Staphylococcus spp
GENERAL INFORMATION:
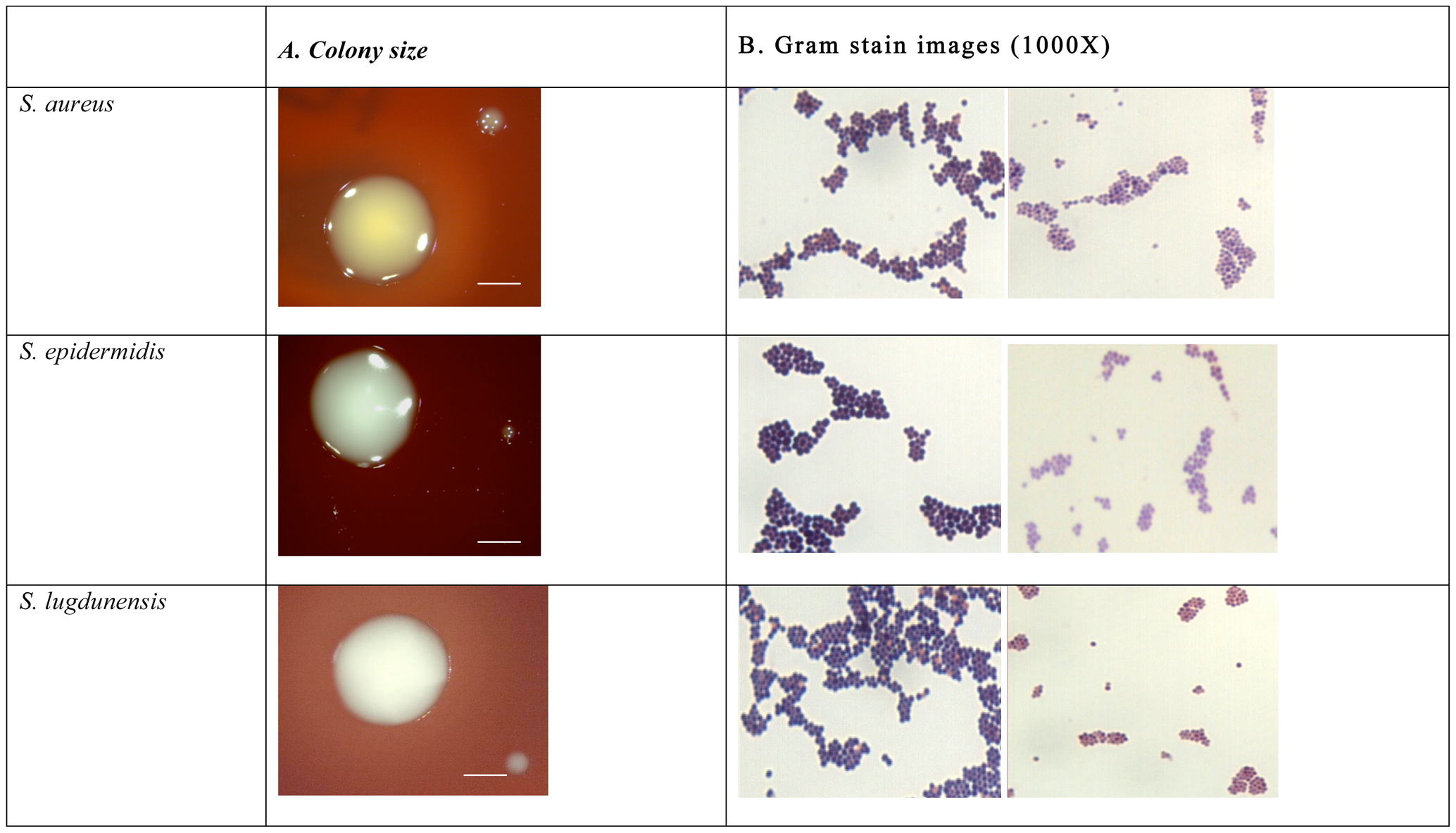
==Appearance:==
- Cocci
- Clusters resembling bunches of grapes
- Opaque, moderately-sized white or golden colonies
@@Habitat:@@
- Commensal on skin and mucous membranes
- Stable in the environment
Characterization:
- Gram-positive
- Catalase-positive
- Non-motile
- Oxidase-negative
- Facultative anaerob
- Coagulase-positive
- Non-sporulating
- Haemolysis differ between species and strains
- Exceptions: S. anaerobius and S. saccharolyticus → anaerobic and catalase-negative
SPECIES AND CLINICAL CONDITIONS:
| ==SPECIES:== | %%HOSTS:%% | ^^CLINICAL CONDITIONS:^^ |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | Cattle | Mastitis, udder impetigo |
| Sheep | Mastitis, tick pyaemia (almbs), benign folliculitis (lambs), dermatitis | |
| Goat | Mastitis, dermatitis | |
| Pig | Botryomycosis and impetigo of mammary glands | |
| Horse | Scirrhous cord, mastitis | |
| Dog and cat | Similar to S. pseudintermedius | |
| Poultry | Arthritis and septicaemia (turkey), bumblefoot, omphalitis (chicks) | |
| S. pseudintermedius | Dog | Pyoderma, endometriti, cystitis, otitis externa |
| Cat | Pyogenic conditions | |
| Pig | ||
| S. hyicus | Pig | Greasy-pig disease |
| Cattle | Mastitis (rare) | |
| S. aureus subsp. aureus | Sheep | Lymphadenitis |
| S. delphini | Dolphin | Suppurative skin lesions |
| S. schleiferi subsp. coagulans | Dog | Otitis externa |
PATHOGENESIS AND PATHOGENICITY:
- Coagulase-positive species have a higher patogenicity
- Some species are opportunistic pathogens causing pyogenic infections
- Infections associated with trauma, immunosuppression, intercurrent parasitic or fungal infection, allergic conditions or endocrine and metabolic disturbances
- Infections maybe endogenous or exogenous in origin
