AP Bio Unit 2 Review
Cell Theory and Cell Types
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells, emphasizing cells as the fundamental building blocks of life.
The cell is the basic unit of life, capable of carrying out all life processes like metabolism and reproduction.
Rudolf Virchow's concept states that all cells arise from pre-existing cells, highlighting the continuity of life.
Endosymbiotic Theory: The theory that eukaryotic organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free living prokaryotes that were ingested by a larger prokaryotic host cell
The fact they both have ribosomes (despite difference in shape) proves common ancestry
Cellular Organelles and Functions
Endomembrane System - a network of membranes within eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins
includes Nucleus, ER, Golgi Apparatus, etc.
Nucleus
Function: Stores genetic material (DNA) and regulates cellular activities through gene expression.
Structure: Surrounded by a double membrane (nuclear envelope) with nuclear pores for selective transport.
Ribosomes
Function: Sites of protein synthesis, translating mRNA into polypeptide chains.
Location: Free-floating in the cytosol or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Rough ER: Synthesizes and transports proteins, studded with ribosomes.
Smooth ER: Involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage.
Golgi Apparatus
Function: Modifies, sorts, and ships proteins and lipids received from the ER.
Structure: Composed of flattened membrane-bound sacs (cisternae) for processing cellular products.
Mitochondria
Function: Generates ATP through cellular respiration, known as the powerhouse of the cell.
Structure: Double membrane with inner membrane folds (cristae) for increased ATP production.
Plant Cells vs. Animals Cells
Plant cells have a cell wall made of cellulose
Plant cells have chloroplasts
most of the cytoplasm within a plant cell is usually taken up by a large vacuole (the central vacuole)
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
AP likes to test this a lot
Prokaryotic Cells:
Lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Found in bacteria and archaea.
Ribosomes are smaller and called “70S“ ribosomes
Components:
plasma membrane
flagella and cilia
cell wall
nucleoid region
ribosomes
circular chromosomes
cytoplasm
Eukaryotic Cells:
Contain a nucleus and various organelles, allowing for specialized cellular functions.
Ribosomes are larger and called “80S“ ribosomes
Components:
nucleus
nucleolus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
smoother endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi body
ribosomes
mitochondria
vacuole
lysosome
peroxisomes
centrioles (animals only)
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
cytoskeleton (microtubules, microfilaments)
central vacuole (plants only)
cell wall (plants, fungi, and some protists)
Membrane Structure and Transport
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes the cell membrane (plasma membrane) as a dynamic phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates.
Phospholipids: Form a semi-permeable barrier with hydrophilic heads outward and hydrophobic tails inward.
The hydrophobic nature of the inside of the membrane is responsible for its selective permeability
Membrane Proteins
Transport Proteins: Facilitate substance movement across the membrane for selective permeability.
Receptors: Bind signaling molecules to initiate cellular responses.
Ex: aquaporins - water specific channels that allow water to traverse the membrane despite the membrane being nonpolar
Glucose and ions such as Na+ and K+ are also transported across plasma membranes through membrane proteins
membranes may become polarized as these ions move across them
Selective Permeability
Definition: Allows certain substances to cross more easily, maintaining homeostasis.
Examples: Diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion based on molecule characteristics.
They do this because substances want to move down a concentration gradient, going from high concentration to low concentration (diffusion)
Transport through the membrane depends on size and polarity of the molecules and concentration gradients
Facilitated diffusion - When diffusion required the help of a channel protein
Osmosis - When water is diffusing
Water is usually present as a solution
The solvent (water) can move toward equilibrium in order to make the concentration the same across the membrane
Water moves to “dilute“ a solution
Can be tricky because one side may look like it “gains“ water even though it has a higher concentration already, however that concentration is the solute and water as the solvent moves to dilute the solute
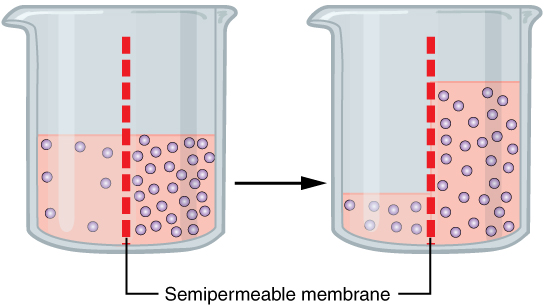
Transport Across the Membrane
Passive Transport: Includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Active Transport: Requires ATP to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
Ex: Sodium-potassium pump
Pumps are ALWAYS active transport as they move things against a concentration gradient
Shoots out three sodium ions and brings in two potassium ions across the cell membrane
This pump depends on ATP to get ions across that would otherwise remain in regions of higher concentration
Types of Cellular transport
Simple diffusion
Ex: Steroids such as testosterone are hydrophobic lipids. Therefore, testosterone can cross the inner region of the phospholipid bilayer
Facilitated transport
Active Transport
Bulk Flow
Dialysis
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Surface Area to volume ratio
Higher surface area to volume ratio is more efficient to diffuse more
When there is insufficient surface area to support a cell's increasing volume, a cell will either divide or die
Tonicity
Tonicity: The relative solute concentration in a solution affecting water movement across cell membranes.
