Lesson 7: Summarizing Virtualization and Cloud Concepts
Client-side Virtualization:
Overview of Virtualization:
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems (OS) to run simultaneously on a single system (e.g., macOS, Windows 11, Linux Ubuntu).
Each OS is independent, sharing the same physical hardware.
Types of Virtualization:
Desktop Virtualization: Runs multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a desktop OS.
Server Virtualization: A server hosts multiple VMs, commonly used in enterprises.
Virtualization has been in use since the 1960s with IBM mainframes.
Use Cases:
Legacy Software: Run older software alongside newer OS versions.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Run multiple OSes (macOS, Windows, Linux) without extra hardware.
Hypervisors:
Software that manages VMs, allocating CPU, memory, and storage.
Types of hypervisors:
Intel VT
AMD-V
Requirements for Virtualization:
Requires compatible hardware (CPU with virtualization support), ample RAM, sufficient storage, and proper networking.
Development and Testing:
Sandboxing: VMs provide isolated environments for testing applications.

Snapshots: Capture VM states for easy reversion.
Security Concerns:
VM Escaping: Malware may access the hypervisor from a compromised VM.
Security Measures: Use firewalls, antivirus, and ensure VMs are created securely.
Networking in Virtualization:
Shared Network Address: VMs share the host’s IP.
Bridged Network Address: VMs have unique IPs, enabling direct network access.
Private Addressing: Isolated local network with no external communication.
Software Defined Networking (SDN):
Cloud Computing & SDN Overview:
SDN helps transition from physical networking devices to virtualized platforms in cloud environments.

SDN Layers:
Infrastructure/Data Plane: Handles traffic forwarding, encryption, and address translation.
Control Plane: Manages dynamic routing protocols and forwarding tables.
Application Plane: Provides management access through APIs.
Benefits of SDN:
