12-14: Light Dependent Reactions
Photosynthesis is the opposite of cellular respiration → takes in carbon dioxide and water, takes out carbohydrates and oxygen 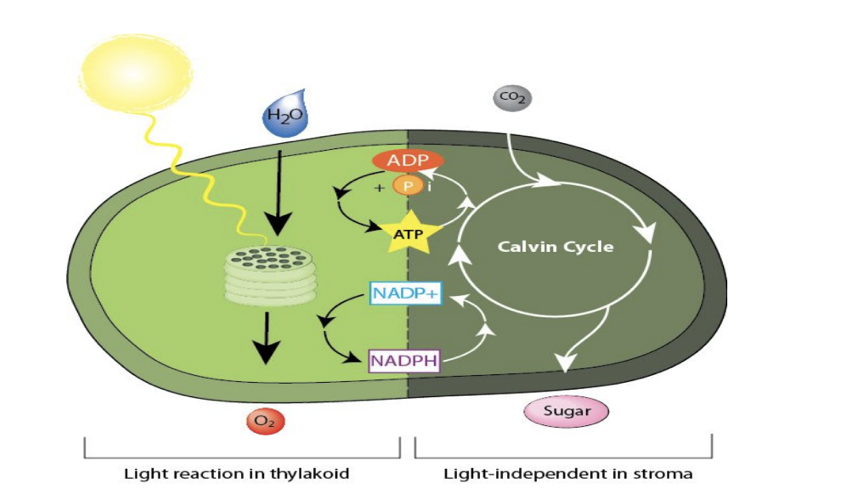
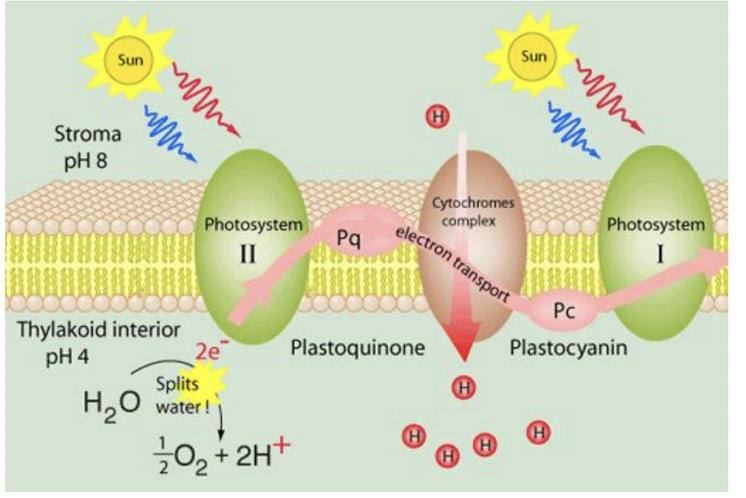
Photosystem 2 Photoexcitation
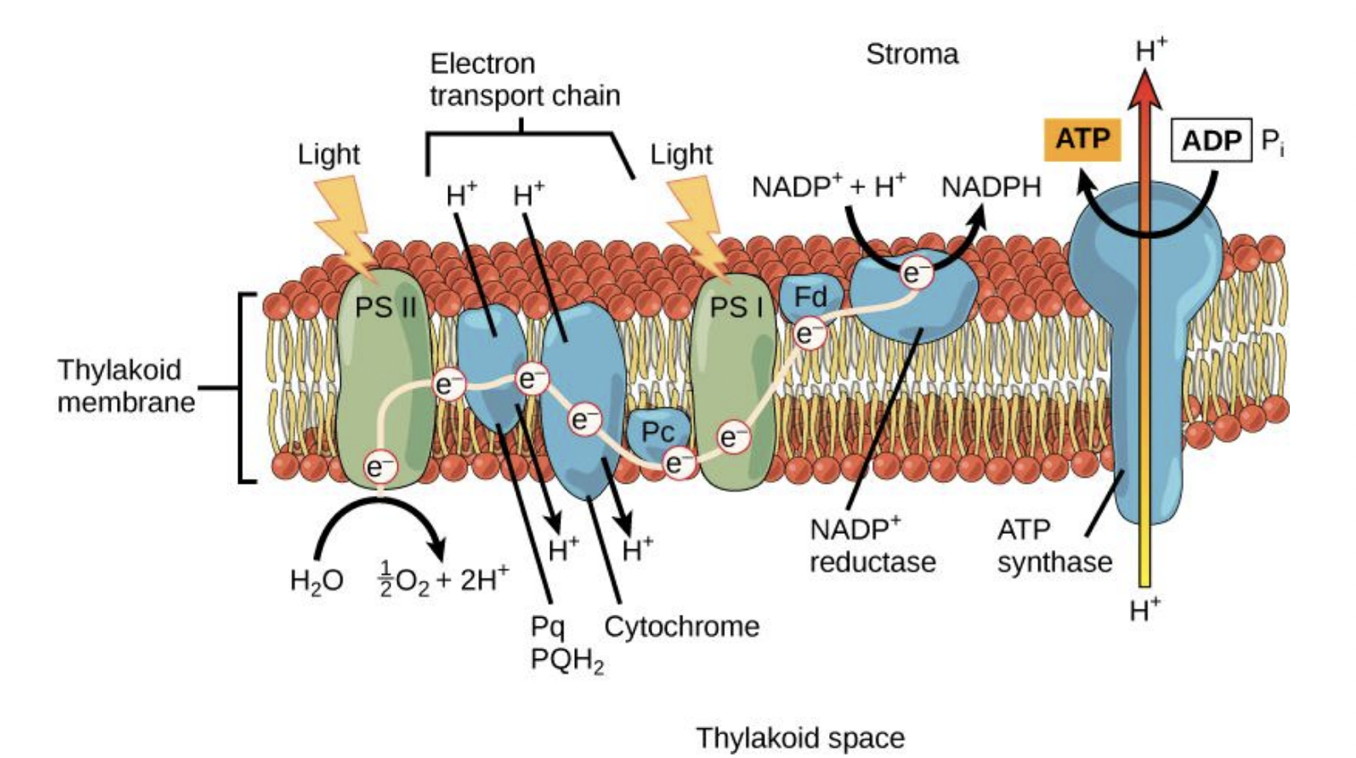
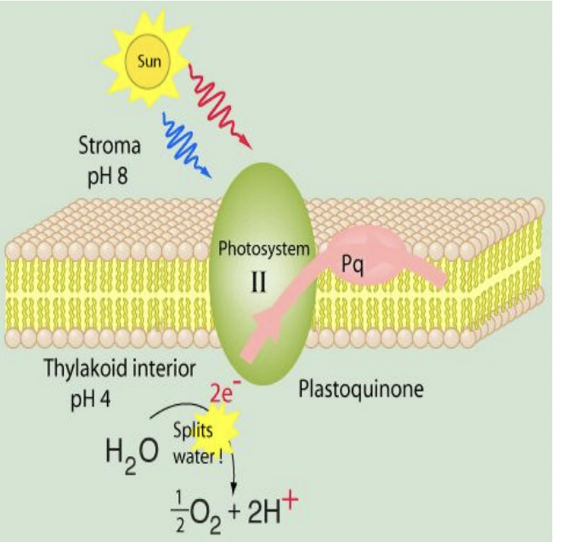
photosystem 2 starts the light dependent reactions
the light antenna complex absorbs a photon and transfers it to p680 chlorophyll molecule which excites an electron
the electron gets transferred to the acceptor which makes the p680 positively charged
p680 gets its electron back from the water splitting complex
each water molecule donates 2 electrons so the process happens twice to produce oxygen
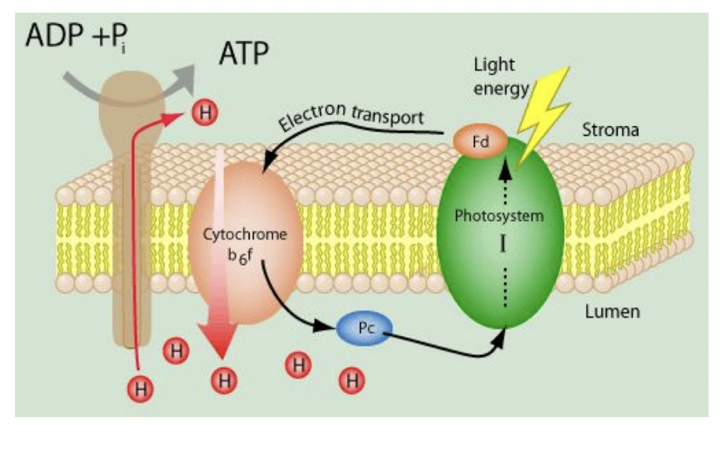
