Unit 2. Industrial Revolution
Before and After
America in 1860
Used lanterns to light up homes; could not go out at night
Railroads connected the northeast to west, unsettled lands in between
Made clothes and furniture by themselves
Little town stores (mom & pop stores)
Most lived on countryside
Limited contact outside of community
America in 1920
Invention of electricity
Automobiles were invented
Large corporations
Half lived in big cities
Telephone wires & railroads connected the cities
People bought from chain stores, catalogues, and department stores
How the Country Grew
Large Resources
Allowed the country to make new stuff uninhabited
Fertile Soil
Streams
Wood/timber
Ores (coals, phosphate, iron, and copper)
“Free Enterprise” System
Capitalism: People can privately own property, assets, operations, etc without interference of the government
American culture emphasized individual achievement and materialism
Social Darwinism: Successful people are blessed with certain traits, and poor people are poor because themselves and not their environment
Role of Government: Government played a hands-on approach and barely interfered with businesses: “laissez-faire“ capitalism
Patent: A system set up to protect inventors and scientists and make them more willing to share ideas with the people and the market
They were then able to figure out problems faster and be more creative because they had outside help
Tariffs: Incentivized against outsourcing to other countries and incentivized producing it in land.
*Protected American Corp and Businesses from foreign companies
Legacy of First American Revolution
Early inventions/innovations helped innovate more inventions in the U.S. (steam boats, railroads, factory production)
Economic Stimulus Provided by Civil War
Production doubled in factories due to the demand/war effort
Gave more people jobs
Businesses sold more
Abolition of Slavery united the North & South as a free market
More Acts Passed to Stimulate Economic Growth:
Morill Act (agricultural colleges were built for new farming techniques/crops)
Morill Tariff (protected U.S. Manufactures against using foreign companies)
Pacific Railroad Act (gave railroad companies land grants to build the railroad)
Homestead Act (provided 150 acres of free land to farmers in the West)
National Banking Act (provided a national banking system using a charting system & national currency)
America Second Industrial Revolution
Spread of Railroads was the thing that paved the way for the Second American Industrial Revolution
Impact of Railroads on American Lifestyles
Need for uniformed time zones in country
Central, Pacific, and Eastern
Stimulus for iron, steel, and coal companies
Transportation of goods, people, and animals from one point to another
Cheaper form of transportation
Expanded farming and ranch industry
Shipped butchered animals in Chicago and ship to markets in Northeast
A Growing Population
Between 1860 to 1920, population TRIPLED
Rapid influx of European & Asian Immigrants
Demand for business growth
rising demand for goods and cheap labor
Immigrants did undesired jobs
Brought skills
Rise of Corporation
Corporation: Business chartered by federal or state government as a separate “person” and gave stocks to stockholders
Stocks: A share of the company that received a percentage of profit in dividends
Before the Civil War, businesses were owned by a small group or 1 individual
the death of the owner meant the closing of the business
owners are liable for debt of business
After the Civil War, corporations were on the rise and led to the entrepreneurial spirit that took over America
death of stockholder does not affect business
Debts of business are not the responsibility of the stockholder
Pros
Monopolies had a large scale of economics
A cheaper supply of resources
Efficient management
Cons
Monopolies had total control over the industry with no competitors
Monopolies could overcharge customers
Monopolies had no incentive to improve products
Entrepreneur
Entrepreneurs are those who take risks when engaging in business
Captains of Industry: those who innovate and lead the way for a certain industry
adopted new technology to make better/cheaper products for industry out of new corporations
Robber Barons: those who use harmful practices to make a profit
exploited workers
exercised monopolies over customers
Great Entrepreneurs of Gilded Age
Andrew Carnegie
Was the entrepreneur of the Steel Industry
Achievements:
Built major infrastructure around the U.S. (cities, bridges, & railroads)
Adopted the Bessemer Process from Britain and made it cheaper/faster than anyone else in the U.S.