Enables software-based networking devices and creates modular layers for communication.
Cloud Models and Characteristics:
Cloud Overview:
The cloud includes off-site resources beyond just storage, providing scalable and flexible computing power.
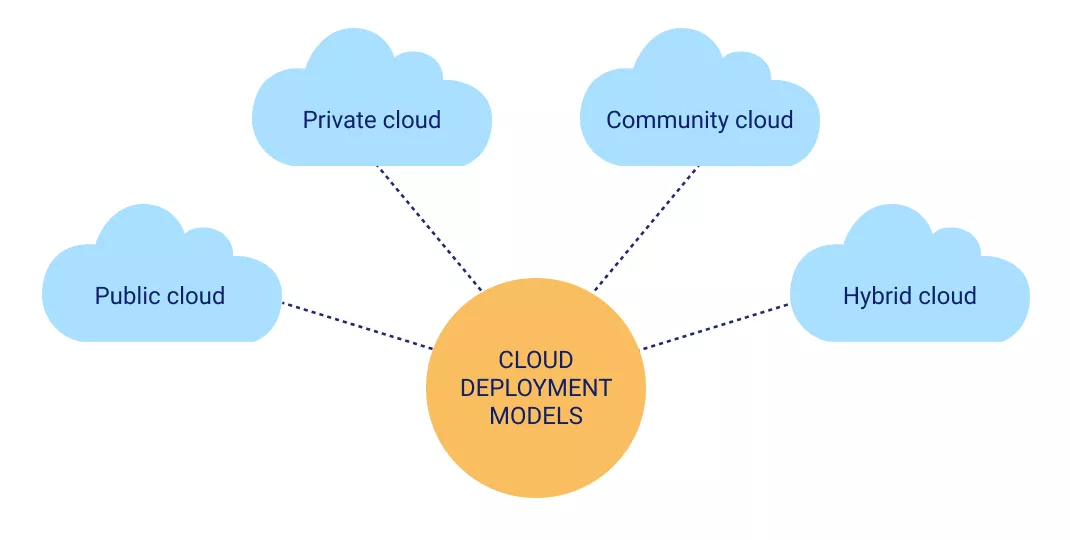
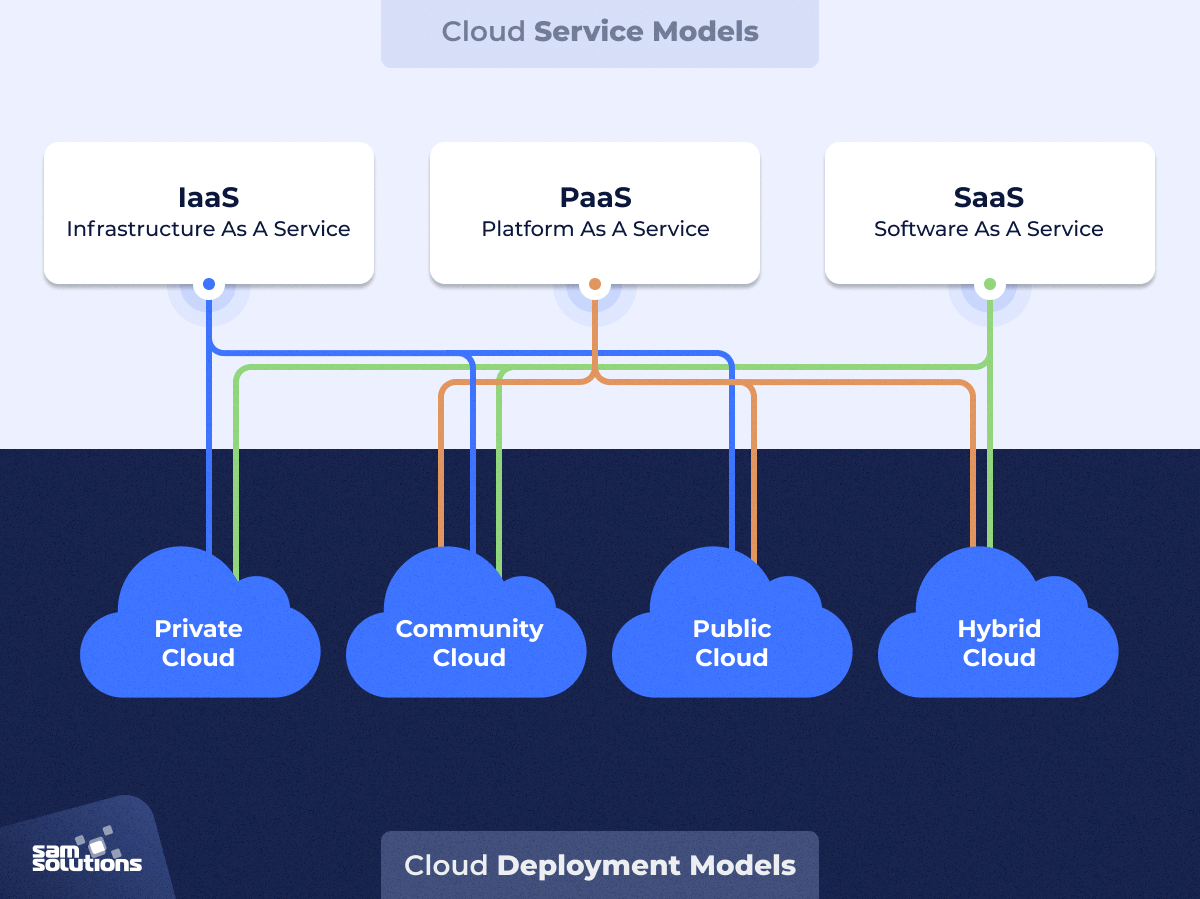
Cloud Deployment Models:
Public Cloud: Services offered by providers like Amazon or Microsoft, accessible globally.
Private Cloud: Cloud infrastructure managed and accessed only by one organization.
Hybrid Cloud: Combination of public and private cloud resources.
Community Cloud: Shared cloud infrastructure among organizations with similar needs.
Cloud Service Models:
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Users purchase infrastructure (e.g., storage, CPU) and manage their own software.
SaaS (Software as a Service): End users access software over the internet, with providers managing maintenance (e.g., Google Mail, Microsoft 365).
PaaS (Platform as a Service): Provides platforms for application development without extensive coding (e.g., Salesforce).
On-Premises Model:
Infrastructure and applications are entirely managed by the client, unlike cloud services where part of the management is outsourced.
Cloud Characteristics:
Cloud Instances:
Internal Cloud: Built on an internal network with an in-house data center.
External Cloud: Uses third-party providers’ resources, typically in multiple data centers.
Cost Structures:
Metered Services: Charges based on usage (e.g., data storage, uploads).
Non-Metered Services: Fixed monthly pricing with no additional charges (e.g., Dropbox).
Cloud Advantages:
Scalability: Seamlessly add/remove resources based on demand.
Rapid Elasticity: Instant adjustment of resources using cloud technologies.
High Availability: Built-in redundancy and synchronization to ensure uptime.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS):
Entire Windows desktop can run in the cloud, accessible from any device (e.g., Amazon Workspaces).