Chapter 4: Histology
Histology - Study of Tissues
Biopsy - removal of tissues for diagnostic purposes
Autopsy - Examination of organs of a dead body to determine cause of death
Tissues
Classification based on structure of cells, composition of extracellular matrix and cell function
Types
Epithelial
Nervous - Neurons
Muscular - Smooth, Skeletal, Cardiac
Connective
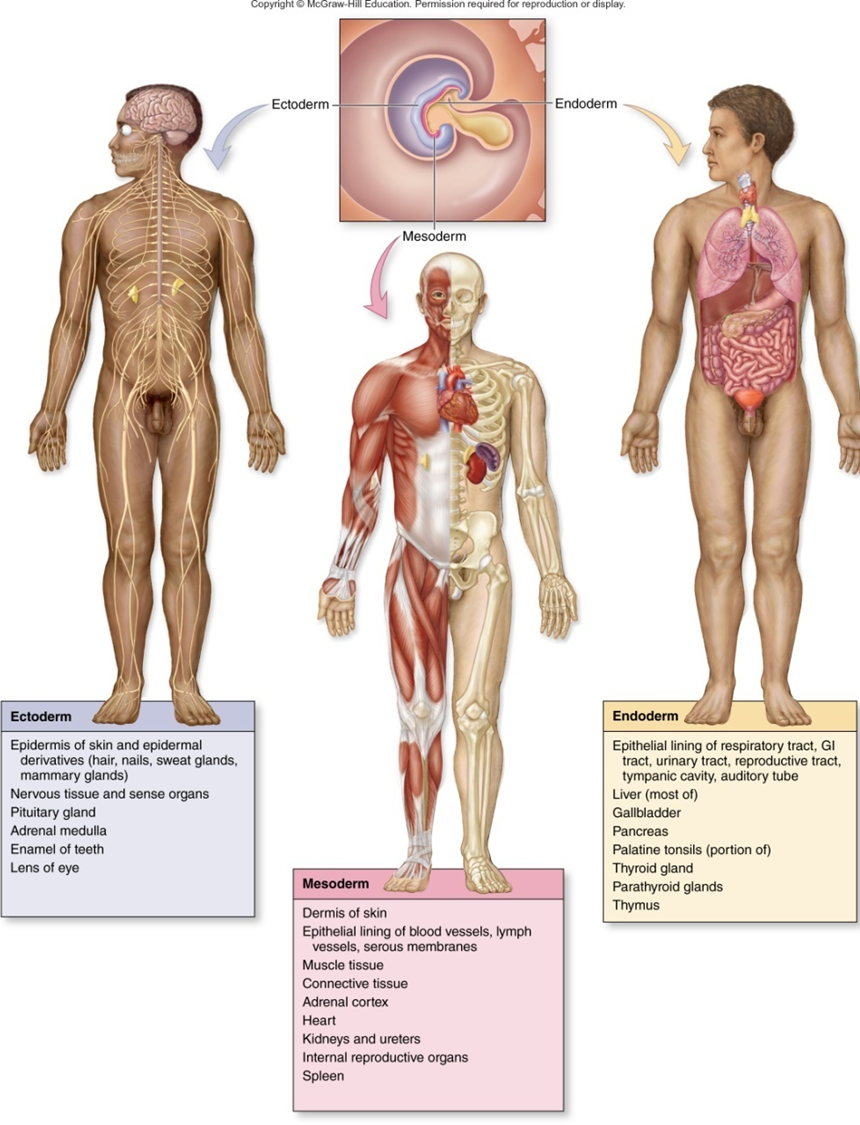
Gastrulation - The cells between the epiblast and hypoblast layers become the primary Germ layer known as mesoderm; Other migrating cells displace the hypoblast cells an become endoderm; cells remaining in the epiblast become ectoderm
Derived from epiblast
Ectoderm Differentiation
On the external surface of embryo
Develop into:
Epidermis of Skin
Hair and Nails
Nervous system
Mesoderm Differentiation
5 regions
Notochord - Tightly Packed Midline cells
Paraxial Mesoderm - Beside notochord; develops into units (somites) that form axial Skeleton, muscle, dermis Skin, Connective Tissue
Intermediate Mesoderm - lateral to Paraxial; urinary and reproductive systems
Lateral Plate Mesoderm - lateral to intermediate: cardiovascular system, body Cavil, lining, connective tissue lining
Head Mesenchyme - Forms connective tissue and musculature of the face
Endoderm Differentiation
Develop into:
lining of digestive, respiratory, and urinary systems
liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid gland
Thymus
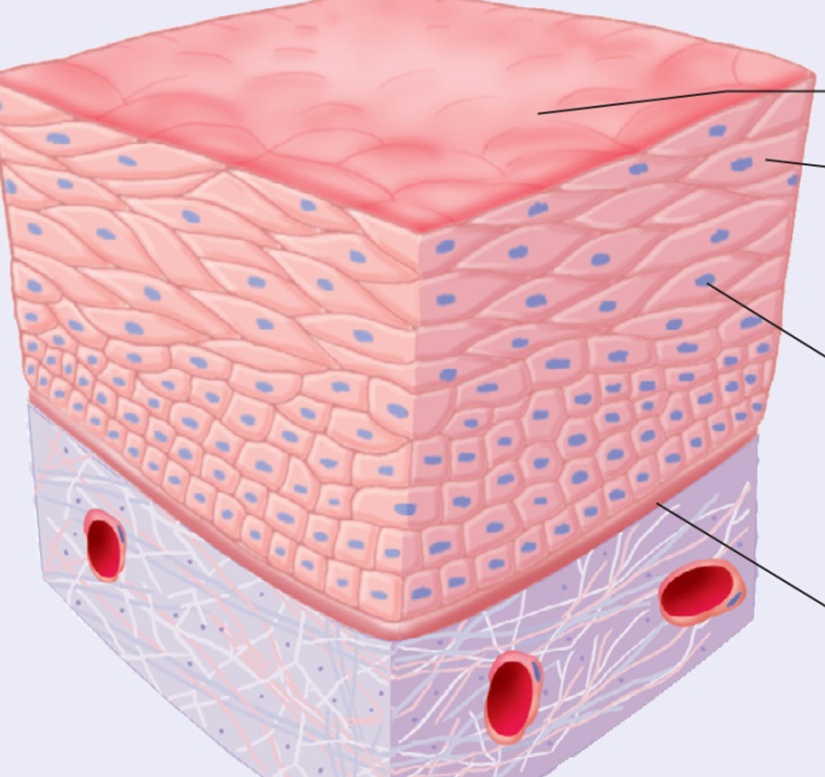
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue - covers body surfaces and forms glands
Outside surface of body
Lining of digestive, respiratory and urogenital systems
Lining of heart and blood vessels
Linings of mam, body cavities
Functions of Epithelial Cells
Protect underlying Structures
Barrier
Permit passage of substances
Secrete substances
Absorb substances
Increase surface area
Epithelial Surfaces
Basement Membrane - Base barrier: Protection
Free surface - smooth, reduce friction
Microvilli - increase surface area for absorption/ secretion
Cilla - Mire materials across surface
Lateral Surfaces
Epithelial Cells | # of layers | Characteristics |
Simple | 1 | allows diffusion of gases, filtration of blood, secretion, absorption |
Stratified | >1 | protection, particularly against abrasion |
Pseudostratified | 1 | secretion |
Shape | ||
Squamous | Flat | allows diffusion or acts as filter |
Cuboidal | Cube | secretion or absorption. |
Columnar | Column | secretion or absorption. |
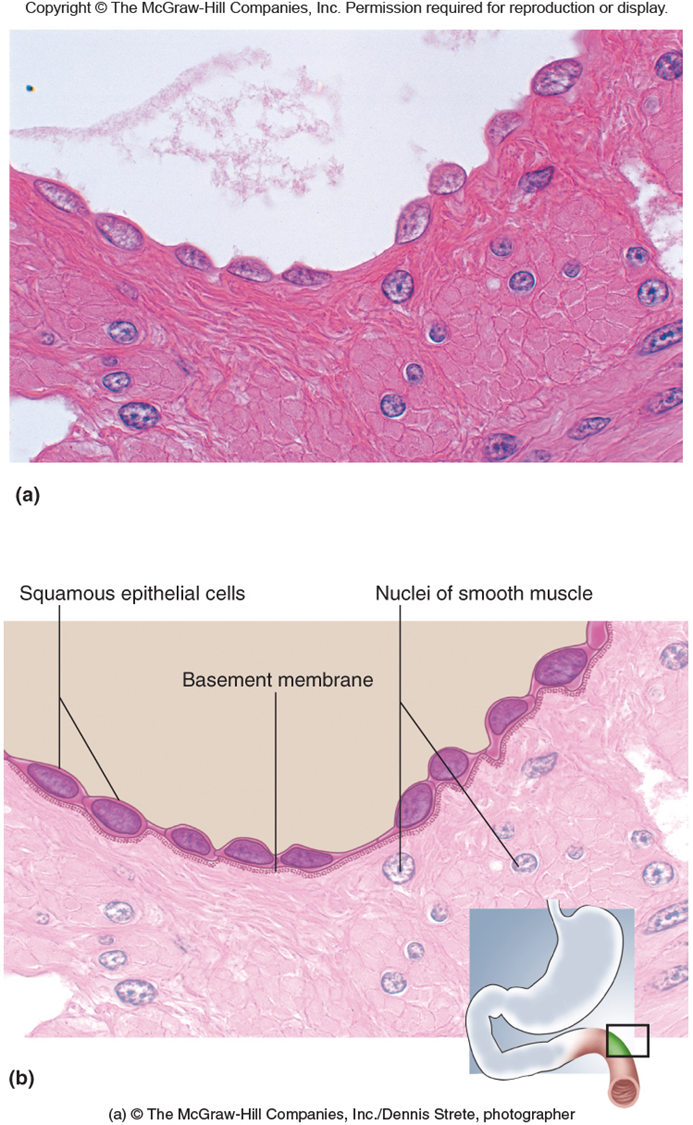
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Function
Filtration, Diffusion, secretion, absorption
Secretes lubricating fluids
