Matter & Change
Chemistry: the study of matter and changes that are associated with it. ex: physical and/or chemical
Properties of Matter: matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
^^5 Indicators of a Chemical Change:^^
- emission of light and/or heat
- formation of a gas
- formation of a precipitate
- change in color
- emission of odor
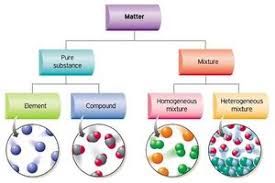
All matter can be classified into three groups:
elements
compounds
mixtures
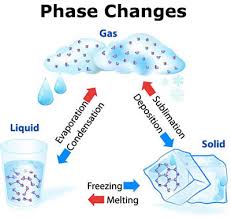
States of Matter:
Solid
- has a definite volume and shape
- the particles of a solid are packed close together in relatively fixed positions
- particles are held by very strong forces between them
- the particles of a solid simply vibrate about a fixed position
Liquid
- has a definite volume but no definite shape
- assumes the shape of the container
- the particles of a liquid are held close together but because they are moving faster they can overcome the attractive forces and move one another
Gas/Plasma
has neither a definite shape nor definite volume
composed of particles that move very rapidly and are at a great distance from one another, making the attractive forces between the particles very weak
==plasma==: a high-temperature physical state of matter in which atoms lose most of their electrons
can be found in lightning, stars, and some TV screens
Endothermic vs Exothermic
==Endothermic==
definition: a reaction that ==releases energy to the surroundings==, causing the reaction mixture and its surroundings to become ==hotter==
examples: burning/combustion, neutralization, and displacement
^^Exothermic^^
definition: a reaction in which ^^energy is absorbed from the surroundings^^, causing the reaction mixture and its surroundings to become ^^cooler^^
examples: evaporating or melting