Practiced Vertical Integration
Sold Carnegie Steel to J.P. Morgan in 1901
Became a philanthropist
John D. Rockefeller
Was the entrepreneur of the Oil industry
Achievements:
During Civil War, he invested in oil refineries to make a profit
Formed Standard Oil and took over 90% of U.S. oil refineries
Practiced Horizontal Integration
When Edison made the lightbulb, his business took a hit, since no one used oil lamps anymore, but had a comeback when oil was used to make gasoline for automobiles
Became a philanthropist
J.P. Morgan
Was the entrepreneur of the banking/finance industry
Achievements:
Helped Thomas Edison form Edison Electric Company in 1892
Kicked out Thomas Edison from Edison Electric Company when Tesla proved Edison wrong to make General Electric GE Company
Formed a commercial and banking institution called J.P. Morgan & Company in 1895,
Bought out Carnegie Steel to make U.S. Steel in 1901
Henry Flagler
Helped John D. Rockefeller expand oil refinement business
Built the Florida East Coast Railroads
Developed Florida
Built expensive hotels in Florida
Horizontal vs Vertical Integration
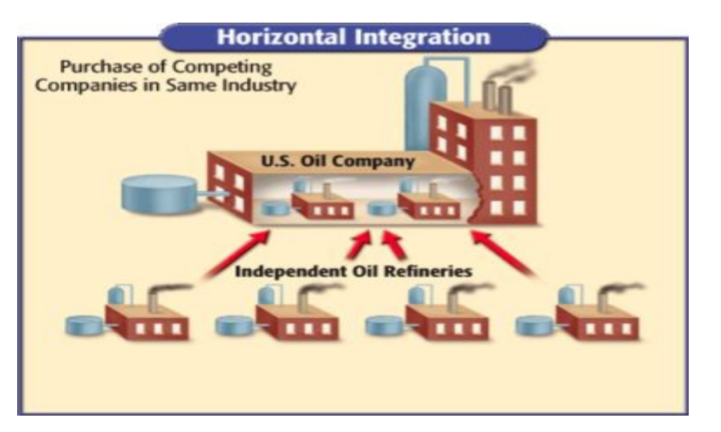
A person owns a single step in the industry
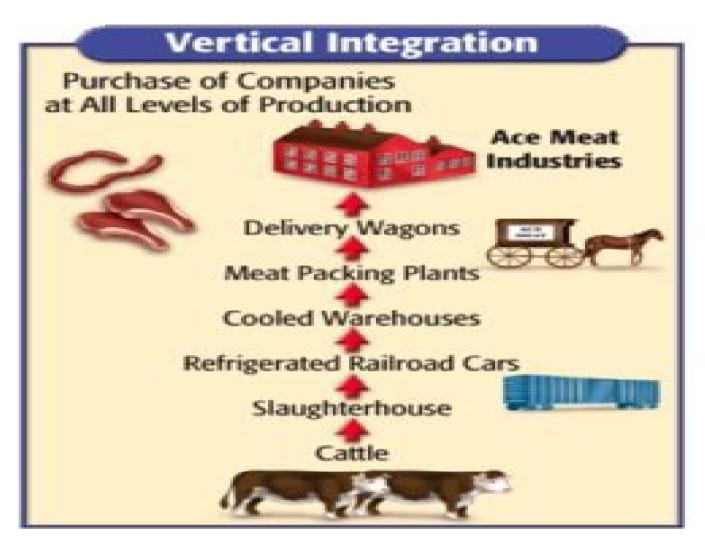
A person owns every step of the industry
Economic Depression
A prolonged business downturn with high rate of unemployment
In 1873, after the mania of laying down new railroads, many people started speculating and selling out their stocks and ended up causing an economic collapse
Monopolies
Many entrepreneurs like John D. Rockefeller and William Carnegie emerged and started to buyout the competition and drive them out of business
Falling prices and “cutthroat competition” (temporarily lowering prices to drive competitors out of business) made rival companies team up
So they could make a monopoly out of driving off competitors
Monopoly Disadvantages
Could overcharge
Companies had no need to improve products
Government
Reformers: people who fought for change
Due to laissez faire style of government, government was not supposed to interfere with business owners and employees or producers and buyers
Many business/corporation owners bribed government officials to break unions demanding for change
Reformers demanded government regulate “Big Business” and stop monopolies from forming
Anti-Trust Laws
Laws against Monopolies
Sherman Anti-Trust Law 1890: Combinations in “restraint of trade” are prohibited
Munn vs. Illinois - Supreme Court ruled that state could regulate businesses like railroads that are in the “public interest”
Wabash vs Illinois - The Supreme Court ruled that only Congress can regulate interstate commerce and states cannot regulate railroads
Interstate Commerce Act - established Interstate Commerce Committee and prohibited unfair railroad practices
Railroad companies cannot charge more for shorter distance over long distances
Railroad companies cannot charge different rates for same freight and same distance
Cannot give rebates