Unit 11.4 Pseudocode - Arrays & Records
Aims
Know what is meant by the term array, including the difference between 1D and 2D arrays.
Know what is meant by the term record structure.
Be able to write pseudocode that uses arrays and records.
Arrays are list of variables with the same data type and have same identifier name, can be 1D (stores in linear, single row and data is in consecutive locations), or 2D (stores in grid-like structure)
One-dimensional Array
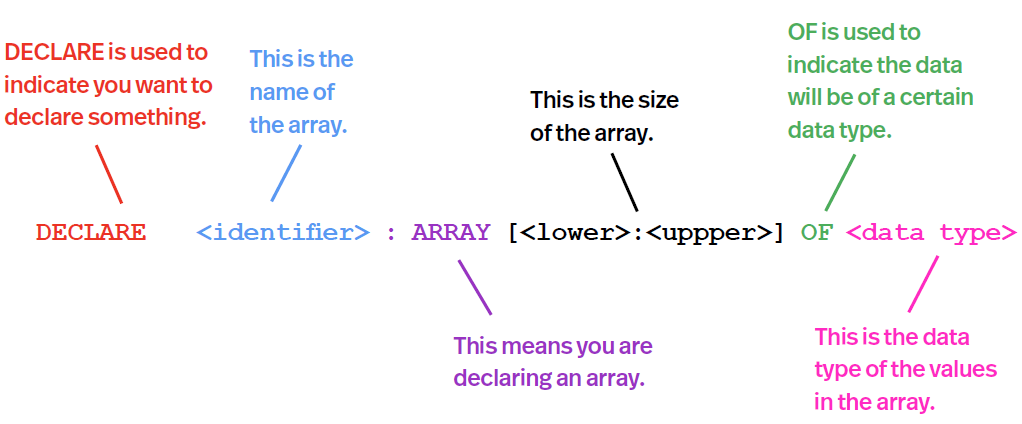
Syntax:
E.g. 1D array - letters with 30 spaces
DECLARE letters : ARRAY [1:30] OF STRING
Each element is given an index number which represents its position e.g. letters [1] is X

Two-dimensional Arrays
Syntax (same as 1D but need to specify second dimension)

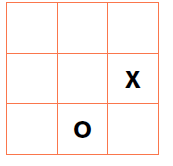
E.g. 2D array - noughtsAndCrosses, 3 rows and 3 columns
DECLARE noughtsAndCrosses : ARRAY [1:3, 1:3] OF CHAR
Each element is given an index number to represent its position e.g. noughtsAndCrosses [3:2] is O
Defining Records
Record structures allows storage of multiple related items of different data types together
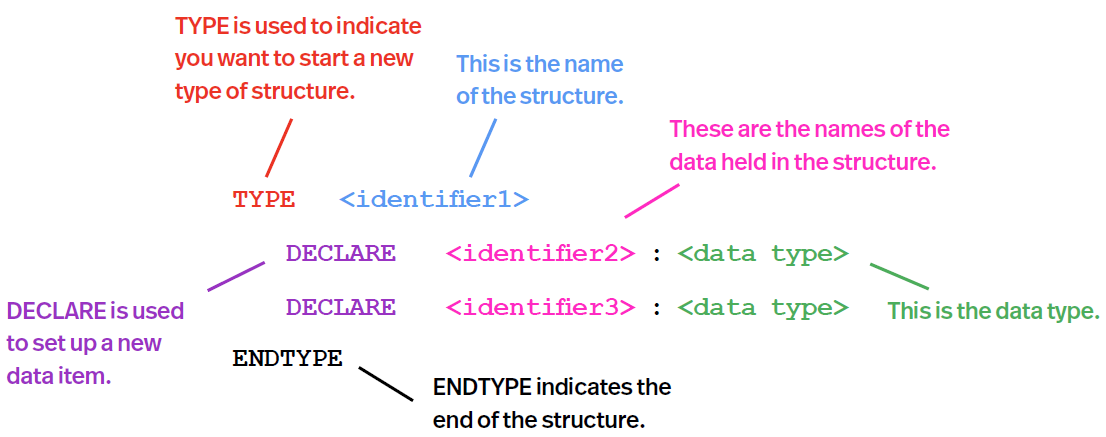
Syntax:
E.g. Record structure called users to store details of User ID, first name, surname and DOB
TYPE users
DECLARE userID : INTEGER
DECLARE firstName : STRING
DECLARE surname : STRING
DECLARE dateOfBirth : DATE
ENDTYPE
Once the record structure has been created, data can then be added:
DECLARE user1 : users
user1.userID ← 1
user1.firstName ← “Leroy”
user1.surname ← “Johnson”
user1.dateOfBirth ← 02/01/95
Linear search e.g. (not taught, e.g. from question)
DECLARE nameToSearch : STRING
DECLARE count : INTEGER
INPUT nameToSearch
FOR count ← 1 TO 4
// IF names[count] = nameToSearch THEN
// OUTPUT “The name exists”
// ENDIF
Next count
Change data in a 2D array e.g (not taught e.g. from question)
scores [2:3] ← 6