Science PeTa 2.1
Procedure 1.A (Capsule)
I. Small Concepts
Airbags are helpful in car crashes because they help reduce the impact force on the occupants. When a car suddenly stops due to a collision, the occupants continue moving forward at the same speed. The airbag rapidly inflates and cushions the impact, extending the time it takes for the occupants to come to a stop. This increases the time over which the change in momentum occurs, reducing the force exerted on the occupants. As a result, airbags help prevent or minimize injuries by reducing the impulse experienced during a car crash.
There are several factors that can help prevent an egg from falling:
Cushioning material: Placing the egg in a soft material, such as foam or bubble wrap, can absorb shock and prevent it from breaking upon impact.
Protective container: Using a sturdy container, such as a box or a plastic case, can provide an extra layer of protection for the egg.
Handling with care: Being gentle while handling the egg can minimize the chances of dropping or mishandling it.
Controlled descent: Lowering the egg slowly and steadily, rather than dropping it abruptly, can reduce the impact force and increase the chances of it surviving the fall.
Parachute or padding: Attaching a parachute or padding to the egg can help slow down its descent and cushion the impact.
II. Capsule making
a. Materials
One paper cup
Ten straws
Scotch tape
b. Design/s
c. Explanation/procedure (Main concept)
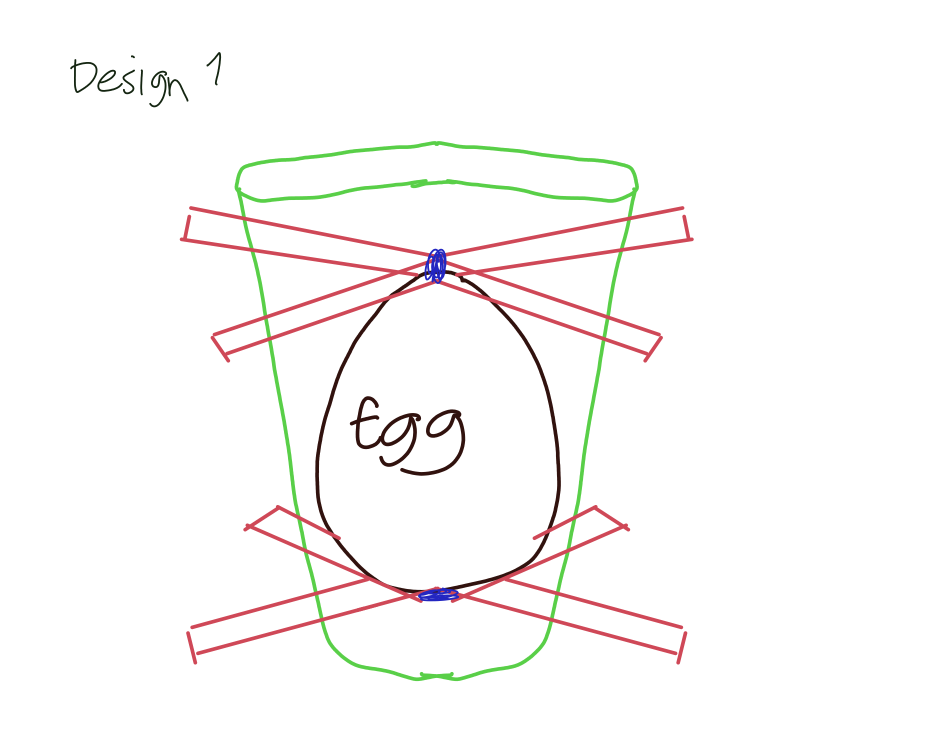
Design 1
Prepare one paper cup and make eight holes that are across each other (4 holes at the bottom and another at the top)
Insert two staws that intersect each other in the bottom hole
Tape the middle part where the staws intersect
Insert the egg above the staws
Insert another two straws in the top hole and make an intersection
The straws in the bottom part serves as a cushion for the egg and as for the top part, it prevents the egg from leaving the cup.
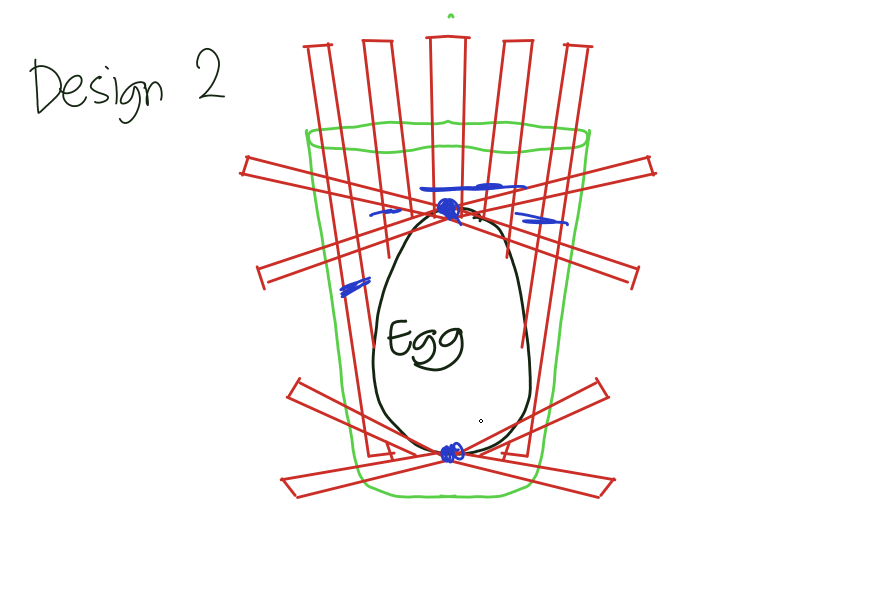
Design 2
Prepare one paper cup and make four holes that are across each other (4 holes at the bottom)
Insert two straws that intersect each other in the bottom hole
Tape the middle part where the staws intersect.
