Cardiovascular System
Word Parts
angi/o: vessel
aort/o: aorta
ateri/o: artery
ather/o: fatty
atri/o: atrium
brady-: slow
cardi/o: heart
coron/o: crown
-ecstasis: dilation, expansion
-emia: blood
endo-: inner, within
erythr/o: red
-gram: written record
hem/o: blood
hemat/o: blood
isch: restricting, narrowing
leuk/o: white
my/o: muscle
peri-: around, surrounding
phleb/o: vein
-stenosis: narrowing
tachy-: fast
brady-: slow
thromb/o: clot
valv/o: valve
valvul/o: valve
varic/o: dilated
vas/o: vessel
ven/o: vein
ventric/o: ventricle
Abbreviations
A-fib: atrial fibrillation
AV: atrioventricular
BP: blood pressure
CABG: coronary artery bypass graft
CAD: coronary artery disease
CCU: cardiac care unit
CHF: congestive heart failure
DIC: disseminated intravascular coagulation
DVT: deep vein thrombosis
ECG/EKG: electrocardiogram, electrocardiograph, electrocardiography
Hb: hemoglobin
Structure and Function
Cardiovascular system consists of:
Heart
Blood
Blood vessels
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Cardiac: pertaining to the heart
Coronary: pertaining to the crown or encircling (reference to around the heart)
Pericardial: pertaining to the pericardium
Vascular: pertaining to blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Functions
Forms transportation system that delivers oxygen and nutrients to body’s cells
Returns carbon dioxide and wastes to be eliminated
Helps regulate body temperature
Heart pumps blood within blood vessels to all parts of the body
Pulmonary circuit: passage of blood from heart’s right ventricle, through lung’s pulmonary arteries, back through pulmonary veins to heart’s left atrium
Systemic circuit: circulation of blood through arteries, capillaries, and veins of general system
Heart
Four-chambered hollow organ with three layers
Apex: lowermost tip
Endocardium: innermost layer
Myocardium: middle layer; actual heart muscle and thickest of three layers
Epicardium: outer layer; surrounded by pericardium, a sac that surrounds the heart
Heart Chambers
Right atrium: upper right chamber that receives blood from all body parts except lungs; receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava
Right ventricle: lower right chamber that receives blood from right atrium and pumps it to the lungs
Left atrium: upper left chamber that receives oxygen-rich blood as it returns from the lungs
Left ventricle: lower left chamber that pumps blood out of aorta to all parts of the body
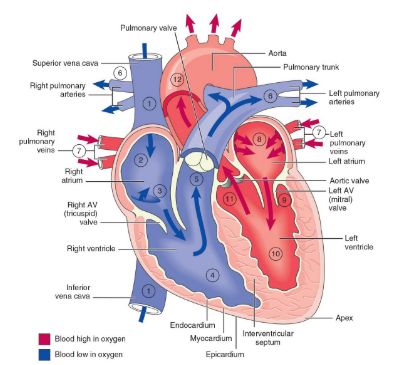
Superior and inferior vena cava: large vein carrying deoxygenated blood to the right atrium
Right atrium: receives deoxygenated blood and pumps it to the right ventricle
Tricuspid valve: the valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle
Right ventricle: pumps deoxygenated blood from the heart to he lungs for oxygenation
Pulmonary valve: controls the flow of blood from the heart to the lugs
Pulmonary arteries: blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation
Pulmonary veins: carries oxygenated blood to the left atrium
Left atrium: receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it into the left ventricle
Mitral valve: keeps blood moving in the right direction from left atrium to left ventricle
Left ventricle: pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body
Aortic valve: regulated the flow of blood from left ventricle into the aorta
Aorta: largest artery in the body; transport oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
Conducting system of heart generates and transmits signals that stimulate heart to contract and relax in sequence
Sino-atrial (SA) node: pacemaker of the heart
Atrioventricular (AV) nod
Bundle of His
Purkinje fibers
Blood Vessels
Arteries: carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
Arterioles: smaller branches of the arteries; small vessels that receive blood from the arteries
Capillaries: blood vessels that connect arterial and venous systems; microscopic vessels through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body
Veins: blood vessels that return blood back to the heart
Venules: smaller branches of the veins; smaller vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins
Lumen: tubular space through which blood flows
Vasodilation: lumen opened
Vasoconstriction: lumen closed
Vasodilation and vasoconstriction can each have an effect on blood pressure (BP)
Blood Elements
Plasma
Erythrocytes: red blood cells (RBCs)
Main function is to transport oxygen
Leukocytes: white blood cells (WBCs)
Body’s main defense against harmful organisms
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Thrombocytes: platelets
Play important role in blood-clotting process
Types of Donors and Recipients
Blood Type | Can Donate To | Can Receive From |
A | A or AB only | A or O only |
B | A or AB only | B or O only |
AB (universal recipient) | AB only | A, B, AB, O |
O (universal donor) | A, B, AB, O | O only |
Heartbeat
Heart contracts and releases in a rhythmic cycle
Systole = contraction
Diastole = relaxation
Heart rate (HR) = number of contractions per minute
Blood pressure: measurement of amount of pressure exerted against walls of blood vessels; pressure exerted by the blood upon the walls of the blood vessels, especially arteries.
Recorded as a fractional number, systolic over diastolic
Measured by an instrument called sphygmomanometer (BP cuff)
Expressed in mmHg
Electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG): electrical activity of heart recorded
Electrocardiograph: machine that does the recording
Angiogram: x-ray of blood vessels following injection with radio-opaque material
Echocardiogram: ultrasound of the heart
Diseases
Coronary artery disease (CAD): narrowing of lumen of one or more coronary arteries, usually due to atherosclerosis; disease of arteries surrounding the heart
Atherosclerosis: progressive buildup of plaque or fatty deposits on inner arterial walls, lumen narrows → hardening and narrowing of the arteries
Hyperlipidemia: increased blood fat (lipid)
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
Arteriosclerosis: hardening and loss of elasticity in artery impeding blood flow to heart muscle caused by fatty deposits
Ischemia: inadequate supply of blood and oxygen to tissues
Thrombus: blood clot in a blood vessel
Thrombosis: formation of a thrombus
Embolus: blood clot that moves throughout the bloodstream
Myocardial infarction (MI): heart attack, results from lack of oxygen supply to myocardium
Symptoms include: chest pain (feeling as if elephant is sitting on chest), diaphoretic, jaw pain, indigestion, pain radiating down the left arm
Congestive heart failure (CHF): heart cannot pump enough blood to meet body’s needs for oxygen and nutrients
Arrhythmia: any irregularity of heart’s rhythm
Bradycardia: slower than normal HR (< 60 bpm)
Tachycardia: faster than normal HR (> 100bpm)
Fibrillation: rapid, random, and ineffective contractions of the heart
Atrial fibrillation (A-fib): atria beats faster than ventricles; rapid, random, and ineffective contraction of the atrium. Most common arrhythmia. May cause blood clots to be formed in the atrium.
Ventricular fibrillation: ventricles ineffectively pump blood, can be fatal
Hypertension: high blood pressure (the force of the blood pushing against artery walls is consistently too high); silent killer
Systolic reading > 140 mmHg or diastolic > 90 mmHg
Secondary hypertension: related to another medical problem
Arteriosclerosis: hardening of the arteries
Left ventricular hypertrophy: oversized left ventricle
Cyanosis: a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from poor circulation or inadequate oxygenation of the blood
Deep Vein Thrombosis: blood clot forms in a large vein, usually in a lower limb
Phlebitis: inflammation of a vein
Murmur: abnormal swishing sound of the heart caused by improper closure of the heart valves
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD): a hole in the interventricular septum; occurs during pregnancy; lets venous blood pass from the right to the left ventricle and out to the aorta without oxygenation
Myocarditis: inflammation of the heart muscle
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF): Rare heart condition where baby is born with four different heart problems that cause altered blood flow through heart and body (a ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, and an overriding aorta)
Stroke: When blood flow to the brain is blocked
Symptoms: facial palsy, slurred speech and one sided weakness.
Blood Disorders
Anemia: deficiency of RBC or low level of Hb
Leukemia: increased number of WBCs
Clotting disorders
Hemophilia: genetic bleeding disorder that impairs the body's ability to form blood clots, leading to prolonged bleeding
Thrombocytopenia: abnormal decrease in number of thrombocytes or platelets
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Treatments
Antiarrhythmic medication: drug used to treat heart rhythm abnormalities
Cardioversion: treatment for fibrillation; applying electric current to restore normal heart rhythm
Ablation therapy: apply radio frequency waves to the heart
Surgical procedures:
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)
Angioplasty: procedure that involves opening up a narrowed or blocked blood vessel → surgical repair of blood vessel; opens a blocked artery by inflating a small balloon within a catheter to widen and restore blood flow in the artery
Arterial stent
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
Endarterectomy
Statin: medicine to take for hypercholesterolemia
Aspirin: can be given to someone with heart attack symptoms
Practitioners
Cardiologist: diagnose and treat heart disorders
Cardiovascular surgeons: surgically correct disorders of cardiovascular system
Hematologist: treat disorders of the blood