the acceptor molecules that took p680’s electron passes it to a molecule of plastiquinone (PQ)
Electron Transport Shuttles
the PQ molecule accepts an electron from photosystem 2 as well as protons (H⁺) from the stroma
the electron then travels through the thylakoid membrane and donates the electron to the cytochrome complex
at the same time, it releases the H⁺ into the lumen which increases the proton complex
the cytochrome complex passes the electron to another shuttle molecule PQ which carries it to photosystem 1
Photosystem 1 and Photoexcitation
when a photon of light strikes photosystem 1, an electron in the p700 molecule is excited
this excited electron is transferred to another acceptor leaving p700 with a positive charge
the electron transferred from photosystem 2 is delivered by PQ to neutralize p700
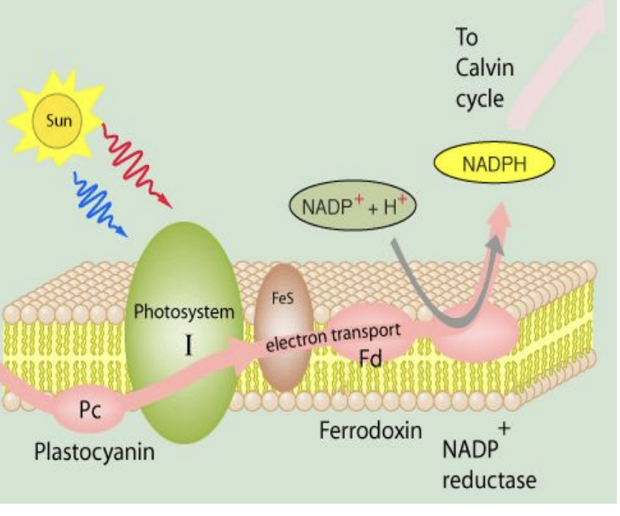
Ferredoxin and NADPH
the electron from photosystem 1 gets transferred to ferredoxin (an iron sulfur protein)
oxidation of ferredoxin transfers the electron to NADP+ making NADP
a second ferredoxin adds another electron along with H⁺ from the stroma to make NADPH
all of this happens with an enzyme called NADP+ reductase
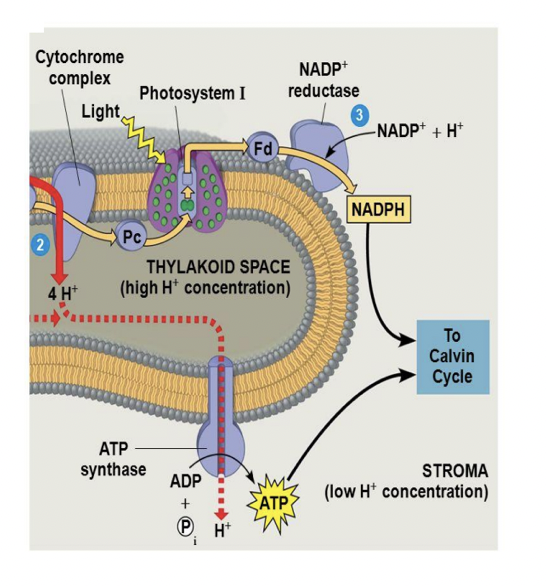
Proton Gradient
all this activity has increased the proton concentration in the thylakoid lumen and decreased it in the stroma
- splitting of water produces protons in lumen
- PQ and cytochrome complex transport protons from storm to lumen
- NADPH production removes protons from stroma solution
this proton gradient can be used for chemiosmosis
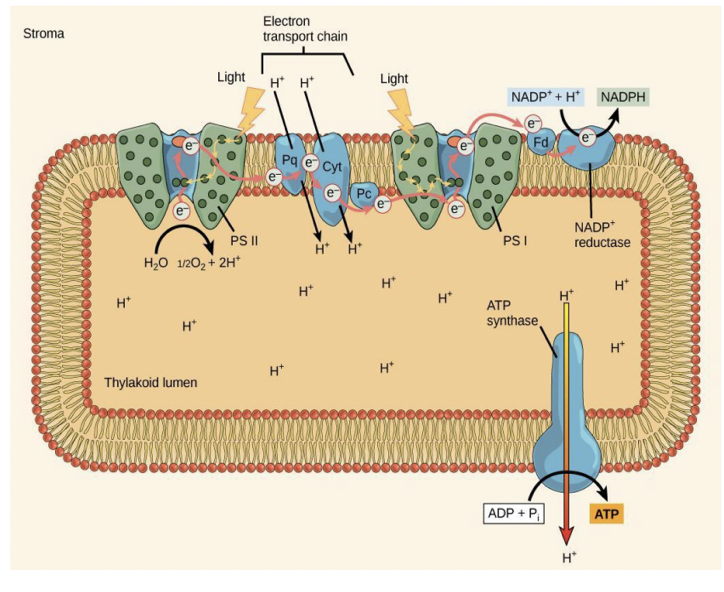