Cut open six straws.
Insert three straws inside the cup and tape it to the side
Tape another three straws outside the cup
Insert the egg
Just like the 1st design, the straws inside serve as a protection to the egg. The straws outside serves as a foundation for the capsule.
Procedure 1. B (Experiment/Data Gathering)
Using the triple beam balance, get the mass of the following:
Capsule 1 (g&kg)
Capsule 2 (g&kg)
Egg (g&kg)
Capsule and Egg (Kg)
1 kg = 1000 g
Experiment
1st
Ready capsule 1 with egg
Height is 2m
2 trials
Use stopwatch for time
get final height
Ready capsule 1 with egg (again)
Height is 4m
2 trials
Use stopwatch for time
get final height
2nd
Ready capsule 2 with egg
Height is 2m
2 trials
Use stopwatch for time
get final height
Ready capsule 2 with egg (again)
Height is 2m
2 trials
Use stopwatch for time
get final height
Replace the egg immediately if broken
Note: The data will be encoded for Tables 1,2 and 3
Table 3
Get initial velocity
Solve for final velocity
Equation: mgh=1/2mv²
m represents the mass of the object.
g is the acceleration due to gravity.
ℎ denotes the height from which the object falls
Encode final velocity
Table 4
Get the initial velocity
Solve the Initial Momentum
Get the final velocity
Solve the final Momentum
Table 5
Get the average for all trials
Equation: t1+t2 / 2
Encode the previous Initial and Final Momentum
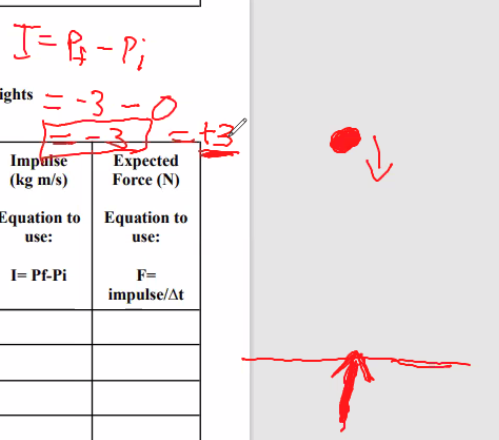
Solve for Impulse
Equation: I= Pf-Pi
I = Final momentum - Initial momentum
Solve for Expected Force (N)
Equation: F=impulse/∆t
Force is equal to impulse divided by the change in time
or F = Impulse/t2-t1
III. Data Gathering 1. C (Explanation ni sir)
Table 1
The grams in the table are the ones measured with the triple-beam balance
Add the mass of the capsule and egg in kg
Table 2
Input the time trials
Write observations in bullet form
Write the trial then Y or N
Table 3
Rewrite the mass of the system
Final height = 0 m
Initial velocity is 0
v² = final velocity
g = -9.8
The final velocity is in the negative value
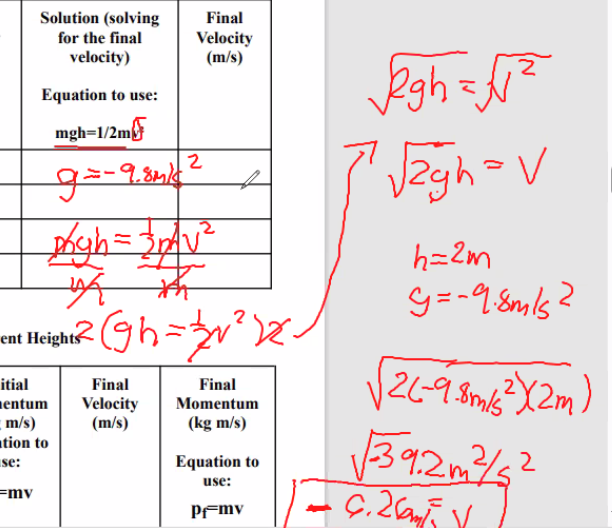
Table 4
Rewrite the mass of the capsule and egg
Initial momentum is zero
The final momentum is negative also
Momentum at different heights (Graph)
Final momentum at different heights
The graph is in quadrant 4
Table 5
Rewrite the average time
Impulse is in the opposite value of the momentum (Impules is positive)