Location
Lungs - alveoli
Kidneys - Tubules and glomerular Capsule
Endothelium - lining of BVs (Blood Vessels)
Mesothelium - Serious membrane of ventral body cavity
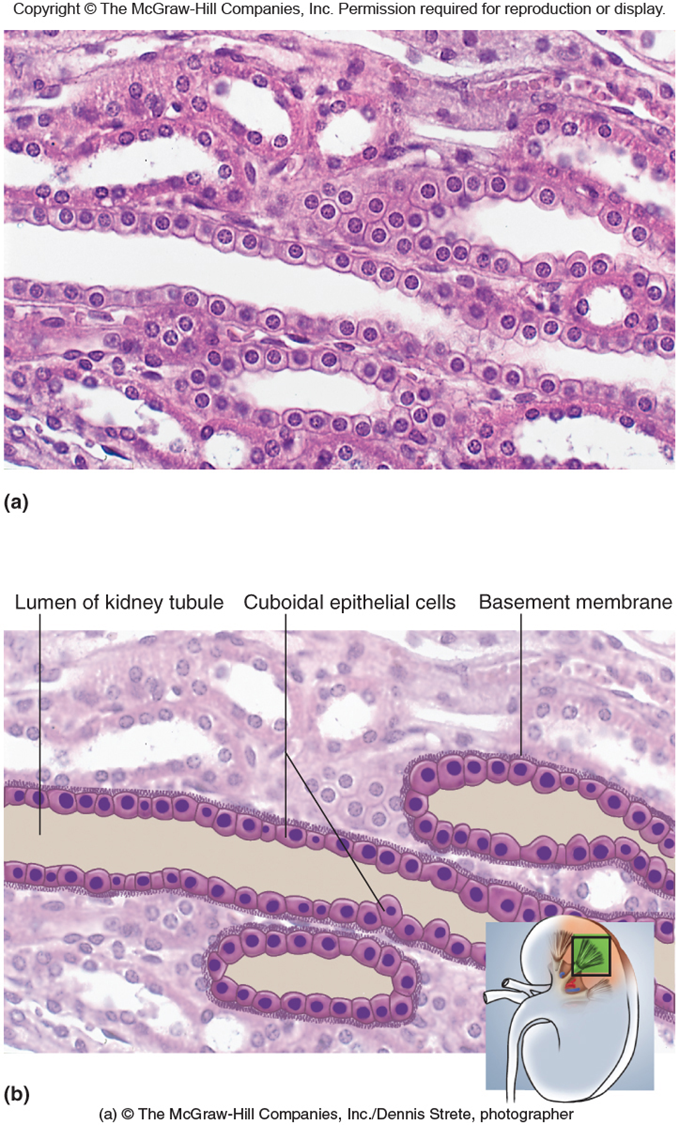
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Function
Secretion
Absorption
Mucous production
Location
Kidney Tubules - storage
Lungs - bronchioles
Glands
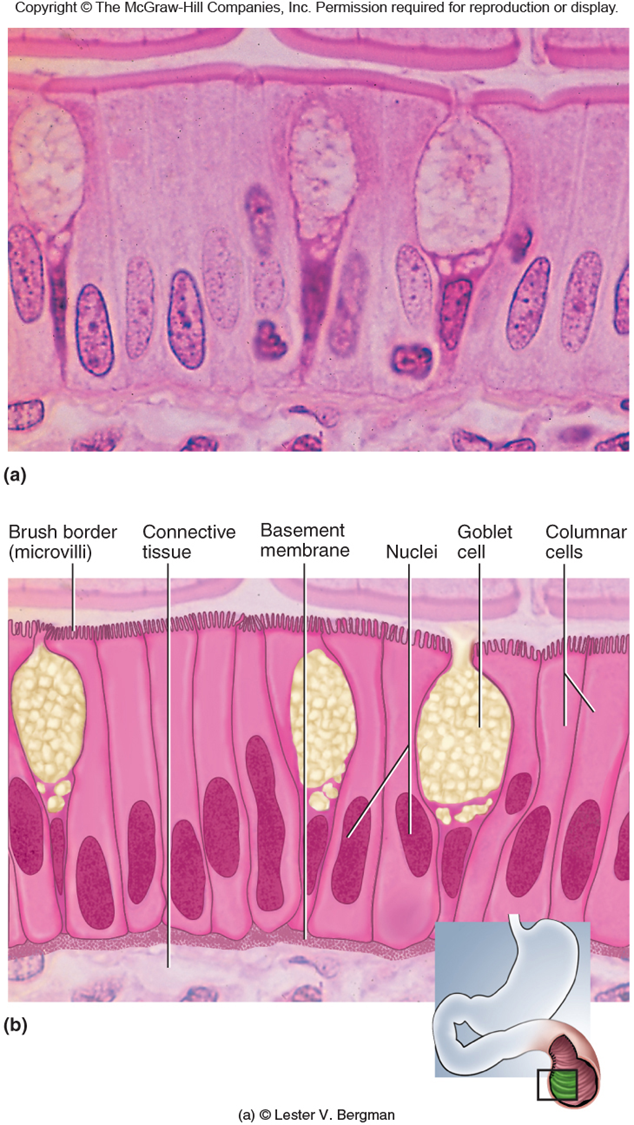
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Function
Absorption
Secretion of mucous
Location
Digestive - stomach lining
Reproductive Systems
Modification
Cilia - Material Movement
Microvilli - increase surface area for absorption; small intestine
Goblet cells - Secrete mucous for lubrication
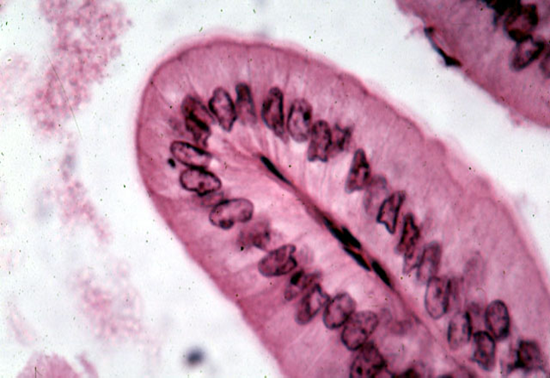
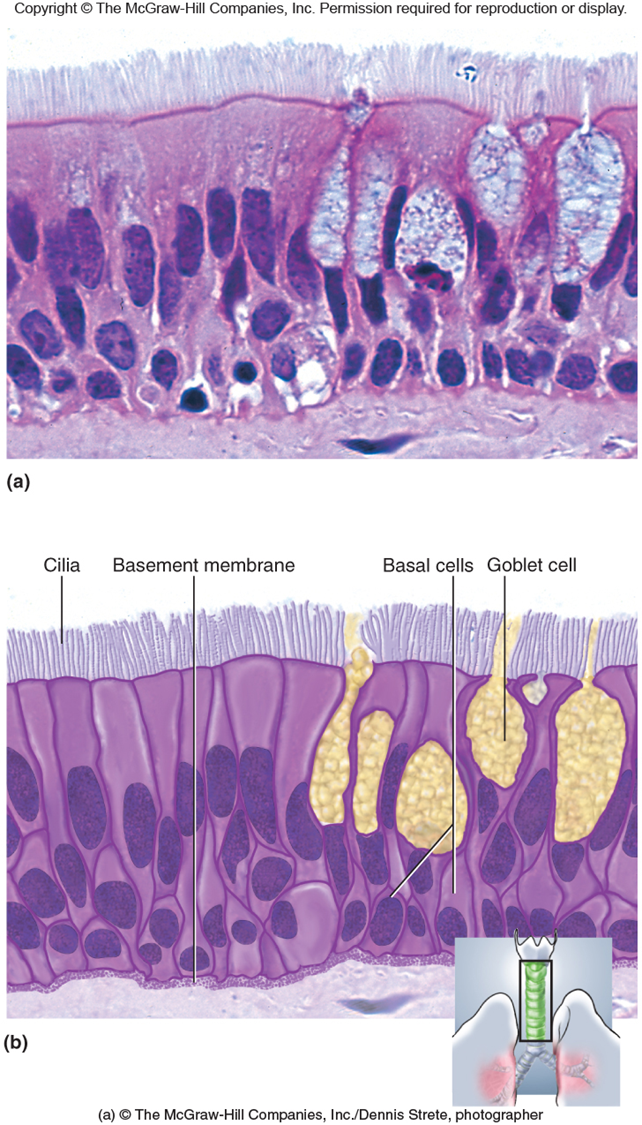
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Modified Simple Epithelium
Rest on basement membrane
Nuclei at different levels
Location
Respiratory and male reproduction systems
Function
Secretion mucous
Modifications
• Cilla - Respiratory system
• Goblet cells - respiratory system
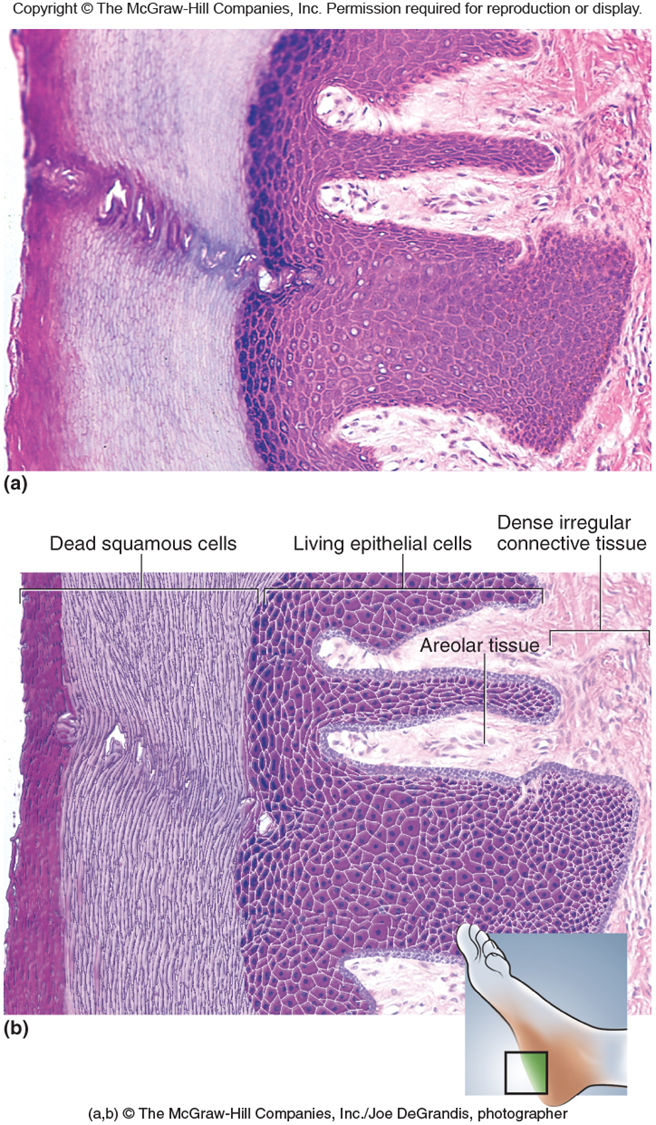
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Function
Protection from abrasion, Pathogens
Reduces water loss - Keratinized
Location
Keratinized - water proof
Non Keratinized - Mules membrane
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Location
Ducts of sweat glands
Follicles of ovary
Seminiferous tubules of testis
Function
Sweat and Hormone Secretion
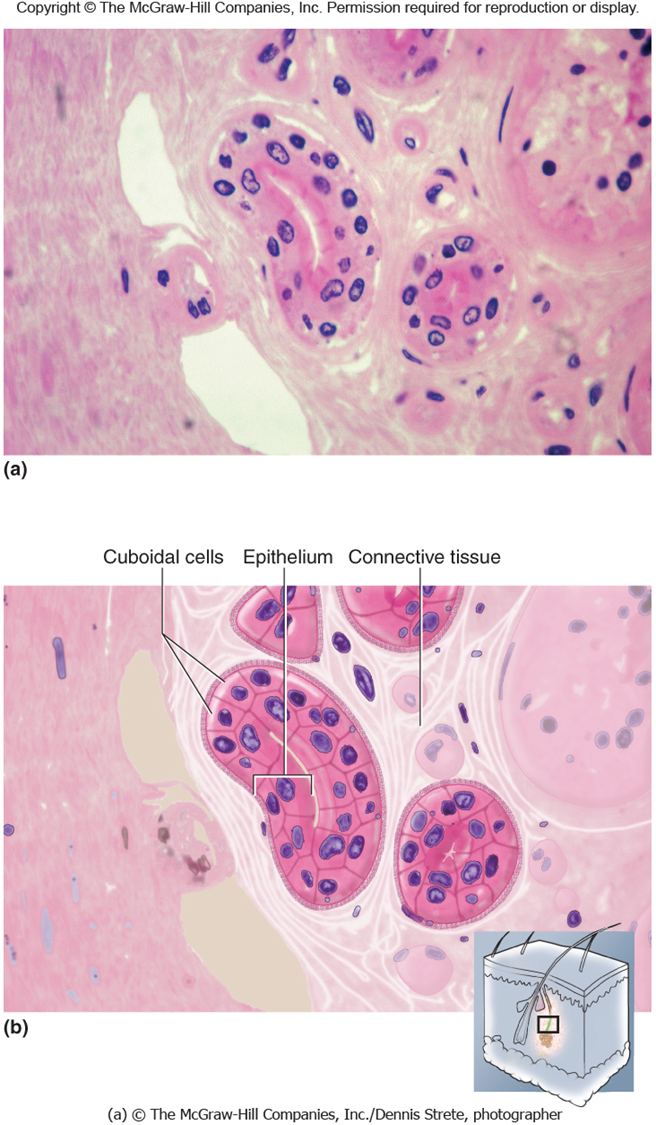
Stratified Columnar Epithelial
Location
Male urethra
Mammary Gland duet
Function
Mucus and fluid secretion
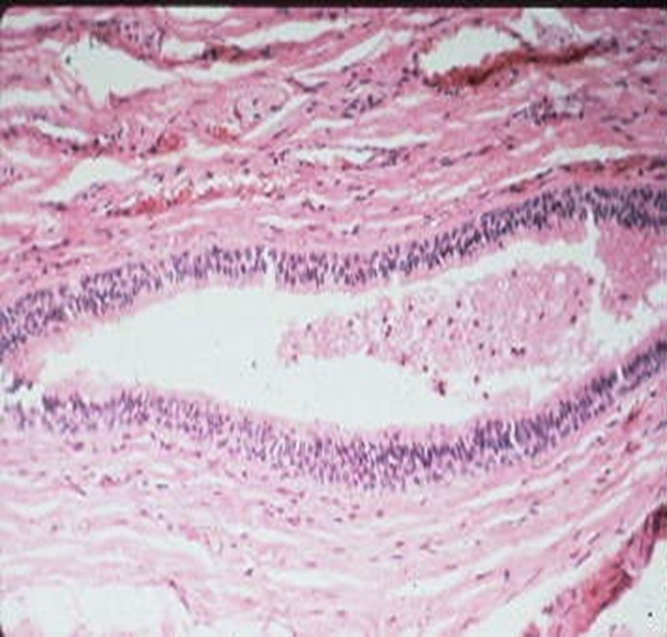
Transitional Epithelium
Stretched - uppermost are squamous
relaxed - uppermost are cuboidal
Location
Kidney
Ureter
Bladder
Urethra
Function
Stretches for storage
Cell Growth - bottom new, Top old
Glands
Infoldings of Epithelium
2 Types
Endocrine - no open contact with exterior: no ducts: produce hormones
Exocrine - open contact with Exterior; ducts
Structure
Unicellular → Goblet Cells → Produce → Mucus
Multicellular
Connective Tissue
Loose (areolar) - collagenous fibers are loosely aranged
Dense - Fibers form thick bundles that nearly fill all extracellular space
Supporting Connective Tissue
Cartilage
Bone
Fluid connective Tissue
blood
Features of Connective Tissue
Well-innervated - A lot of nerves
Highly vascular; NOT cartilage
Few cells embedded in large amount extracellular Matrix
each type has own cell type and matrix
Functions
Enclosed organs
Connect tissues
Support and Movement
Storage
Cushion and Insulate
Transport
Protect
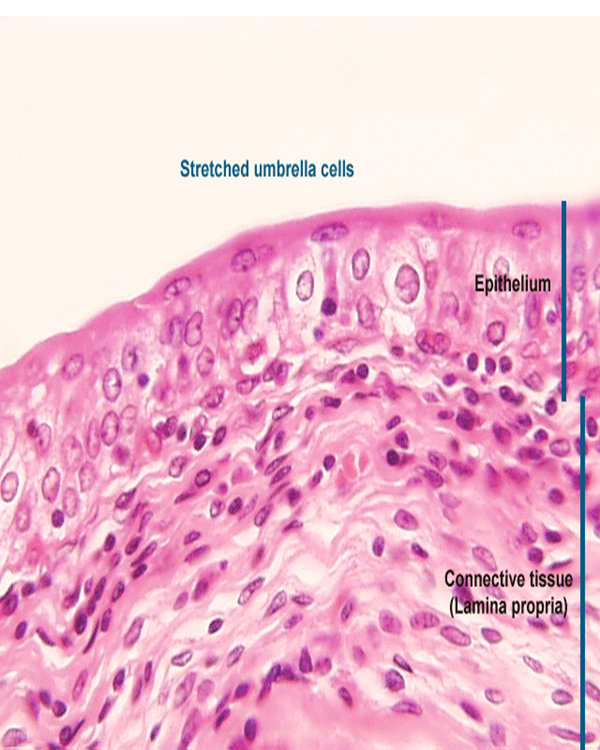
