Ch.8
8.1: Lewis Symbols and the Octet
Valance Electrons are outermost electrons involved in chemical bonding
Lewis dot structure or Lewis symbol is used to show valance electrons of an atom.

Atoms gain or lose electrons to achieve the same number of electrons as noble gases
- 8 valance electrons
Octet rule: Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until they are surrounded by eight valance electrons
- full s and p shells
8.2: Ionic Bonding
Ionic substances are formed between metals and nonmetals
- Sodium and chlorine form sodium chloride or table salt
- Sodium lost an electron that Chlorine gained
- Ionic compounds are all exothermic
Lattice energy is the energy required to completely separate one mole of solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions.
- lattice energy increases as the charges on the ions increase and as their radii decrease
- enough to compensate the loss of up to three electrons
8.3: Covalent Bonding
- How a covalent bond woks (H2 for example)
- When two H atoms are close together their nuclei repel each other (same charges), the two negatively charged electrons repel each other, however, the positive nucleus and the negative electrons repel each other, and since the atom is stable we know that the attraction of the protons and electrons is stronger than the two repulsions.
- Atoms are capable of forming
- single bond: shared electron pair with one covalent bond
- H2
- multiple bonds: more than one covalent bond
- double bond: CO2
- triple bond: N2
- The length of the bond between two atoms decreases as the number of shared electron pair increases
8.4: Bond Polarity and Electronegativity
Bond polarity: the measure of how equally or unequally the electrons in any covalent bond are shared
- Nonpolar covalent bond: equally shared electrons: Cl2 or N2
- Polar covalent bonds: one of the atoms exerts a greater attraction on the bonding electrons: water
- Electronegativity is used to determine bond polarity
- Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself
- decreases with increasing atomic number
- Examples:
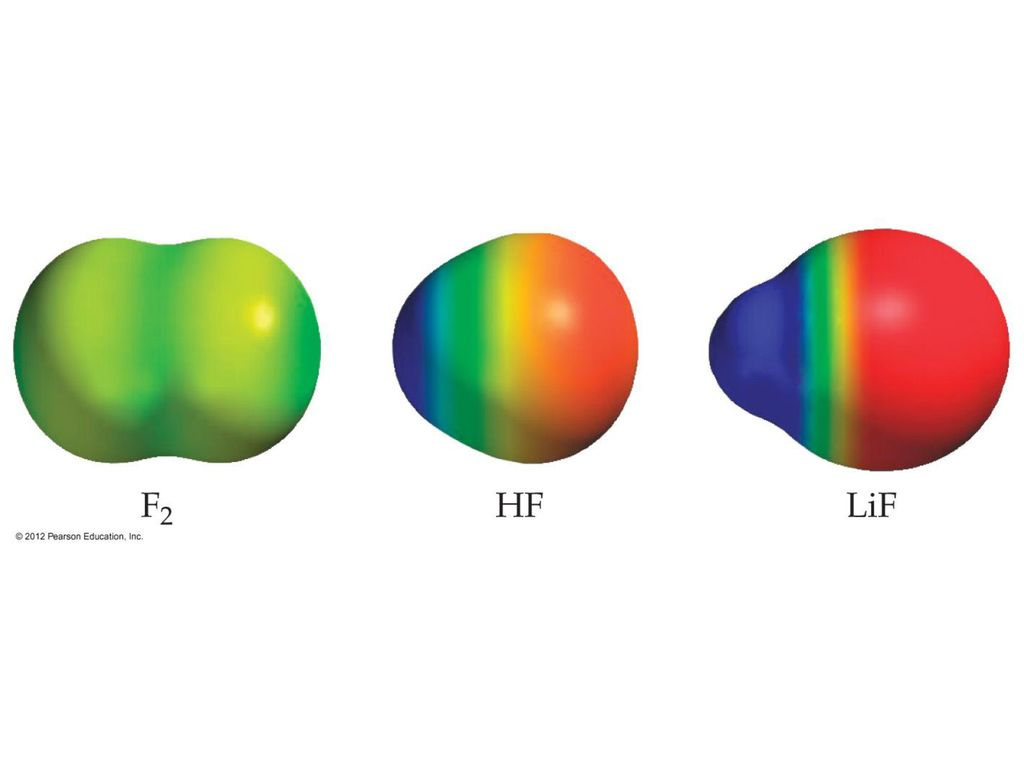
- F2-- the two fluorine atoms have the same electronegative, so therefore no atom is pulling electrons towards itself. and thus the molecule itself is non polar
- HF-- the fluorine atom is more electronegative than Hydrogen and therefore the hydrogen atom will pull the shared electrons more towards itself making the molecule polar
- LiF--the electronegativity difference between Lithium and Fluorine are so large that Lithium’s electron is transferred to Fluorine.
- Dipole is established when two electrical charges of equal magnitudes but opposite signs are separated by distance
- Covalent bonding:
- low melting and boiling point
- no electrolyte behavior
- Ionic Bonding:
- High melting and boiling points
- electrolyte behavior when dissolved in water
- brittle
- extended lattice structures
8.5: Drawing Lewis Dot Structures
formal charge is the charge the atom would have if each bonding electron pair was shared equally between its atoms.
- formal charge= valence electron- 1/2 of bonding- non bonding electrons
- formal charge on a neutral atom add to 1
- formal charge on an ion add to the charge on the ion
8.6: Resonance Structure
placement of atoms in two alternate yet equal Lewis dot structures are called resonance structures
- one or more resonance structure and can be dominant
8.7: Exceptions to the Octet Rule
atoms which are satisfied with less/more than 8 valence electrons
- Boron:6
- Beryllium: 6
- Phosphorus10
hypervalent are molecules are molecules with more than an octet of electrons around the central atom
- Only formed for central atoms from period 3 and below
8.8: Strengths and Lengths of Covalent Bongs
As the number of bonds increase between the atoms, the bond length decreases and bond enthalpy increases
- bond enthalpy is the bond strength