Chapter 1: Introduction to Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Introduction:
Economics is divided into two main branches: Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
Microeconomics: Derived from the Greek word "Mikros" meaning "small." It studies individual units like consumers, firms, and markets.
Macroeconomics: Derived from "Makros," meaning "large." It examines aggregate variables such as national income, employment, inflation, and GDP.
The terms were coined by Norwegian economist Ragnar Frisch in 1933.
Historical Development:
Microeconomics: Originated from the Classical Economists (Adam Smith, David Ricardo, J.S. Mill). Alfred Marshall popularized the field through his book Principles of Economics (1890).
Macroeconomics: Though macroeconomic ideas were present in the work of Mercantilists and Physiocrats, macroeconomics gained prominence after the Great Depression (1930s). John Maynard Keynes introduced macroeconomic analysis in his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money (1936).
Microeconomics:
Definitions:
Maurice Dobb: “Microeconomics is in fact a microscopic study of the economy.”
A.P. Lerner: “Micro economics consists of looking at the economy through a microscope, as it were, to see how the millions of cells in the body of economy – the individuals or households as consumers and individuals or firms as producers play their part in the working of the whole economic organism.”
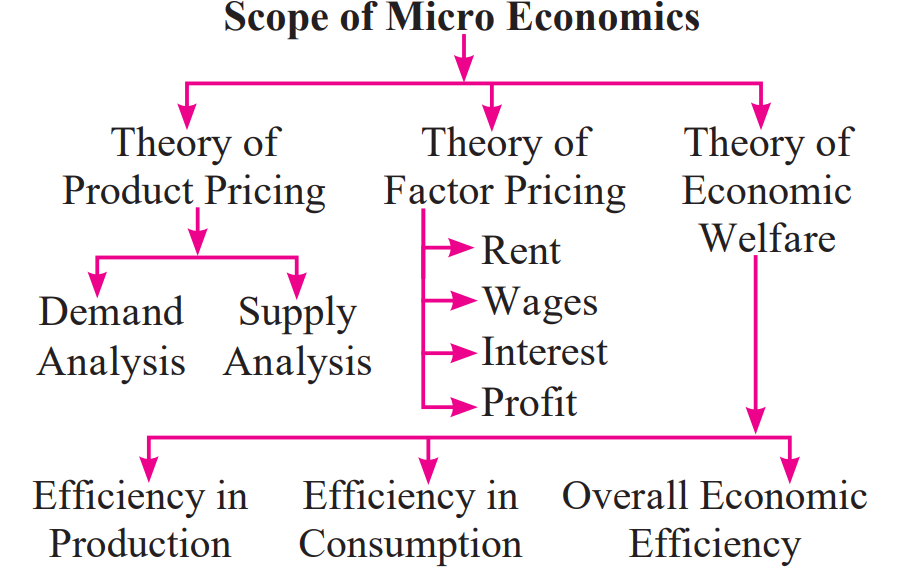
Scope of Microeconomics:
Theory of Product Pricing: Prices of goods are determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
Theory of Factor Pricing: Involves determining the rewards for factors of production (rent for land, wages for labor, interest for capital, and profit for entrepreneurs).
Theory of Economic Welfare: Focuses on efficiently allocating resources to maximize social welfare. It involves:
Production efficiency: Producing the maximum output with the given resources.
Efficiency in consumption: Distributing resources to maximize societal satisfaction.
Overall economic efficiency: Producing goods that are most desired by society.
Features of Microeconomics:
Study of Individual Units: Focuses on individual consumers, firms, and markets.
Price Theory: Deals with how prices of goods and services, and factors of production are determined.
Partial Equilibrium: Analyzes equilibrium in individual markets without considering external influences.
Based on Assumptions: Includes assumptions such as "other things being equal" (ceteris paribus).
Slicing Method: Break down the economy into smaller parts (e.g., individual demand vs. aggregate demand).
Use of Marginalism: Examines how additional units of goods or factors affect the total.
Analysis of Market Structure: Studies different market structures (e.g., perfect competition, monopoly).
Limited Scope: Focuses on individual units, ignoring macroeconomic issues like inflation and unemployment.
Importance of Microeconomics:
Price Determination: Explains how prices for goods and services are set in the market.
Free Market Economy: Helps understand the functioning of economies with little government intervention.
Foreign Trade: Assesses aspects of international trade, such as tariffs and exchange rates.
Business Decisions: Provides tools for firms to make decisions related to costs, output, and profit.
Useful to Government: Helps formulate policies like taxation and pricing.
Welfare Economics: Studies how to achieve the best allocation of resources to improve welfare.
Macroeconomics:
Definitions:
J.L. Hansen: “Macroeconomics is that branch of economics which considers the relationship between large aggregates such as the volume of employment, total amount of savings, investment, national income, etc.”