Extracellular Matrix
Protein fibers
Collagen - most common protein in body; strong, flexible, inelastic
Reticular - framework, fills spaces between tissues and organs. Fine collagenous, form branching network
Elastin - Returns to its original shape after distension or compression. Elastin resembles coiled springs
Cells of Connective Tissue
Specialized cells produce Extracellular matrix
Word Stems:
• Blast - Create matrix
• Cyte - Matin Matrix
• Clast - Break down matrix to remodel
Types of Connective Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue: Areolar
Loose packing, support, nourishment
Attaches skin to underlying tissues
Contains: Collagen, reticular elasic fibers
Cell Types - fibroblast, mast cells, lymphocytes adipose cans, macrophages
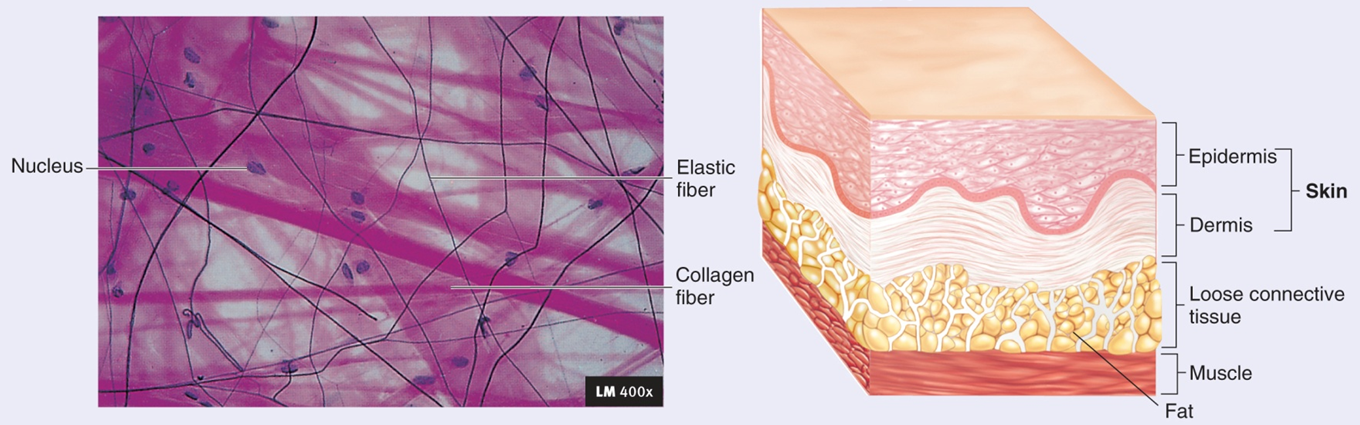
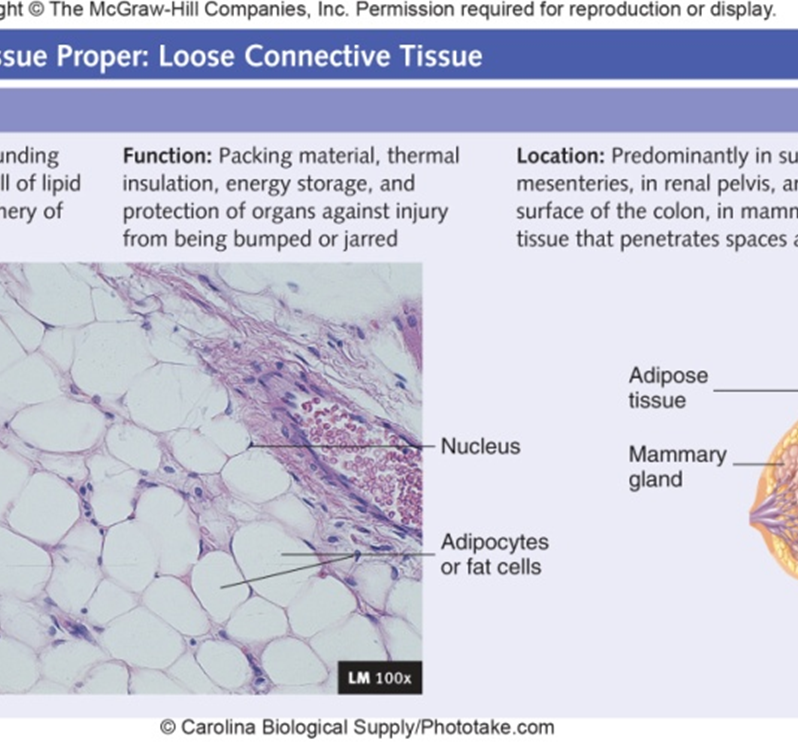
Adipose
Padding, insulation, energy storage
Cells are adipocytes, little ECM
Yellow (white) - most abundant type has a wide distribution. White at birth, yellows with age
Brown - found only in specific areas of body: axillae new, near Kidneys
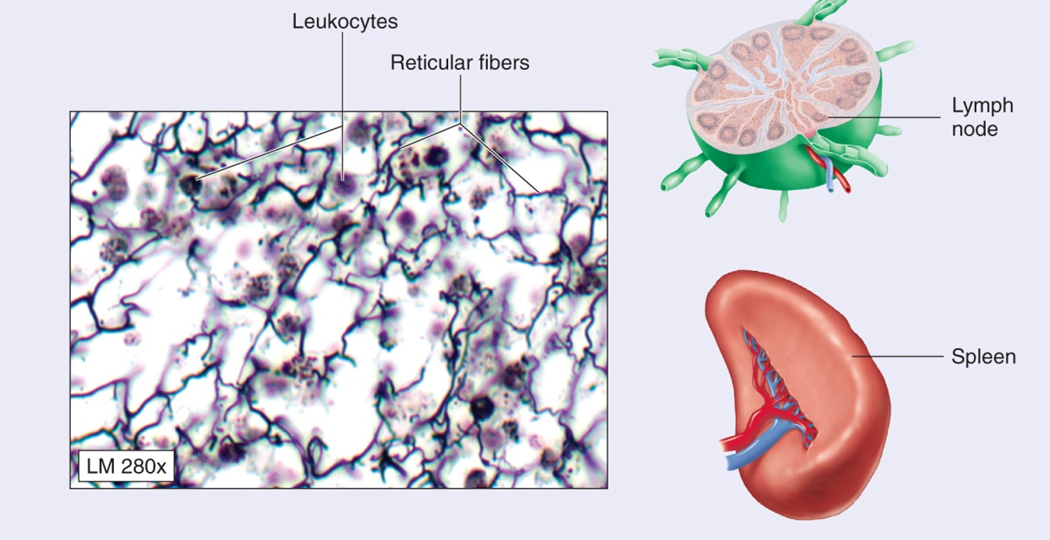
Reticular
Forms superstructure of lymphatic and hemopoietic tissues
Found in: lymph modes, spleen, liver, Kidney
Network of fine reticular fibers and cells
Spaces between cans contain whit cans and dendrite cells
