W9 L2 Adolescent Development: Moral and Social Development
Adolescent Development: Moral and Social Development
Scope
Focus on moral and social development in adolescents, linked to learning outcomes three and four.
Main theorists discussed: Lawrence Kohlberg and Erik Erikson.
Relationships in adolescence, especially parent-child relationships.
Touch on emerging adulthood as a stage between adolescence and adulthood.
Moral Development in Adolescents
Definition of Morality
Morality pertains to beliefs about right and wrong, good and bad.
Moral reasoning develops from late childhood into adolescence.
Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development
Based on moral dilemmas posed to individuals.
Example dilemma: Is it acceptable to steal medicine to save a life?
Focus on reasoning rather than answers given by participants.
Proposed three levels of moral development:
Level 1: Preconventional
Level 2: Conventional
Level 3: Postconventional
Components of Kohlberg's Theory
Preconventional Level
Stage 1: Obedience and punishment orientation: following rules to avoid punishment.
Stage 2: Individualism and exchange: following rules for personal gain or reward.
Conventional Level
Stage 3: Good interpersonal relationships: moral reasoning based on gaining approval from others.
Stage 4: Maintaining social order: law and order mentality; performing duties to uphold societal rules.
Postconventional Level
Stage 5: Social contract orientation: interpreting rules for greater fairness and rights (e.g., right to life over property laws).
Stage 6: Universal ethical principles: moral reasoning based on personal principles regarding equality and justice; may lead to defiance of laws perceived as immoral.

Distinction and Evidence
Debate over whether there is a distinction between stages five and six.
Cited studies suggest postconventional reasoning is more prevalent in individualistic cultures than in collectivist ones.
Parenting style, education, and peer interactions also influence moral development.
Emotional Development and Morality
Children begin experiencing guilt around age two, indicating early awareness of right and wrong.
Development of conscience through parenting styles:
Freud's suggestion: conscience develops through interaction with parents, particularly through authoritative parenting.
Erikson's Theory: Key Issues in Adolescence
Erikson's Psychosocial Development
Each developmental stage characterized by a psychosocial crisis.
Crisis of Identity vs. Role Confusion
Adolescence marked by exploration of identity based on factors like gender, ethnicity, and social groups.
Culture affects identity perception.
Development of strengths, weaknesses, and values rooted in family and peer influences.
Progression from Childhood to Adolescence
Earlier stages include:
Trust vs. mistrust (infancy)
Autonomy vs. shame and doubt (1-3 years)
Initiative vs. guilt (3-6 years)
Industry vs. inferiority (6-adolescence)
Understanding of self transitions to questions of identity and social role.

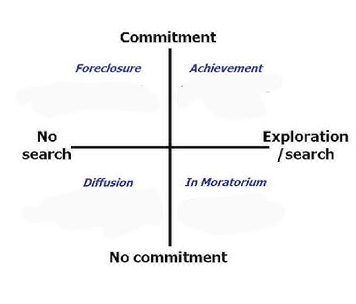
Marcia’s Theory of Identity Development
James Marcia's Four Identity Statuses
Emphasizes exploration and commitment:
Identity Diffusion: No clear sense of choice or commitment.
Identity Foreclosure: Commitment to values/goals without exploration; often externally defined by others (e.g., parents).
Identity Moratorium: Currently in crisis, exploring options, but not yet committed.
Identity Achievement: Resolved crisis and made personal commitments to roles/values.
Transitions Between Statuses
Adolescents may transition between statuses in various life domains (vocational, religious, etc.).
Many move toward higher statuses (e.g., from diffusion to moratorium or achievement).
Delayed adulthood trends noted in modern society contribute to identity achievement timeline.

Relationships in Adolescence
Parent-Child Dynamics
Relationship quality carried over from childhood; changes during adolescence.
Longitudinal Australian study:
70% of teens felt respected, understood, and trusted by their parents.
Relationships improve with increased independence.
Confidences vs. deception in communication with parents noted.
Parent-Child Conflicts
Conflicts peak during early adolescent transitions (13-14 years).
Differences observed in conflict frequency between firstborn and secondborn children.
Impact of Parenting on Identity Formation
Positive parenting correlates with better identity outcomes.
Findings showed perceptions of caring behaviors and emotional autonomy predict identity statuses.
Emerging Adulthood
Definition
A stage occurring between adolescence and adulthood characterized by delayed commitments (e.g., marriage, parenthood, education).
Emerges as a response to modern societal changes.
Associated with self-exploration, freedom, and fewer social obligations.
Research Insights
Arnett's study exploring feelings of adulthood across age groups showed ambiguity in self-identification as adults in late teens/early twenties.
Conclusion
Summary of developmental psychology themes in adolescents:
Physical, cognitive, moral, and psychosocial aspects highlighted in presentations.
Learning objectives:
Moral Development in Adolescence
Morality: Understanding right and wrong; develops from late childhood to adolescence.
Kohlberg’s Theory: Three levels of reasoning:
Preconventional: Avoid punishment / seek reward.
Conventional: Seek approval / follow laws for order.
Postconventional: Uphold fairness and justice beyond laws.
Influences: Culture (individualistic = more postconventional), education, parenting, peers.
Emotions & Parenting: Guilt and empathy support morality; authoritative parenting promotes moral reasoning.
🧠 Psychosocial Development in Adolescence
Erikson’s Stage: Identity vs. Role Confusion — forming a stable sense of self based on values, culture, and goals.
Success → identity achievement; failure → role confusion.
Influenced by family, peers, and culture.
Marcia’s Identity Statuses:
Diffusion – no direction or commitment.
Foreclosure – commitment without exploration.
Moratorium – exploring but undecided.
Achievement – explored and committed.
Adolescents move between statuses; delayed adulthood extends exploration.