Ch 2: Ecosystems and Ecology
2.1 - Species and Populations
Ecology: the study of how organisms interact with the environment
In scientific names, the genus name is given first with a capital letter which is followed by the species name. ex: Homosapien
Species: is a group of organisms (living things) sharing common characteristics that interbreed and produce fertile offspring
Population: a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time, which are capable of interbreeding
Three factors affecting populations:
- Natality (birth rate)
- Morality (death rate)
- Migration: immigration (moving into the area), emigration (moving out of the area)
Habitat: the environment in which a species normally lives
- Abiotic factors: non-living physical factors that influence the organisms and ecosystems. Example: temperature, sunlight, pH, Salinity, pollutants
- Biotic factors: living components of an ecosystem that directly or indirectly affect another organism.
A niche describes the particular set of abiotic and biotic conditions and resources to which an organism or population responds
- Fundamental niche: describes the full range of conditions and resources in which a species could survive and reproduce
- Realised niche: describes the actual conditions and resources in which a species exists due to biotic interactions
A niche is how an organism makes a living:
- Biotic factors: every relationship an organism has, where it lives, how to respond to resources, how it alters these biotic factors
- Abiotic factors: how much space there is, availability of light
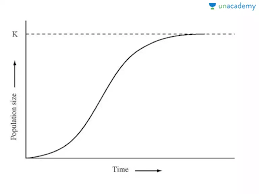
Limiting factors: factors which slow down growth of a population as it reaches it carrying capacity
Carrying capacity: maximum number of species or load that can be sustainably supported by a given area
Population dynamic: the study of the factors that cause changes to population sizes
- Intraspecific competition: between members of the same species. As population grows, competition increases
- Interspecific competition: individuals of different species could be competing for the same resource
The principle of competitive exclusion: states that two species competing for the same resources cannot coexist
- Competition reduces the carrying capacity for each of the competing species, as both species use the same resources
Predation: when one animal (predator), eats another animal (prey). Broad definition, consumption of one organism by another
Herbivory: a herbivore animal eating a green plant some plants may have defence mechanisms
Forms of symbiosis:
- Parasitism: relationship between two species in which one species lives in or on another (host), gaining food from it.
- The parasites are not preys and will not kill the host
- Mutualism: relation between two species where everyone benefits and no one suffers
- Form of symbiosis (living together)
Commensalism: when one partner is helped and another is significantly harmed
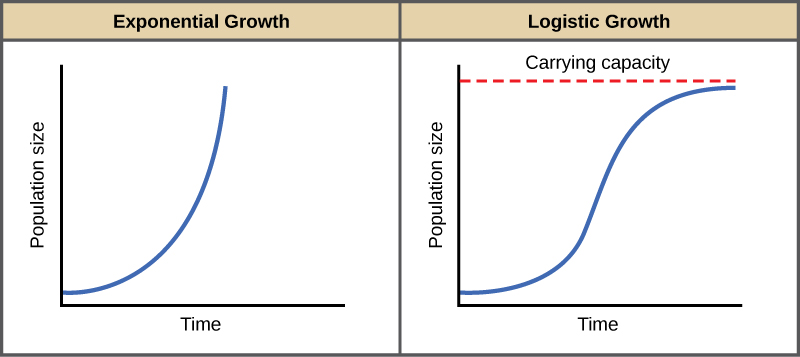
Exponential or geometric growth: if no limiting factors are affecting or slowing down growth
S and J population curves describe a generalised response of populations to a particular set of conditions:
S shaped growth: starts with exponential growth, no limiting factors affect the growth. Growth rate gradually slows down after a certain population size
J shaped growth: population grows exponentially at first then collapses → called diebacks
2.2 - Communities and Ecosystems
Community is a group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat (same place)
Ecosystem: is a community and the physical environment it interact with
Respiration is the conversion of organic matter into carbon dioxide and water in all living organisations, releasing energy
Photosynthesis: the process by which green plants make their food from water and carbon dioxide using energy from sunlight
Compensation point: point where a plant is neither adding biomass nor using it to stay alive
A Trophic level is the position that an organism occupies in a food chain, or a group of organisms in a community that occupy the same position in food chains. A food chain is the flow of energy from one organism to another.
- Producers:
- Autotrophs: make their own food from carbon dioxide and water using energy from sunlight
- Chemosynthetic organism: make their own food from simple compounds
- Consumers: feed on other consumers to get energy
Ecological footprint: are quantitative models which are usually measured for a given area and time. These include pyramids of number, biomass, and productivity
- Pyramid of productivity: shows the rate of flow of energy or biomass through each trophic level
2.3 - Flows of Energy and Matter
Productivity: conversion of energy into biomass over a given period of time. It is the rate of growth or biomass in plants and animals
Gross: total amount of something made as a result of an activity
Net: amount left after deductions are made; what you have left, always lower than the gross amount
Gross productivity: total gain in energy or biomass of an organism before any reductions
Net productivity: gain in energy or biomass that remains after deductions due to respiration
Gross primary productivity: total gain in energy or biomass by green plants. It's the energy converted from light to chemical energy by photosynthesis in green plants
Net primary productivity: total gain in energy or biomass by green plants after allowing for losses to respiration. The increase in biomass of the planet and is the biomass that is potentially available to consumers that eat plants
Glucose produced in photosynthesis:
- Provides for growth, maintenance and reproduction with energy being lost as heat during respiration
- Rest is deposited in and around the cell
- NPP = GPP - R
- Net secondary productivity (NSP): total gain in energy or biomass by consumers after allowing for losses to respirate
- GSP = food eaten - faecal loss
Biogeochemical cycles: the natural pathways by which essential elements of living matter are circulated
- 4 main cycles: water, carbon, nitrogen, sulphur
- plants use carbon dioxide to make food (photosynthesis) carbon becomes stored food
Nitrogen Cycle:
- nitrogen fixation: when atmospheric nitrogen is made available to plans through fixation of atmospheric nitrogen
- nitrification: nitrifying bacteria in the soil which are able to convert ammonium to nitrates
- denitrification: denitrifying bacteria in waterlogged and anaerobic conditions
- decomposition of dead animals provides nitrogen for uptake by plants
- decomposition of dead animals provides nitrogen for uptake by plants
Efficiency of assimilation: gross productivity * 100 / food eaten
Efficiency of biomass productivity: net productivity *100 / gross productivity
→ Energy budget: can measure the quantities of energy entering and leaving the animal or population
→ Maximum sustainable yield: largest crop or catch that can be taken from the stock of a species without depleting the stock
2.4 - Biomes, Zonation, and Succession
Biome: is a collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions
- Aquatic: fresher and marine, freshwater, marine.
- Deserts, forest, tundra, grassland
Biosphere: part of the earth inhabited by organisms
- Latitude: distance north or south from the equator
- Altitude: height above sea level
Zonation: change in community and ecosystem aking and environmental gradient due to changes in altitude, latitude, tidal level or distance from shore/coverage by water
Primary succession: process of creating life in an area where no life previously existed
Secondary succession: when an established community is suddenly destroyed, an abridged version of succession starts
A sub-climax community is one which will only continue its development if the limiting factor is removed
→ K - strategies: long life, slower growth, late maturity. Fewer large offspring, predator, high trophic level
→ R-strategist: short life, rapid growth, early maturity, prey, lower trophic level