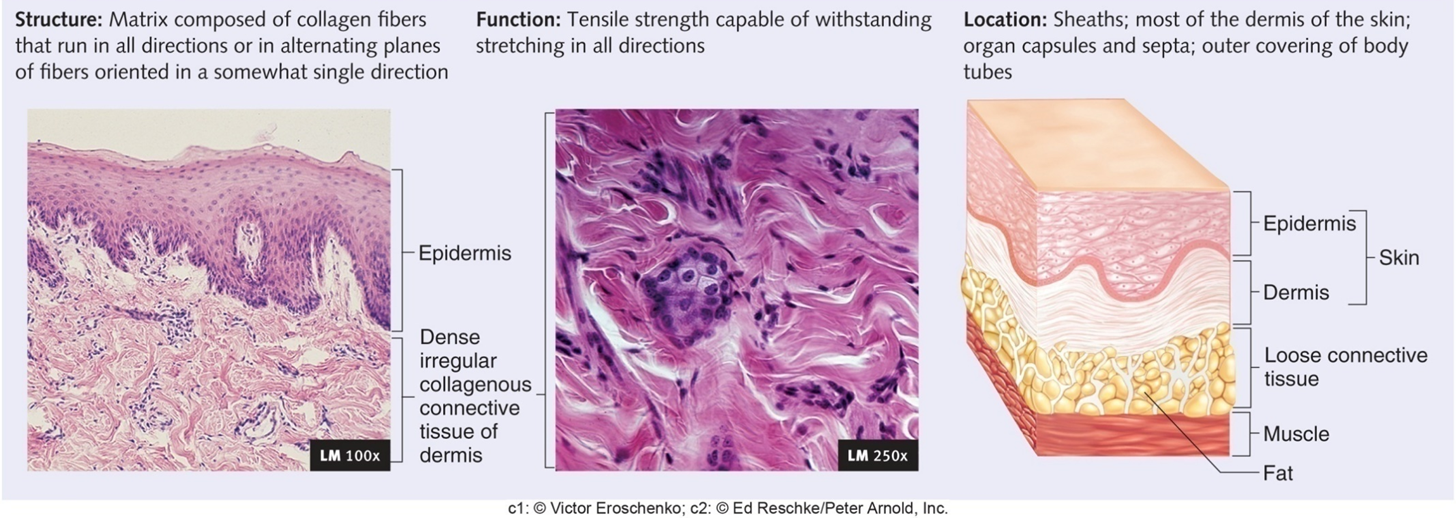
Dense Connective Tissue: Irregular Collagenous
Innermost layer of the dermis of the skin, scars, capsules of organs
Protein fibers randomly oriented network
Irregular Elastic
Walls of elastic arteries
Bundles and Sheets of collagenous fibers in multiple directions
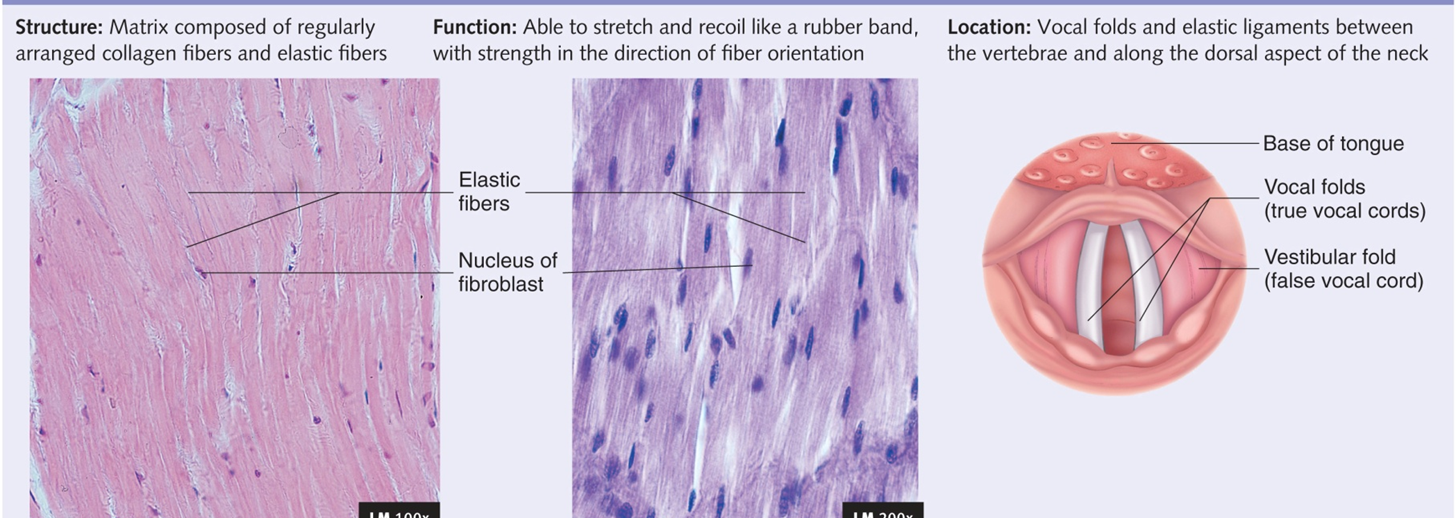
Regular Elastic
Ligaments in vocal folds; nuchal ligament
collagen fibers give strength [EX. Shouting): Elastic fibers are more prevalent
Regular collagenous
Abundant Collagen fibers that resist stretching
Tendons = connect muscles to bones: non parallel Fibers
Ligaments - connect bones to bones: less compact collagen: flattened: sheets and bands
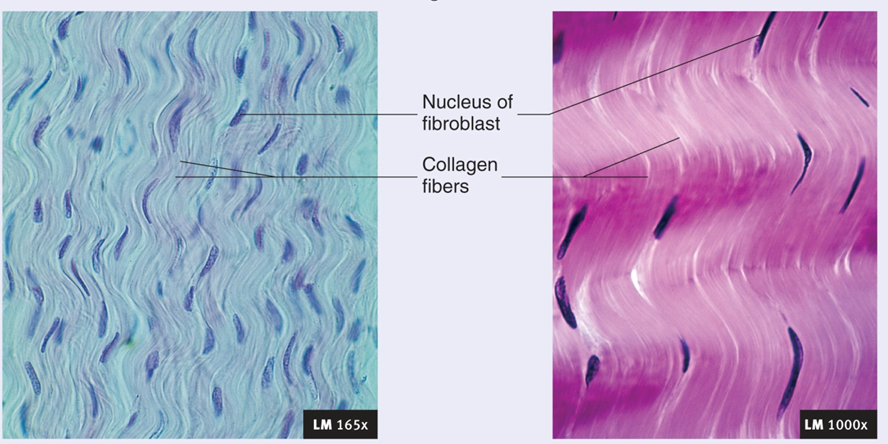
Supporting Connective Tissue: Cartilage
Types
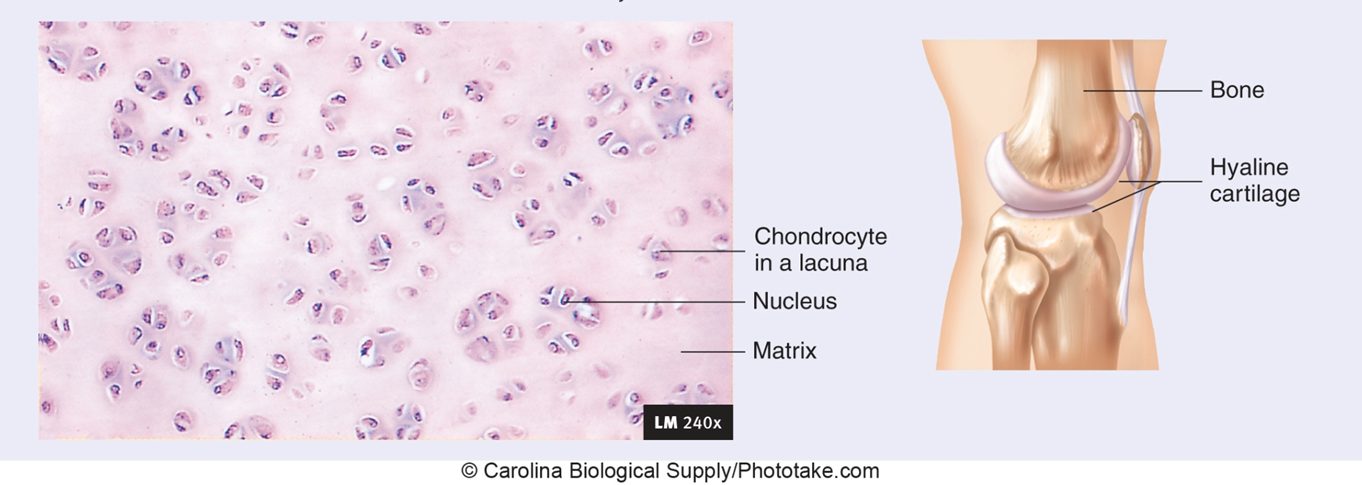
Hyaline
large amount of collagen fibers evenly distributed in proteoglycan matrix
in Areas that support flexibility: ribcage, trachea, bronchi
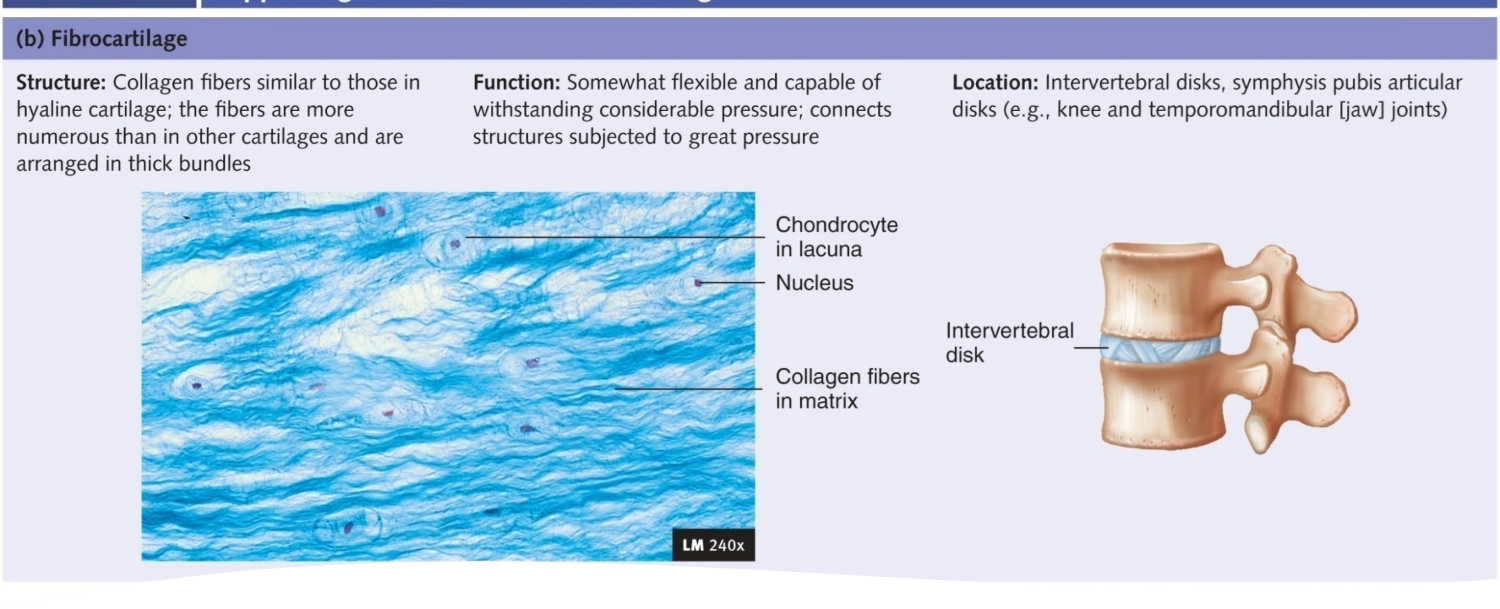
Fibrocartilage
found where a lot of pressure is applied to joints: knee, Jaw, vertebra
Thick collogen fibers distributed in proteoglycan matrix; slightly compressible, very tough
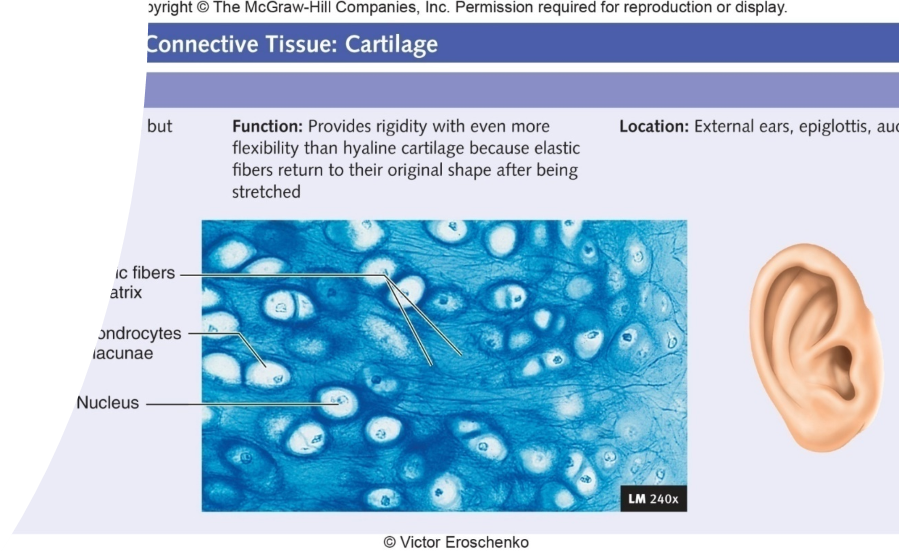
Elastic
External Ears and epiglottis: ridges w/ elastic properties
