Female Reproductive System
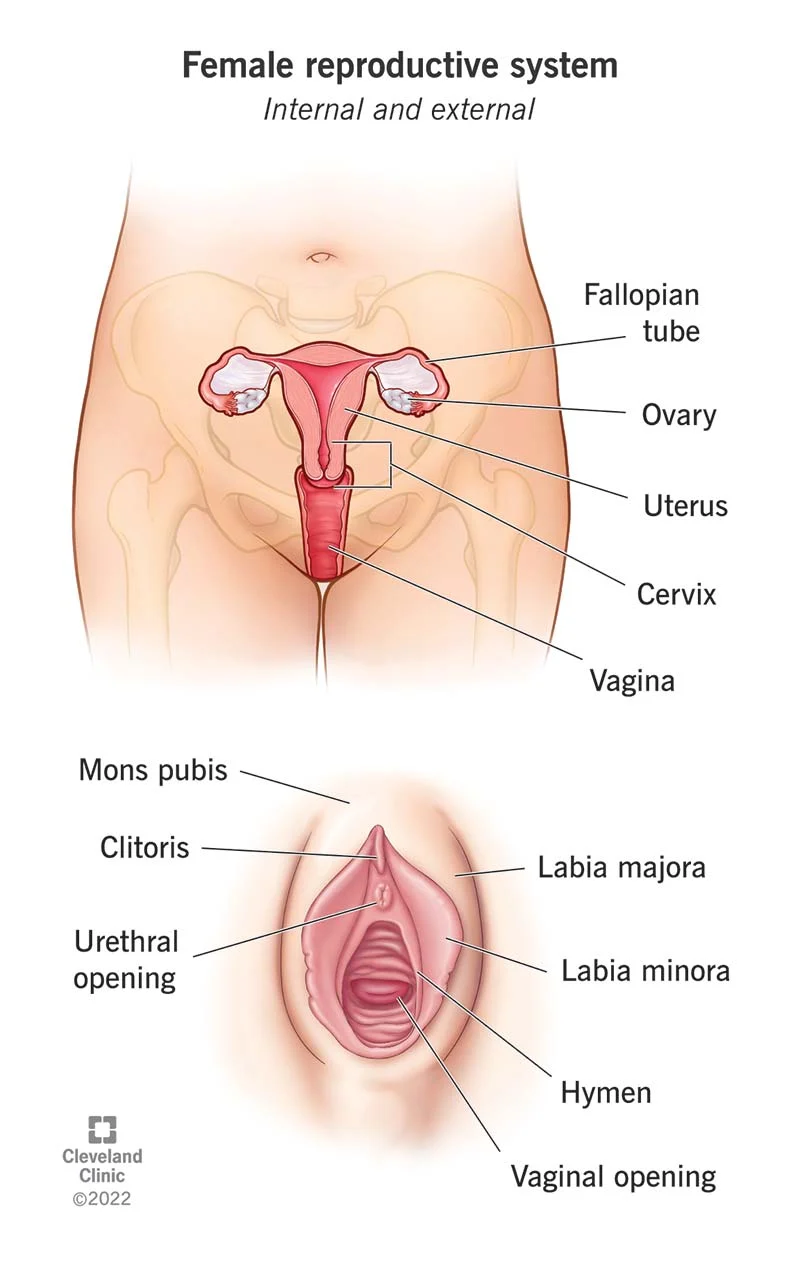
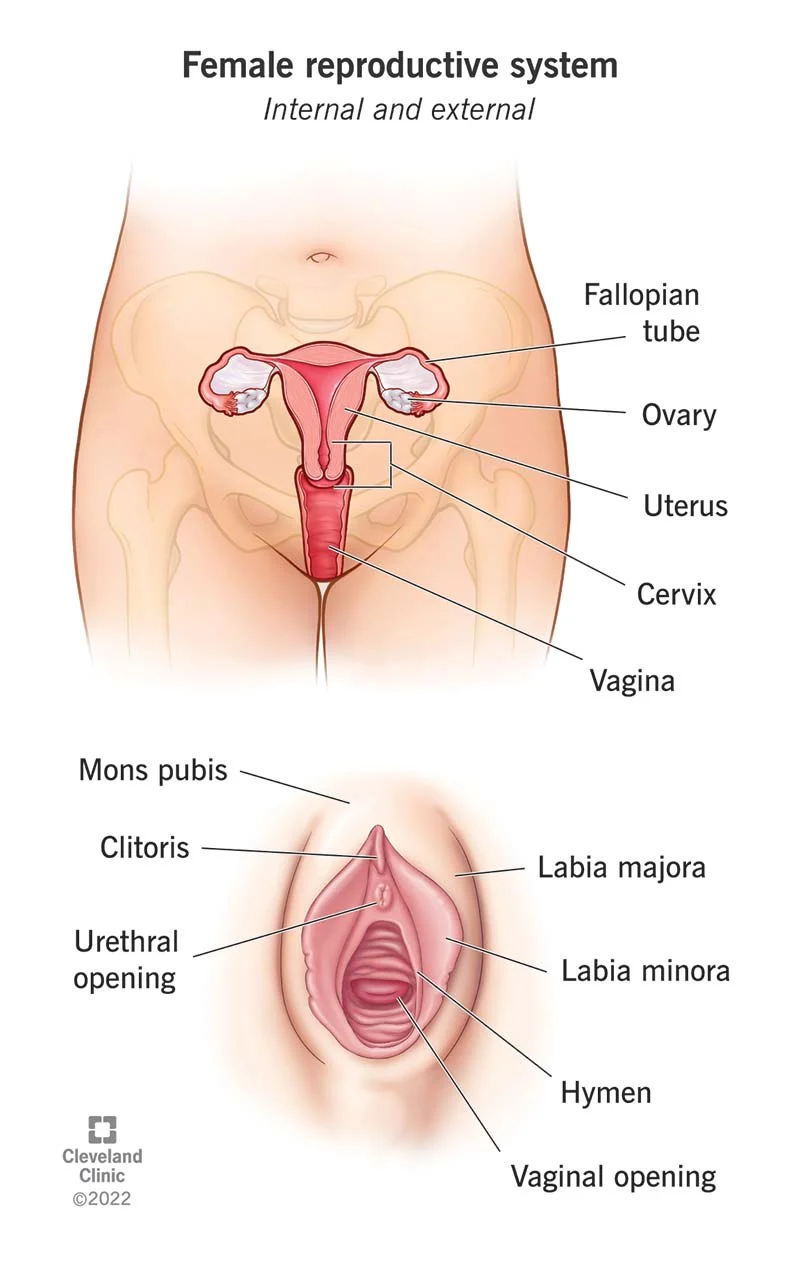
Path of the EGG: 1. Ovary 2. Fallopian Tube 3. Uterus 4. Cervix 5. Vagina | EGGS: female sex cell |
|---|
OVULATION: egg is released from ovary |
|---|
MENSTRUATION: release (shedding) of the endometrium (inner lining of the uterus) |
|---|
MENOPAUSE: ovaries stop releasing eggs and reproductive years end; onset is usually late 40s or early 50s |
|---|
Female Reproductive System
OVARIES | - mature and release eggs (ovulation)
- produce estrogen and progesterone
|
|---|
FALLOPIAN TUBES | - tube that transports the egg (ovum) to the uterus (womb)
- What important event takes place in the fallopian tube?
fertilization (conception) |
|---|
UTERUS (WOMB) | - muscular organ where fertilized egg develops
- Endometrium: inner lining that provides place for implantation of a fertilized egg; lining that is shed during menstruation
- Myometrium: middle, muscular layer contracts during labor
- Perimetrium: outer layer
|
|---|
CERVIX (part of the uterus) | - narrow opening to the uterus lined with a mucous membrane
- mucous released changes during menstrual cycle and pregnancy to form a barrier against certain types of bacteria
Must dilate (widen) to 10cm during labor for a vaginal birth to occur |
|---|
VAGINA | - tube lined with a moist membrane that connects to the uterus/cervix
- birth canal - passage through which a baby is delivered
- hymen: thin fleshy tissue located at the entrance of the vagina;
|
|---|
VULVA | - external female anatomy that includes the labia and clitoris
- labia: skin folds that surround the openings to the vagina and urethra
- clitoris: located above the vaginal opening containing sensitive erectile tissue
|
|---|
URETHRA | - tube connected to the bladder allowing urine to exit the body
|
|---|

