
Science 2nd Quarter Reviewer
★★ HEAT AND TEMPERATURE
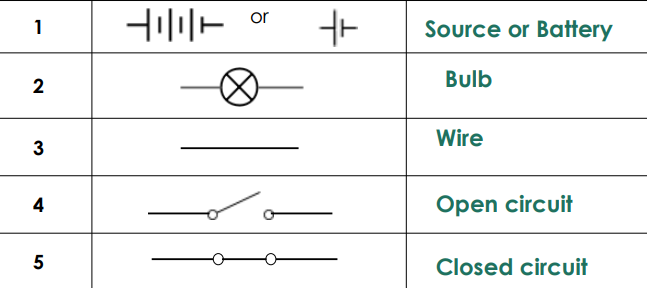
Heat (Q) - transfer of kinetic energy from one medium or object to another; total kinetic energy
Heat flows from a warmer object to a colder object’
Heat SI Units - Joule, Calorie
Heat Measuring Device - Calorimeter
Temperature (T) - a measure of thermal energy or average heat of the molecules in a substance; average kinetic energy
Higher temperature: faster-moving molecules
Temperature rises when heated and falls when cooled
Temperature SI Units - Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin
Heat Measuring Device - Thermometer
Thermal Equilibrium - said that two substances that are at the same temperature meaning there is no more heat energy transferred
*rely on the written methods for the conversion of units of temperature
★★ ELECTRICITY
Electricity - a natural phenomenon that occurs throughout nature and takes many different forms; flow of electric charge
Electrodynamics – deals with electrical charges in motion
Electric Circuit – a closed conducting path where charges flow.
Electric Current – the flow of charged particles (electrons & ions); charge particles are referred to as charge carriers
Potential Difference – the work done by a charge carrier (electron, ion, etc) when passing through an electrical component
Electrical Power - the rate at which electric energy is transferred within a circuit; rate of consumption of electrical energy by a device
Electrical Energy - generated from the potential difference in a circuit, causing current to flow; the energy generated due to the movement of charge carriers in a conductor
Conductors – allow electric charges to flow (e.g: steel, silver, gold, copper,
Insulators – resist the flow of electric charges (e.g: wood, glass, rubber, oil, plastic)
Alessandro Volta - Italian physicist known for the invention of the electrochemical cell also known as the battery
André Ampère - a French physicist and mathematician; discovered electromagnetism
Georg Ohm - a German physicist; determined that there is a direct proportionality between the voltage applied across a conductor and the electric current
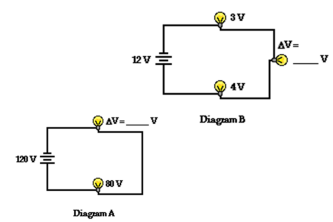
Voltage - the charge that causes the current to flow; symbol and Unit: V
Current - flow of electricity; will only flow if there’s voltage; symbol: I; Unit: A (Ampere)
Resistance - it opposes the push from the voltage source and affects the speed of the current; symbol: R; Unit: Ω (Ohms)
Ohm’s Law - states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through the resistance
Measuring devices:
Voltage - voltmeter, Current - ammeter, Resistance - ohmmeter
Formulas:
Voltage - V = I x R, Current - I = V/R, Resistance - R = V/I
Simple Circuit - the path that an electric current travels on
Three parts of a circuit:
- the source of voltage
- conductive path
- resistor
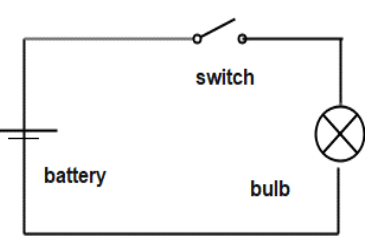
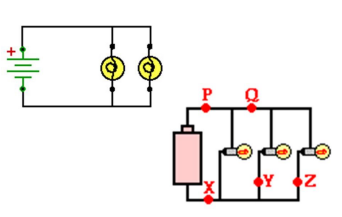
Series Circuit - only one path for the current, and a break in the circuit stops the current
Parallel Circuit - there are multiple pathways or branches
Series Circuit
Parallel Circuit
Integrated Circuit - thousands combined series and parallel; also called microelectronic circuit
★★ HEAT AND TEMPERATURE
Heat (Q) - transfer of kinetic energy from one medium or object to another; total kinetic energy
Heat flows from a warmer object to a colder object’
Heat SI Units - Joule, Calorie
Heat Measuring Device - Calorimeter
Temperature (T) - a measure of thermal energy or average heat of the molecules in a substance; average kinetic energy
Higher temperature: faster-moving molecules
Temperature rises when heated and falls when cooled
Temperature SI Units - Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin
Heat Measuring Device - Thermometer
Thermal Equilibrium - said that two substances that are at the same temperature meaning there is no more heat energy transferred
*rely on the written methods for the conversion of units of temperature
★★ ELECTRICITY
Electricity - a natural phenomenon that occurs throughout nature and takes many different forms; flow of electric charge
Electrodynamics – deals with electrical charges in motion
Electric Circuit – a closed conducting path where charges flow.
Electric Current – the flow of charged particles (electrons & ions); charge particles are referred to as charge carriers
Potential Difference – the work done by a charge carrier (electron, ion, etc) when passing through an electrical component
Electrical Power - the rate at which electric energy is transferred within a circuit; rate of consumption of electrical energy by a device
Electrical Energy - generated from the potential difference in a circuit, causing current to flow; the energy generated due to the movement of charge carriers in a conductor
Conductors – allow electric charges to flow (e.g: steel, silver, gold, copper,
Insulators – resist the flow of electric charges (e.g: wood, glass, rubber, oil, plastic)
Alessandro Volta - Italian physicist known for the invention of the electrochemical cell also known as the battery
André Ampère - a French physicist and mathematician; discovered electromagnetism
Georg Ohm - a German physicist; determined that there is a direct proportionality between the voltage applied across a conductor and the electric current
Voltage - the charge that causes the current to flow; symbol and Unit: V
Current - flow of electricity; will only flow if there’s voltage; symbol: I; Unit: A (Ampere)
Resistance - it opposes the push from the voltage source and affects the speed of the current; symbol: R; Unit: Ω (Ohms)
Ohm’s Law - states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through the resistance
Measuring devices:
Voltage - voltmeter, Current - ammeter, Resistance - ohmmeter
Formulas:
Voltage - V = I x R, Current - I = V/R, Resistance - R = V/I
Simple Circuit - the path that an electric current travels on
Three parts of a circuit:
- the source of voltage
- conductive path
- resistor


Series Circuit - only one path for the current, and a break in the circuit stops the current
Parallel Circuit - there are multiple pathways or branches
Series Circuit

Parallel Circuit

Integrated Circuit - thousands combined series and parallel; also called microelectronic circuit