INTELLECTUAL REVOLUTION
Can be defined as the historical changes in the thoughts, beliefs and social institutions due to new ideas and principles.
SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION
Science has always been interwoven with the society.
Science is as old as the world itself.
There is no individual that can identify when and where science began.
Science as a BODY KNOWLEDGE.
It is a subject or a discipline or a field of study, it deals with the process of learning about the natural and physical world.
“Scientific Revolution" refers to historical changes in thought & belief, to changes in social & institutional organization, that unfolded in Europe between 1550-1700.
Science as an INTELLECTUAL ACTIVITY.
The study involves systematic observations and experimentations.
Science as a PERSONAL and SOCIAL ACTIVITY.
Science is both knowledge and activities by humans to develop better understanding of the world around them.
SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION EXAMPLES:
Earliest brain surgery from 6000 years ago in CAPPADOCIA, TURKEY.
Trepanation - making an opening like a small round hole in the head.
Thousand years old agricultural practice of China’s solution to sustainable faming.
The practice of raising fish in rice paddies by Chinese.
Mummification in the Philippines.
MUMMIFICATION is a process of preserving a deceased human.
MUMMIES are classified based on the method and the medium of preservation.
People developed noble ideas, later known as Philosophy to provide possible explanation to certain phenomena.
People used religion to rationalize the origin of life.
SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION AND ENLIGHTENMENT
Was the period of enlightenment when developments in the fields of mathematics ,physics, astronomy, biology and chemistry.
Started in Europe.
Explains the emergence or birth of modern science as a result of these developments.
RELIGION VS SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION
Scientific individuals were sentenced to death suffered condemnation.
These did not stop scientists to satisfy their curiosity of the natural and physical world.
SOME INDIVIDUALS & THEIR REVOLUTONARY IDEAS
NICHOLAS COPERNICUS

Developed (Copernican Model) heliocentrism, it is the name given to the astronomical model published in 1543.
It positioned the Sun near the center of the
Universe.
Copernican Model was banned & ignored by Rome (16th century)
CHARLES DARWIN

Famous for his Theory of Evolution by Means of Natural Selection.
Came from a line of intellectually gifted and wealthy family.
Joined the 5 year voyage through HMS Beagle on the island of Galapagos.
Published The Origin of Species in 1859.
Challenge religious and unscientific ideas.
Provided the framework for doing scientific activities marked by observations & experiments.
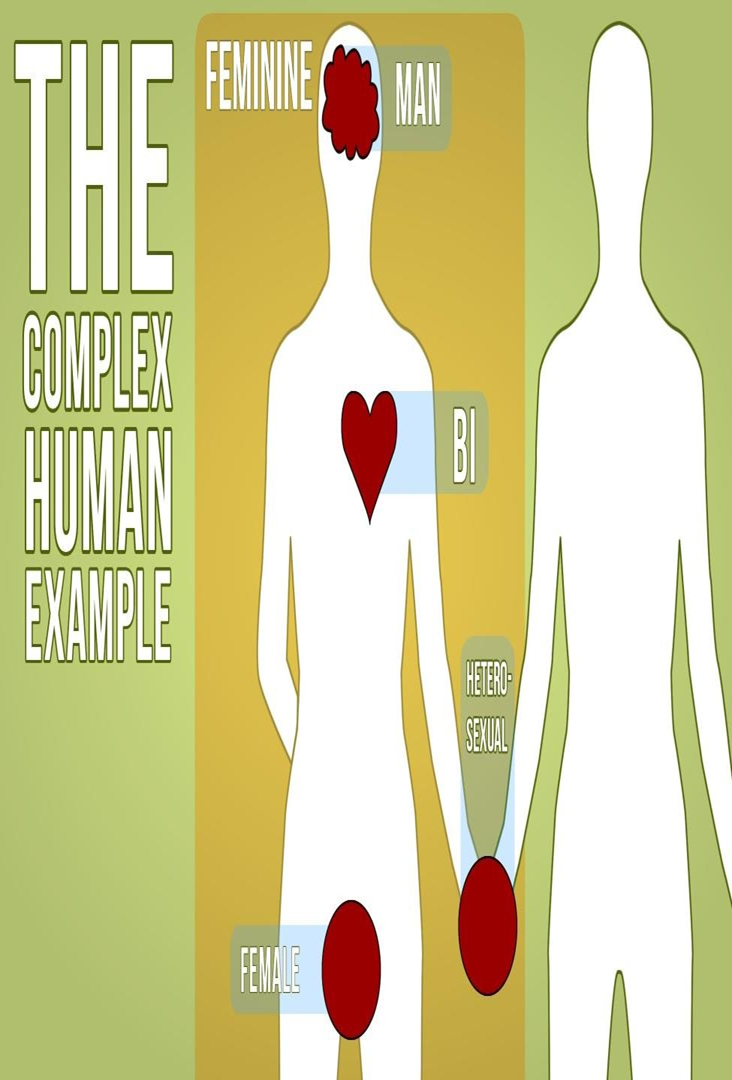
SIGMUND FREUD

Famous figure in the field of Psychology.
Method of Psychoanalysis- a scientific way to study human mind & neurotic illness.
This method was unorthodox focuses human sexuality and & the evil Nature of man.
HUMAN SEXUALITY is the way people experience and express themselves sexually. This involves biological, erotic, physical, emotional, social, or spiritual feelings and behaviors.