Carl Shapiro: “Macroeconomics deals with the functioning of the economy as a whole.”
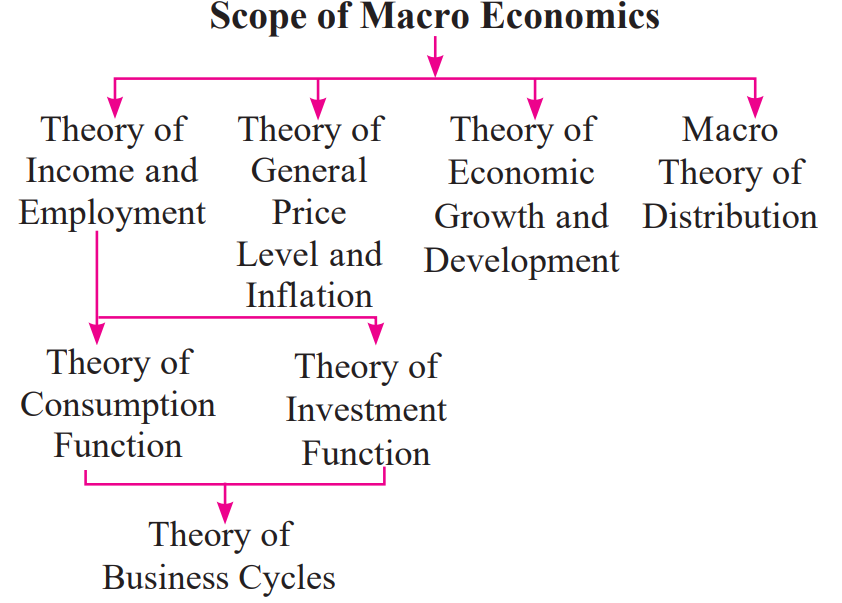
Scope of Macroeconomics:
Theory of Income and Employment: Studies what determines national income and employment levels.
Theory of General Price Level and Inflation: Analyzes how prices are set across the entire economy and what causes inflation and deflation.
Theory of Economic Growth and Development: Studies factors that promote or hinder economic development.
Macro Theory of Distribution: Examines how the national income is distributed among rent, wages, interest, and profit.
Theory of Business Cycles: Focuses on the fluctuations of economic activity (booms and recessions).
Features of Macroeconomics:
Study of Aggregates: Focuses on total variables like national income, output, and employment.
Income Theory: Studies national income, social accounting, and their impact on the economy.
General Equilibrium: Analyze the interrelation of demand, supply, and prices in the economy as a whole.
Interdependence: Considers the relationships between different aggregate variables (income, output, prices).
Lumping Method: Looks at the economy as a whole instead of focusing on individual parts.
Growth Models: Studies models that explain economic development and growth.
General Price Level: Studies inflation, deflation, and the causes behind changes in the price level.
Policy-Oriented: Macroeconomics provides solutions to economic issues like unemployment and inflation.
Importance of Macroeconomics:
Functioning of the Economy: Explains how the economy operates at a national level.
Economic Fluctuations: Helps understand business cycles and how to control them.
National Income: Provides insights into national income measurement and its importance in policymaking.
Economic Development: Assists in understanding problems like poverty and inequality, and helps suggest development strategies.
Performance of an Economy: National income estimates help gauge the overall performance of an economy.
Level of Employment: Analyzes overall employment trends and government interventions.
Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics:
Basis | Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
Scope | Studies individual units like consumers | Studies the whole economy |
Focus | Price theory and allocation of resources | National income and overall employment |
Tools | Individual demand and supply | Aggregate demand and supply |
Examples | Pricing of a product, behavior of a firm | National income, inflation, employment |
Important questions:
Explain the scope of microeconomics and its key components.
Discuss the features of microeconomics and explain how it is useful for government policy-making.
What is the Theory of Economic Welfare? How does microeconomics contribute to efficient resource allocation?
Explain the scope of macroeconomics with reference to income, employment, and inflation.
Compare and contrast microeconomics and macroeconomics in detail with suitable examples.
What is the importance of macroeconomics in understanding economic growth and development? Explain with examples.
Discuss the Theory of General Price Level and Inflation in macroeconomics.
Explain how microeconomic analysis is used by firms and governments in decision-making.
Answers:
1.Explain the scope of microeconomics and its key components.
Microeconomics studies how individual units like consumers and firms make decisions about resource allocation. It focuses on:
Product Pricing: Prices are determined by the interaction of supply and demand, analyzing consumer behavior and producer decisions.
Factor Pricing: Microeconomics explains how the factors of production (land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship) are rewarded in the form of rent, wages, interest, and profit.
Economic Welfare: This component focuses on achieving efficiency in resource allocation, maximizing satisfaction through optimal production and consumption.