proteoglycans and hyalvaronic acid complexed together
Trap large amounts of water
Avascular and no nerve supply: slow Healer
Perichondrium - Dense irregular connective Tissue that surrounds cartilage
Bone
Spongy Bone - Light weight
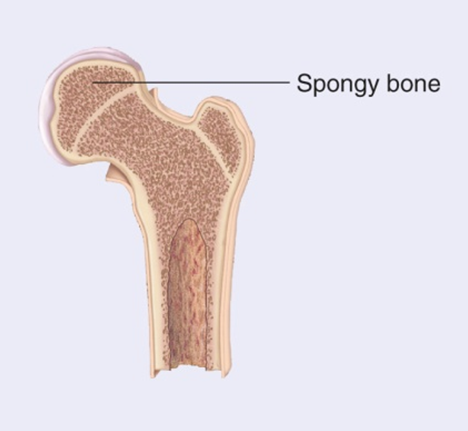
Compact Bone - structure
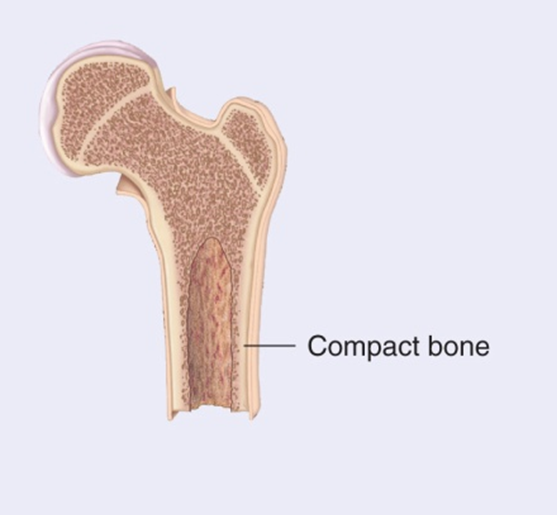
Hard Connective Tissue composed of living cells, (osteocytes) one mineralized Matrix
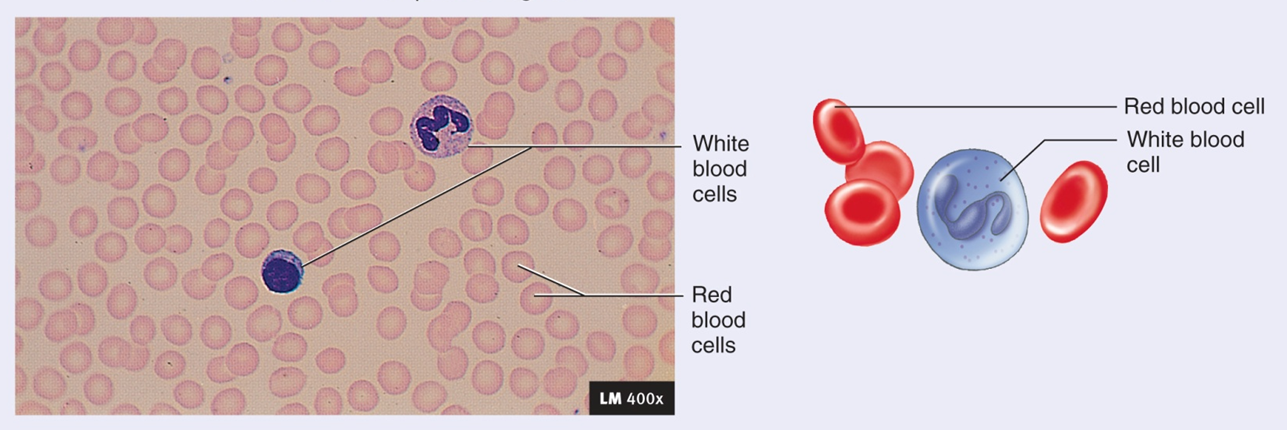
Fluid Connective Tissue: Blood
Matrix: Plasma
formed by other tissues
Moves through vessels, fluid and cells can travel in and out of vessels
Consists of: Red cells, white calls, platelets
Made by Hemopoietic tissue
Hemopoietic Tissue - Produces new blood cells
Osteons - mature bone
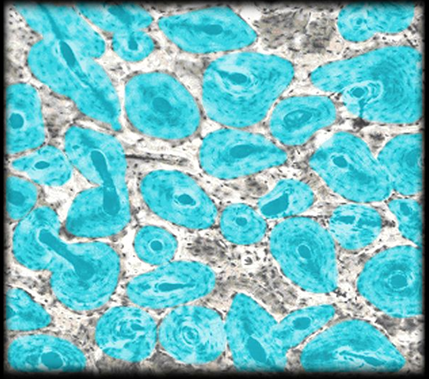
Perforating / Central canals - nutrient travel
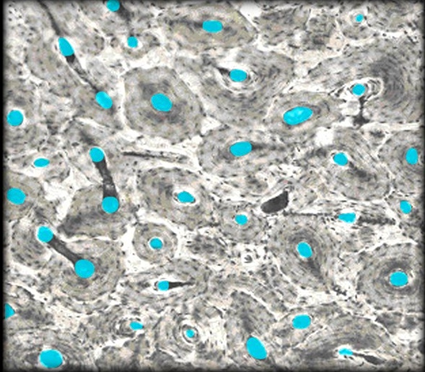
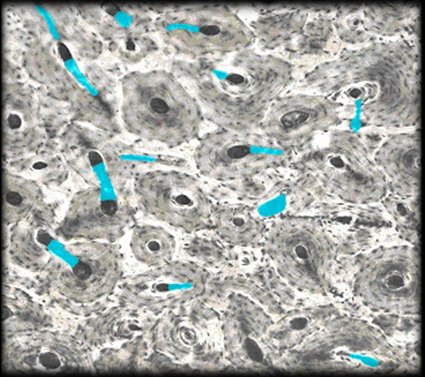
Hemopoietic Tissue
Bone Marrow - Produces new blood cells stores lipids
Red Bone Marrow - Hemopoietic tissue surrounded by reticular fibers: produces red and white cells
Yellow Bone Marrow - yellow adipose tissue
Muscle Tissue
Contracts with force
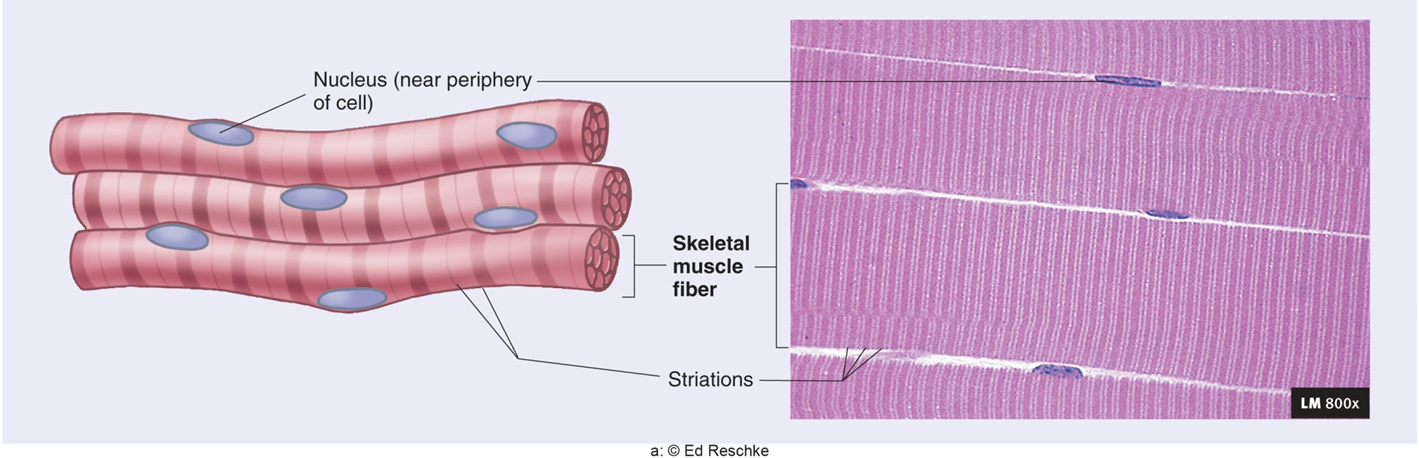
Skeletal - striated and voluntary
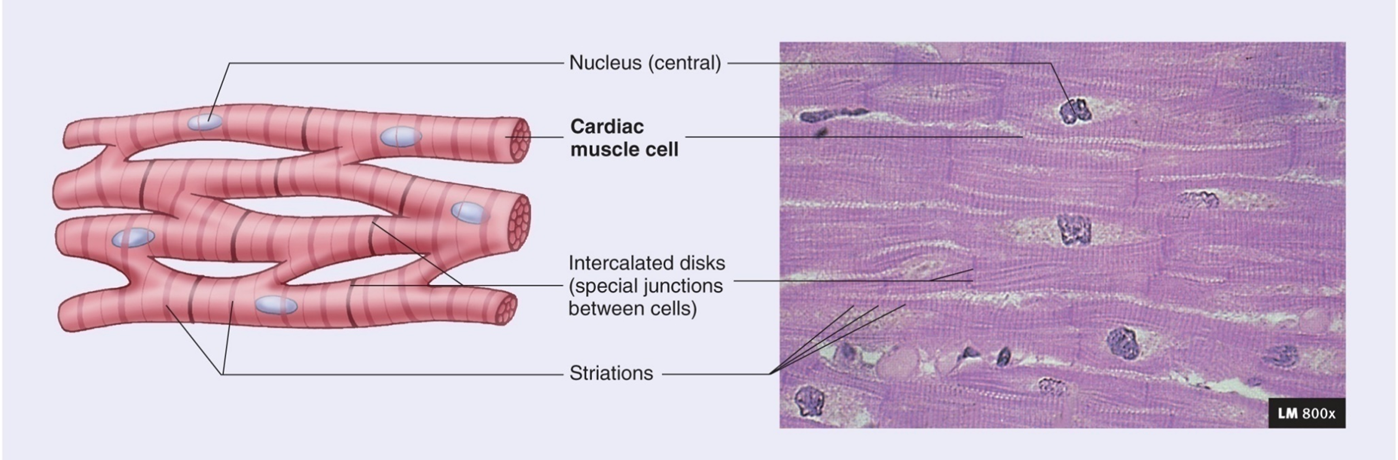
Cardiac - striated and Involuntary: Heart only
