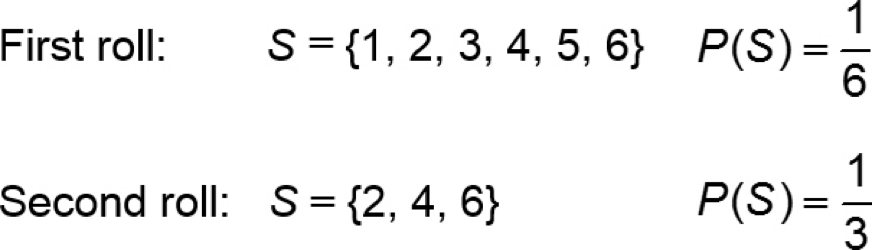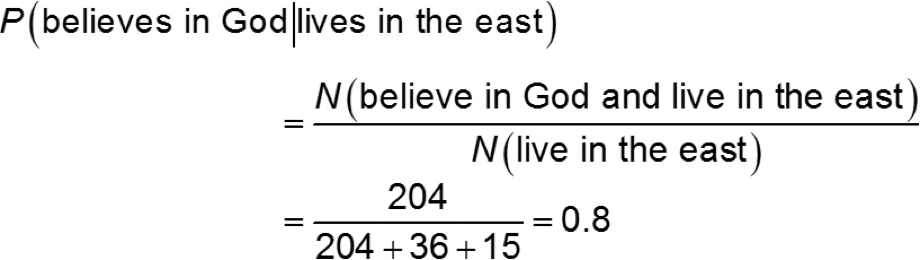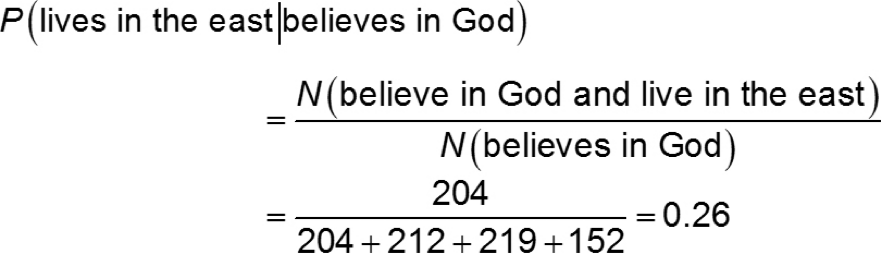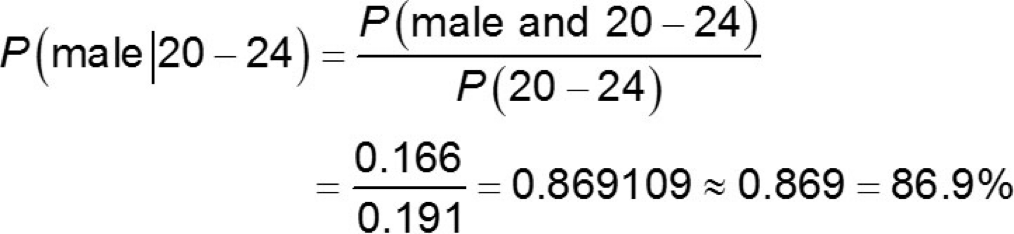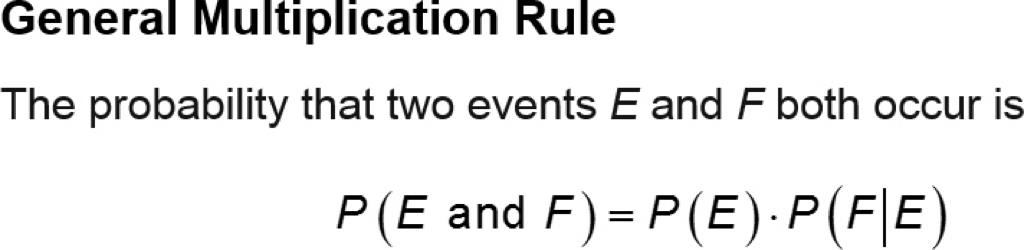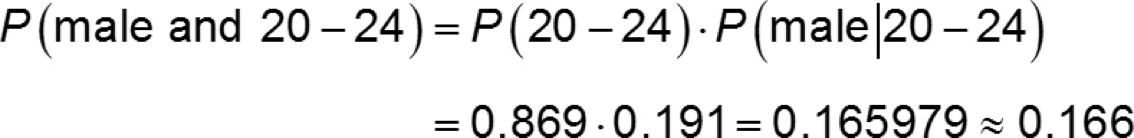5.4: Conditional Probability and the General Multiplication Rule
Learning Objectives
1. Compute conditional probabilities
2. Compute probabilities using the General Multiplication Rule
Conditional Probability
“Conditional Probability” is the probability that the event F occurs given that event E has occurred.