2. Discuss the features of microeconomics and its usefulness for government policy-making.
Features of Microeconomics:
Study of Individual Units: It analyzes the behavior of specific consumers, firms, and markets rather than the entire economy.
Price Theory: Deals with how the prices of goods and services, as well as production factors, are determined.
Partial Equilibrium: It focuses on achieving equilibrium in a particular sector or market, assuming other factors remain constant.
Marginalism Principle: Microeconomics uses marginal analysis to study changes in consumption and production behavior.
Slicing Method: The economy is split into smaller units for detailed study, like analyzing individual income or demand.
Usefulness in Government Policy: Microeconomic principles assist the government in formulating policies related to taxation, subsidies, and price controls. It also helps in understanding the behavior of markets, ensuring optimal resource allocation, and creating welfare programs for social benefit.
3.What is the Theory of Economic Welfare? How does microeconomics contribute to efficient resource allocation?
The Theory of Economic Welfare examines how resources can be distributed efficiently to maximize societal satisfaction. It aims to achieve:
Efficiency in Production: Maximizing output with given resources.
Efficiency in Consumption: Distributing goods to achieve the highest satisfaction for society.
Overall Economic Efficiency: Ensuring that the goods most desired by society are produced.
Microeconomics contributes by studying individual behavior (both consumers and producers) and guiding decisions to allocate resources where they generate the highest utility, ensuring optimal distribution in both production and consumption.
4.Explain the scope of macroeconomics with reference to income, employment, and inflation.
Macroeconomics deals with aggregate variables and studies the economy as a whole. Its scope includes:
National Income: It analyzes the total income generated within an economy, measuring it through methods like GDP and GNP. Macroeconomics examines factors influencing income growth and distribution.
Employment: The study focuses on the factors determining employment levels in the economy, including labor markets, job creation, and government interventions to address unemployment.
Inflation: Macroeconomics studies the general rise in prices (inflation) and its impact on the economy, such as reducing purchasing power and savings.
5.Compare and contrast microeconomics and macroeconomics in detail with suitable examples.
Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
Studies of individual units like consumers and firms | Studies the economy as a whole, focusing on aggregates |
Focuses on price determination and resource allocation | Focuses on national income, employment, and inflation |
Uses demand and supply for analysis | Uses aggregate demand and supply for analysis |
Examples: Pricing of a product, firm behavior | Examples: National income, inflation levels, unemployment |
Examples:
Microeconomics: Examining how a firm sets the price of a product based on consumer demand.
Macroeconomics: Analyzing how fiscal policy affects national unemployment rates.
6.What is the importance of macroeconomics in understanding economic growth and development? Explain with examples.
Macroeconomics is essential for understanding and fostering economic growth and development:
National Income: By measuring national income and output, macroeconomics helps track economic progress and the overall health of an economy.
Example: Tracking GDP growth over several years to see if a country is expanding or contracting.
Employment: Economic growth usually leads to job creation. Macroeconomics helps governments implement policies that promote employment.
Example: A country experiencing rapid industrialization often sees an increase in jobs within that sector.
Economic Development: It studies the causes of poverty and inequality, suggesting policies for sustainable development.
Example: Governments may use macroeconomic policies to reduce poverty through investments in education and infrastructure.
7.Discuss the Theory of General Price Level and Inflation in macroeconomics.
General Price Level refers to the average prices of goods and services in an economy, reflecting the purchasing power of money. Inflation is the persistent increase in this price level over time.
Causes of Inflation:
Demand-Pull Inflation: Occurs when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply.
Example: A booming economy where high consumer demand pushes prices up.
Cost-Push Inflation: Results from rising production costs, such as increased wages or raw materials.
Example: A surge in oil prices leads to higher transportation costs, which in turn raises the prices of goods.
Consequences of Inflation:
Decreased purchasing power: As prices rise, the value of money falls, reducing what consumers can buy with the same amount of money.
Uncertainty: High inflation creates instability in investment and savings, affecting long-term economic growth.
8.Explain how microeconomic analysis is used in decision-making by firms and governments.
Microeconomic analysis helps both firms and governments make informed decisions:
For Firms:
Pricing Strategy: Microeconomics helps firms understand demand elasticity and set prices that maximize profits.
Example: A company may lower prices to boost sales if demand is highly elastic.
Cost Control: Firms use microeconomic tools to minimize production costs and maximize efficiency.
Example: A firm outsourcing production to reduce labor costs and increase profit margins.
For Governments:
Taxation: Governments apply microeconomic principles to design taxes that minimize negative effects on the economy.
Example: Higher taxes on luxury goods help generate revenue without significantly reducing demand.
Subsidies: Microeconomics helps governments decide which sectors need subsidies to ensure public welfare.
Example: Subsidies on essential goods like rice or fuel ensure affordability for the public, especially in low-income areas.