3.1F Transition Metals
Transition Metals
Transition metal: an element whose atoms have incomplete d-sublevels or that can give rise to cations with incomplete d-sublevels
d-orbitals that are not completely filled
They are found in the d-block of the periodic table.
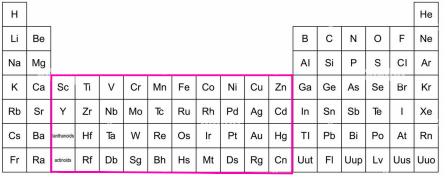 Zinc is NOT considered to be a transition metal
Zinc is NOT considered to be a transition metal
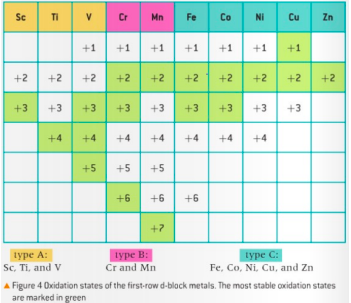
 Transition metals have variable oxidation states
Transition metals have variable oxidation states
 Transition metals form complexes
Transition metals form complexes
Central transition metal ion is surrounded by ligands
Ligands have a lone pair of electrons. They can make co-ordinate covalent bonds with the transition metal ion
Together, the central ion and the ligands form a complex
 Transition metal complexes are coloured
Transition metal complexes are coloured
Ligands split d-orbitals (more on this tomorrow)
When light is shone on the complex, light of a particular wavelength is absorbed as an electron is promoted. The colour that we see is white light minus whatever colour is absorbed.
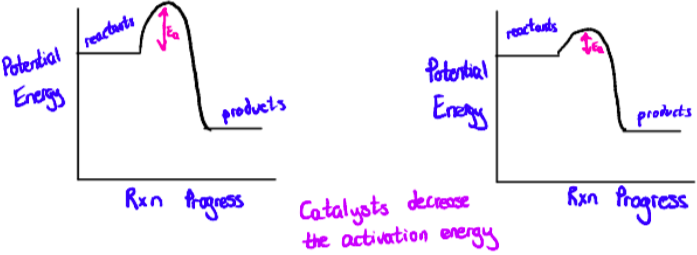
Transition metals are catalysts
Catalysts increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed in the process.
 Transition metals exhibit magnetism
Transition metals exhibit magnetism
Magnetic strength depends on the number of unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals