Introduction to electric machines
First here are a few key terms:

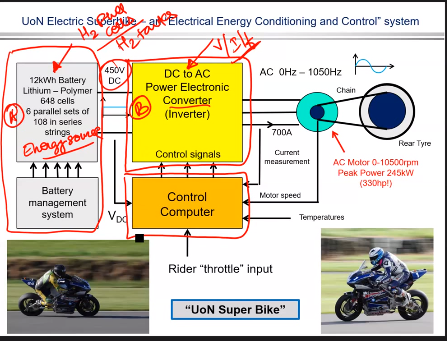
In an example like UoN super bike we start with an energy source to provide energy which is connected to a battery management system to ensure batter last for as long as possible.
Then you have a DC to AC power electronic converter which is controlled by the control computer that is affected by the speed of the motor bike
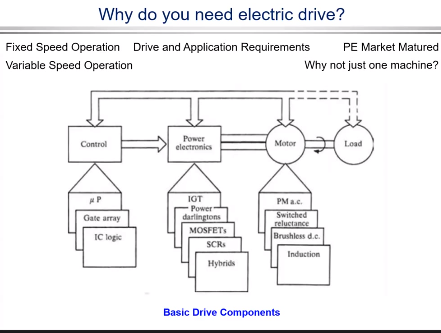
Why do we need electric drive?
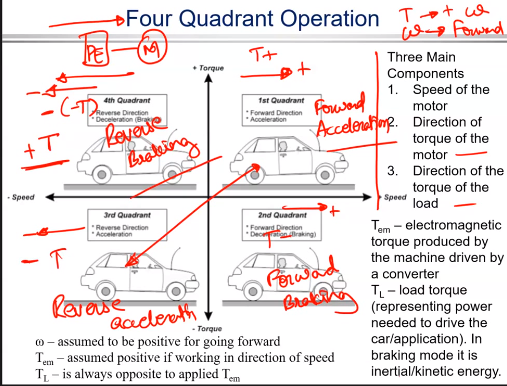
 Four Quadrant operation
Four Quadrant operation
Lets use a car as an example
Three main components:
Speed of motor
Direction of the torque
Direction of the torque of the load
Torque is positive if it is in the direction of motion
There is 4 different ways of driving car
Going forwards,Reverse, Down hill and up hill
1st Quadrant
When driving the car forwards your torque will be forward as there is a forward accelaration
2nd Quadrant
When going downhil you are breaking so car doesnt go too fast so you may be going upwards but the torqur is going to be negative
3rd Quadrant
Reversing,
Torque is negative and speed is negative as u are accelerating backwards
4th Quadrant
Your going up hill but reversing so Torque is positive
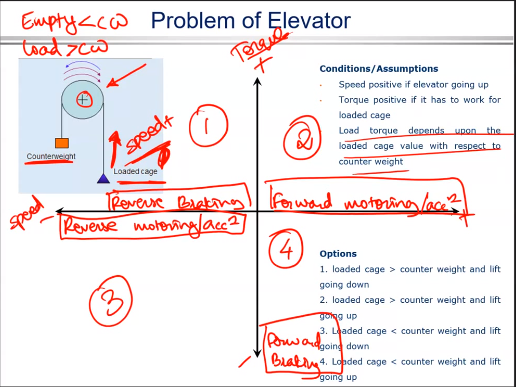
 Another example is an elevator
Another example is an elevator
 Introduction on power electronics
Introduction on power electronics

 This is universal speed equation
This is universal speed equation
N(rpm) = 120f/P
N = speed of the machine
f = supply frequency to the machine
P = number of poles in the machine
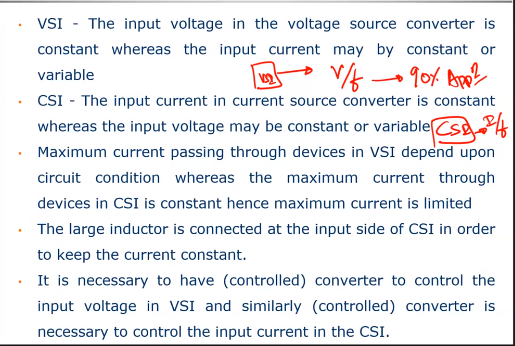 With VSI you can change the voltage and frequency . 90% of applications use this because CSI needs a Large inductor.
With VSI you can change the voltage and frequency . 90% of applications use this because CSI needs a Large inductor.
Introduction to Electrical Machines
Applications
Anything that moves, Anything that rotates , Anything that converts Electrical to Mechanical or vice versa
There are 3 types of electrical machines
Universal Motor
Single Phase motors and
Three phases
These aren’t the actual terminologies
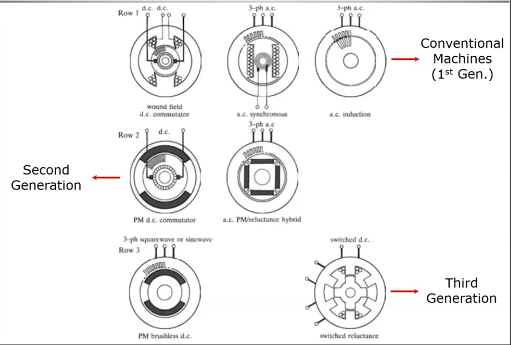
Conventional Machines(1st gen)
1. DC Machine
2. Induction Machine
3. Synchronous Machine
Second generation Machines
Brushed PM DC machine
PM AC Machines
Third Gen Machines
Brushless PM DC Machine
Brushless PM AC machine
Reluctance MAchines