IB (SL) / AP Chemistry 1 Unit 3 Quantitative Chemistry
The Periodic Table and Physical Properties
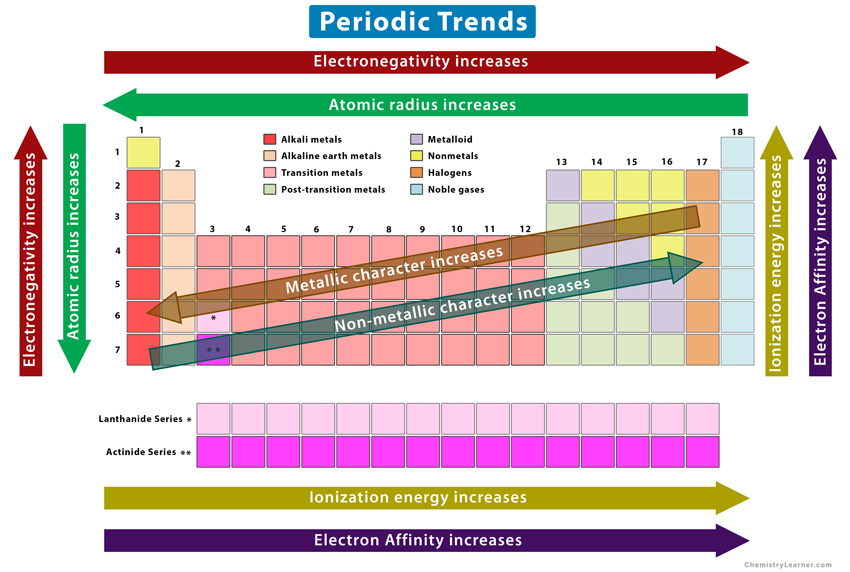
The Periodic Table
Elements are placed in order of increasing atomic number.
Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons.
Elements in the same period have the same outer shell of valence electrons.
Group 1 - Alkali metals
Group 17 - Halogens
Group 18 - Noble Gases
Elements in the same period or group share similar properties and change in properties, this is called periodicity.
Atomic Radius
The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron.
Atomic radius increases as you head to the left and down (Rb).
Ionic Radius
Cations - fewer electrons than protons (smaller).
Anions - more electrons that protons (larger).
Ionic radius increases as you head to the left and down.
Melting Points
Melting point depends on the structure of the atom and the type of IMF.
Electronegativity
The relative measure of the attraction that an atom has for a shared pair of electrons when it is covalently bonded to another atom. As the size of the atom decreases the electronegativity increases.
Electronegativity increases as you head right and up.
First Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove one electron from an atom in its gaseous state.
First Ionization Energy increases as you head up and generally right.
The Period Table and Chemical Properties
Group 1 - The Alkali Metals
Alkali metals react with water to form an alkali solution of the metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
They all react with chlorine, bromine, and iodine to form ionic salts.
Group 7 - Halogens
Halogens react by gaining one or more electrons to form halide ions. They are good oxidizing agents. The reactivity decreases down the group.
 Knowt
Knowt