is represented as P(F|E)
EXAMPLE An Introduction to Conditional Probability
Suppose that a single six-sided die is rolled.
What is the probability that the die comes up 4?
Now suppose that the die is rolled a second time, but we are told the outcome will be an even number. What is the probability that the die comes up 4?
Conditional Probability Rule
P(F|E) can be found in one of two ways:
by dividing the probability of E and F by the probability of E
by dividing the number of outcomes in E and F by the number of outcomes in E.
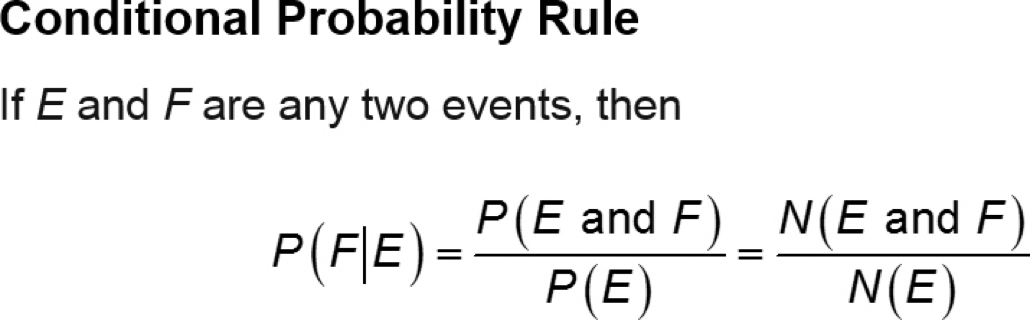
EXAMPLE Conditional Probabilities on Belief about God and Region of the Country
A survey was conducted by the Gallup Organization conducted May 8 − 11, 2008 in which 1,017 adult Americans were asked, “Which of the following statements comes closest to your belief about God – you believe in God, you don’t believe in God, but you do believe in a universal spirit or higher power, or you don’t believe in either?” The results of the survey, by region of the country, are given in the table below:
Believe in God | Believe in universal spirit | Don’t believe in either | |
East | 204 | 36 | 15 |
Midwest | 212 | 29 | 13 |
South | 219 | 26 | 9 |
West | 152 | 76 | 26 |
(a) What is the probability that a randomly selected adult American who lives in the East believes in God?
(b) What is the probability that a randomly selected adult American who believes in God lives in the East?
EXAMPLE Murder Victims
In 2005, 19.1% of all murder victims were between the ages of 20 and 24 years old. Also in 2005, 16.6% of all murder victims were 20 − 24 year old males.
What is the probability that a randomly selected murder victim in 2005 was male given that the victim is 20 − 24 years old?
The General Multiplication Rule
the probability of E and F is the probability of event E occurring times the probability of event F occurring, given the occurrence of event E.
EXAMPLE General Multiplication Rule
In 2005, 19.1% of all murder victims were between the ages of 20 and 24 years old. Also in 2005, 86.9% of murder victims were male given that the victim was 20 − 24 years old.
What is the probability that a randomly selected murder victim in 2005 was a 20 − 24 year old male?