Motion introduction summary:
Linear motion - motion that is moving forwards or backwards (directional line),
Parabolic motion - motion that can curve, usually a ball bouncing,
Rotational motion - motional that moves around a fixed point.
→Changing velocity:
It is when speed is changing, when direction is changing or when both are changing.
The types of acceleration:
Constant acceleration - this is when the velocity is changing by the same amount over a period of time.
Changing acceleration - this is when velocity is changing by a different amount over a period of time.
→Displacement:
When an object moves upwards or right it will have a positive displacement, whereas when an object moves downwards or left it will have a negative displacement.
→Symbols:
(s): represents displacement
(u): represents initial velocity
(v): represents final velocity
(a): represents acceleration
(t): represents time
Equations:
Average speed= distance travelled/time
Average velocity= displacement/time
acceleration= change in velocity/time
The velocity vector always points in the direction of motion. But the acceleration vector may point in the same direction, or the opposite direction to the velocity vector.
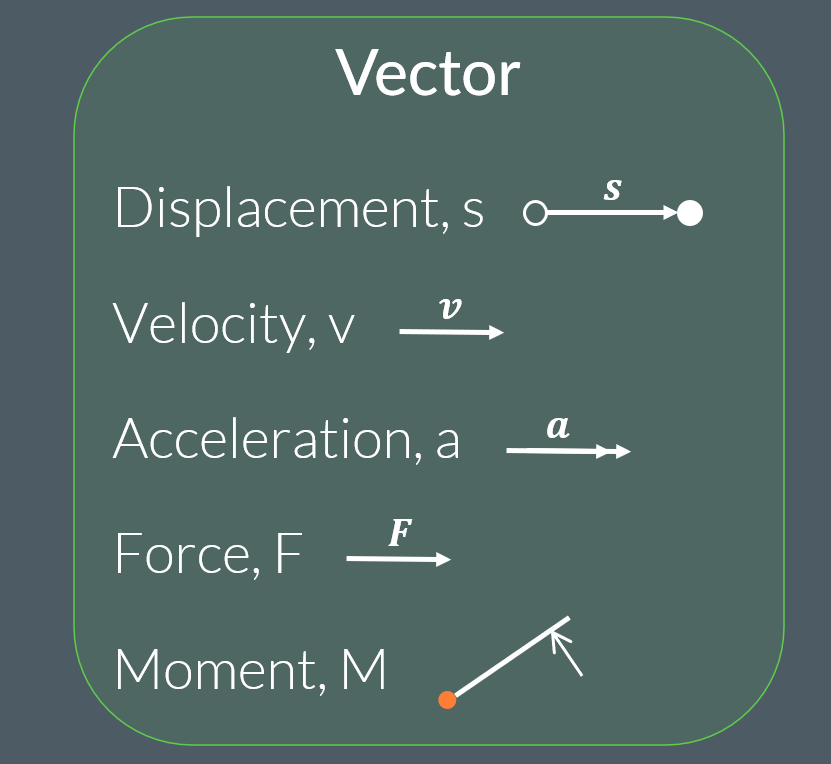
Vectors:
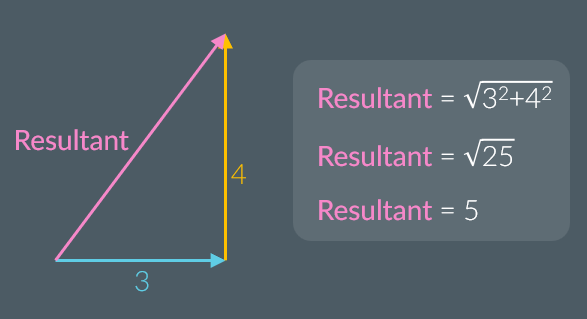
A vector is an arrow that represents the magnitude and direction of a quantity. The combined effect of two or more vectors results in the resultant vector; it’s magnitude can be found using Pythagoras’ theorem and the angle of the resultant vector can be found using trigonometry.
Definitions:
Velocity- The speed of something in a given direction.
Acceleration- A change in velocity over a period of time.
Scalar- A quantity that has magnitude but no direction.
Vector- A quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Displacement- the distance from where an object starts to where it ends.