Isotonic: Solution with the same solute concentration as the cell, resulting in no net water movement.
Hypertonic: Solution with higher solute concentration than the cell, causing water to move out of the cell and into the solution.
Hypotonic: Solution with lower solute concentration than the cell, causing water to move away from the solution and into the cell.
Water moves from hypotonic areas to hypertonic areas “moves to dilute solute“
Water moves from high water potential to low water potential
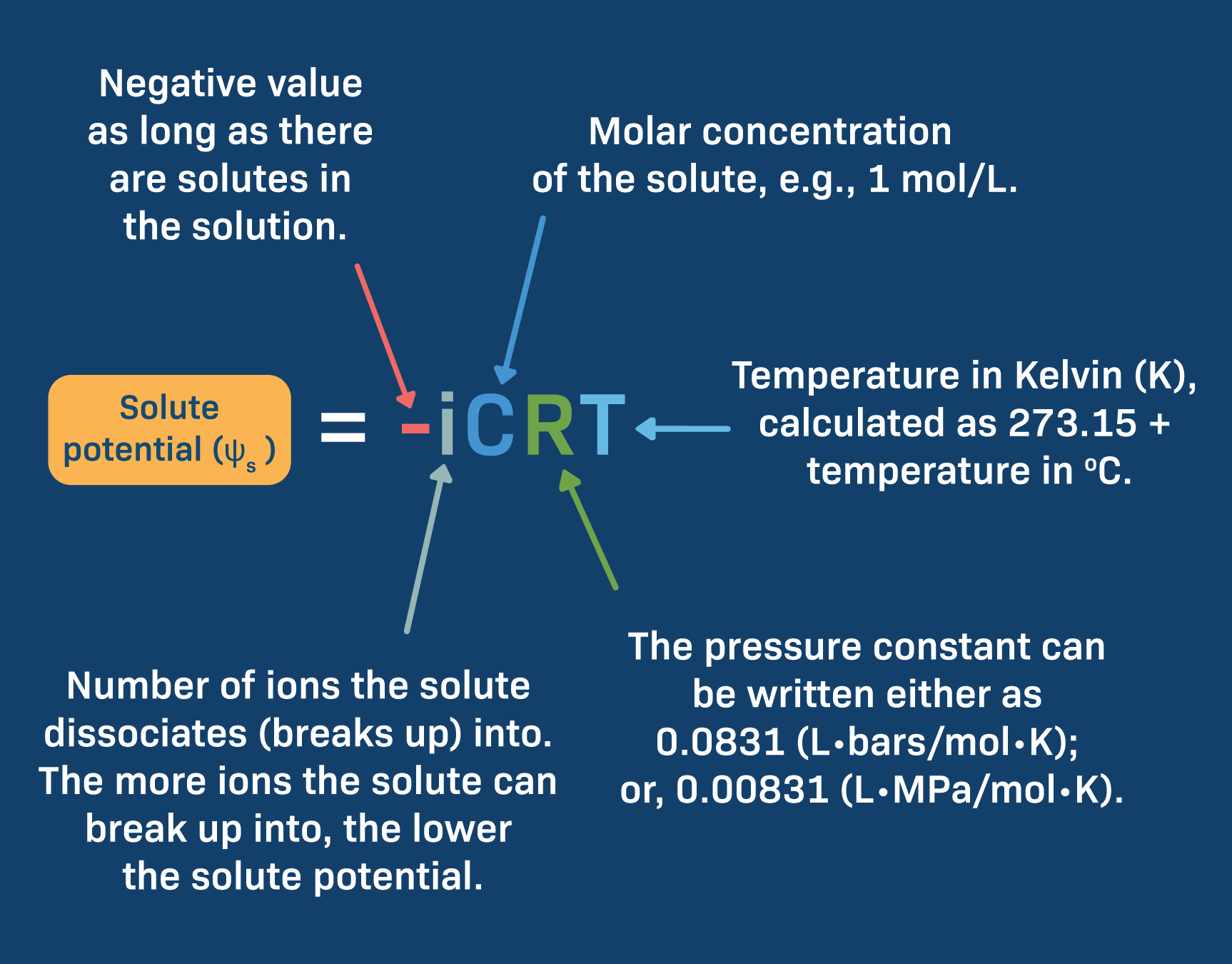
Water Potential Equations

Solute Potential of a Solution
Energy Conversion and Communication
Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration
Aerobic Respiration: Converts glucose and oxygen into ATP through Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and Electron Transport Chain.
Function: Essential for converting stored glucose energy into usable ATP.
Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis
Equation: CO₂ + H₂O + Light → Glucose + O₂.
Process: Occurs in chloroplasts, with light reactions and Calvin cycle in different compartments.
Cell Communication
Signaling Pathways: Cells communicate through chemical signals and signal transduction for specific responses.
Types of Signaling: Autocrine, Paracrine, and Endocrine signaling pathways.
Key Terms
Endocytosis - The process by which cells internalize substances from their external environment by engulfing them in a membrane-bound vesicle.
Exocytosis - The process through which a cell expels materials by packaging them into vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents outside the cell.
Bulk Flow - The movement of fluids (liquids or gases) driven by pressure differences, facilitating the transport of substances over long distances within a biological system.
Dialysis - diffusion of solutes across a selectively permeable membrane
Ex: Kidney Dialysis is a specialized process where blood is filtered by using machines and concentration gradients
Gives substances present at high levels an opportunity to diffuse out of the blood
Light Microscopes: Microscopes that use visible light and lenses to magnify objects, typically up to 1,000 times.
Can visualize plant, animal, and bacterial cells
Electron Microscopes: Microscopes that use electron beams instead of light for higher magnifications (up to 2 million times).
Can visualize cell organelle structures such as the nuclear membrane
Nucleoid: Region in prokaryotic cells where DNA is located, not surrounded by a membrane.
Flagella: Long, whip-like appendages used by some cells (e.g., bacteria, sperm) for movement.
Capsule: Protective outer layer in some prokaryotic cells made of polysaccharides.
Phospholipid Bilayer: Double layer of phospholipids forming the cell membrane, with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
Peripheral Proteins: Proteins temporarily attached to the surface of the cell membrane.
Integral Proteins: Proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer, may span the entire membrane.
Transmembrane Proteins: A type of integral protein that spans the entire phospholipid bilayer.
Adhesion Proteins: Membrane proteins that help cells adhere to each other or the extracellular matrix.
Receptor Proteins: Membrane proteins that bind to signaling molecules (e.g., hormones) to initiate a cellular response.
Transport Proteins: Membrane proteins that help move substances across the cell membrane.
Channel Proteins: Transport proteins that form channels or pores in the membrane to allow specific molecules to pass.
Cell Surface Markers: Glycoproteins or glycolipids on the outer surface of the cell membrane that aid in cell recognition.
Carbohydrate Side Chains: Chains of sugars attached to proteins or lipids on the cell membrane for recognition and signaling.
Cristae: Folds within the inner membrane of mitochondria that increase surface area for ATP synthesis.
Centrioles: Cylindrical structures involved in organizing microtubules during cell division.
Microtubule Organizing Centers (MTOCs): Structures (like centrioles) that organize microtubules, especially during cell division.
Peroxisomes: Organelles involved in fatty acid breakdown and detoxification, producing hydrogen peroxide.
Microtubules: Tubular structures made of tubulin, providing structural support and helping with cell division and transport.
Microfilaments: Thin actin fibers that provide mechanical support and assist in cell movement and muscle contraction.
Tubulin: Protein subunits that make up microtubules.
Cilia: Short, hair-like projections on cells used for movement or moving substances around the cell.
Euglena: A genus of flagellated protists that can perform photosynthesis.
Paramecium: A genus of ciliated protozoa that live in water and use cilia for movement and feeding.
Chitin: A polysaccharide found in fungal cell walls and arthropod exoskeletons.
Tonicity: The relative solute concentration in a solution affecting water movement across cell membranes.
Isotonic: Solution with the same solute concentration as the cell, resulting in no net water movement.
Hypertonic: Solution with higher solute concentration than the cell, causing water to move out of the cell.
Hypotonic: Solution with lower solute concentration than the cell, causing water to move into the cell.
Water moves from hypotonic areas to hyper tonic areas “moves to dilute solute“
Water moves from high water potential to low water potential
Pinocytosis: Endocytosis where the cell engulfs extracellular fluid and its solutes.
Phagocytosis: Endocytosis where the cell engulfs large particles (e.g., debris or microorganisms).
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis: Endocytosis where specific molecules are taken in by binding to cell surface receptors.
Clathrin: Protein that helps form coated pits during receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Bulk Flow: Movement of large amounts of fluid or substances within a system, often driven by pressure differences.