- Zoonotic potenial in strains
- Risk groups: pig farmers and others in contact with pigs
- Virulence factors differ between species.
| VIRULENCE FACTOR (of S. aureus): | %%PATHOGENIC EFFECTS:%% |
|---|---|
| Coagulase | Conversion of fibrinogen → fibrin → shield from phagocytic cells |
| Enzymes (i.e. lipase, elastase and phospholipase) | Tissue destruction |
| Protein A | Binds Fc portion of IgG and inhibits opsonization |
| Leukocidin | Cytolytic destruction of phagocytes |
| Alpha-toxin | Spasm of smooth muscle |
| Beta-toxin | Damage cell membranes |
| Exfoliative toxins | Skin lesion development |
| Enterotoxins | Food poisoning |
| TSST | Induce excessive lymphokine production → tissue damage |
DISEASES OF IMPORTANCE:
- Treatment against Staphylococcus:
- Vaccines are ineffective
- Problem with MRSA
- Diseases of importance:
- %%Mastitis%%
- Cause: usually S. aureus
- Host: usually bovine
- Classification: subclinical, acute and chronic
- Spread: worldwide
- ^^Tick pyaemia^^
- Cause: S. aureus through tick bites or skin trauma
- Host: lambs
- Characterization: 2 alternatives
- Septicemia and rapid death
- Localized abscess formation in organs
- Treatment: antibiotics and tick control
- ==Greasy-pig disease==
- Cause: S. hyicus
- Host: pigs (<3 months of age - deathly)
- Spread: worldwide
- Characterization: excessive sebaceous secretion, exfoliation and exudation on skin surface
- Pre-disposing stress factors: agalactia in the sow, intercurrent infections and weaning
- Treatment:
- Antibotic combined with topical treatment with antiseptic or antibiotic suspensions
- Cleaning and disinfection
- Isolation
- Wash sows with antiseptic soap
- Botryomycosis
- Cause: S. aureus often linked to castration in horses and mammary tissues of sows
- Characterization: chronic, suppurative granulomatous condition