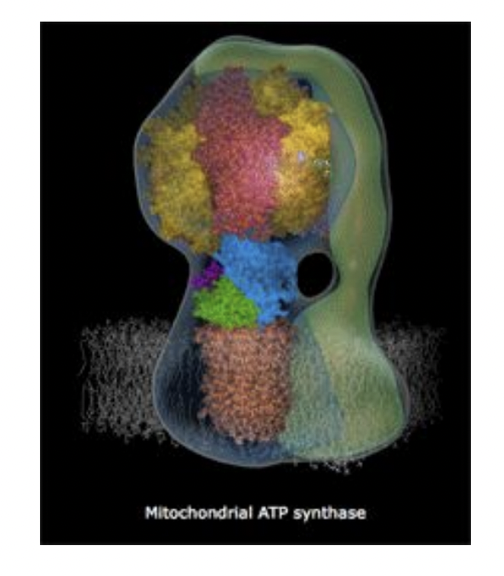
ATP Synthase
identical to ATP synthase in mitochondria
this time app is produced by photophosphorylation (uses light energy, no oxidation occurred to produce the proton gradient)
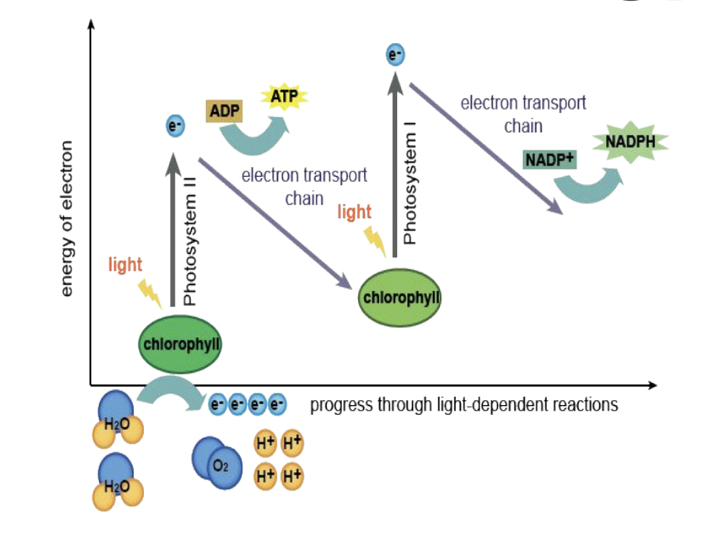
Electron Energy
the boost in energy provided by the photons in sunlight gradually decreases as the electrons move through ETCs of photosystem 1 and 2
Cyclic Electron Transport
photosystem 1 works independently of photosystem 2 if the electron on ferredoxin is transferred to PQ rather than NADP+ reductase
this continuously pumps protons into the lumen, thus producing more ATP
more ATP is needed than NADPH in the Calvin cycle → making this process very useful
- 9 ATP and 6 NADPH are needed to make 1 G3P (half a glucose)