathway of methamphetamine including the structures.
Cannabis
The name of the plant from which cannabis is extracted.
There are four: sativa, indica, ruderalis, and hybrids
Which is the main factor that affects the purity on Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the plant.
more heat and less humidity means the leaves dry a bit and concentrate the THC
in more humid areas, the concentration is more dilute
The receptors responsible for the effects of Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol at CNS.
CB1 and CB2 receptors
What is the hysteresis effect?
Delta9-THC is rapidly absorbed and distributed to tissues. Initial changes in blood concentrations are out of phase with the physiological and behavioral changes.
The endogenous compounds that regulate the endocannabinoid system.
The complete metabolic pathway of delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinol to 11-OH-tetrahydrocannabinol and 11-nor-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (with structures).
If the metabolites of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol are active.
Which is the disadvantage after per os use of cannabis product in terms of the bioavailability of Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
Cannabis’ behavioral effects.
Cannabis’ acute toxic effects.
What is the volume of distribution (number with units) of Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and how it affects its partition in the human body.
Which is the main tissue at which Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol is accumulated.
The elimination half life for cannabis acute and long-term users.
The lipophilicity factor of Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
How the normalization of urine cannabinoid concentrations is calculated and how this can be used to decide if a new episode of drug exposure has been occurred.
ASB036 standard
The definitions:
Accuracy/Bias: An estimate of systematic measurement error, calculated as the difference between the mean of several measurements under identical conditions, to a known “true” value. Often reported as a percent difference.
Precision: The measure of the closeness of agreement between a series of measurements obtained from multiple samplings of the same homogenous sample.
Biological Fluid: Any liquid biological specimen that is typical pipetted for analysis
Fortified Matrix Sample: A blank matrix sample spiked with target analyte and/or internal standard using reference materials.
Interferences: Non-targeted analytes which may impact the ability to detect, identify, or quantitate a targeted analyte.
Carryover: The appearance of unintended analyte signal in samples after the analysis of a positive sample.
Blank Matrix Sample: A biological fluid or tissue (or synthetic substitute) without target analyte or internal standard.
Limit of Detection (LOD): An estimate of the lowest concentration of an analyte in a sample that can be reliably measured with acceptable bias and precision.
Lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ)/Decision Limit: An estimate of the lowest concentration of an analyte in a sample that can be reliably measured with acceptable bias and precision.
Stability: An analyte’s resistance to chemical change in a matrix under specific conditions for given time intervals.
Tissues: Any solid biological specimen that is generally weighed for analysis.
Reference material: Material, sufficiently homogeneous and stable with reference to specified properties, which have been established to be fit for its intended use in a measurement or in examination of nominal properties.
Dilution Integrity: the process of assessing whether diluting a sample impacts the accuracy and precision of the measured concentration of an analyte
Matrix effect: the influence of sample components other than the analyte (the substance being measured) on the analytical signal, potentially leading to inaccurate or inconsistent results.
Calibration modeling: the process of ensuring a measuring instrument or method produces accurate results
Specificity: the ability of an enzyme or assay to specifically recognize and interact with its target molecule or analyte, without reacting with other similar molecules
Selectivity: the ability of a process or reagent to preferentially react with or discriminate between different components in a mixture, leading to the formation of a specific product or the separation of specific components
Which are the two phases of method development.
Instrumental and data acquisition/processing parameters
Sample preparation
The required validation parameters for Immunoassay screening methods.
Limit of detection
Precision (at the decision point)
Processed sample stability (if applicable)
The required validation parameters for screening methods other than Immunoassays.
Interference studies
Limit of detection
Ionization suppression/enhancement (for applicable techniques, such as LC/MS
Processed sample stability
The required validation parameters for qualitative identification methods.
Carryover
Interference studies
Ionization suppression/enhancement (for applicable techniques, such as LC/MS)
Limit of detection
Processed sample stability (if applicable)
The required validation parameters for quantitative methods.
Bias
Calibration Model
Carryover
Interference Studies
Ionization suppression/enhancement (for applicable techniques, such as LC/MS)
Limit of detection
Limit of quantitation
Precision
Dilution integrity (if applicable)
Processed sample stability (if applicable)
How the Within-Run and Between-Run bias and precision are calculated.
The acceptance criteria for %CV of bias and precision.
The maximum acceptable bias shall be +/-20% at each concentration
For precision, %CV shall not exceed 20% at each concentration
The grand mean +/- two standard deviations of the low and high concentration pools shall not overlap with the mean of the decision point
Which are the calibration models used.
Simple linear regression model using the least squares method
Which is the least number of non-zero concentration calibrator samples that must be used to establish a calibration model.
Four
How the Limit of Detection can be calculated.
How the Limit of Quantification can be calculated.
LOQ = 10(Sy/Avgm)