1.4C Empirical and Molecular Formula
The empirical formula of a compound gives the simplest ratio of each element present in that compound.
Formulas of all ionic compounds are empirical
e. g. NaCI , InBr2, MgCO3
The molecular formula gives the actual number of atoms of each element present in a molecule. It is a multiple of the empirical formula.
e.g. glucose CH2O (empirical) C6H12o3 (molecular)
Steps to find Empirical Formulas
1. Convert percentages into mass values.
2. Use the molar masses of each element to find the amount in moles for each element.
3. Divide the mole values from step 2 by the lowest mole value.
(Multiply until you get whole numbers if you have a fraction)
4. Use the values from steps 3 as subscripts in empirical formula.
Hydrates
A hydrated salt is a compound that contains a fixed ratio of water molecules within the crystalline structure of the compound. This water of crystallization can be driven off by heating, resulting in an anhydrous salt.
Steps to find Hydrates
Find the mass of water by seeing how much was lost
Find the salt’s molar mass
Find moles of salt and divide it by itself (for mole ratio)
Divide water’s mols by the salt’s moles
You found water’s x!
Steps to find molecular formulas
1. Find the empirical formula if it is not given.
2. Determine the molar mass of the empirical formula.
3. Divide the molar mass of the compound (given in the question) by the molar mass of the empirical formula.
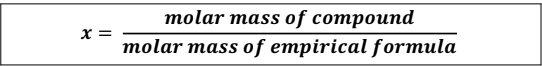
4. Multiply the subscripts in the empirical formula by X.