Smooth - non striated and Involuntary
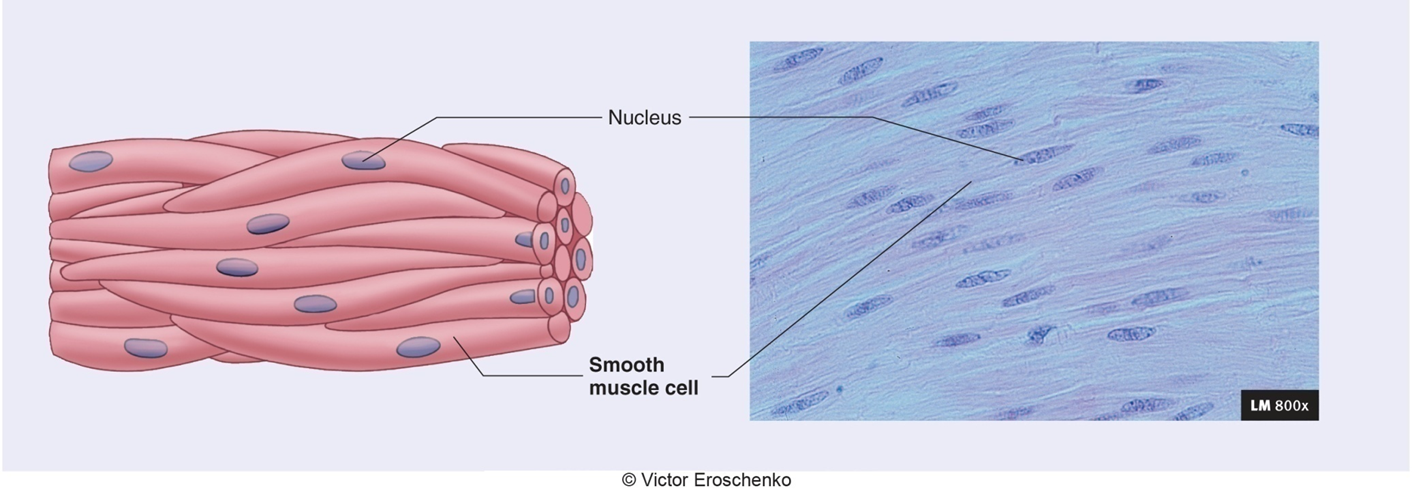
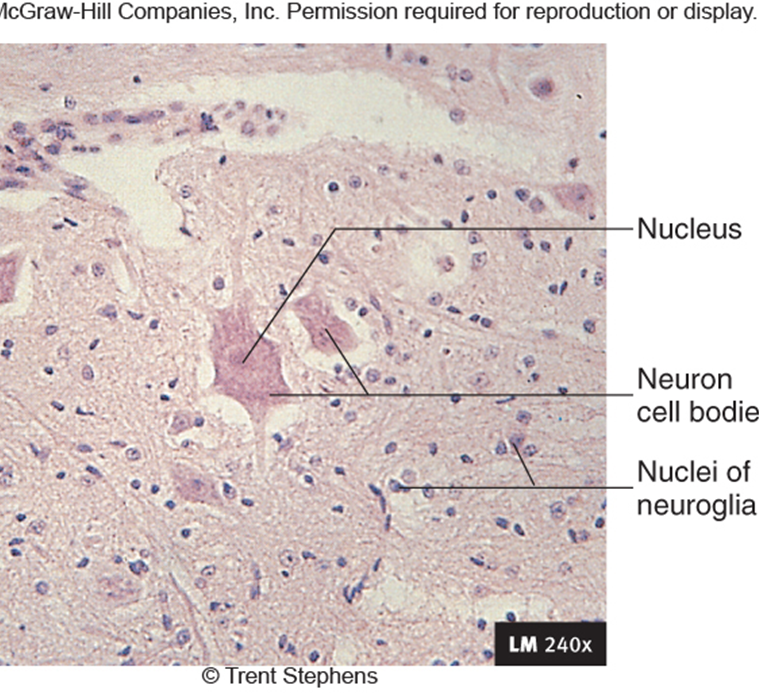
Nervous Tissue
Neurons / nerve cans have ability to produce action
Potentials: Multipolar, bipolar, unipolar
Neuroglia
Support cells of the brain, spinal cord, nerves
Nourish, Protect, Insulate Neurons
Schwan cells
Tissue Regeneration
Tissue regeneration is the process by which damaged tissues are repaired or replaced
Quick regeneration: epithelial tissues such as skin, connective tissue have the greatest regenerative capabilities. Keep in mind that some connective tissue like cartilage don’t have much regenerative capabilities due to poor blood supply. As far as muscle tissue goes, skeletal and smooth muscle have good tissue regeneration with smooth muscle having more regenerative capability than skeletal muscle. Cardiac and nervous tissue have the worst regenerative capability.
Tissue damage --> inflammation phase --> proliferation phase --> either fibrotic scar formation (tissue repair) or complete restoration of that tissue (tissue regeneration)
In the inflammation phase, is the first stage of tissue repair and is characterized by pain, swelling, redness, and heat. The inflammatory phase prepares the groundwork for the remaining two phases of the repair of injured tissue.
 Knowt
Knowt